Abstract
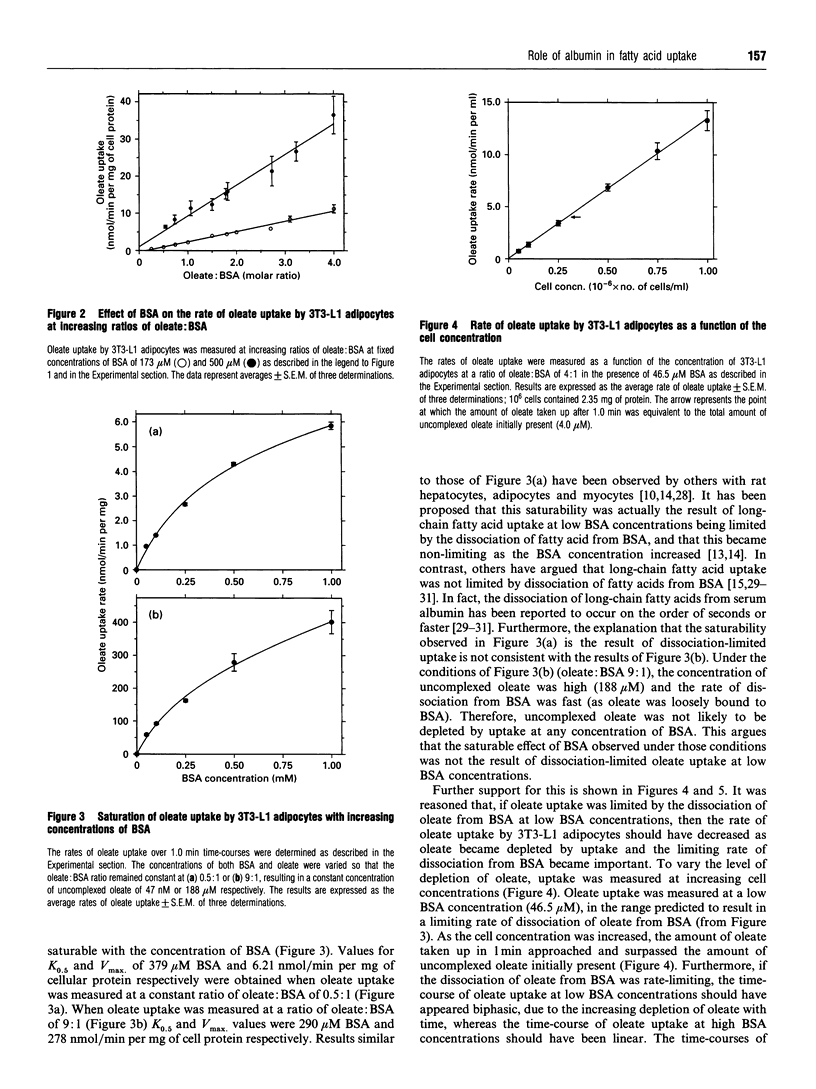
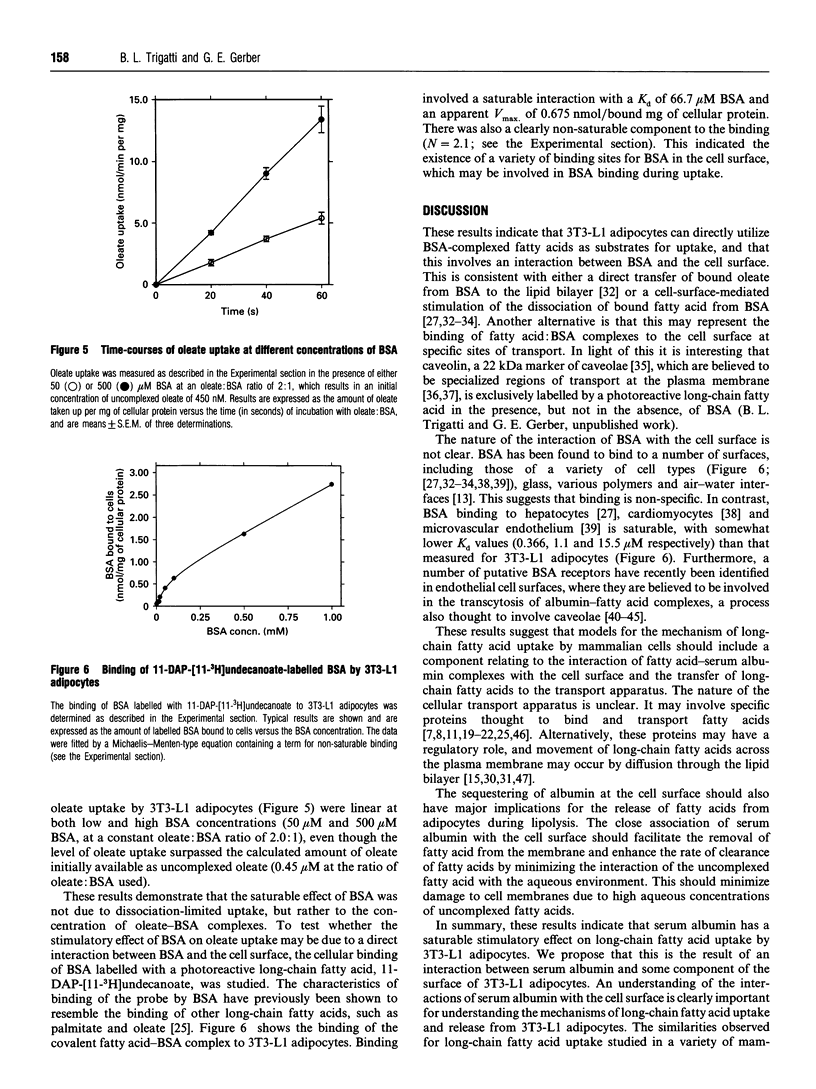
The interaction of long-chain fatty acids with cells is important for their uptake and metabolism, as well as their involvement in signalling processes. The majority of long-chain fatty acids circulating in plasma exist as complexes with serum albumin. Thus an understanding of the involvement of serum albumin in these processes is vitally important. The effect of serum albumin on the uptake of long-chain fatty acids was studied in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Serum albumin had a stimulatory effect on oleate uptake at all ratios of oleate: serum albumin tested. Furthermore, the rate of oleate uptake was saturable with increasing concentrations of serum albumin when the oleate: serum albumin ratio, and therefore the concentration of uncomplexed oleate, remained constant. This was not due to uptake being limited by dissociation of oleate from serum albumin, because oleate did not appear to be limiting. Furthermore, at very high ratios of oleate: serum albumin, when the concentration of uncomplexed oleate was predicted to be large relative to the amount of oleate taken up by cells, the rate of oleate uptake was still dependent on the albumin concentration. Serum albumin, covalently labelled with the photoreactive fatty acid 11-m-diazirinophenoxy[11-3H]undecanoate, bound to cells in a manner exhibiting both saturable (Kd 66.7 microM) and non-saturable processes. These results indicate that the stimulatory effect of serum albumin on the rate of oleate uptake is due to a direct interaction of serum albumin with the cells and point to an involvement of albumin binding sites in the cell surface in the cellular uptake of long-chain fatty acids.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abumrad N. A., Perkins R. C., Park J. H., Park C. R. Mechanism of long chain fatty acid permeation in the isolated adipocyte. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9183–9191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amri E. Z., Ailhaud G., Grimaldi P. A. Fatty acids as signal transducing molecules: involvement in the differentiation of preadipose to adipose cells. J Lipid Res. 1994 May;35(5):930–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. G., Kamen B. A., Rothberg K. G., Lacey S. W. Potocytosis: sequestration and transport of small molecules by caveolae. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):410–411. doi: 10.1126/science.1310359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. G. Potocytosis of small molecules and ions by caveolae. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;3(3):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burczynski F. J., Cai Z. S. Palmitate uptake by hepatocyte suspensions: effect of albumin. Am J Physiol. 1994 Sep;267(3 Pt 1):G371–G379. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1994.267.3.G371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burczynski F. J., Moran J. B., Cai Z. S. Uptake of organic anions by hepatocyte monolayers: codiffusion versus facilitated dissociation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;71(12):863–867. doi: 10.1139/y93-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burczynski F. J., Pond S. M., Davis C. K., Johnson L. P., Weisiger R. A. Calibration of albumin-fatty acid binding constants measured by heptane-water partition. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 1):G555–G563. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.265.3.G555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai Z. S., Burczynski F. J., Luxon B. A., Forker E. L. On the design and interpretation of experiments to elucidate albumin-dependent hepatic uptake. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 1):G1127–G1137. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.6.G1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels C., Noy N., Zakim D. Rates of hydration of fatty acids bound to unilamellar vesicles of phosphatidylcholine or to albumin. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 18;24(13):3286–3292. doi: 10.1021/bi00334a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel R. J., Robinson G. S., Spiegelman B. M. Fatty acid regulation of gene expression. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5937–5941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziarski R. Cell-bound albumin is the 70-kDa peptidoglycan-, lipopolysaccharide-, and lipoteichoic acid-binding protein on lymphocytes and macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 12;269(32):20431–20436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber G. E., Mangroo D., Trigatti B. L. Identification of high affinity membrane-bound fatty acid-binding proteins using a photoreactive fatty acid. Mol Cell Biochem. 1993 Jun 9;123(1-2):39–44. doi: 10.1007/BF01076473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghinea N., Eskenasy M., Simionescu M., Simionescu N. Endothelial albumin binding proteins are membrane-associated components exposed on the cell surface. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4755–4758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghinea N., Fixman A., Alexandru D., Popov D., Hasu M., Ghitescu L., Eskenasy M., Simionescu M., Simionescu N. Identification of albumin-binding proteins in capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):231–239. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. A., Civelek V. N., Kamp F., Tornheim K., Corkey B. E. Changes in internal pH caused by movement of fatty acids into and out of clonal pancreatic beta-cells (HIT). J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 19;269(33):20852–20856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horie T., Mizuma T., Kasai S., Awazu S. Conformational change in plasma albumin due to interaction with isolated rat hepatocyte. Am J Physiol. 1988 Apr;254(4 Pt 1):G465–G470. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.4.G465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamp F., Hamilton J. A., Kamp F., Westerhoff H. V., Hamilton J. A. Movement of fatty acids, fatty acid analogues, and bile acids across phospholipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 19;32(41):11074–11086. doi: 10.1021/bi00092a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamp F., Hamilton J. A. pH gradients across phospholipid membranes caused by fast flip-flop of un-ionized fatty acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11367–11370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz K. T., Jump D. B., MacDougald O. A., Lane M. D. Transcriptional control of the stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 gene by polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Apr 29;200(2):763–768. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc P., Capone J., Gerber G. E. Synthesis and biosynthetic utilization of radioactive photoreactive fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14586–14589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordway R. W., Singer J. J., Walsh J. V., Jr Direct regulation of ion channels by fatty acids. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Mar;14(3):96–100. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popov D., Hasu M., Ghinea N., Simionescu N., Simionescu M. Cardiomyocytes express albumin binding proteins. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1992 Sep;24(9):989–1002. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(92)91865-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter B. J., Sorrentino D., Berk P. D. Mechanisms of cellular uptake of free fatty acids. Annu Rev Nutr. 1989;9:253–270. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.09.070189.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. G., Burrington C. M. The albumin receptor effect may be due to a surface-induced conformational change in albumin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9867–9872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg K. G., Heuser J. E., Donzell W. C., Ying Y. S., Glenney J. R., Anderson R. G. Caveolin, a protein component of caveolae membrane coats. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):673–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90143-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer J. E., Lodish H. F. Expression cloning and characterization of a novel adipocyte long chain fatty acid transport protein. Cell. 1994 Nov 4;79(3):427–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90252-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer J. E., Carley W. W., Palade G. E. Specific albumin binding to microvascular endothelium in culture. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 2):H425–H437. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.254.3.H425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer J. E., Oh P., Pinney E., Allard J. Filipin-sensitive caveolae-mediated transport in endothelium: reduced transcytosis, scavenger endocytosis, and capillary permeability of select macromolecules. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(5):1217–1232. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.5.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer J. E., Sung A., Horvat R., Bravo J. Preferential interaction of albumin-binding proteins, gp30 and gp18, with conformationally modified albumins. Presence in many cells and tissues with a possible role in catabolism. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24544–24553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer J. E. gp60 is an albumin-binding glycoprotein expressed by continuous endothelium involved in albumin transcytosis. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jan;262(1 Pt 2):H246–H254. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.1.H246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino D., Robinson R. B., Kiang C. L., Berk P. D. At physiologic albumin/oleate concentrations oleate uptake by isolated hepatocytes, cardiac myocytes, and adipocytes is a saturable function of the unbound oleate concentration. Uptake kinetics are consistent with the conventional theory. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1325–1333. doi: 10.1172/JCI114301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A. Fatty acid binding to plasma albumin. J Lipid Res. 1975 May;16(3):165–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A., John K., Fletcher J. E. Binding of long-chain fatty acids to bovine serum albumin. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jan;10(1):56–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stremmel W., Berk P. D. Hepatocellular influx of [14C]oleate reflects membrane transport rather than intracellular metabolism or binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3086–3090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stremmel W. Fatty acid uptake by isolated rat heart myocytes represents a carrier-mediated transport process. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):844–852. doi: 10.1172/JCI113393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stremmel W. Mechanism of hepatic fatty acid uptake. J Hepatol. 1989 Nov;9(3):374–382. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(89)90148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tebbey P. W., McGowan K. M., Stephens J. M., Buttke T. M., Pekala P. H. Arachidonic acid down-regulates the insulin-dependent glucose transporter gene (GLUT4) in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by inhibiting transcription and enhancing mRNA turnover. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):639–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres J. M., Anel A., Uriel J. Alpha-fetoprotein-mediated uptake of fatty acids by human T lymphocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Mar;150(3):456–462. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041500305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres J. M., Darracq N., Uriel J. Membrane proteins from lymphoblastoid cells showing cross-affinity for alpha-fetoprotein and albumin. Isolation and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Sep 4;1159(1):60–66. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(92)90075-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trigatti B. L., Mangroo D., Gerber G. E. Photoaffinity labeling and fatty acid permeation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22621–22625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uriel J., Torres J. M., Anel A. Carrier-protein-mediated enhancement of fatty-acid binding and internalization in human T-lymphocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Feb 17;1220(3):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(94)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnotte C., Gilon P., Nenquin M., Henquin J. C. Mechanisms of the stimulation of insulin release by saturated fatty acids. A study of palmitate effects in mouse beta-cells. Diabetes. 1994 May;43(5):703–711. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.5.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisiger R., Gollan J., Ockner R. Receptor for albumin on the liver cell surface may mediate uptake of fatty acids and other albumin-bound substances. Science. 1981 Mar 6;211(4486):1048–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.6258226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolkoff A. W. The role of an albumin receptor in hepatic organic anion uptake: the controversy continues. Hepatology. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4):777–779. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou S. L., Stump D., Sorrentino D., Potter B. J., Berk P. D. Adipocyte differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells involves augmented expression of a 43-kDa plasma membrane fatty acid-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14456–14461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



