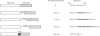Abstract
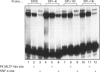
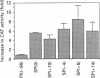
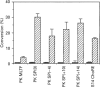
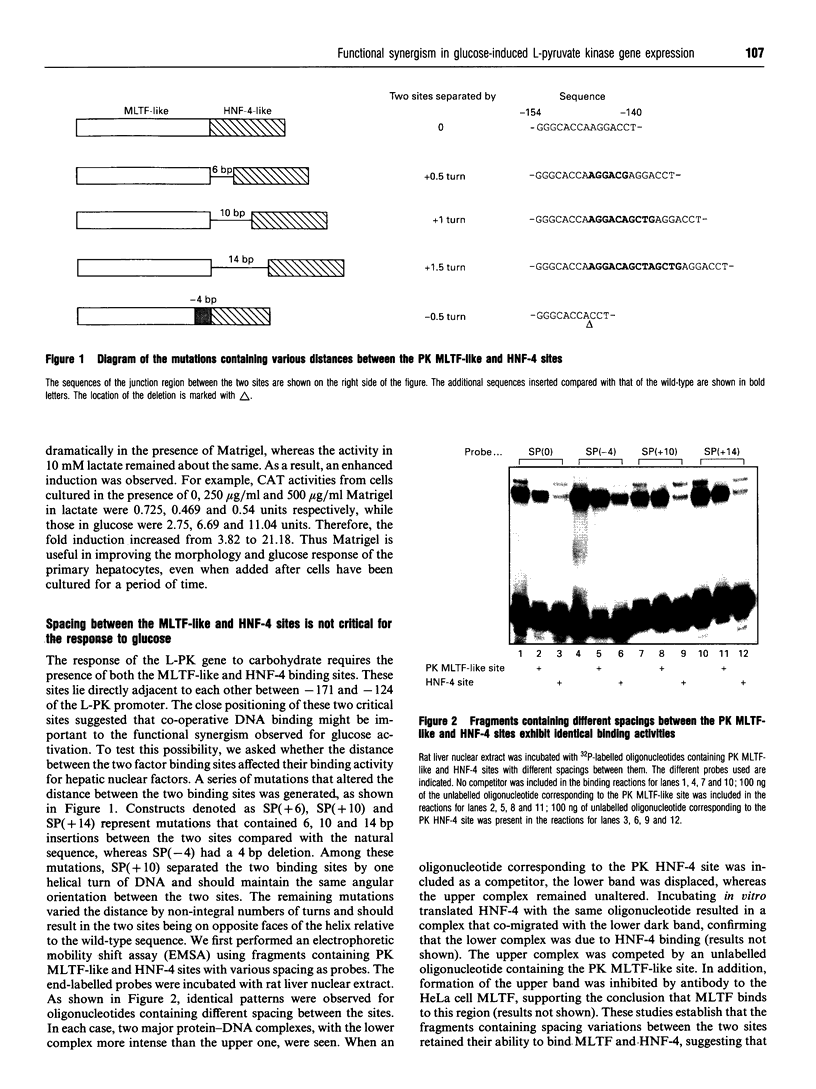
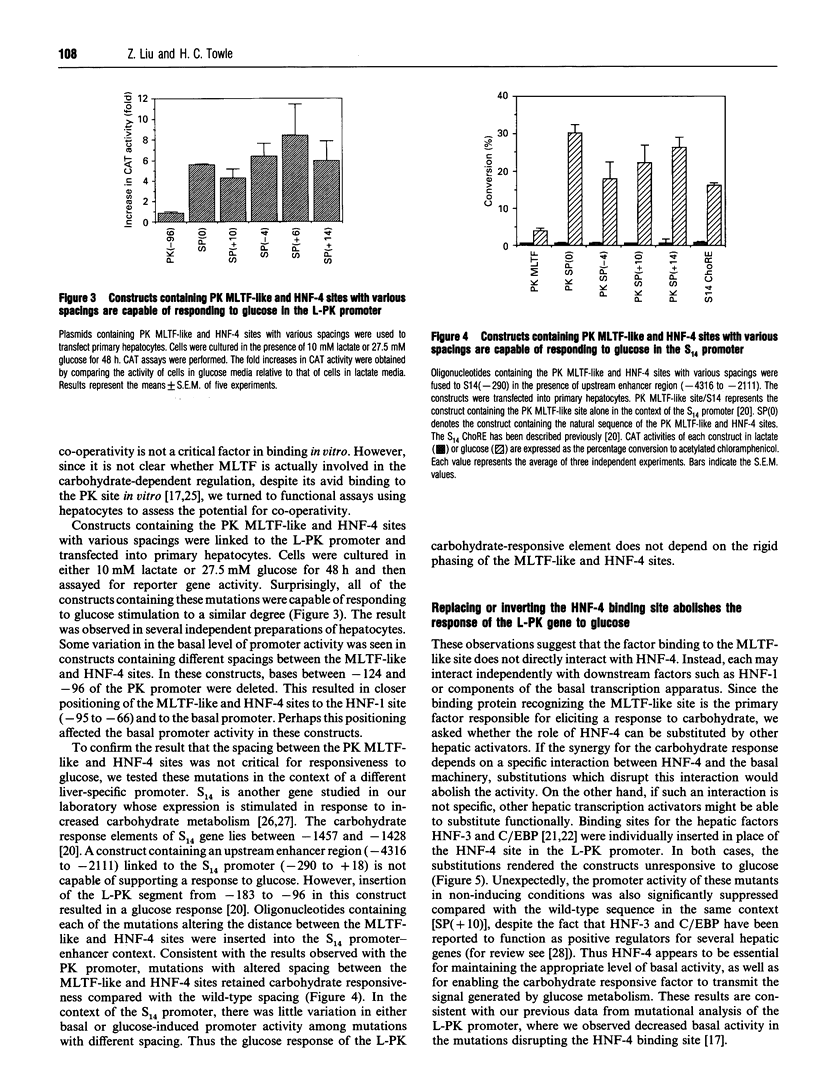
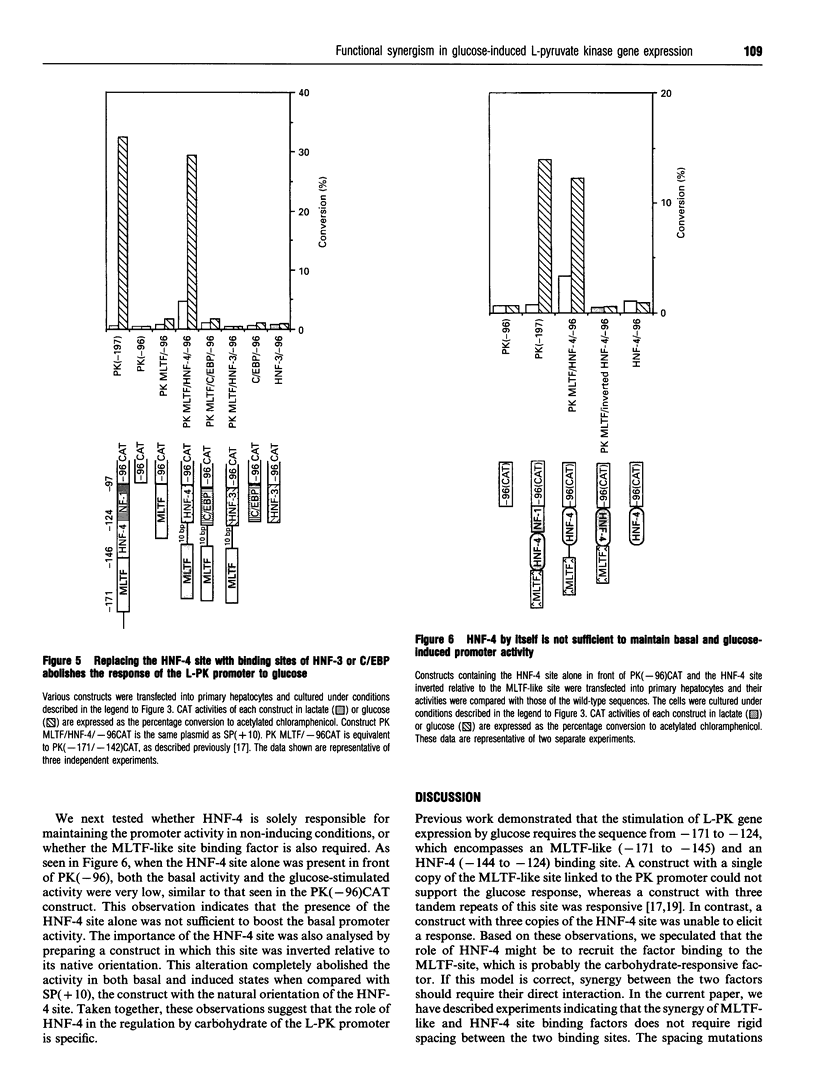
Hepatic expression of the liver-type pyruvate kinase (L-PK) gene is induced at the transcriptional level by increased carbohydrate metabolism in the rat. The carbohydrate response of the L-PK gene requires sequences from -171 to -124, which encompass adjacent major late transcription factor (MLTF)-like and hepatic nuclear factor (HNF)-4 binding sites. Neither site alone is capable of conferring a response, prompting us to explore the mechanism of synergy between the MLTF-like factor and HNF-4. Spacing requirements between the two factor binding sites were tested by generating a series of mutations that altered the distance between these sites. Surprisingly, all of the constructs with spacing mutations were capable of responding to elevated glucose when introduced into primary hepatocytes. Thus the glucose response does not depend on the rigid phasing of the MLTF-like and HNF-4 factors, suggesting that the factors binding to these two sites do not interact directly with each other. Substitution or inversion of the PK HNF-4 site abrogated the response to glucose and also significantly suppressed the promoter activity under non-inducing conditions. We conclude that the MLTF-like factor and HNF-4 co-operate functionally to maintain the basal activity, as well as the carbohydrate responsiveness, of the L-PK gene. A mechanism other than co-operative DNA binding is responsible for the synergism.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergot M. O., Diaz-Guerra M. J., Puzenat N., Raymondjean M., Kahn A. Cis-regulation of the L-type pyruvate kinase gene promoter by glucose, insulin and cyclic AMP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 25;20(8):1871–1877. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.8.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun T., Roche E., Kim K. H., Prentki M. Glucose regulates acetyl-CoA carboxylase gene expression in a pancreatic beta-cell line (INS-1). J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18905–18911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Ptashne M. A mechanism for synergistic activation of a mammalian gene by GAL4 derivatives. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):361–364. doi: 10.1038/345361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Multiple hepatocyte-enriched nuclear factors function in the regulation of transthyretin and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1415–1425. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Lai E., Grayson D. R., Darnell J. E., Jr The cell-specific enhancer of the mouse transthyretin (prealbumin) gene binds a common factor at one site and a liver-specific factor(s) at two other sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):81–90. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Simone V., Cortese R. Transcriptional regulation of liver-specific gene expression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;3(6):960–965. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90114-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decaux J. F., Antoine B., Kahn A. Regulation of the expression of the L-type pyruvate kinase gene in adult rat hepatocytes in primary culture. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11584–11590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz Guerra M. J., Bergot M. O., Martinez A., Cuif M. H., Kahn A., Raymondjean M. Functional characterization of the L-type pyruvate kinase gene glucose response complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7725–7733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foufelle F., Gouhot B., Pégorier J. P., Perdereau D., Girard J., Ferré P. Glucose stimulation of lipogenic enzyme gene expression in cultured white adipose tissue. A role for glucose 6-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20543–20546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodridge A. G., Fantozzi D. A., Klautky S. A., Ma X. J., Roncero C., Salati L. M. Nutritional and hormonal regulation of genes for lipogenic enzymes. Proc Nutr Soc. 1991 Aug;50(2):115–122. doi: 10.1079/pns19910022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granner D., Pilkis S. The genes of hepatic glucose metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10173–10176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschlag D., Johnson F. B. Synergism in transcriptional activation: a kinetic view. Genes Dev. 1993 Feb;7(2):173–179. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarnagin W. R., Debs R. J., Wang S. S., Bissell D. M. Cationic lipid-mediated transfection of liver cells in primary culture. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4205–4211. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jump D. B., Bell A., Santiago V. Thyroid hormone and dietary carbohydrate interact to regulate rat liver S14 gene transcription and chromatin structure. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3474–3478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jump D. B., Oppenheimer J. H. High basal expression and 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine regulation of messenger ribonucleic acid S14 in lipogenic tissues. Endocrinology. 1985 Dec;117(6):2259–2266. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-6-2259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jump D. B., Tao T. Y., Towle H. C., Oppenheimer J. H. Dissociation of hepatic messenger ribonucleic acidS14 levels and nuclear transcriptional rates in suckling rats. Endocrinology. 1986 May;118(5):1892–1896. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-5-1892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinlaw W. B., Tron P., Friedmann A. S. Nuclear localization and hepatic zonation of rat "spot 14" protein: immunohistochemical investigation employing anti-fusion protein antibodies. Endocrinology. 1992 Dec;131(6):3120–3122. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.6.1446647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liaw C., Seelig S., Mariash C. N., Oppenheimer J. H., Towle H. C. Interactions of thyroid hormone, growth hormone, and high carbohydrate, fat-free diet in regulating several rat liver messenger ribonucleic acid species. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):213–221. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Carey M. F., Ptashne M., Green M. R. GAL4 derivatives function alone and synergistically with mammalian activators in vitro. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):659–664. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Carey M., Ptashne M., Green M. R. How different eukaryotic transcriptional activators can cooperate promiscuously. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):359–361. doi: 10.1038/345359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Mechanism of action of an acidic transcriptional activator in vitro. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):971–981. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90321-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z., Thompson K. S., Towle H. C. Carbohydrate regulation of the rat L-type pyruvate kinase gene requires two nuclear factors: LF-A1 and a member of the c-myc family. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12787–12795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariash C. N., Seelig S., Schwartz H. L., Oppenheimer J. H. Rapid synergistic interaction between thyroid hormone and carbohydrate on mRNAS14 induction. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9583–9586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger S., Halaas J. L., Breslow J. L., Sladek F. M. Orphan receptor HNF-4 and bZip protein C/EBP alpha bind to overlapping regions of the apolipoprotein B gene promoter and synergistically activate transcription. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16831–16838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyori A., Tashiro H., Kimura A., Akagi K., Yamamura K., Mori M., Takiguchi M. Determination of tissue specificity of the enhancer by combinatorial operation of tissue-enriched transcription factors. Both HNF-4 and C/EBP beta are required for liver-specific activity of the ornithine transcarbamylase enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1323–1331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi T., Inoue H., Tanaka T. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of L-type pyruvate kinase in diabetic rat liver by insulin and dietary fructose. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14393–14397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Mariash C. N., Kinlaw W. B., Wong N. C., Freake H. C. Advances in our understanding of thyroid hormone action at the cellular level. Endocr Rev. 1987 Aug;8(3):288–308. doi: 10.1210/edrv-8-3-288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih H. M., Towle H. C. Definition of the carbohydrate response element of the rat S14 gene. Evidence for a common factor required for carbohydrate regulation of hepatic genes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13222–13228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih H., Towle H. C. Definition of the carbohydrate response element of the rat S14 gene. Context of the CACGTG motif determines the specificity of carbohydrate regulation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 25;269(12):9380–9387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K. S., Towle H. C. Localization of the carbohydrate response element of the rat L-type pyruvate kinase gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8679–8682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Cooperative binding of steroid hormone receptors contributes to transcriptional synergism at target enhancer elements. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):443–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90919-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaulont S., Kahn A. Transcriptional control of metabolic regulation genes by carbohydrates. FASEB J. 1994 Jan;8(1):28–35. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.1.8299888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaulont S., Munnich A., Decaux J. F., Kahn A. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of L-type pyruvate kinase gene expression in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7621–7625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaulont S., Puzenat N., Levrat F., Cognet M., Kahn A., Raymondjean M. Proteins binding to the liver-specific pyruvate kinase gene promoter. A unique combination of known factors. J Mol Biol. 1989 Sep 20;209(2):205–219. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90273-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Perisic O., Lis J. T. Cooperative binding of Drosophila heat shock factor to arrays of a conserved 5 bp unit. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90242-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Noguchi T., Miyazaki J., Matsuda T., Takenaka M., Yamamura K., Tanaka T. Tissue-specific expression of rat pyruvate kinase L/chloramphenicol acetyltransferase fusion gene in transgenic mice and its regulation by diet and insulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Aug 31;171(1):243–249. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91383-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]