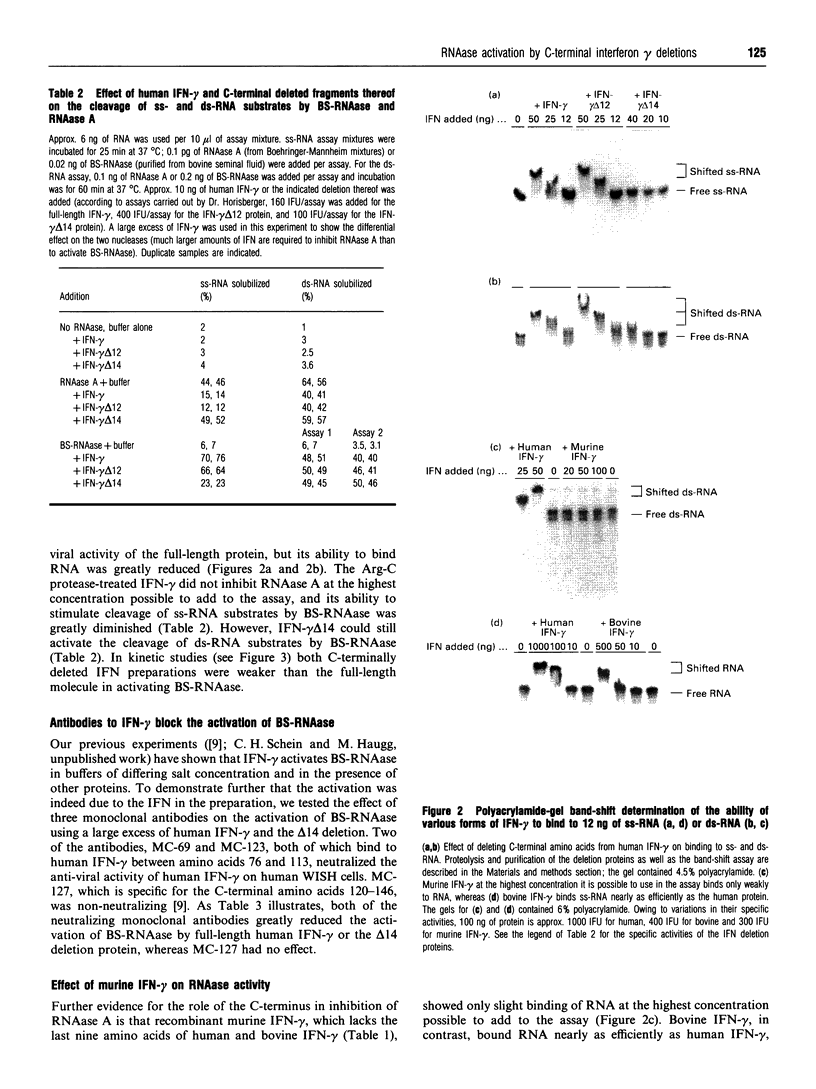
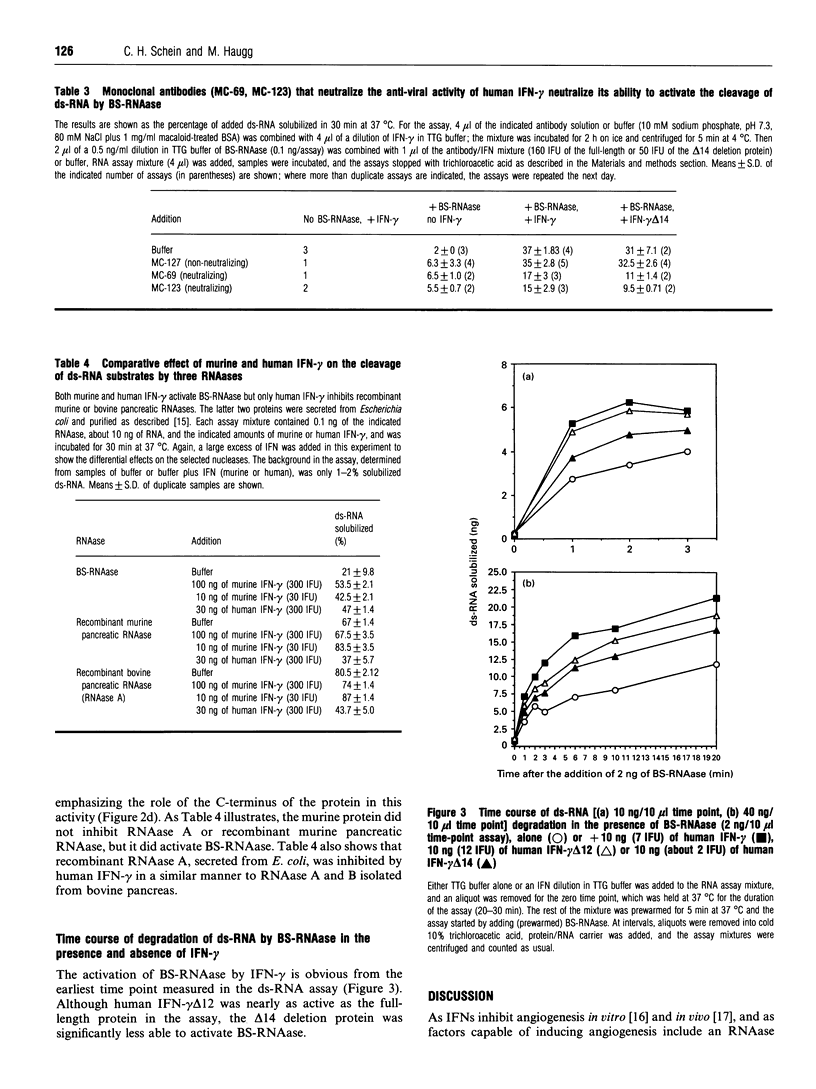
Abstract
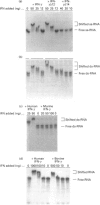
Recombinant interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) from three species activates the cleavage of double stranded (ds-) RNA by the dimeric RNAase isolated from bovine semen (BS-RNAase). Human and bovine IFN-gamma bind RNA tightly enough to inhibit cleavage by RNAase A [Schein, Haugg and Benner (1990) FEBS Lett. 270, 229-232]. Murine IFN-gamma and a proteolytic fragment of human IFN-gamma, both of which lack part of the positively charged C-terminus, bind RNA weakly and do not inhibit RNAase A. Their ability to activate BS-RNAase is proportional to their activity in the anti-viral assay. Two monoclonal antibodies that neutralize the anti-viral activity of human IFN-gamma inhibit the activation of BS-RNAase by both full-length and proteolysed human IFN-gamma. Our results demonstrate that the C-terminus of IFN-gamma contributes to RNA binding and activation of BS-RNAase, as well as to anti-viral activity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benner S. A., Allemann R. K. The return of pancreatic ribonucleases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Oct;14(10):396–397. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantoulakis P., Campbell M., Felber B. K., Nasioulas G., Afonina E., Pavlakis G. N. Inhibition of Rev-mediated HIV-1 expression by an RNA binding protein encoded by the interferon-inducible 9-27 gene. Science. 1993 Feb 26;259(5099):1314–1318. doi: 10.1126/science.7680491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alessio G., Di Donato A., Parente A., Piccoli R. Seminal RNase: a unique member of the ribonuclease superfamily. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Mar;16(3):104–106. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90042-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois M. F., Mezger V., Morange M., Ferrieux C., Lebon P., Bensaude O. Regulation of the heat-shock response by interferon in mouse L cells. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Oct;137(1):102–109. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041370112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ealick S. E., Cook W. J., Vijay-Kumar S., Carson M., Nagabhushan T. L., Trotta P. P., Bugg C. E. Three-dimensional structure of recombinant human interferon-gamma. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):698–702. doi: 10.1126/science.1902591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish E. N., Hannigan G. E., Banerjee K., Williams B. R. The interaction of interferon-alpha and -gamma: regulation of (2-5)A synthetase activity. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90661-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Manly S. P., McMahon M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of interferon-induced gene expression in human cells. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):745–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garotta G., Ozmen L., Fountoulakis M., Dembic Z., van Loon A. P., Stüber D. Human interferon-gamma receptor. Mapping of epitopes recognized by neutralizing antibodies using native and recombinant receptor proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6908–6915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel-Bellan A., Brini A. T., Farrar W. L. IFN-gamma inhibits c-myc gene expression by impairing the splicing process in a colony-stimulating factor dependent murine myeloid cell line. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):1012–1017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. S., Fox E. A., Zhou H. M., Strydom D. J., Vallee B. L. Primary structure of human placental ribonuclease inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8545–8553. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lortat-Jacob H., Grimaud J. A. Interferon-gamma binds to heparan sulfate by a cluster of amino acids located in the C-terminal part of the molecule. FEBS Lett. 1991 Mar 11;280(1):152–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80225-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luk S. K., Jay E., Jay F. T. Structure-function analysis of the human interferon gamma. The COOH terminus is not essential for functional activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13314–13319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meegan J. M., Marcus P. I. Double-stranded ribonuclease coinduced with interferon. Science. 1989 Jun 2;244(4908):1089–1091. doi: 10.1126/science.2471268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo G., Fiorucci G., Rossi G. B. Interferons in cell growth and development. Trends Genet. 1989 Jan;5(1):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum M. G., Cheung L., Kessler D. Differential activity of the 30-kD and the 100-kD forms of 2'-5'An synthetase induced by recombinant human interferon-alpha and interferon-gamma. J Interferon Res. 1988 Jun;8(3):275–282. doi: 10.1089/jir.1988.8.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein S., Familletti P. C., Pestka S. Convenient assay for interferons. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):755–758. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.755-758.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Mechanisms of the antiviral action of interferons. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1988;35:27–72. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein C. H., Boix E., Haugg M., Holliger K. P., Hemmi S., Frank G., Schwalbe H. Secretion of mammalian ribonucleases from Escherichia coli using the signal sequence of murine spleen ribonuclease. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 1;283(Pt 1):137–144. doi: 10.1042/bj2830137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein C. H., Haugg M., Benner S. A. Interferon-gamma activates the cleavage of double-stranded RNA by bovine seminal ribonuclease. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 17;270(1-2):229–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81275-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidky Y. A., Borden E. C. Inhibition of angiogenesis by interferons: effects on tumor- and lymphocyte-induced vascular responses. Cancer Res. 1987 Oct 1;47(19):5155–5161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair D. K., Rybak S. M., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Angiogenin abolishes cell-free protein synthesis by specific ribonucleolytic inactivation of 40S ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 20;27(19):7263–7268. doi: 10.1021/bi00419a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuruoka N., Sugiyama M., Tawaragi Y., Tsujimoto M., Nishihara T., Goto T., Sato N. Inhibition of in vitro angiogenesis by lymphotoxin and interferon-gamma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 30;155(1):429–435. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicentini A. M., Kieffer B., Matthies R., Meyhack B., Hemmings B. A., Stone S. R., Hofsteenge J. Protein chemical and kinetic characterization of recombinant porcine ribonuclease inhibitor expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8827–8834. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel R., Perry L. J., Veilleux C., Chang G. Mutational analysis of the C-terminus of human interferon-gamma. Protein Eng. 1990 Jul;3(7):611–623. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.7.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. R. Transcriptional regulation of interferon-stimulated genes. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Aug 15;200(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb21041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]