Abstract
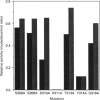
Phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) enzymes have considerable structural similarity within limited regions (X and Y) implicated in catalysis. The role of residues contained within a highly conserved sequence present in the X region was investigated by site-directed mutagenesis of PLC-delta 1 isoenzyme. Seven residues (Ser-308, Ser-309, Ser-310, His-311, Thr-313, Tyr-314, and Gln-319) were individually replaced by alanine or glutamine (His-311). Replacement of two residues, His-311 and Tyr-314, resulted in a dramatic reduction of enzyme activity. The kcat of hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate by H311A and Y314A mutants was reduced 1000- and 10-fold respectively, with little effect on Km. Further analysis of H311A and Y314A mutants, using limited proteolysis and circular dichroism, had shown that no major structural alterations had occurred. Since site-directed mutagenesis demonstrated the importance of histidine residues, their role in enzyme function was also analysed by chemical modification with diethyl pyrocarbonate. This modification of histidine residues resulted in the reduction of enzyme activity and also indicated that more than one residue could be important.
Full text
PDF

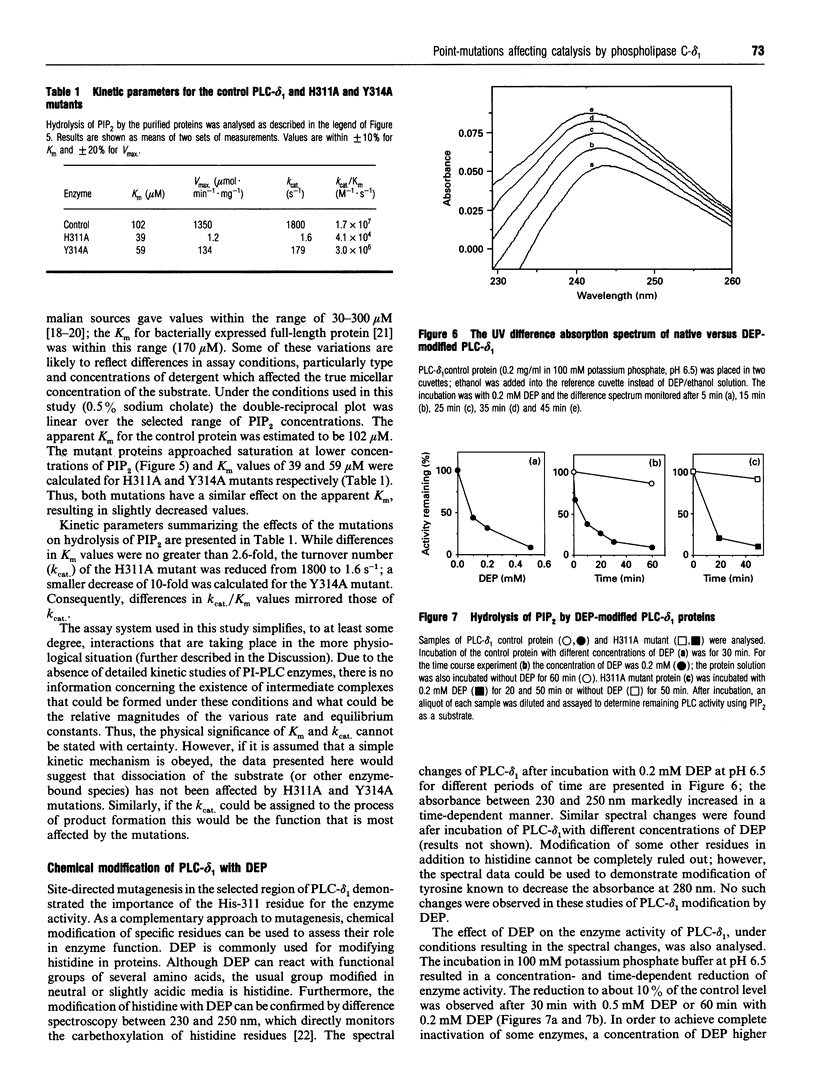


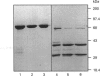
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya D. K., Bandyopadhyay U., Banerjee R. K. Chemical and kinetic evidence for an essential histidine in horseradish peroxidase for iodide oxidation. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9800–9804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristol A., Hall S. M., Kriz R. W., Stahl M. L., Fan Y. S., Byers M. G., Eddy R. L., Shows T. B., Knopf J. L. Phospholipase C-148: chromosomal location and deletion mapping of functional domains. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):915–920. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cifuentes M. E., Honkanen L., Rebecchi M. J. Proteolytic fragments of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C-delta 1. Catalytic and membrane binding properties. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11586–11593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayer A. L., van Haastert P. J. Molecular cloning and expression of a phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18387–18392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis M. V., Carne A., Katan M. Structural requirements of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C delta 1 for enzyme activity. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Apr 1;213(1):339–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori Y., Homma Y., Sorimachi H., Kawasaki H., Nakanishi O., Suzuki K., Takenawa T. A second type of rat phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C containing a src-related sequence not essential for phosphoinositide-hydrolyzing activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21885–21890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flick J. S., Thorner J. Genetic and biochemical characterization of a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5861–5876. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui T., Lutz R. J., Lowenstein J. M. Purification of a phospholipase C from rat liver cytosol that acts on phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17730–17737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginger R. S., Parker P. J. Expression, purification and characterisation of a functional phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C-delta 1 protein in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Nov 15;210(1):155–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen S., Hough E., Svensson L. A., Wong Y. L., Martin S. F. Crystal structure of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus complexed with a substrate analog. J Mol Biol. 1993 Nov 5;234(1):179–187. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katan M., Kriz R. W., Totty N., Philp R., Meldrum E., Aldape R. A., Knopf J. L., Parker P. J. Determination of the primary structure of PLC-154 demonstrates diversity of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C activities. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90549-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M. J., Bahk Y. Y., Min D. S., Lee S. J., Ryu S. H., Suh P. G. Cloning of cDNA encoding rat phospholipase C-beta 4, a new member of the phospholipase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jul 30;194(2):706–712. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppe A., Evans L. M., McMillen D. A., Griffith O. H. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of Bacillus cereus: cloning, sequencing, and relationship to other phospholipases. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6077–6083. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6077-6083.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma H. W., Blitzer R. D., Healy E. C., Premont R. T., Landau E. M., Iyengar R. Receptor-evoked Cl- current in Xenopus oocytes is mediated through a beta-type phospholipase C. Cloning of a new form of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):19915–19918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles E. W. Modification of histidyl residues in proteins by diethylpyrocarbonate. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:431–442. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebecchi M. J., Rosen O. M. Purification of a phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12526–12532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Choi K. D. Multiple forms of phospholipase C isozymes and their activation mechanisms. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1992;26:35–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Choi K. D. Regulation of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12393–12396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Suh P. G., Cho K. S., Lee K. Y., Rhee S. G. Bovine brain cytosol contains three immunologically distinct forms of inositolphospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6649–6653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su X., Chen F., Hokin L. E. Cloning and expression of a novel, highly truncated phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C cDNA from embryos of the brine shrimp, Artemia. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 29;269(17):12925–12931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzman L., Ellis C., Lin L. L., Pawson T., Knopf J. Platelet-derived growth factor increases the in vivo activity of phospholipase C-gamma 1 and phospholipase C-gamma 2. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2018–2025. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]