Abstract
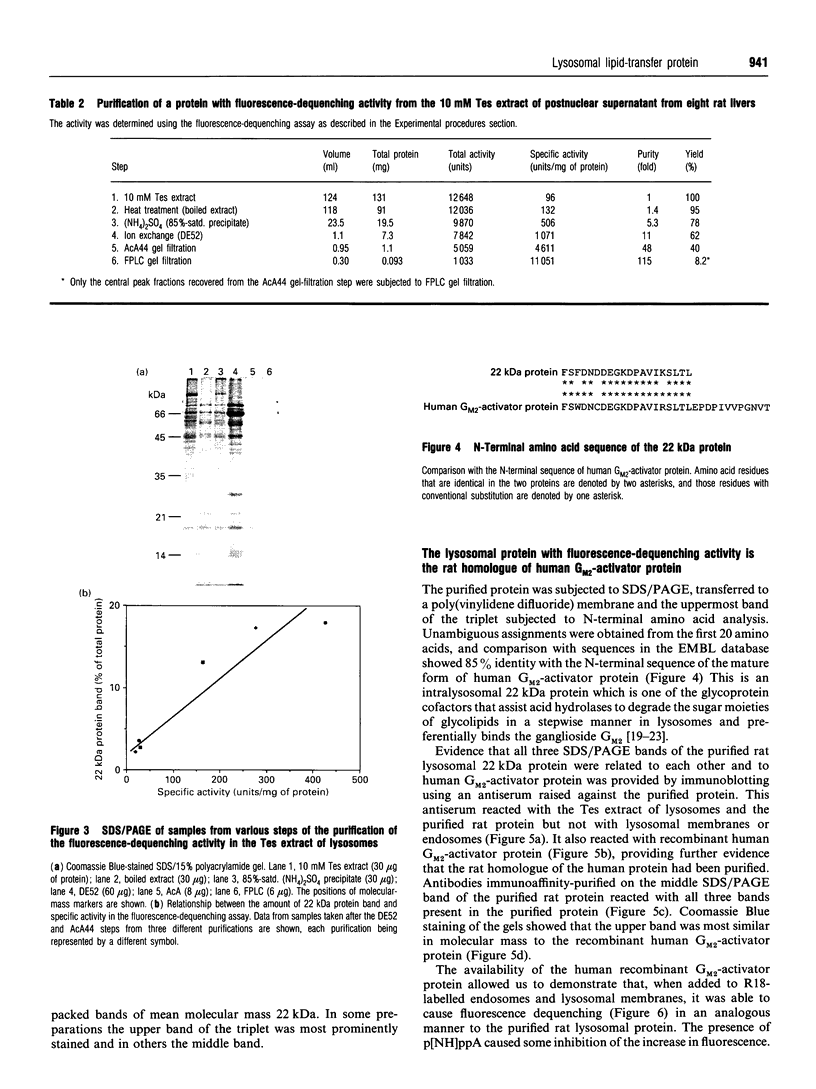
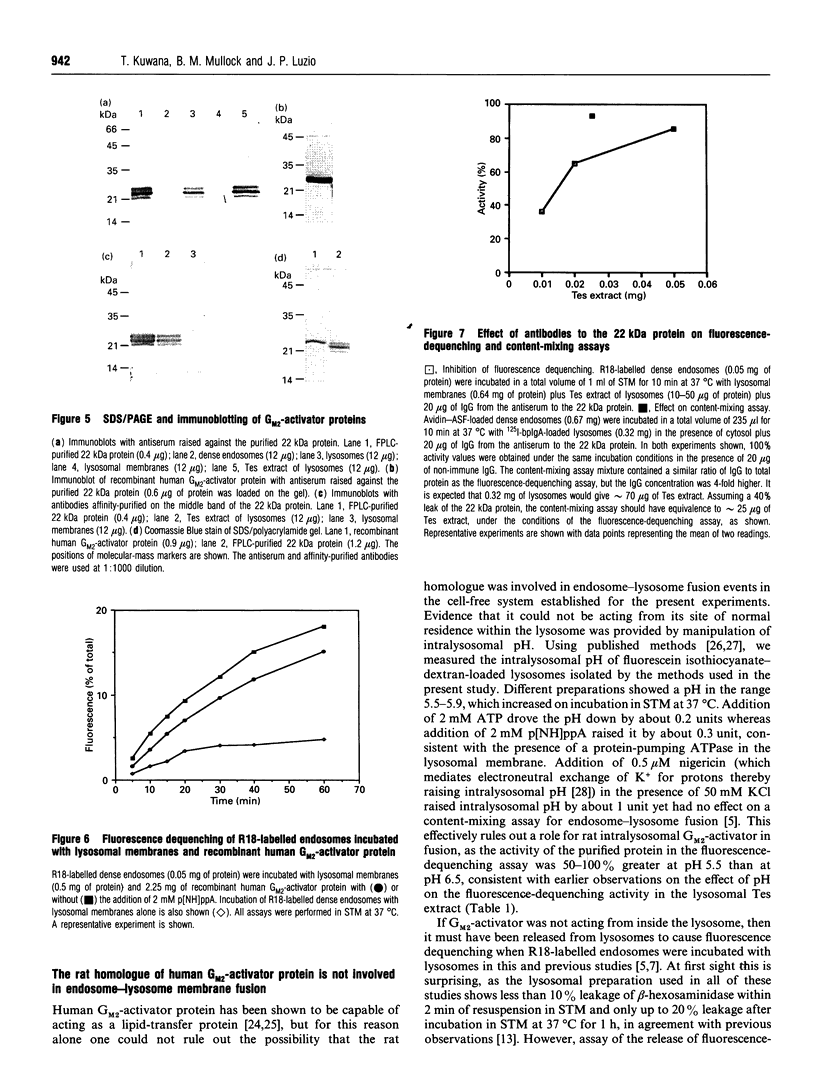
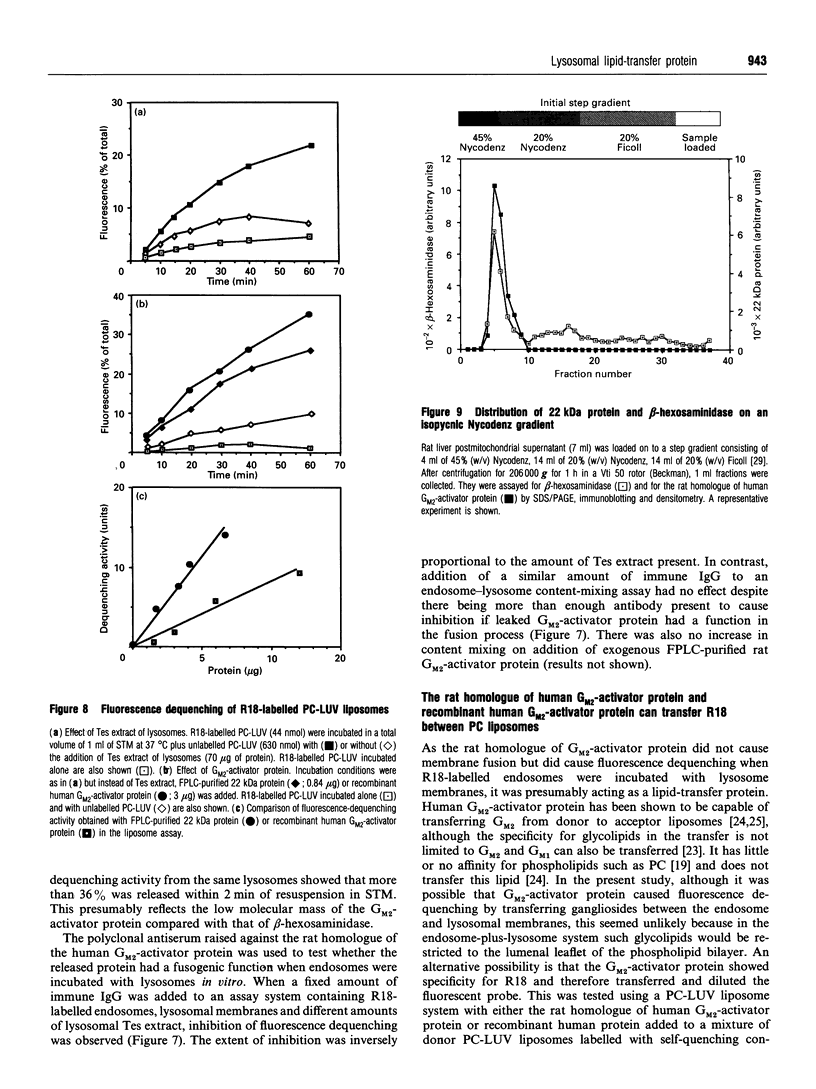
In the present and previous studies [Mullock, Perez, Kuwana, Gray and Luzio (1994) J. Cell Biol. 126, 1173-1182], we have attempted to investigate endosome-lysosome fusion using an assay based on the dilution of the self-quenching fluorescent lipid probe octadecylrhodamine. Although some characteristics of fluorescence dequenching were consistent with those observed in other cell-free assays, we have now demonstrated that increased fluorescence was due to leakage of an intralysosomal lipid-transfer protein. This protein was purified and found to be a 22 kDa molecule with sequence, immunological and functional characteristics strongly suggesting that it is the rat homologue of human GM2-activator protein. Both the 22 kDa protein and recombinant human GM2-activator protein caused fluorescence dequenching either when mixed with octadecylrhodamine-loaded endosomes and lysosomal membranes or in a liposome system. The data were consistent with GM2-activator protein acting as an octadecylrhodamine-transfer protein. Antibodies to the 22 kDa protein added to cell-free endosome-lysosome content-mixing assays had no effect, although they could inhibit fluorescence dequenching caused by the protein. Thus this protein is not required in any fusion event involved in delivery of ligands from endosomes to lysosomes. The existence within an intracellular organelle of a protein capable of acting as an octadecylrhodamine-transfer protein suggests the need for caution in the interpretation of fluorescence-dequenching assays using mammalian subcellular fractions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraha A., Morgan B. P., Luzio J. P. The preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to human complement component C8 and their use in purification of C8 and C8 subunits. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):285–292. doi: 10.1042/bj2510285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A., Burg J., Conzelmann E., Carroll M., Sandhoff K. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the ganglioside GM2-activator protein. Screening of normal human tissues and body fluids, of tissues of GM2 gangliosidosis, and for its subcellular localization. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1984 Mar;365(3):347–356. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1984.365.1.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brake B., Braghetta P., Banting G., Bressan G., Luzio J. P., Stanley K. K. A new recombinant DNA strategy for the molecular cloning of rare membrane proteins. Biochem J. 1990 May 1;267(3):631–637. doi: 10.1042/bj2670631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleves A., McGee T., Bankaitis V. Phospholipid transfer proteins: a biological debut. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;1(1):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90067-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobaleda C., García-Sastre A., Villar E. Fusion between Newcastle disease virus and erythrocyte ghosts using octadecyl Rhodamine B fluorescence assay produces dequenching curves that fit the sum of two exponentials. Biochem J. 1994 Jun 1;300(Pt 2):347–354. doi: 10.1042/bj3000347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann E., Burg J., Stephan G., Sandhoff K. Complexing of glycolipids and their transfer between membranes by the activator protein for degradation of lysosomal ganglioside GM2. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):455–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann E., Sandhoff K. AB variant of infantile GM2 gangliosidosis: deficiency of a factor necessary for stimulation of hexosaminidase A-catalyzed degradation of ganglioside GM2 and glycolipid GA2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3979–3983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann E., Sandhoff K. Activator proteins for lysosomal glycolipid hydrolysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;138:792–815. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)38068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowhan W. Phospholipid-transfer proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;3(4):621–625. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90032-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst W., Sandhoff K. Activator proteins and topology of lysosomal sphingolipid catabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jun 5;1126(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90210-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst W., Schubert J., Machleidt W., Meyer H. E., Sandhoff K. The complete amino-acid sequences of human ganglioside GM2 activator protein and cerebroside sulfate activator protein. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Sep 24;192(3):709–714. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadella T. W., Jr, Bastiaens P. I., Visser A. J., Wirtz K. W. Shape and lipid-binding site of the nonspecific lipid-transfer protein (sterol carrier protein 2): a steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence study. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 4;30(22):5555–5564. doi: 10.1021/bi00236a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway C. J., Dean G. E., Fuchs R., Mellman I. Analysis of endosome and lysosome acidification in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:601–611. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Gruenberg J. The arguments for pre-existing early and late endosomes. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;1(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90047-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D. Fluorescence assays to monitor membrane fusion: potential application in biliary lipid secretion and vesicle interactions. Hepatology. 1990 Sep;12(3 Pt 2):61S–66S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D., de Boer T., Klappe K., Wilschut J. Fluorescence method for measuring the kinetics of fusion between biological membranes. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5675–5681. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins C. R., Gibson A., Shipman M., Miller K. Movement of internalized ligand-receptor complexes along a continuous endosomal reticulum. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):335–339. doi: 10.1038/346335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klima H., Klein A., van Echten G., Schwarzmann G., Suzuki K., Sandhoff K. Over-expression of a functionally active human GM2-activator protein in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1993 Jun 1;292(Pt 2):571–576. doi: 10.1042/bj2920571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. G., Marciniak S. J., MacLean C. M., Edwardson J. M. Pancreatic plasma membranes: promiscuous partners in membrane fusion. Biochem J. 1994 Mar 15;298(Pt 3):599–604. doi: 10.1042/bj2980599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. C., MacDonald R. I., Menco B. P., Takeshita K., Subbarao N. K., Hu L. R. Small-volume extrusion apparatus for preparation of large, unilamellar vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 30;1061(2):297–303. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90295-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire G. A., Docherty K., Hales C. N. Sugar transport in rat liver lysosomes. Direct demonstration by using labelled sugars. Biochem J. 1983 Apr 15;212(1):211–218. doi: 10.1042/bj2120211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire G. A., Luzio J. P. The presence and orientation of ecto-5'-nucleotidase in rat liver lysosomes. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 21;180(1):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80244-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier E. M., Schwarzmann G., Fürst W., Sandhoff K. The human GM2 activator protein. A substrate specific cofactor of beta-hexosaminidase A. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1879–1887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullock B. M., Branch W. J., van Schaik M., Gilbert L. K., Luzio J. P. Reconstitution of an endosome-lysosome interaction in a cell-free system. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2093–2099. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullock B. M., Luzio J. P. Reconstitution of rat liver endosome-lysosome fusion in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1992;219:52–60. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)19009-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullock B. M., Perez J. H., Kuwana T., Gray S. R., Luzio J. P. Lysosomes can fuse with a late endosomal compartment in a cell-free system from rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;126(5):1173–1182. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.5.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. F. Maturation models for endosome and lysosome biogenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;1(4):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak A., Lowden J. A. GM2 ganglioside activator occurs in multiple forms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Mar 2;1199(2):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(94)90117-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Moriyama Y., Takano T. Identification and characterization of a proton pump on lysosomes by fluorescein-isothiocyanate-dextran fluorescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2758–2762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Poole B. Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3327–3331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roederer M., Barry J. R., Wilson R. B., Murphy R. F. Endosomes can undergo an ATP-dependent density increase in the absence of dense lysosomes. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;51(2):229–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Phospholipid transfer market. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):519–520. doi: 10.1038/347519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder M., Klima H., Nakano T., Kwon H., Quintern L. E., Gärtner S., Suzuki K., Sandhoff K. Isolation of a cDNA encoding the human GM2 activator protein. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):197–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81454-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder M., Schnabel D., Suzuki K., Sandhoff K. A mutation in the gene of a glycolipid-binding protein (GM2 activator) that causes GM2-gangliosidosis variant AB. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 23;290(1-2):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81211-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., Schoen P., Bron R., Wey J., Bartoldus I., Ortiz A., Nieva J. L., Wilschut J. Evaluation of viral membrane fusion assays. Comparison of the octadecylrhodamine dequenching assay with the pyrene excimer assay. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 26;32(42):11330–11337. doi: 10.1021/bi00093a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson S., Taylor P. W., Luzio J. P. Transfer of phospholipid and protein into the envelope of gram-negative bacteria by liposome fusion. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8303–8311. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M. Viral and cellular membrane fusion proteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:675–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz K. W., Gadella T. W., Jr Properties and modes of action of specific and non-specific phospholipid transfer proteins. Experientia. 1990 Jun 15;46(6):592–599. doi: 10.1007/BF01939698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz K. W. Phospholipid transfer proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:73–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.000445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunderli-Allenspach H., Günthert M., Ott S. Inactivation of PR8 influenza virus through the octadecylrhodamine B chloride membrane marker. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 26;32(3):900–907. doi: 10.1021/bi00054a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie B., Mahuran D. The GM2 activator protein does not play a critical role in endosome and lysosome membrane fusion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 May 30;201(1):90–93. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie B., McInnes B., Neote K., Lamhonwah A. M., Mahuran D. Isolation and expression of a full-length cDNA encoding the human GM2 activator protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jun 28;177(3):1217–1223. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90671-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlatkine P., el Yandouzi E. H., Op den Kamp J. A., Le Grimellec C. Incorporation of exogenous phosphatidylcholine in the plasma membrane of MDCK cells by a specific transfer protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 18;1065(2):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90234-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]