Abstract
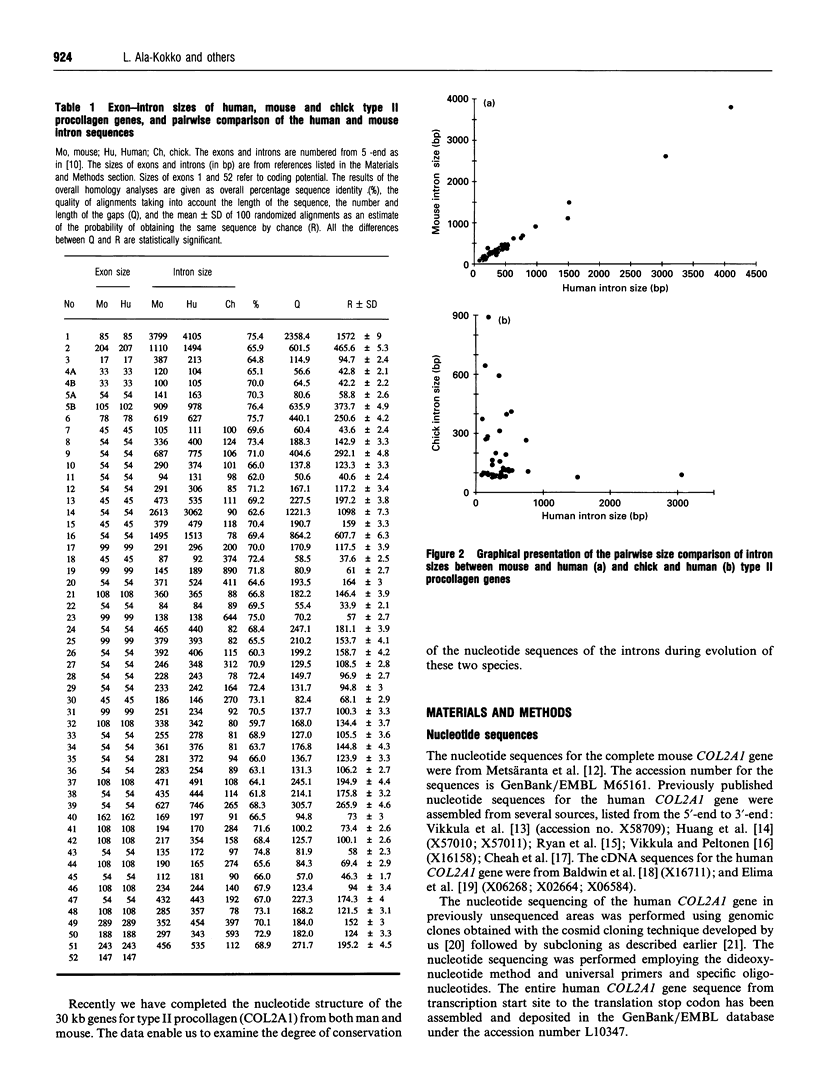
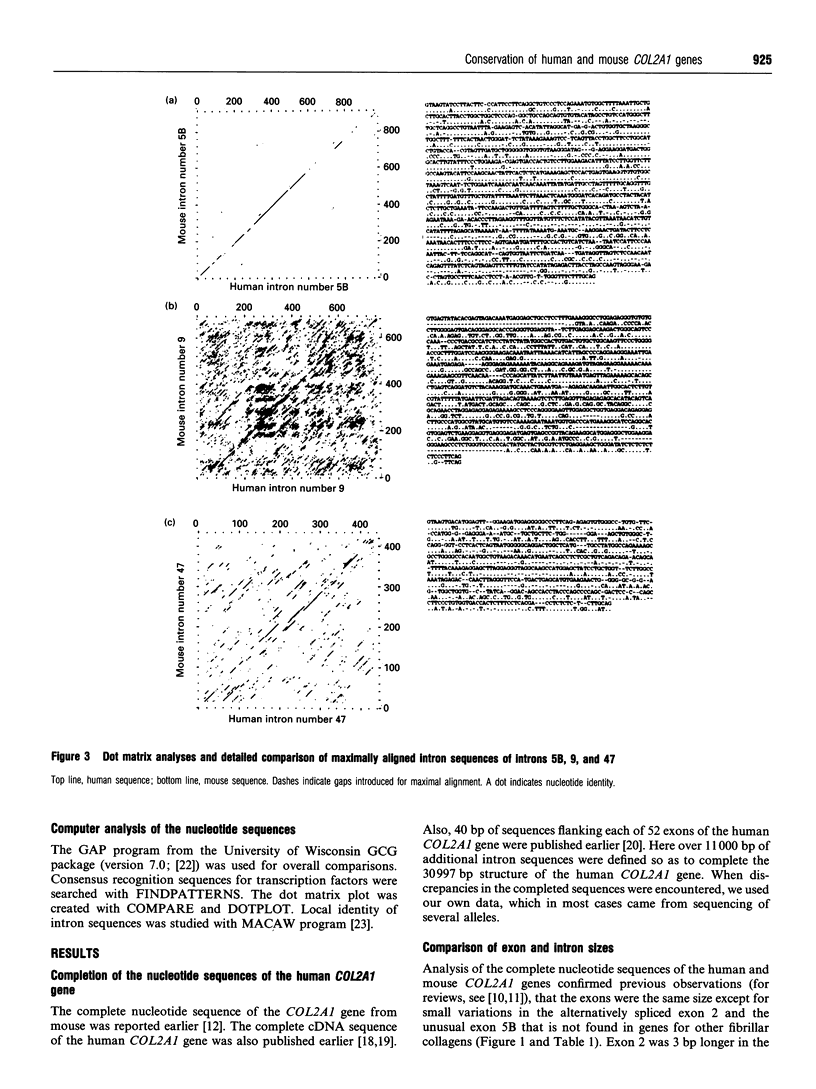
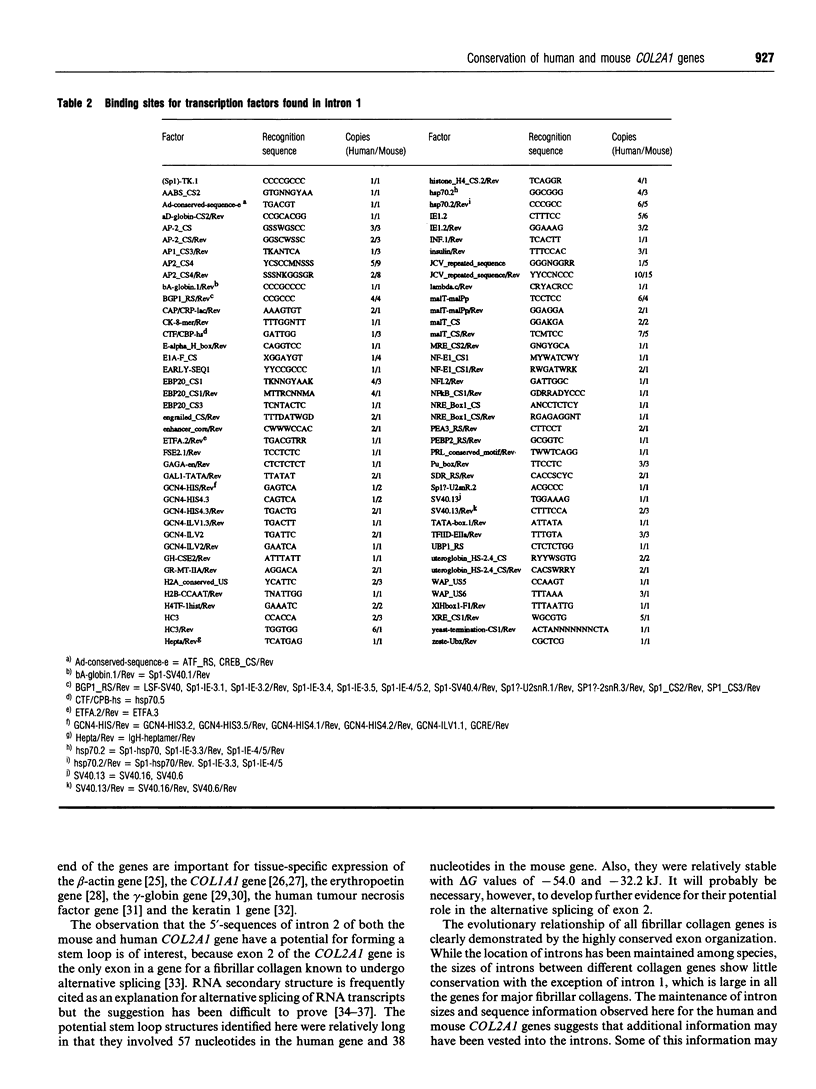
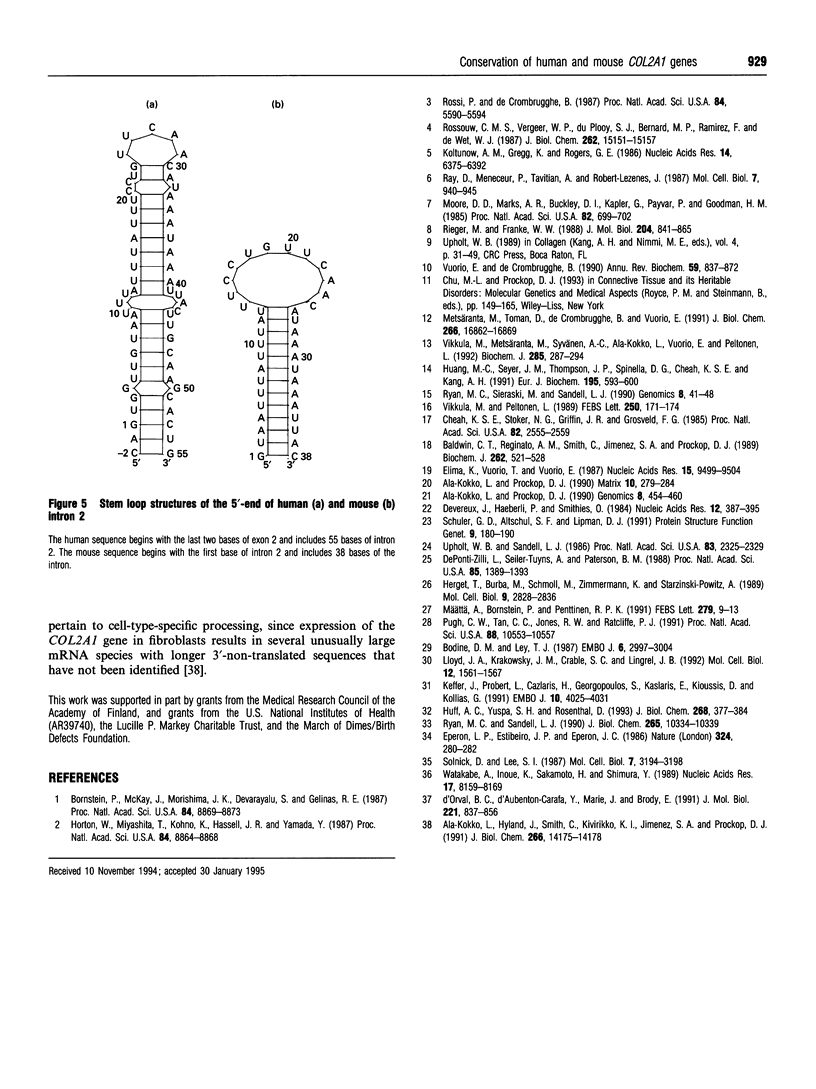
Over 11,000 bp of previously undefined sequences of the human COL2A1 gene were defined. The results made it possible to compare the intron structures of a highly complex gene from man and mouse. Surprisingly, the sizes of the 53 introns of the two genes were highly conserved with a mean difference of 13%. After alignment of the sequences, 69% of the intron sequences were identical. The introns contained consensus sequences for the binding of over 100 different transcription factors that were conserved in the introns of the two genes. The first intron of the gene contained 80 conserved consensus sequences and the remaining 52 introns of the gene contained 106 conserved sequences for the binding of transcription factors. The 5'-end of intron 2 in both genes had a potential for forming a stem loop in RNA transcripts.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ala-Kokko L., Hyland J., Smith C., Kivirikko K. I., Jimenez S. A., Prockop D. J. Expression of a human cartilage procollagen gene (COL2A1) in mouse 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14175–14178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ala-Kokko L., Prockop D. J. Completion of the intron-exon structure of the gene for human type II procollagen (COL2A1): variations in the nucleotide sequences of the alleles from three chromosomes. Genomics. 1990 Nov;8(3):454–460. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90031-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ala-Kokko L., Prockop D. J. Efficient procedure for preparing cosmid libraries from microgram quantities of genomic DNA fragments size fractionated by gel electrophoresis. Matrix. 1990 Oct;10(5):279–284. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8832(11)80182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin C. T., Reginato A. M., Smith C., Jimenez S. A., Prockop D. J. Structure of cDNA clones coding for human type II procollagen. The alpha 1(II) chain is more similar to the alpha 1(I) chain than two other alpha chains of fibrillar collagens. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):521–528. doi: 10.1042/bj2620521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodine D. M., Ley T. J. An enhancer element lies 3' to the human A gamma globin gene. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2997–3004. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02605.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., McKay J., Morishima J. K., Devarayalu S., Gelinas R. E. Regulatory elements in the first intron contribute to transcriptional control of the human alpha 1(I) collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8869–8873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheah K. S., Stoker N. G., Griffin J. R., Grosveld F. G., Solomon E. Identification and characterization of the human type II collagen gene (COL2A1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2555–2559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouet d'Orval B., d'Aubenton-Carafa Y., Brody J. M., Brody E. Determination of an RNA structure involved in splicing inhibition of a muscle-specific exon. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 5;221(3):837–856. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80179-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePonti-Zilli L., Seiler-Tuyns A., Paterson B. M. A 40-base-pair sequence in the 3' end of the beta-actin gene regulates beta-actin mRNA transcription during myogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1389–1393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elima K., Vuorio T., Vuorio E. Determination of the single polyadenylation site of the human pro alpha 1(II) collagen gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9499–9504. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon L. P., Estibeiro J. P., Eperon I. C. The role of nucleotide sequences in splice site selection in eukaryotic pre-messenger RNA. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):280–282. doi: 10.1038/324280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herget T., Burba M., Schmoll M., Zimmermann K., Starzinski-Powitz A. Regulated expression of nuclear protein(s) in myogenic cells that binds to a conserved 3' untranslated region in pro alpha 1 (I) collagen cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2828–2836. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton W., Miyashita T., Kohno K., Hassell J. R., Yamada Y. Identification of a phenotype-specific enhancer in the first intron of the rat collagen II gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8864–8868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. C., Seyer J. M., Thompson J. P., Spinella D. G., Cheah K. S., Kang A. H. Genomic organization of the human procollagen alpha 1(II) collagen gene. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Feb 14;195(3):593–600. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15742.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff C. A., Yuspa S. H., Rosenthal D. Identification of control elements 3' to the human keratin 1 gene that regulate cell type and differentiation-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):377–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keffer J., Probert L., Cazlaris H., Georgopoulos S., Kaslaris E., Kioussis D., Kollias G. Transgenic mice expressing human tumour necrosis factor: a predictive genetic model of arthritis. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4025–4031. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04978.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koltunow A. M., Gregg K., Rogers G. E. Intron sequences modulate feather keratin gene transcription in Xenopus oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6375–6392. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd J. A., Krakowsky J. M., Crable S. C., Lingrel J. B. Human gamma- to beta-globin gene switching using a mini construct in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1561–1567. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metsäranta M., Toman D., de Crombrugghe B., Vuorio E. Mouse type II collagen gene. Complete nucleotide sequence, exon structure, and alternative splicing. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16862–16869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. D., Marks A. R., Buckley D. I., Kapler G., Payvar F., Goodman H. M. The first intron of the human growth hormone gene contains a binding site for glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):699–702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mättä A., Bornstein P., Penttinen R. P. Highly conserved sequences in the 3'-untranslated region of the COL1A1 gene bind cell-specific nuclear proteins. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 11;279(1):9–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80237-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh C. W., Tan C. C., Jones R. W., Ratcliffe P. J. Functional analysis of an oxygen-regulated transcriptional enhancer lying 3' to the mouse erythropoietin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10553–10557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray D., Meneceur P., Tavitian A., Robert-Lezenes J. Presence of a c-myc transcript initiated in intron 1 in Friend erythroleukemia cells and in other murine cell types with no evidence of c-myc gene rearrangement. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):940–945. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieger M., Franke W. W. Identification of an orthologous mammalian cytokeratin gene. High degree of intron sequence conservation during evolution of human cytokeratin 10. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 20;204(4):841–856. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi P., de Crombrugghe B. Identification of a cell-specific transcriptional enhancer in the first intron of the mouse alpha 2 (type I) collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5590–5594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossouw C. M., Vergeer W. P., du Plooy S. J., Bernard M. P., Ramirez F., de Wet W. J. DNA sequences in the first intron of the human pro-alpha 1(I) collagen gene enhance transcription. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15151–15157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. C., Sandell L. J. Differential expression of a cysteine-rich domain in the amino-terminal propeptide of type II (cartilage) procollagen by alternative splicing of mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10334–10339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. C., Sieraski M., Sandell L. J. The human type II procollagen gene: identification of an additional protein-coding domain and location of potential regulatory sequences in the promoter and first intron. Genomics. 1990 Sep;8(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90224-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G. D., Altschul S. F., Lipman D. J. A workbench for multiple alignment construction and analysis. Proteins. 1991;9(3):180–190. doi: 10.1002/prot.340090304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D., Lee S. I. Amount of RNA secondary structure required to induce an alternative splice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3194–3198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upholt W. B., Sandell L. J. Exon/intron organization of the chicken type II procollagen gene: intron size distribution suggests a minimal intron size. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2325–2329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vikkula M., Metsäranta M., Syvänen A. C., Ala-Kokko L., Vuorio E., Peltonen L. Structural analysis of the regulatory elements of the type-II procollagen gene. Conservation of promoter and first intron sequences between human and mouse. Biochem J. 1992 Jul 1;285(Pt 1):287–294. doi: 10.1042/bj2850287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vikkula M., Peltonen L. Structural analyses of the polymorphic area in type II collagen gene. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80713-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuorio E., de Crombrugghe B. The family of collagen genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:837–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watakabe A., Inoue K., Sakamoto H., Shimura Y. A secondary structure at the 3' splice site affects the in vitro splicing reaction of mouse immunoglobulin mu chain pre-mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 25;17(20):8159–8169. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.20.8159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




