Abstract
The specificity of the enzyme(s) catalysing the covalent link between the hydroxyl side chains of serine or threonine and the sugar moiety N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) is unknown. Pattern recognition by artificial neural networks and weight matrix algorithms was performed to determine the exact position of in vivo O-linked GalNAc-glycosylated serine and threonine residues from the primary sequence exclusively. The acceptor sequence context for O-glycosylation of serine was found to differ from that of threonine and the two types were therefore treated separately. The context of the sites showed a high abundance of proline, serine and threonine extending far beyond the previously reported region covering positions -4 through +4 relative to the glycosylated residue. The O-glycosylation sites were found to cluster and to have a high abundance in the N-terminal part of the protein. The sites were also found to have an increased preference for three different classes of beta-turns. No simple consensus-like rule could be deduced for the complex glycosylation sequence acceptor patterns. The neural networks were trained on the hitherto largest data material consisting of 48 carefully examined mammalian glycoproteins comprising 264 O-glycosylation sites. For detection neural network algorithms were much more reliable than weight matrices. The networks correctly found 60-95% of the O-glycosylated serine/threonine residues and 88-97% of the non-glycosylated residues in two independent test sets of known glycoproteins. A computer server using E-mail for prediction of O-glycosylation sites has been implemented and made publicly available. The Internet address is NetOglyc@cbs.dtu.dk.
Full text
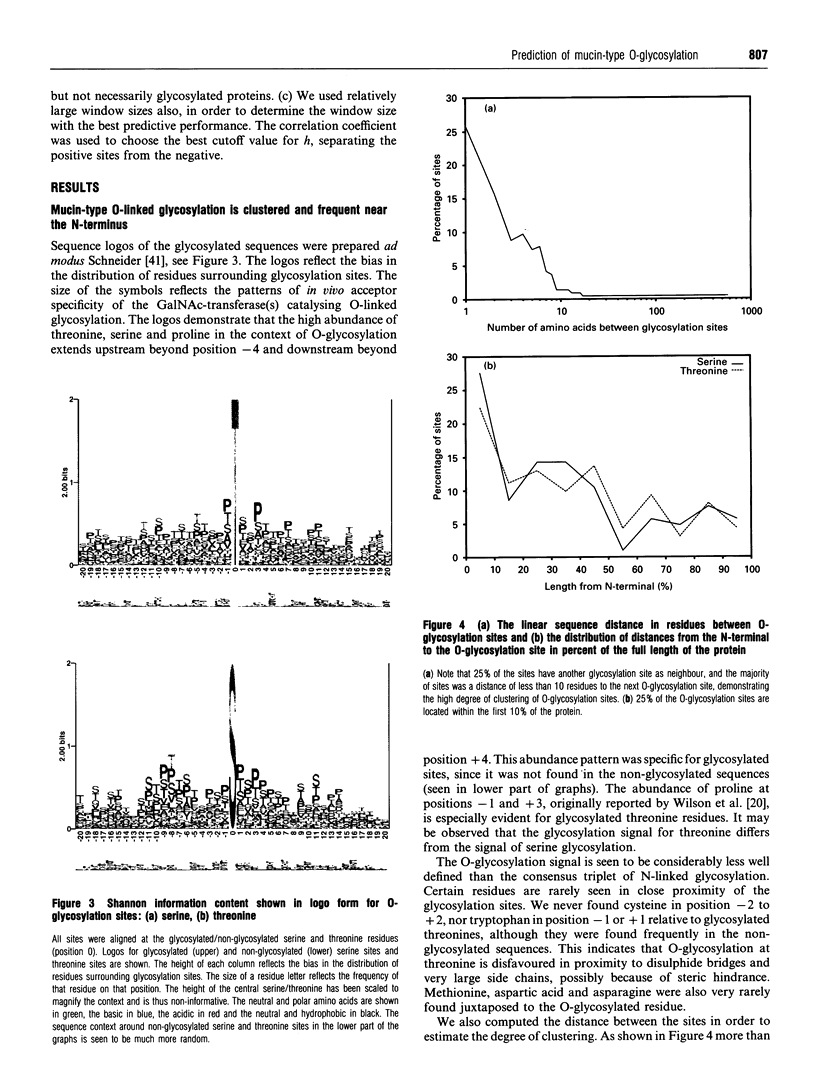
PDF


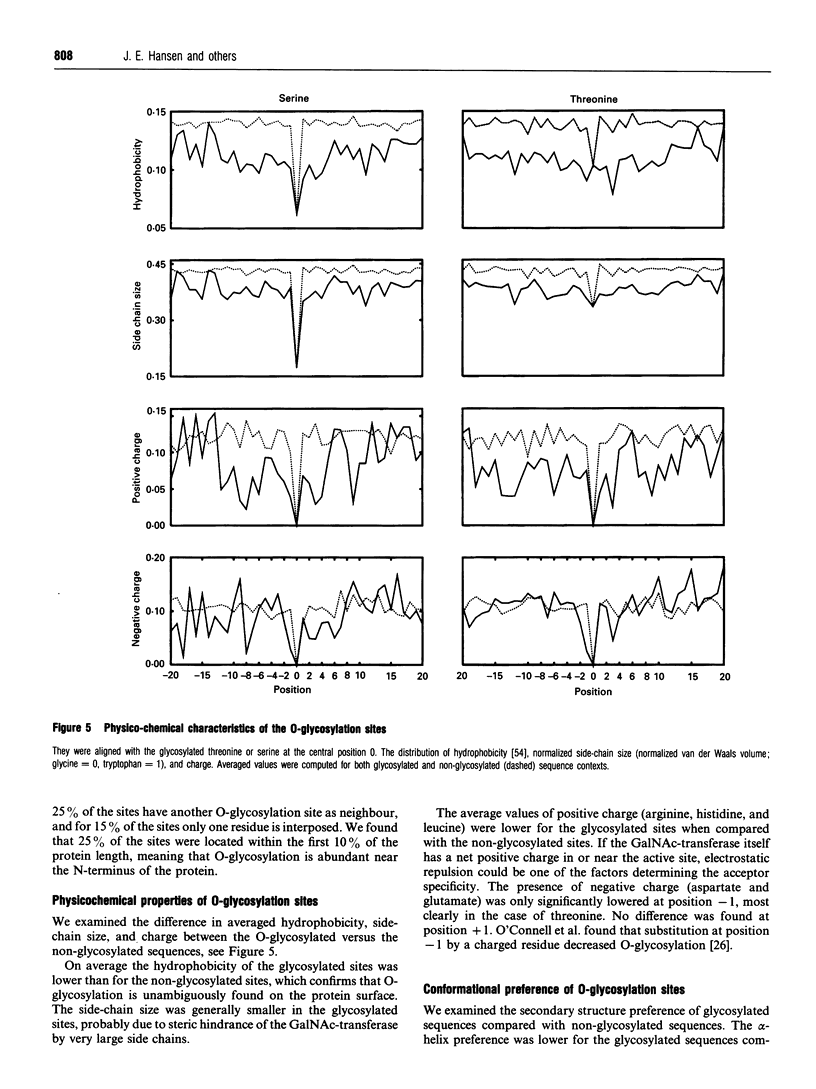


Images in this article
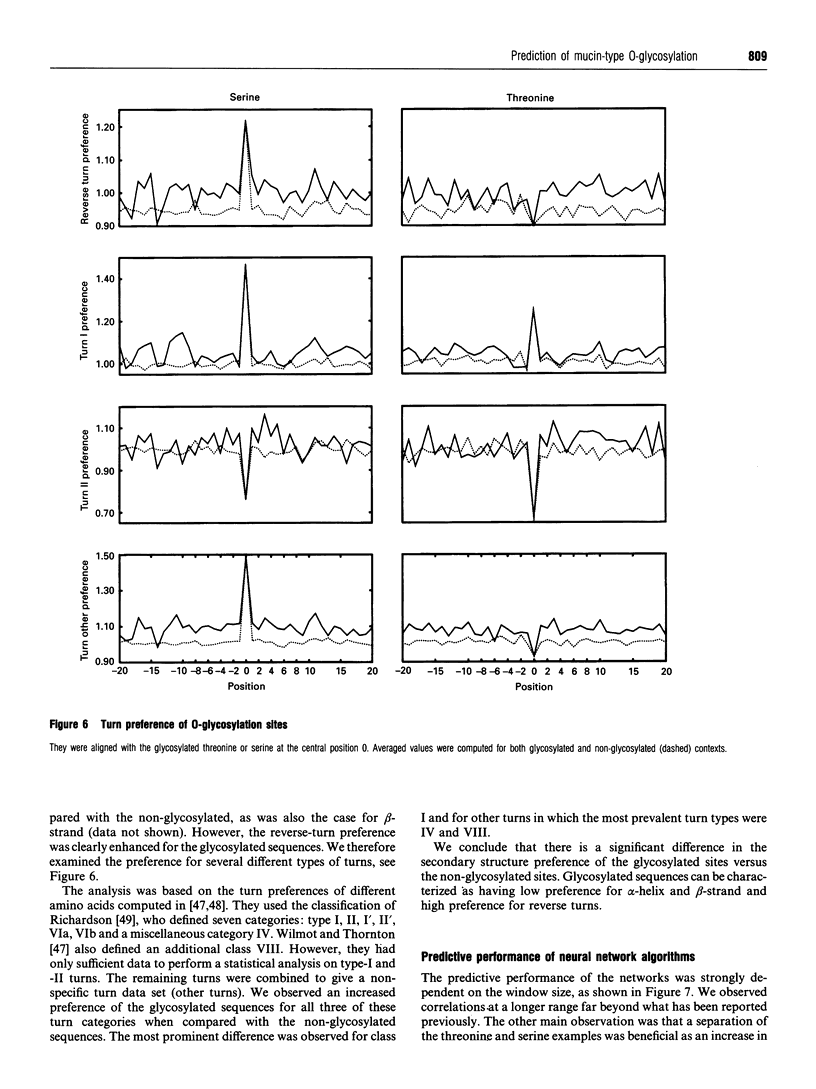
Selected References
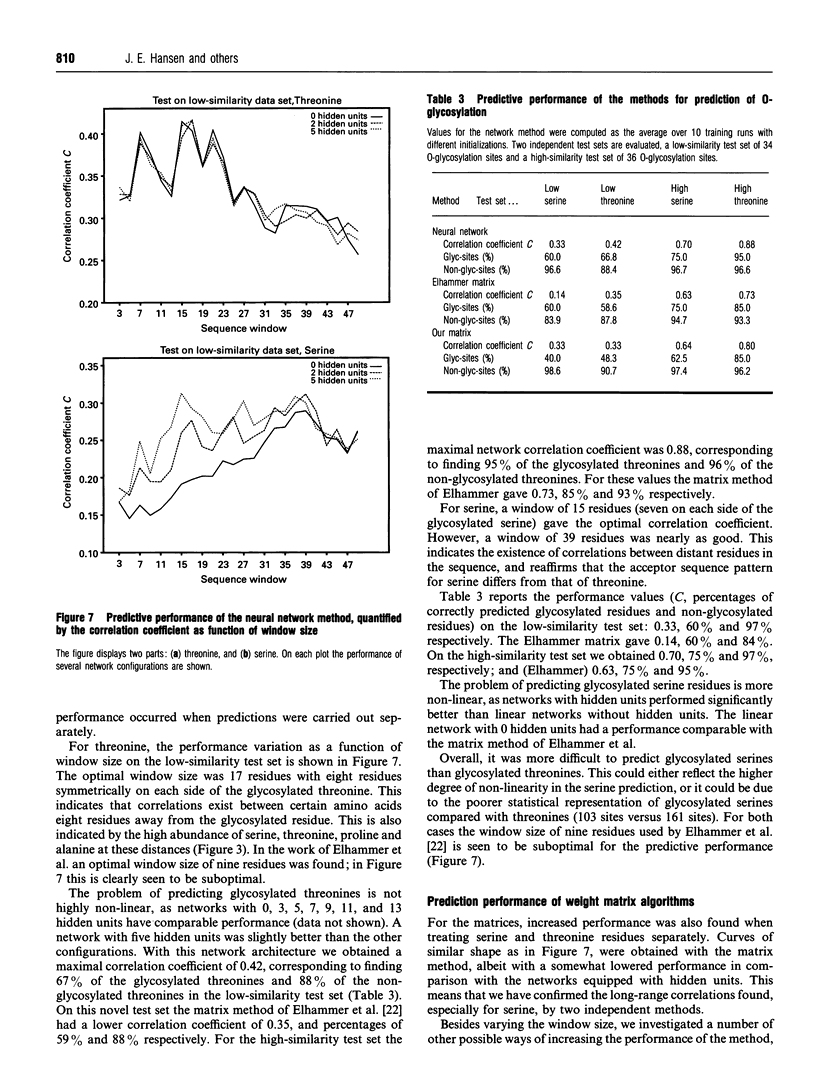
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adolf G. R., Kalsner I., Ahorn H., Maurer-Fogy I., Cantell K. Natural human interferon-alpha 2 is O-glycosylated. Biochem J. 1991 Jun 1;276(Pt 2):511–518. doi: 10.1042/bj2760511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen A. K., Desai N. N., Neuberger A., Creeth J. M. Properties of potato lectin and the nature of its glycoprotein linkages. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 1;171(3):665–674. doi: 10.1042/bj1710665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubert J. P., Biserte G., Loucheux-Lefebvre M. H. Carbohydrate-peptide linkage in glycoproteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Aug;175(2):410–418. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90528-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bairoch A., Boeckmann B. The SWISS-PROT protein sequence data bank, recent developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3093–3096. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker W. C., George D. G., Mewes H. W., Pfeiffer F., Tsugita A. The PIR-International databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3089–3092. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bause E. Structural requirements of N-glycosylation of proteins. Studies with proline peptides as conformational probes. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 1;209(2):331–336. doi: 10.1042/bj2090331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett H. P., Seidah N. G., Benjannet S., Solomon S., Chrétien M. Reinvestigation of the disulfide bridge arrangement in human pro-opiomelanocortin N-terminal segment (hNT 1-76). Int J Pept Protein Res. 1986 Mar;27(3):306–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1986.tb01825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birken S., Agosto G., Amr S., Nisula B., Cole L., Lewis J., Canfield R. Characterization of antisera distinguishing carbohydrate structures in the beta-carboxyl-terminal region of human chorionic gonadotropin. Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):2054–2063. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-5-2054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock S. C., Skriver K., Nielsen E., Thøgersen H. C., Wiman B., Donaldson V. H., Eddy R. L., Marrinan J., Radziejewska E., Huber R. Human C1 inhibitor: primary structure, cDNA cloning, and chromosomal localization. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 29;25(15):4292–4301. doi: 10.1021/bi00363a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr H., Bohr J., Brunak S., Cotterill R. M., Lautrup B., Nørskov L., Olsen O. H., Petersen S. B. Protein secondary structure and homology by neural networks. The alpha-helices in rhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 5;241(1-2):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brain S. D., Tippins J. R., Morris H. R., MacIntyre I., Williams T. J. Potent vasodilator activity of calcitonin gene-related peptide in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Oct;87(4):533–536. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12455620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer H. B., Jr, Shulman R., Herbert P., Ronan R., Wehrly K. The complete amino acid sequence of alanine apolipoprotein (apoC-3), and apolipoprotein from human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4975–4984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunak S., Engelbrecht J., Knudsen S. Prediction of human mRNA donor and acceptor sites from the DNA sequence. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jul 5;220(1):49–65. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90380-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvete J. J., Muñiz-Diaz E. Localization of an O-glycosylation site in the alpha-subunit of the human platelet integrin GPIIb/IIIa involved in Baka (HPA-3a) alloantigen expression. FEBS Lett. 1993 Aug 9;328(1-2):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80959-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson S. R., Lycksell P. O., Fukuda M. Assignment of O-glycan attachment sites to the hinge-like regions of human lysosomal membrane glycoproteins lamp-1 and lamp-2. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Jul;304(1):65–73. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway K. L., Hull S. R. Cell surface mucin-type glycoproteins and mucin-like domains. Glycobiology. 1991 Mar;1(2):131–138. doi: 10.1093/glycob/1.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clogston C. L., Hu S., Boone T. C., Lu H. S. Glycosidase digestion, electrophoresis and chromatographic analysis of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor glycoforms produced in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Chromatogr. 1993 May 7;637(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(93)83098-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahms N. M., Hart G. W. Influence of quaternary structure on glycosylation. Differential subunit association affects the site-specific glycosylation of the common beta-chain from Mac-1 and LFA-1. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13186–13196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahr W., Beyreuther K. A revision of the N-terminal structure of sialoglycoprotein D (glycophorin C) from human erythrocyte membranes. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Nov;366(11):1067–1070. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.2.1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Trivedi B., Baxter R. C. Serum "big insulin-like growth factor II" from patients with tumor hypoglycemia lacks normal E-domain O-linked glycosylation, a possible determinant of normal propeptide processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5823–5827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Caro A. M., Adrich Z., Fournet B., Capon C., Bonicel J. J., De Caro J. D., Rovery M. N-terminal sequence extension in the glycosylated forms of human pancreatic stone protein. The 5-oxoproline N-terminal chain is O-glycosylated on the 5th amino acid residue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 23;994(3):281–284. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90305-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis J. W. N-linked oligosaccharide processing and tumor cell biology. Semin Cancer Biol. 1991 Dec;2(6):411–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Do S. I., Cummings R. D. Presence of O-linked oligosaccharide on a threonine residue in the human transferrin receptor. Glycobiology. 1992 Aug;2(4):345–353. doi: 10.1093/glycob/2.4.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhammer A. P., Poorman R. A., Brown E., Maggiora L. L., Hoogerheide J. G., Kézdy F. J. The specificity of UDP-GalNAc:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase as inferred from a database of in vivo substrates and from the in vitro glycosylation of proteins and peptides. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10029–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiat A. M., Jollès J., Aubert J. P., Loucheux-Lefebvre M. H., Jollès P. Localisation and importance of the sugar part of human casein. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(2):333–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04946.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara S., Shinkai H., Mann K., Timpl R. Structure and localization of O- and N-linked oligosaccharide chains on basement membrane protein nidogen. Matrix. 1993 May;13(3):215–222. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8832(11)80005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda M. Leukosialin, a major O-glycan-containing sialoglycoprotein defining leukocyte differentiation and malignancy. Glycobiology. 1991 Sep;1(4):347–356. doi: 10.1093/glycob/1.4.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G., Ekblom M., Andersson L. C. Differentiation of human erythroid cells is associated with increased O-glycosylation of the major sialoglycoprotein, glycophorin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6752–6756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gejyo F., Chang J. L., Bürgi W., Schmid K., Offner G. D., Troxler R. F., Van Halbeek H., Dorland L., Gerwig G. J., Vliegenthart J. F. Characterization of the B-chain of human plasma alpha 2HS-glycoprotein. The complete amino acid sequence and primary structure of its heteroglycan. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4966–4971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer R., Dabrowski J., Dabrowski U., Linder D., Schlüter M., Schott H. H., Stirm S. Oligosaccharides at individual glycosylation sites in glycoprotein 71 of Friend murine leukemia virus. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 12;187(1):95–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
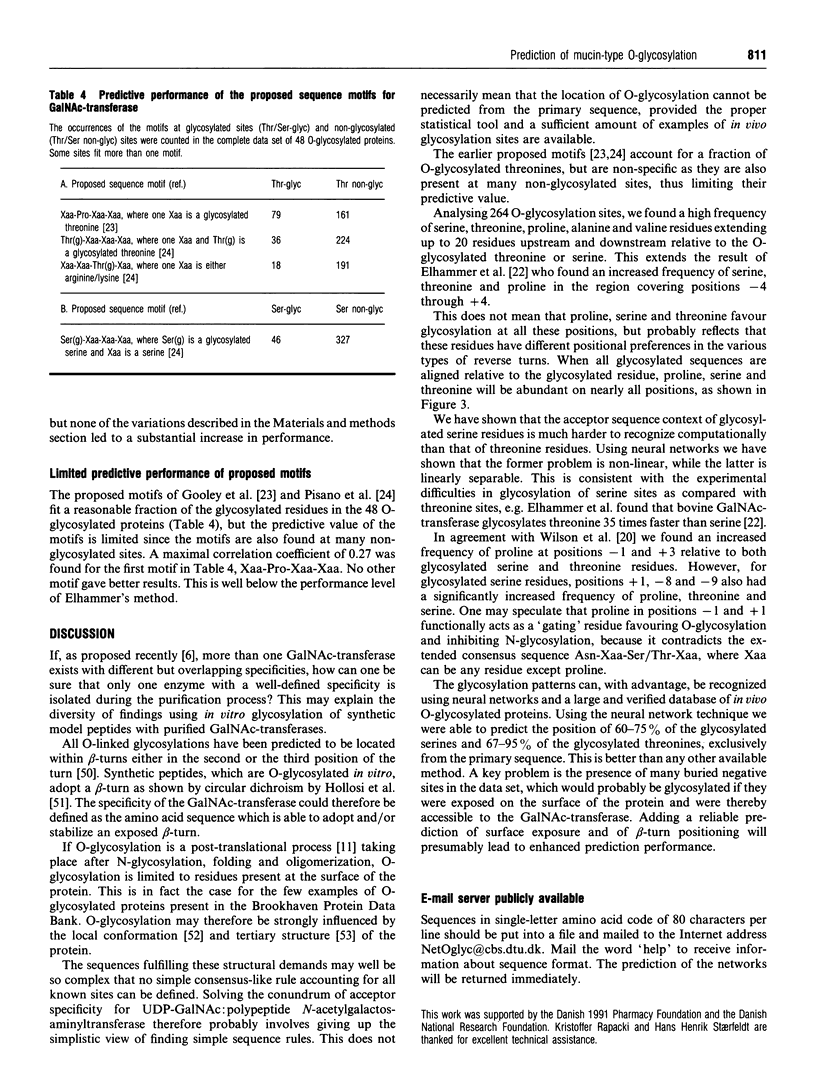
- Gooley A. A., Classon B. J., Marschalek R., Williams K. L. Glycosylation sites identified by detection of glycosylated amino acids released from Edman degradation: the identification of Xaa-Pro-Xaa-Xaa as a motif for Thr-O-glycosylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):1194–1201. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gooley A. A., Williams K. L. Towards characterizing O-glycans: the relative merits of in vivo and in vitro approaches in seeking peptide motifs specifying O-glycosylation sites. Glycobiology. 1994 Aug;4(4):413–417. doi: 10.1093/glycob/4.4.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltiwanger R. S., Kelly W. G., Roquemore E. P., Blomberg M. A., Dong L. Y., Kreppel L., Chou T. Y., Hart G. W. Glycosylation of nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins is ubiquitous and dynamic. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 May;20(2):264–269. doi: 10.1042/bst0200264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Fosang A. J. Proteoglycans: many forms and many functions. FASEB J. 1992 Feb 1;6(3):861–870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. W. Glycosylation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;4(6):1017–1023. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90134-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes G. R., Enns C. A., Lucas J. J. Identification of the O-linked glycosylation site of the human transferrin receptor. Glycobiology. 1992 Aug;2(4):355–359. doi: 10.1093/glycob/2.4.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. D., Jr, Schwyzer M., Steinman H. M., Hill R. L. Ovine submaxillary mucin. Primary structure and peptide substrates of UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine:mucin transferase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3799–3804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser K., Schönberger O. L., Rossmanith I., Wachter E. Kunitz-type proteinase inhibitors derived by limited proteolysis of the inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor, V. Attachments of carbohydrates in the human urinary trypsin inhibitor isolated by affinity chromatography. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1981 Oct;362(10):1357–1362. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1981.362.2.1357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley L. H., Karplus M. Protein secondary structure prediction with a neural network. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):152–156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollosi M., Perczel A., Fasman G. D. Cooperativity of carbohydrate moiety orientation and beta-turn stability is determined by intramolecular hydrogen bonds in protected glycopeptide models. Biopolymers. 1990 Oct-Nov;29(12-13):1549–1564. doi: 10.1002/bip.360291206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honma K., Tomita M., Hamada A. Amino acid sequence and attachment sites of oligosaccharide units of porcine erythrocyte glycophorin. J Biochem. 1980 Dec;88(6):1679–1691. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt L. T., Dayhoff M. O. The occurrence in proteins of the tripeptides Asn-X-Ser and Asn-X-Thr and of bound carbohydrate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 May 22;39(4):757–765. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90270-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häusler A., Ballou L., Ballou C. E., Robbins P. W. Yeast glycoprotein biosynthesis: MNT1 encodes an alpha-1,2-mannosyltransferase involved in O-glycosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6846–6850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushansky K., Lopez J. A., Brown C. B. Role of carbohydrate modification in the production and secretion of human granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in genetically engineered and normal mesenchymal cells. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1881–1886. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellermann J., Lottspeich F., Geiger R., Deutzmann R. Human urinary kallikrein: amino acid sequence and carbohydrate attachment sites. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1989;247A:519–525. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9543-4_80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellermann J., Lottspeich F., Henschen A., Müller-Esterl W. Amino acid sequence of the light chain of human high molecular mass kininogen. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1986;198(Pt A):85–89. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5143-6_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen N., Barclay A. N., Willis A. C., Williams A. F. The sequence of rat leukosialin (W3/13 antigen) reveals a molecule with O-linked glycosylation of one third of its extracellular amino acids. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4029–4034. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02747.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kneller D. G., Cohen F. E., Langridge R. Improvements in protein secondary structure prediction by an enhanced neural network. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):171–182. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90154-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lottspeich F., Kellermann J., Henschen A., Foertsch B., Müller-Esterl W. The amino acid sequence of the light chain of human high-molecular-mass kininogen. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 15;152(2):307–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López Otin C., Grubb A. O., Méndez E. The complete amino acid sequence of human complex-forming glycoprotein heterogeneous in charge (protein HC) from one individual. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Feb 1;228(2):544–554. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W. Comparison of the predicted and observed secondary structure of T4 phage lysozyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 20;405(2):442–451. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor M. J., Flores T. P., Sternberg M. J. Prediction of beta-turns in proteins using neural networks. Protein Eng. 1989 May;2(7):521–526. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.7.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamitake Y., Kodama S., Katayama T., Adachi H., Tanaka S., Tsujimoto M. Structure of recombinant human interleukin 5 produced by Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biochem. 1990 Feb;107(2):292–297. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan F. J., Birken S., Canfield R. E. The amino acid sequence of human chorionic gonadotropin. The alpha subunit and beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):5247–5258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu T. Carbohydrate signals in metastasis and prognosis of human carcinomas. Glycobiology. 1993 Aug;3(4):291–296. doi: 10.1093/glycob/3.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama J. I., Tomita M., Hamada A. Primary structure of horse erythrocyte glycophorin HA. Its amino acid sequence has a unique homology with those of human and porcine erythrocyte glycophorins. J Membr Biol. 1982;64(3):205–215. doi: 10.1007/BF01870887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama J. I., Yamashita T., Tomita M., Hamada A. Amino acid sequence and oligosaccharide attachment sites of the glycosylated domain of dog erythrocyte glycophorin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 15;742(3):477–483. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90264-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama J., Utsumi H., Hamada A. Amino acid sequence of monkey erythrocyte glycophorin MK. Its amino acid sequence has a striking homology with that of human glycophorin A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 21;999(3):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima H., Nishikawa K., Ooi T. The folding type of a protein is relevant to the amino acid composition. J Biochem. 1986 Jan;99(1):153–162. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura H., Kawabata S., Kisiel W., Hase S., Ikenaka T., Takao T., Shimonishi Y., Iwanaga S. Identification of a disaccharide (Xyl-Glc) and a trisaccharide (Xyl2-Glc) O-glycosidically linked to a serine residue in the first epidermal growth factor-like domain of human factors VII and IX and protein Z and bovine protein Z. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20320–20325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura H., Takao T., Hase S., Shimonishi Y., Iwanaga S. Human factor IX has a tetrasaccharide O-glycosidically linked to serine 61 through the fucose residue. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17520–17525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell B., Tabak L. A., Ramasubbu N. The influence of flanking sequences on O-glycosylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 31;180(2):1024–1030. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81168-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opdenakker G., Rudd P. M., Ponting C. P., Dwek R. A. Concepts and principles of glycobiology. FASEB J. 1993 Nov;7(14):1330–1337. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.14.8224606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins S. J., Smith K. F., Amatayakul S., Ashford D., Rademacher T. W., Dwek R. A., Lachmann P. J., Harrison R. A. Two-domain structure of the native and reactive centre cleaved forms of C1 inhibitor of human complement by neutron scattering. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 5;214(3):751–763. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90290-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters B. P., Krzesicki R. F., Perini F., Ruddon R. W. O-glycosylation of the alpha-subunit does not limit the assembly of chorionic gonadotropin alpha beta dimer in human malignant and nonmalignant trophoblast cells. Endocrinology. 1989 Apr;124(4):1602–1612. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-4-1602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano A., Redmond J. W., Williams K. L., Gooley A. A. Glycosylation sites identified by solid-phase Edman degradation: O-linked glycosylation motifs on human glycophorin A. Glycobiology. 1993 Oct;3(5):429–435. doi: 10.1093/glycob/3.5.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poorman R. A., Tomasselli A. G., Heinrikson R. L., Kézdy F. J. A cumulative specificity model for proteases from human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2, inferred from statistical analysis of an extended substrate data base. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14554–14561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presnell S. R., Cohen F. E. Artificial neural networks for pattern recognition in biochemical sequences. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1993;22:283–298. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.22.060193.001435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnam F. W., Liu Y. S., Low T. L. Primary structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. IV. Streptococcal IgA1 protease, digestion, Fab and Fc fragments, and the complete amino acid sequence of the alpha 1 heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2865–2874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian N., Sejnowski T. J. Predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins using neural network models. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 20;202(4):865–884. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90564-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S. The anatomy and taxonomy of protein structure. Adv Protein Chem. 1981;34:167–339. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60520-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Kutny R. M., Panico M., Morris H. R., Chowdhry V. Amino acid sequence and post-translational modification of human interleukin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6486–6490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. A., Appella E. Amino acid sequence of a mouse myeloma immunoglobin heavy chain (MOPC 47 A) with a 100-residue deletion. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11418–11430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rost B., Sander C. Combining evolutionary information and neural networks to predict protein secondary structure. Proteins. 1994 May;19(1):55–72. doi: 10.1002/prot.340190108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid K., Hediger M. A., Brossmer R., Collins J. H., Haupt H., Marti T., Offner G. D., Schaller J., Takagaki K., Walsh M. T. Amino acid sequence of human plasma galactoglycoprotein: identity with the extracellular region of CD43 (sialophorin). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):663–667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider T. D., Stephens R. M. Sequence logos: a new way to display consensus sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6097–6100. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Chrétien M. Complete amino acid sequence of a human pituitary glycopeptide: an important maturation product of pro-opiomelanocortin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4236–4240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Glycoproteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1973;27:349–467. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60451-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strous G. J., Dekker J. Mucin-type glycoproteins. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1992;27(1-2):57–92. doi: 10.3109/10409239209082559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Putnam F. W. Periodicity of leucine and tandem repetition of a 24-amino acid segment in the primary structure of leucine-rich alpha 2-glycoprotein of human serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1906–1910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayasu T., Suzuki S., Kametani F., Takahashi N., Shinoda T., Okuyama T., Munekata E. Amino acid sequence of galactosamine-containing glycopeptides in the hinge region of a human immunoglobulin D. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Apr 14;105(3):1066–1071. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi M., Kobata A. Structures and functional roles of the sugar chains of human erythropoietins. Glycobiology. 1991 Sep;1(4):337–346. doi: 10.1093/glycob/1.4.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Takio K., Handa M., Ruggeri Z. M. Amino acid sequence of the von Willebrand factor-binding domain of platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5610–5614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt C. G., Maurer-Fogy I., Adolf G. R. Natural human tumor necrosis factor beta (lymphotoxin). Variable O-glycosylation at Thr7, proteolytic processing, and allelic variation. FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 7;314(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81467-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh K. A., Titani K., Takio K., Kumar S., Hayes R., Petra P. H. Amino acid sequence of the sex steroid binding protein of human blood plasma. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7584–7590. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Agrwal N., Eckhardt A. E., Stevens R. D., Hill R. L. The acceptor substrate specificity of porcine submaxillary UDP-GalNAc:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase is dependent on the amino acid sequences adjacent to serine and threonine residues. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):22979–22983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watzlawick H., Walsh M. T., Yoshioka Y., Schmid K., Brossmer R. Structure of the N- and O-glycans of the A-chain of human plasma alpha 2HS-glycoprotein as deduced from the chemical compositions of the derivatives prepared by stepwise degradation with exoglycosidases. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 8;31(48):12198–12203. doi: 10.1021/bi00163a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernette-Hammond M. E., Lauer S. J., Corsini A., Walker D., Taylor J. M., Rall S. C., Jr Glycosylation of human apolipoprotein E. The carbohydrate attachment site is threonine 194. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9094–9101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. W., Chang A., Juretić D., Loughran S. Secondary structure predictions and medium range interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 26;916(2):200–204. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilmot C. M., Thornton J. M. Analysis and prediction of the different types of beta-turn in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 5;203(1):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. B., Gavel Y., von Heijne G. Amino acid distributions around O-linked glycosylation sites. Biochem J. 1991 Apr 15;275(Pt 2):529–534. doi: 10.1042/bj2750529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing D. R., Rademacher T. W., Schmitz B., Schachner M., Dwek R. A. Comparative glycosylation in neural adhesion molecules. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 May;20(2):386–390. doi: 10.1042/bst0200386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan S. B., Wold F. Neoglycoproteins: in vitro introduction of glycosyl units at glutamines in beta-casein using transglutaminase. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 31;23(16):3759–3765. doi: 10.1021/bi00311a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagishita M., Hascall V. C. Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9451–9454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Tsuchiya D., Sandlin D. E., Holroyde M. J. Enzymic O-glycosylation of synthetic peptides from sequences in basic myelin protein. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 2;18(20):4444–4448. doi: 10.1021/bi00587a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]