Abstract
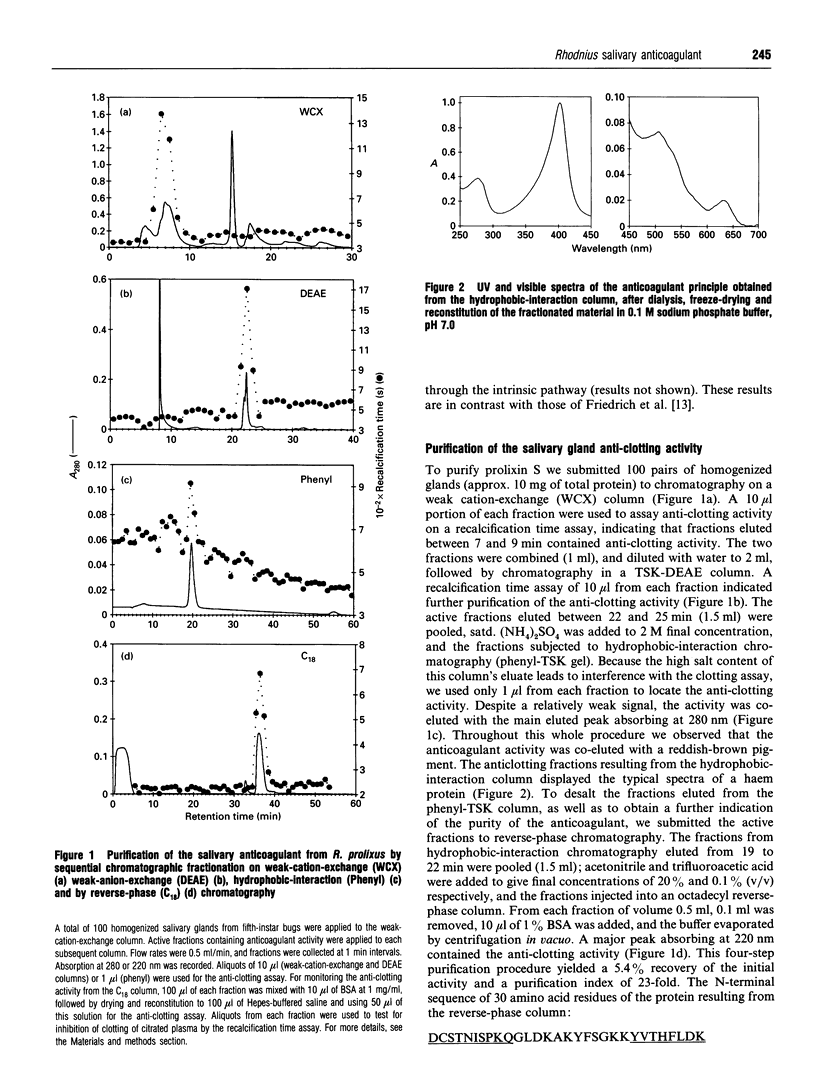
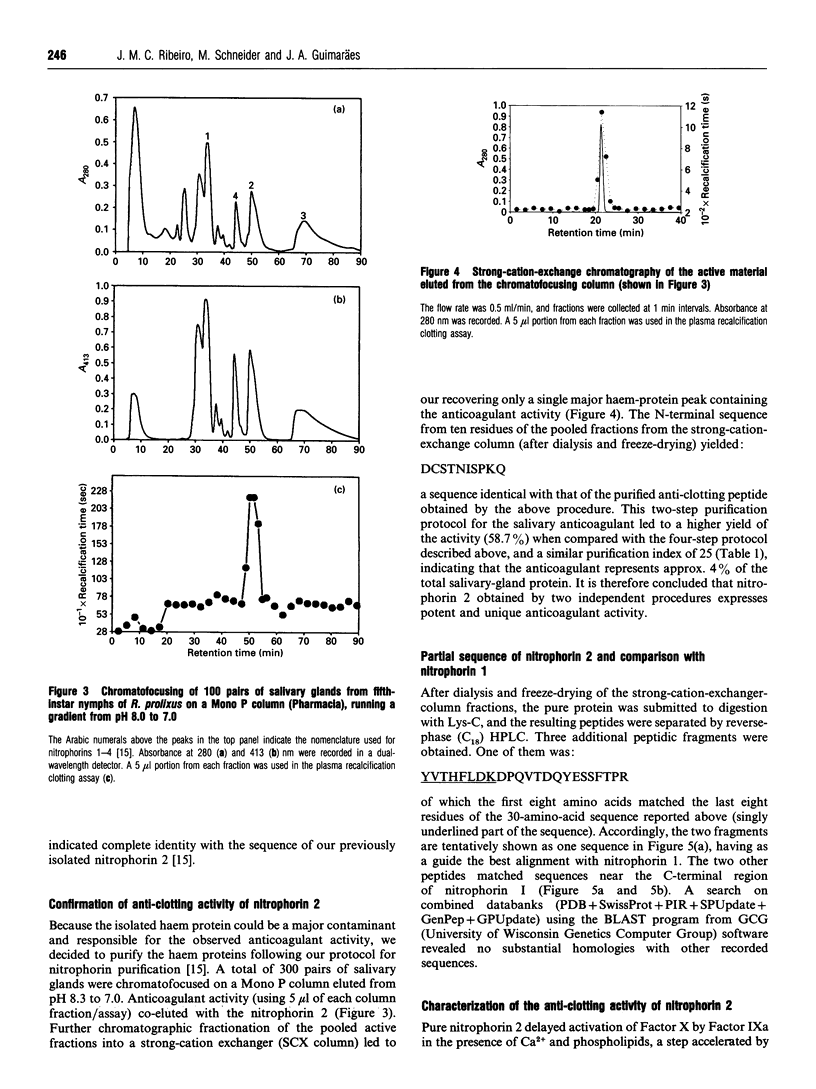
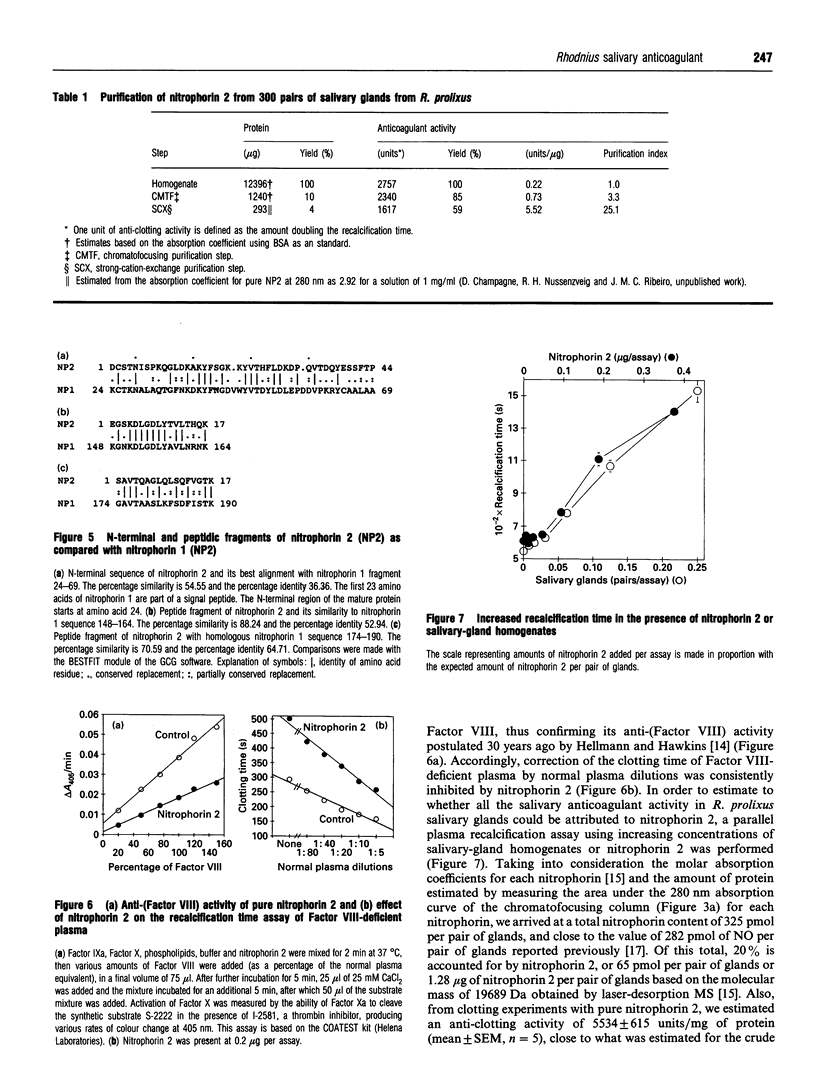
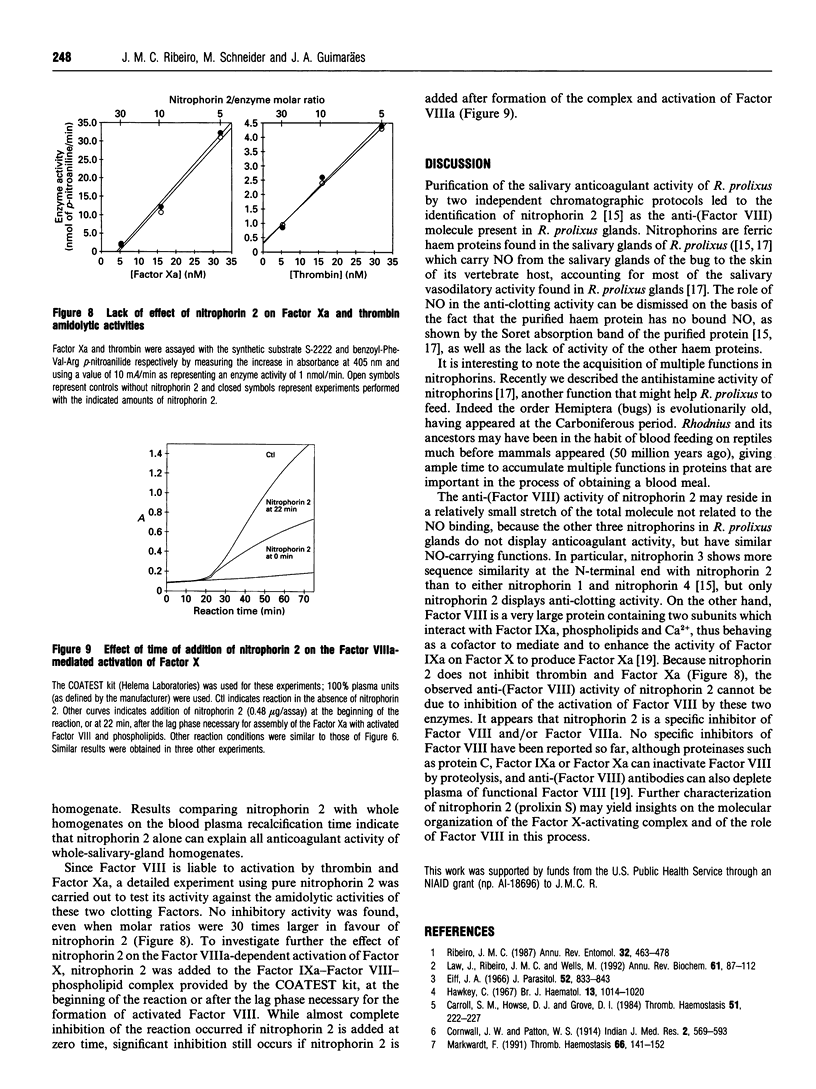
The salivary anticoagulant of the blood-sucking bug Rhodnius prolixus was purified to homogeneity using a protocol consisting of weak cation-exchange, DEAE, hydrophobic-interaction and octadecyl reverse-phase chromatography, yielding a protein with the same N-terminal sequence as nitrophorin 2, one of the four NO haem protein carriers present in the salivary glands of Rhodnius with a molecular mass of 19689 Da [D. Champagne, R.H. Nussenzveig and J.M.C. Ribeiro, (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270, in the press]. To exclude the possibility of the nitrophorin being a contaminant, another chromatographic protocol was performed, consisting of chromatofocusing followed by strong-cation-exchange chromatography. Again the anticoagulant was eluted with nitrophorin 2. Nitrophorin 2 inhibits coagulation Factor VIII-mediated activation of Factor X and accounts for all the anti-clotting activity observed in Rhodnius salivary glands.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cappello M., Clyne L. P., McPhedran P., Hotez P. J. Ancylostoma factor Xa inhibitor: partial purification and its identification as a major hookworm-derived anticoagulant in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;167(6):1474–1477. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.6.1474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. M., Howse D. J., Grove D. I. The anticoagulant effects of the hookworm, ancylostoma ceylanicum: observations on human and dog blood in vitro and infected dogs in vivo. Thromb Haemost. 1984 Apr 30;51(2):222–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiff J. A. Nature of an anticoagulant from the cephalic glands of ancylostoma caninum. J Parasitol. 1966 Oct;52(5):833–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fareed J., Walenga J. M., Iyer L., Hoppensteadt D., Pifarre R. An objective perspective on recombinant hirudin: a new anticoagulant and antithrombotic agent. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1991 Feb;2(1):135–147. doi: 10.1097/00001721-199102000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay P. J. Factor VIII structure and function. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Jul 1;70(1):63–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich T., Kröger B., Bialojan S., Lemaire H. G., Höffken H. W., Reuschenbach P., Otte M., Dodt J. A Kazal-type inhibitor with thrombin specificity from Rhodnius prolixus. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16216–16222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkey C. Inhibitor of platelet aggregation present in saliva of the vampire bat Desmodus rotundus. Br J Haematol. 1967 Nov;13(6):1014–1020. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb08870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellmann K., Hawkins R. I. Prolixins-S and prolixin-G; two anticoagulants from Rhodnius prolixus Stål. Nature. 1965 Jul 17;207(994):265–267. doi: 10.1038/207265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs J. W., Cupp E. W., Sardana M., Friedman P. A. Isolation and characterization of a coagulation factor Xa inhibitor from black fly salivary glands. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Oct 22;64(2):235–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan S. P., Waxman L., Smith D. E., Vlasuk G. P. Tick anticoagulant peptide: kinetic analysis of the recombinant inhibitor with blood coagulation factor Xa. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 18;29(50):11095–11100. doi: 10.1021/bi00502a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law J. H., Ribeiro J. M., Wells M. A. Biochemical insights derived from insect diversity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:87–111. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwardt F. Hirudin and derivatives as anticoagulant agents. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):141–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROCTOR R. R., RAPAPORT S. I. The partial thromboplastin time with kaolin. A simple screening test for first stage plasma clotting factor deficiencies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1961 Sep;36:212–219. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/36.3.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. M., Hazzard J. M., Nussenzveig R. H., Champagne D. E., Walker F. A. Reversible binding of nitric oxide by a salivary heme protein from a bloodsucking insect. Science. 1993 Apr 23;260(5107):539–541. doi: 10.1126/science.8386393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. M. Role of saliva in blood-feeding by arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol. 1987;32:463–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.32.010187.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. M., Walker F. A. High affinity histamine-binding and antihistaminic activity of the salivary nitric oxide-carrying heme protein (nitrophorin) of Rhodnius prolixus. J Exp Med. 1994 Dec 1;180(6):2251–2257. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.6.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman L., Smith D. E., Arcuri K. E., Vlasuk G. P. Tick anticoagulant peptide (TAP) is a novel inhibitor of blood coagulation factor Xa. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):593–596. doi: 10.1126/science.2333510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



