Abstract
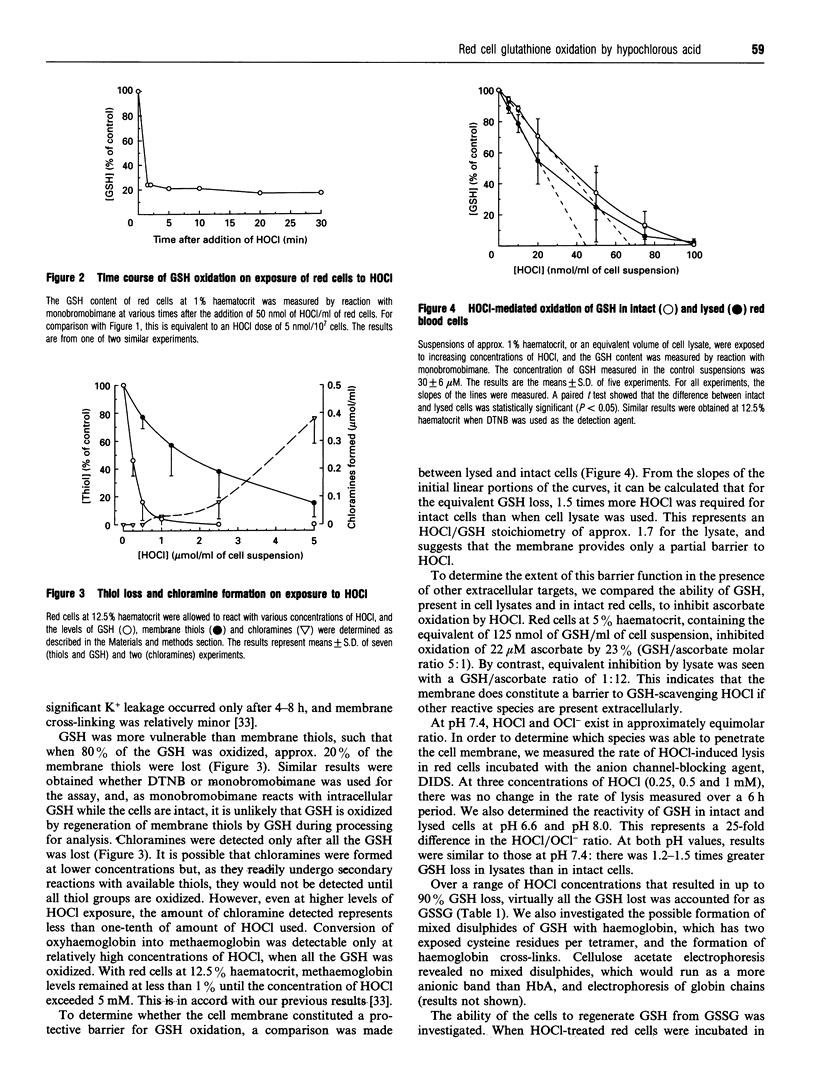
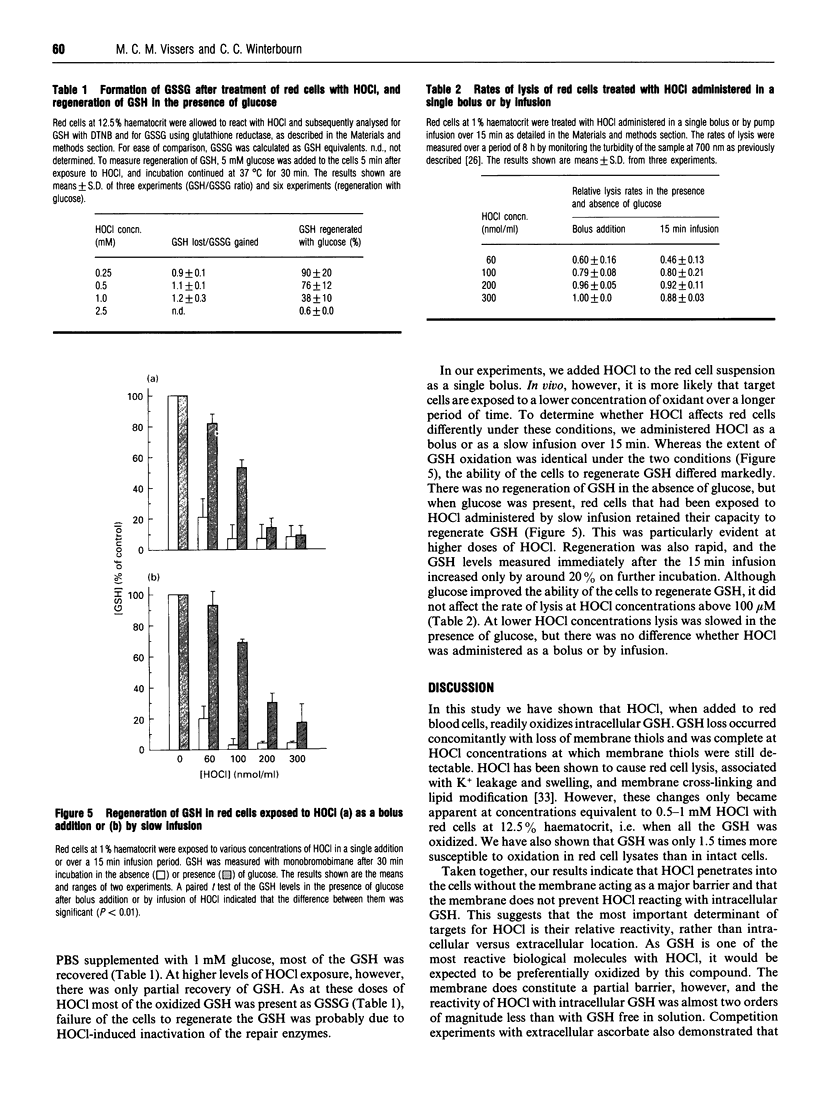
Exposure of human red blood cells to low doses of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) resulted in the loss of intracellular GSH. Oxidation occurred less than 2 min after the addition of HOCl, and required approx. 2.5 mol of HOCl per mol of GSH lost. Loss of GSH preceded oxidation of membrane thiols, the formation of chloramines and haemoglobin oxidation. The susceptibility of intracellular GSH to oxidation by HOCl was two-thirds that of GSH in cell lysates. These results indicate that HOCl can penetrate the red cell membrane, which provides little barrier protection for cytoplasmic components, and that GSH oxidation by HOCl may be a highly selective process. Virtually all of the GSH lost was converted into GSSG. If glucose was added to the medium, most of the GSH oxidized by low doses of HOCl was rapidly regenerated. At higher doses, recovery was less efficient. However, when HOCl was added as a slow infusion rather than in a single bolus, there was increased recovery at higher doses. This indicates that in metabolically active cells regeneration is rapid and GSH may protect cell components from damage by HOCl. HOCl-induced lysis was only slightly delayed by adding glucose to the medium, indicating that lytic injury is not ameliorated by GSH.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrette W. C., Jr, Hannum D. M., Wheeler W. D., Hurst J. K. General mechanism for the bacterial toxicity of hypochlorous acid: abolition of ATP production. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 14;28(23):9172–9178. doi: 10.1021/bi00449a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin A. M. Taurine modulation of hypochlorous acid-induced lung epithelial cell injury in vitro. Role of anion transport. J Clin Invest. 1994 Feb;93(2):606–614. doi: 10.1172/JCI117013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotgreave I. A., Moldéus P. Methodologies for the application of monobromobimane to the simultaneous analysis of soluble and protein thiol components of biological systems. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1986 Nov;13(4-5):231–249. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(86)90102-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallegri F., Ballestrero A., Frumento G., Patrone F. Erythrocyte lysis by PMA-triggered neutrophil polymorphonuclears: evidence for an hypochlorous acid-dependent process. Immunology. 1985 Aug;55(4):639–645. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallegri F., Goretti R., Ballestrero A., Ottonello L., Patrone F. Neutrophil-induced depletion of adenosine triphosphate in target cells: evidence for a hypochlorous acid-mediated process. J Lab Clin Med. 1988 Dec;112(6):765–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. E., Schultz J. Studies on the chlorinating activity of myeloperoxidase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1371–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Johnston R. B., Jr Tissue injury in inflammation. Oxidants, proteinases, and cationic proteins. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):669–674. doi: 10.1172/JCI112869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst J. K., Barrette W. C., Jr, Michel B. R., Rosen H. Hypochlorous acid and myeloperoxidase-catalyzed oxidation of iron-sulfur clusters in bacterial respiratory dehydrogenases. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 18;202(3):1275–1282. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16500.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Clark R. A. Hemolysis and iodination of erythrocyte components by a myeloperoxidase-mediated system. Blood. 1975 May;45(5):699–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakita R. M., Michel B. R., Rosen H. Differential inactivation of Escherichia coli membrane dehydrogenases by a myeloperoxidase-mediated antimicrobial system. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 30;29(4):1075–1080. doi: 10.1021/bi00456a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakita R. M., Rosen H. Penicillin-binding protein inactivation by human neutrophil myeloperoxidase. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):750–754. doi: 10.1172/JCI115372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reglinski J., Hoey S., Smith W. E., Sturrock R. D. Cellular response to oxidative stress at sulfhydryl group receptor sites on the erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12360–12366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddles P. W., Blakeley R. L., Zerner B. Reassessment of Ellman's reagent. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:49–60. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Klebanoff S. J. Oxidation of Escherichia coli iron centers by the myeloperoxidase-mediated microbicidal system. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13731–13735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Orman J., Rakita R. M., Michel B. R., VanDevanter D. R. Loss of DNA-membrane interactions and cessation of DNA synthesis in myeloperoxidase-treated Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10048–10052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schraufstätter I. U., Browne K., Harris A., Hyslop P. A., Jackson J. H., Quehenberger O., Cochrane C. G. Mechanisms of hypochlorite injury of target cells. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):554–562. doi: 10.1172/JCI114472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L., Grisham M. B., Jefferson M. M. Myeloperoxidase-dependent effect of amines on functions of isolated neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):441–454. doi: 10.1172/JCI110992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. L., Grisham M. B., Melton D. F., Jefferson M. M. Evidence for a role of taurine in the in vitro oxidative toxicity of neutrophils toward erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3321–3329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda S., Schneider R. G. Rapid differentiation of polypeptide chains of hemoglobin by cellulose acetate electrophoresis of hemolylsates. Blood. 1969 Aug;34(2):230–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vissers M. C., Fantone J. C. Inhibition of hypochlorous acid-mediated reactions by desferrioxamine. Implications for the mechanism of cellular injury by neutrophils. Free Radic Biol Med. 1990;8(4):331–337. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(90)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vissers M. C., Stern A., Kuypers F., van den Berg J., Winterbourn C. C. Membrane changes associated with lysis of red blood cells by hypochlorous acid. Free Radic Biol Med. 1994 Jun;16(6):703–712. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(94)90185-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vissers M. C., Winterbourn C. C. Myeloperoxidase-dependent oxidative inactivation of neutrophil neutral proteinases and microbicidal enzymes. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):277–280. doi: 10.1042/bj2450277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vissers M. C., Winterbourn C. C. Oxidative damage to fibronectin. I. The effects of the neutrophil myeloperoxidase system and HOCl. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Feb 15;285(1):53–59. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90327-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vissers M. C., Winterbourn C. C. The effect of oxidants on neutrophil-mediated degradation of glomerular basement membrane collagen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 19;889(3):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., LoBuglio A. F. Phagocyte-generated oxygen metabolites and cellular injury. Lab Invest. 1982 Jul;47(1):5–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J. Tissue destruction by neutrophils. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 9;320(6):365–376. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902093200606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterbourn C. C. Comparative reactivities of various biological compounds with myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-chloride, and similarity of the oxidant to hypochlorite. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 18;840(2):204–210. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg J. J., Winterbourn C. C., Kuypers F. A. Hypochlorous acid-mediated modification of cholesterol and phospholipid: analysis of reaction products by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Lipid Res. 1993 Nov;34(11):2005–2012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]