Abstract
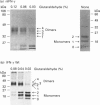
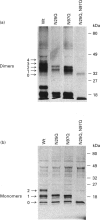
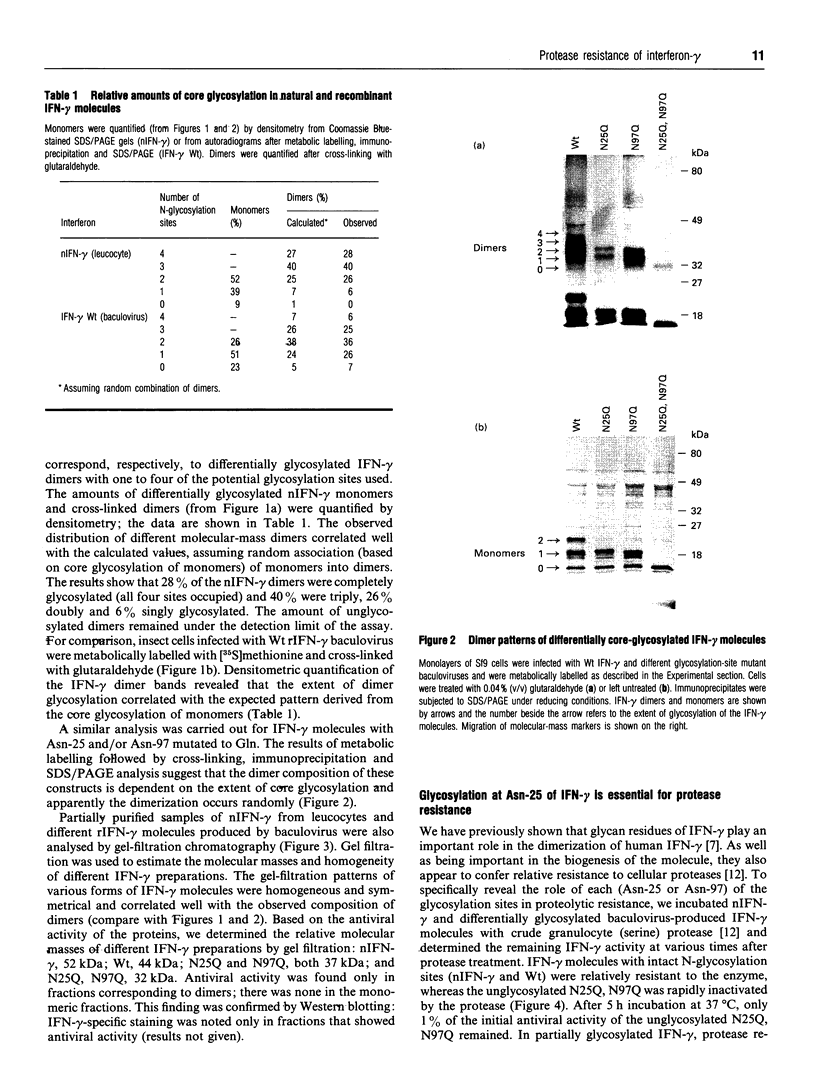
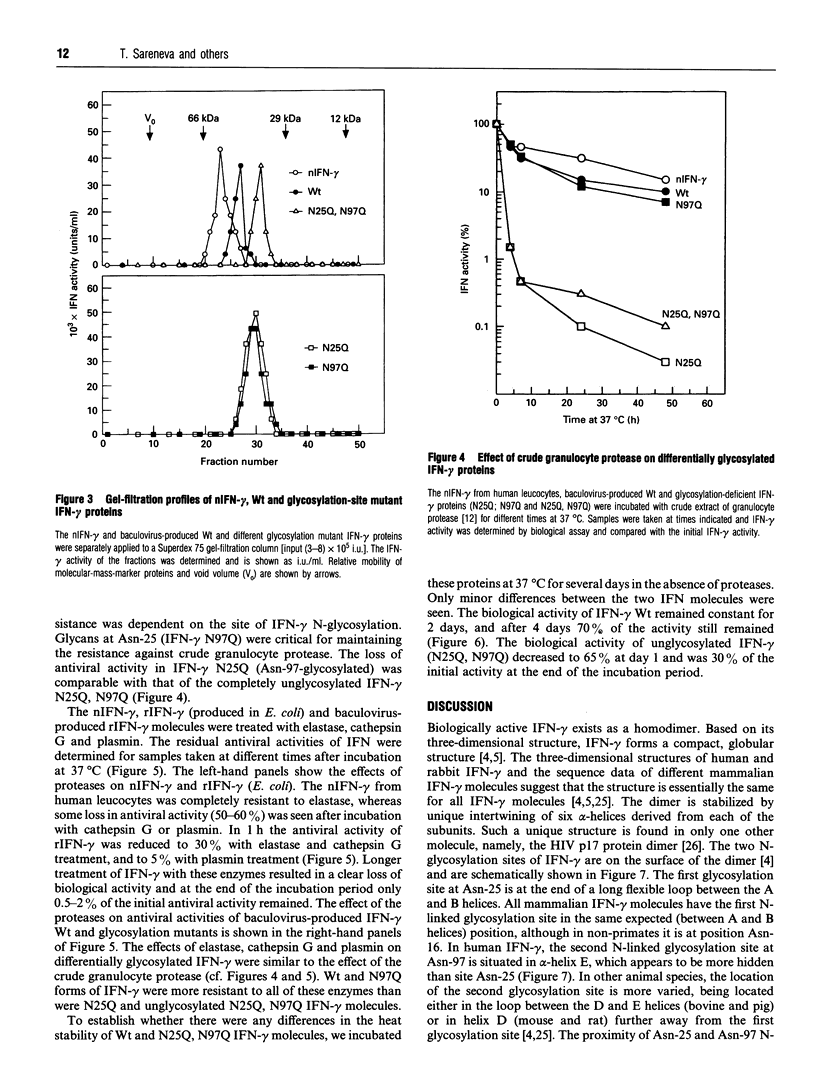
Human interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) is a secretory, dimeric glycoprotein that forms a compact globular structure with potential N-linked glycosylation sites at Asn-25 and Asn-97 on the surface of the dimer. In natural leucocyte IFN-gamma (nIFN-gamma), 52%, 39% and 9% of the monomers are core-glycosylated in two, one or none of the potential N-glycosylation sites respectively. Chemical cross-linking of nIFN-gamma with glutaraldehyde revealed that 4, 3, 2 or 1 glycosylation sites occupied 28%, 40%, 26% and 6% of the dimers respectively. In baculovirus-produced wild-type (Wt) and N-linked glycosylation site-defective mutant (N25Q or N97Q, Asn-25 or Asn-97 substituted by Gln) IFN-gamma proteins, the extent of core glycosylation of monomers reflected the glycan composition of dimers. This suggests that dimers are formed randomly and independently of glycosylation. The glycan residues of IFN-gamma, especially at Asn-25, play an important role in protease resistance. Unglycosylated recombinant IFN-gamma proteins (from Escherichia coli and baculovirus) and N25Q IFN-gamma were sensitive to crude granulocyte protease, purified elastase, cathepsin G and plasmin degradation. Fully glycosylated nIFN-gamma and baculovirus Wt and N97Q IFN-gamma showed full or partial resistance to these proteases. These results emphasize the importance of glycan residues, especially at Asn-25, in the proteolytic stability of human IFN-gamma. Whether the differential glycosylation of n- and recombinant IFN-gamma (rIFN-gamma) is reflected in their biological activities in tissues or their clinical applicability is not known.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauvois B., Sancéau J., Wietzerbin J. Human U937 cell surface peptidase activities: characterization and degradative effect on tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Apr;22(4):923–930. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocci V., Pacini A., Pessina G. P., Paulesu L., Muscettola M., Lunghetti G. Catabolic sites of human interferon-gamma. J Gen Virol. 1985 Apr;66(Pt 4):887–891. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-4-887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantell K., Hirvonen S., Kauppinen H. L., Kalkkinen N. Rapid production of interferon-gamma in uninduced human leukocyte suspensions. J Interferon Res. 1991 Aug;11(4):231–236. doi: 10.1089/jir.1991.11.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantell K., Hirvonen S., Kauppinen H. L. Production and partial purification of human immune interferon. Methods Enzymol. 1986;119:54–63. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)19009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantell K., Hirvonen S., Sareneva T., Pirhonen J., Julkunen I. Differential inactivation of interferons by a protease from human granulocytes. J Interferon Res. 1992 Jun;12(3):177–183. doi: 10.1089/jir.1992.12.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ealick S. E., Cook W. J., Vijay-Kumar S., Carson M., Nagabhushan T. L., Trotta P. P., Bugg C. E. Three-dimensional structure of recombinant human interferon-gamma. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):698–702. doi: 10.1126/science.1902591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar M. A., Schreiber R. D. The molecular cell biology of interferon-gamma and its receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:571–611. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlund A. C., Schreiber R. D., Goeddel D. V., Pennica D. Interferon-gamma induces receptor dimerization in solution and on cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18103–18110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazuda D. J., Strickler J., Kueppers F., Simon P. L., Young P. R. Processing of precursor interleukin 1 beta and inflammatory disease. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6318–6322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelker H. C., Le J., Rubin B. Y., Yip Y. K., Nagler C., Vilcek J. Three molecular weight forms of natural human interferon-gamma revealed by immunoprecipitation with monoclonal antibody. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4301–4304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laouar A., Villiers C., Sancéau J., Maison C., Colomb M., Wietzerbin J., Bauvois B. Inactivation of interleukin-6 in vitro by monoblastic U937 cell plasma membranes involves both protease and peptidyl-transferase activities. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Aug 1;215(3):825–831. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundell D., Lunn C. A., Senior M. M., Zavodny P. J., Narula S. K. Importance of the loop connecting A and B helices of human interferon-gamma in recognition by interferon-gamma receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 10;269(23):16159–16162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundell D., Lunn C., Dalgarno D., Fossetta J., Greenberg R., Reim R., Grace M., Narula S. The carboxyl-terminal region of human interferon gamma is important for biological activity: mutagenic and NMR analysis. Protein Eng. 1991 Feb;4(3):335–341. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.3.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maison C. M., Villiers C. L., Colomb M. G. Proteolysis of C3 on U937 cell plasma membranes. Purification of cathepsin G. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 1;147(3):921–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews S., Barlow P., Boyd J., Barton G., Russell R., Mills H., Cunningham M., Meyers N., Burns N., Clark N. Structural similarity between the p17 matrix protein of HIV-1 and interferon-gamma. Nature. 1994 Aug 25;370(6491):666–668. doi: 10.1038/370666a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmely M. J., Sterner K. E., Gale A., Zhou W. W. U937 cells can utilize plasminogen activator to regulate human interferon-gamma. J Interferon Res. 1993 Dec;13(6):397–406. doi: 10.1089/jir.1993.13.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J. The degradation of cartilage proteoglycans by tissue proteinases. Proteoglycan heterogeneity and the pathway of proteolytic degradation. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 1;167(3):639–646. doi: 10.1042/bj1670639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sareneva T., Cantell K., Pyhälä L., Pirhonen J., Julkunen I. Effect of carbohydrates on the pharmacokinetics of human interferon-gamma. J Interferon Res. 1993 Aug;13(4):267–269. doi: 10.1089/jir.1993.13.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sareneva T., Pirhonen J., Cantell K., Kalkkinen N., Julkunen I. Role of N-glycosylation in the synthesis, dimerization and secretion of human interferon-gamma. Biochem J. 1994 Nov 1;303(Pt 3):831–840. doi: 10.1042/bj3030831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig G. F., Wijdenes J., Nagabhushan T. L., Trotta P. P. Evidence for a polypeptide segment at the carboxyl terminus of recombinant human gamma interferon involved in expression of biological activity. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):1981–1987. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Sappino A. P., Belin D. The plasminogen activator/plasmin system. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1172/JCI115405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann C., Weber H. The interferon genes. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1986;33:251–300. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel R., Perry L. J., Veilleux C., Chang G. Mutational analysis of the C-terminus of human interferon-gamma. Protein Eng. 1990 Jul;3(7):611–623. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.7.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip Y. K., Barrowclough B. S., Urban C., Vilcek J. Purification of two subspecies of human gamma (immune) interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1820–1824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]