Abstract
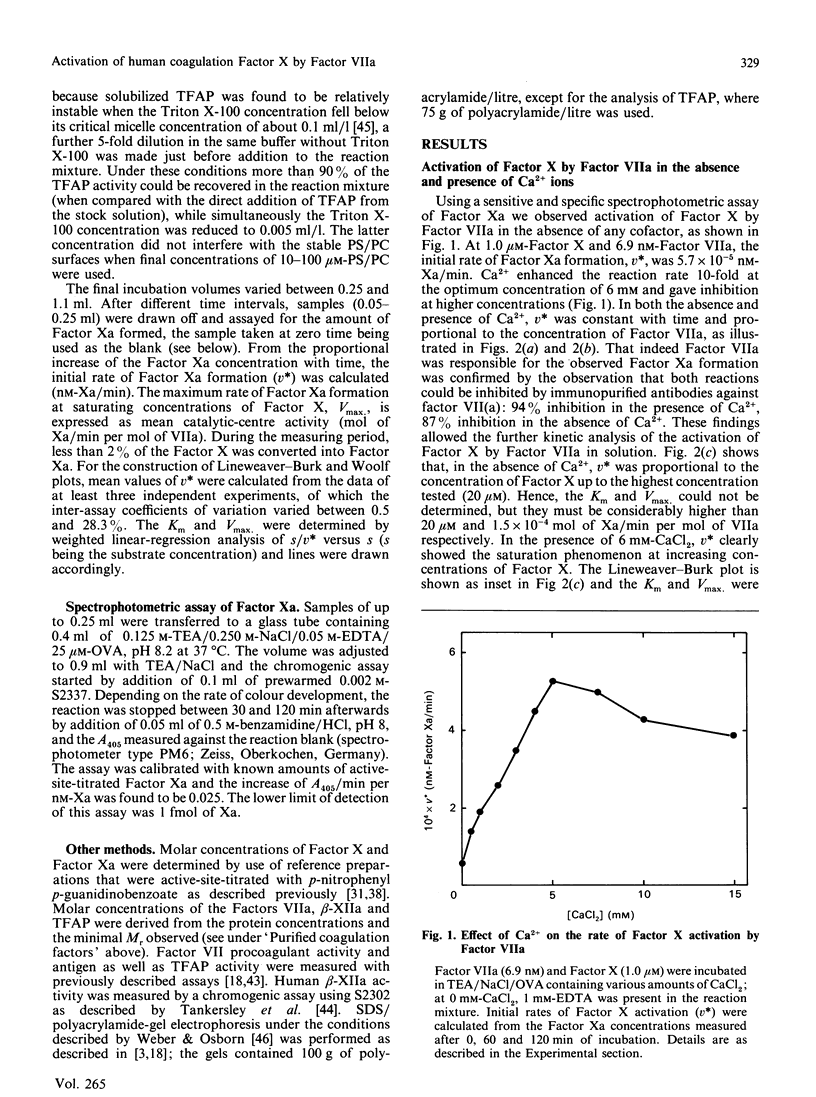
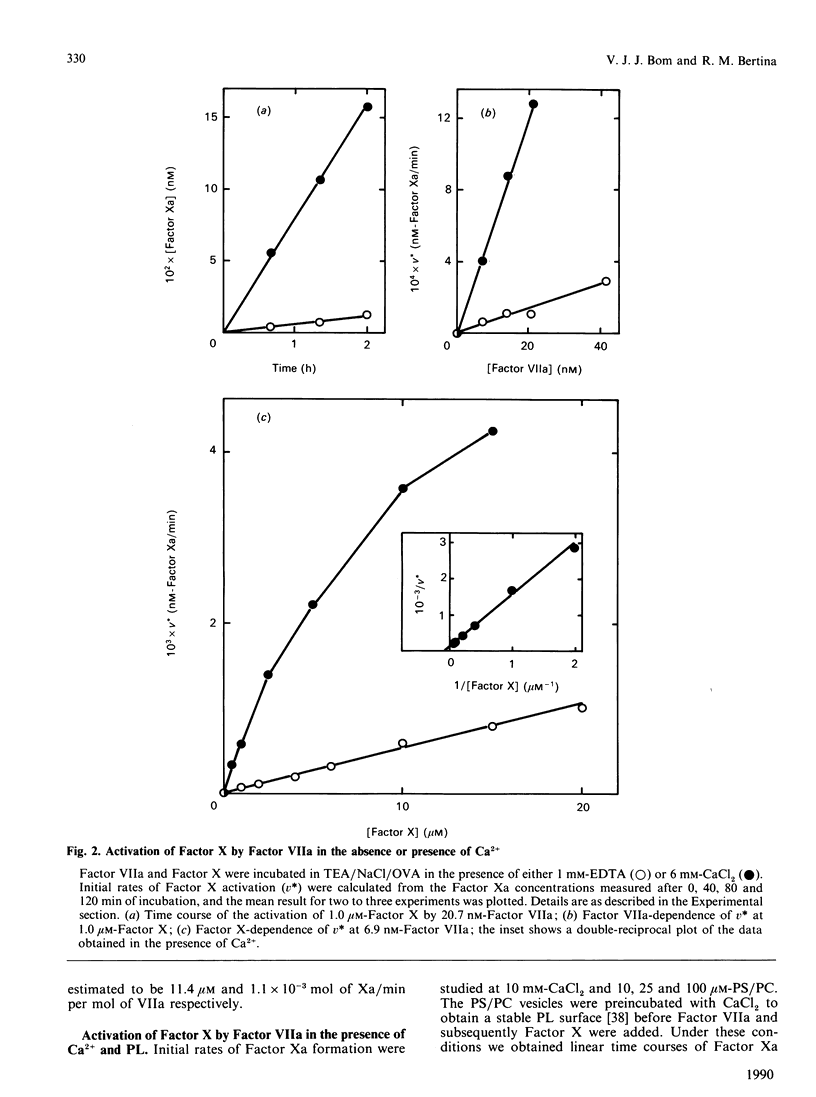
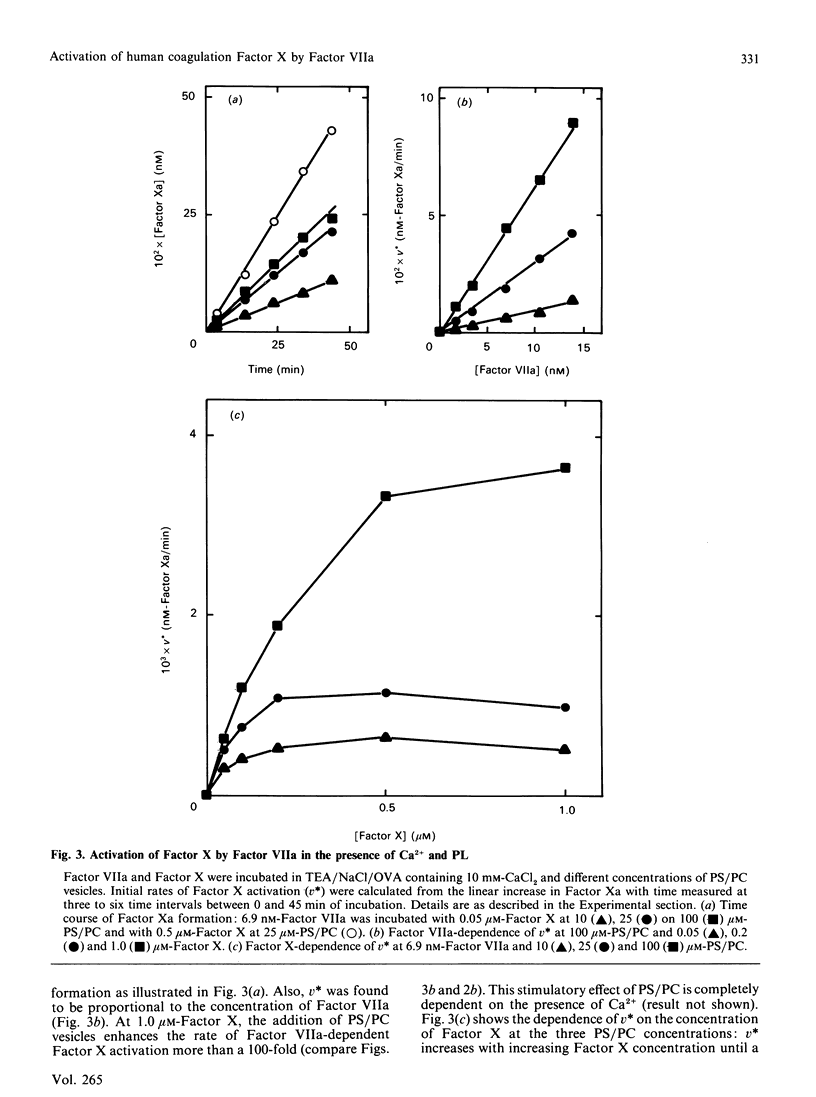
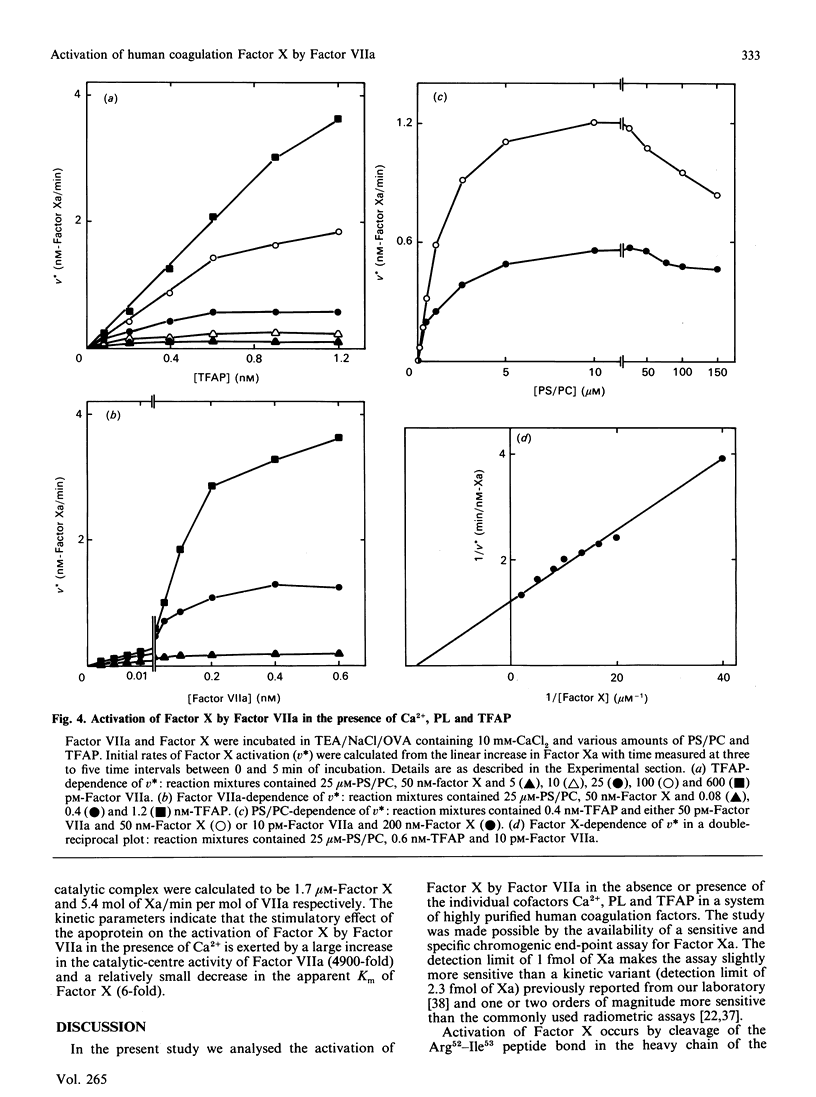
In the extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation, Factor X is activated by a complex of tissue factor, factor VII(a) and Ca2+ ions. Using purified human coagulation factors and a sensitive spectrophotometric assay for Factor Xa, we could demonstrate activation of Factor X by Factor VIIa in the absence of tissue-factor apoprotein, phospholipids and Ca2+. This finding allowed a kinetic analysis of the contribution of each of the cofactors. Ca2+ stimulated the reaction rate 10-fold at an optimum of 6 mM (Vmax. of 1.1 x 10(-3) min-1) mainly by decreasing the Km of Factor X (to 11.4 microM). In the presence of Ca2+, 25 microM-phospholipid caused a 150-fold decrease of the apparent Km and a 2-fold increase of the apparent Vmax. of the reaction; however, both kinetic parameters increased with increasing phospholipid concentration. Tissue-factor apoprotein contributed to the reaction rate mainly by an increase of the Vmax., in both the presence (40,500-fold) and absence (4900-fold) of phospholipid. The formation of a ternary complex of Factor VIIa with tissue-factor apoprotein and phospholipid was responsible for a 15 million-fold increase in the catalytic efficiency of Factor X activation. The presence of Ca2+ was absolutely required for the stimulatory effects of phospholipid and apoprotein. The data fit a general model in which the Ca2(+)-dependent conformation allows Factor VIIa to bind tissue-factor apoprotein and/or a negatively charged phospholipid surface resulting into a decreased intrinsic Km and an increased Vmax. for the activation of fluid-phase Factor X.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach R., Gentry R., Nemerson Y. Factor VII binding to tissue factor in reconstituted phospholipid vesicles: induction of cooperativity by phosphatidylserine. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 15;25(14):4007–4020. doi: 10.1021/bi00362a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach R., Nemerson Y., Konigsberg W. Purification and characterization of bovine tissue factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8324–8331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach R., Oberdick J., Nemerson Y. Immunoaffinity purification of bovine factor VII. Blood. 1984 Feb;63(2):393–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj S. P., Rapaport S. I., Brown S. F. Isolation and characterization of human factor VII. Activation of factor VII by factor Xa. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):253–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj S. P., Rapaport S. I., Russell W. A. Redetermination of the rate-limiting step in the activation of factor IX by factor XIa and by factor VIIa/tissue factor. Explanation for different electrophoretic radioactivity profiles obtained on activation of 3H- and 125I-labeled factor IX. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 16;22(17):4047–4053. doi: 10.1021/bi00286a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bom V. J., Ram I. E., Alderkamp G. H., Reinalda-Poot H. H., Bertina R. M. Application of factor VII-Sepharose affinity chromatography in the purification of human tissue factor apoprotein. Thromb Res. 1986 Jun 1;42(5):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(86)90342-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bom V. J., van Tilburg N. H., Krommenhoek-van Es C., Bertina R. M. Immunoradiometric assays for human coagulation factor VII using polyclonal antibodies against the Ca(II)-dependent and Ca(II)-independent conformation. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Dec 15;56(3):343–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broze G. J., Jr Binding of human factor VII and VIIa to monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):526–535. doi: 10.1172/JCI110644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broze G. J., Jr, Leykam J. E., Schwartz B. D., Miletich J. P. Purification of human brain tissue factor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):10917–10920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broze G. J., Jr, Majerus P. W. Purification and properties of human coagulation factor VII. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1242–1247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Scipio R. G., Hermodson M. A., Yates S. G., Davie E. W. A comparison of human prothrombin, factor IX (Christmas factor), factor X (Stuart factor), and protein S. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):698–706. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Isolation of a membrane-bound cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):859–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman S. D., Nemerson Y. Membrane-dependent coagulation reaction is independent of the concentration of phospholipid-bound substrate: fluid phase factor X regulates the extrinsic system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4675–4679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyssinet J. M., Gauchy J., Cazenave J. P. The effect of phospholipids on the activation of protein C by the human thrombin-thrombomodulin complex. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):151–157. doi: 10.1042/bj2380151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guha A., Bach R., Konigsberg W., Nemerson Y. Affinity purification of human tissue factor: interaction of factor VII and tissue factor in detergent micelles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):299–302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen F. S., Gray C. L., O'Hara P., Grant F. J., Saari G. C., Woodbury R. G., Hart C. E., Insley M., Kisiel W., Kurachi K. Characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor VII. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2412–2416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway P. W. A simple procedure for removal of Triton X-100 from protein samples. Anal Biochem. 1973 May;53(1):304–308. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90436-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultin M. B., Nemerson Y. Activation of factor X by factors IXa and VIII; a specific assay for factor IXa in the presence of thrombin-activated factor VIII. Blood. 1978 Nov;52(5):928–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M. Factor X. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1984;7:55–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesty J., Morrison S. A. The activation of Factor IX by tissue factor-Factor VII in a bovine plasma system lacking Factor X. Thromb Res. 1983 Oct 15;32(2):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90028-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesty J., Silverberg S. A. Kinetics of the tissue factor-dependent activation of coagulation Factors IX and X in a bovine plasma system. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12337–12345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobin F., Esnouf M. P. Studies on the formation of the prothrombin-converting complex. Biochem J. 1967 Mar;102(3):666–674. doi: 10.1042/bj1020666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyt B., Furie B. C., Furie B. Structural transitions in bovine factor X associated with metal binding and zymogen activation. Studies using conformation-specific antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8687–8695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leytus S. P., Chung D. W., Kisiel W., Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor X. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3699–3702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens K., Bertina R. M. Pathways in the activation of human coagulation factor X. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 1;185(3):647–658. doi: 10.1042/bj1850647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens K., Bertina R. M. The contribution of Ca2+ and phospholipids to the activation of human blood-coagulation Factor X by activated Factor IX. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 1;223(3):607–615. doi: 10.1042/bj2230607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens K., Cupers R., Van Wijngaarden A., Bertina R. M. Binding of human blood-coagulation Factors IXa and X to phospholipid membranes. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 1;223(3):599–605. doi: 10.1042/bj2230599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens K., van Wijngaarden A., Bertina R. M. The role of factor VIII in the activation of human blood coagulation factor X by activated factor IX. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Oct 30;54(3):654–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison S. A., Jesty J. Tissue factor-dependent activation of tritium-labeled factor IX and factor X in human plasma. Blood. 1984 Jun;63(6):1338–1347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Broderius M., Martin G. Role of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. Cation specificity of prothrombin and factor X-phospholipid binding. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):6886–6893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L. Interactions of vitamin K-dependent proteins with calcium ions and phospholipid membranes. Fed Proc. 1978 Oct;37(12):2621–2625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsestuen G. L., Kisiel W., Di Scipio R. G. Interaction of vitamin K dependent proteins with membranes. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2134–2138. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y., Bach R. Tissue factor revisited. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1982;6:237–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y., Gentry R. An ordered addition, essential activation model of the tissue factor pathway of coagulation: evidence for a conformational cage. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 15;25(14):4020–4033. doi: 10.1021/bi00362a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y. The reaction between bovine brain tissue factor and factors VII and X. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):601–608. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Taswell J. B., Mann K. G. The contribution of bovine Factor V and Factor Va to the activity of prothrombinase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10952–10962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Tracy R. P., Mann K. G. "Clotspeed," a mathematical simulation of the functional properties of prothrombinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1447–1453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Berre A., Otnaess A. B., Bjorklid E., Prydz H. Activation of the coagulation factor VII by tissue thromboplastin and calcium. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 18;11(15):2853–2857. doi: 10.1021/bi00765a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Rapaport S. I. Activation of factor IX by the reaction product of tissue factor and factor VII: additional pathway for initiating blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5260–5264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusey M. L., Nelsestuen G. L. The physical significance of Km in the prothrombinase reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 29;114(2):526–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90812-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radcliffe R., Nemerson Y. Activation and control of factor VII by activated factor X and thrombin. Isolation and characterization of a single chain form of factor VII. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):388–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosing J., Tans G., Govers-Riemslag J. W., Zwaal R. F., Hemker H. C. The role of phospholipids and factor Va in the prothrombinase complex. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):274–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. S., Waugh D. F. The purification of human prothrombin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 Dec 1;16(3):468–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg S. A., Nemerson Y., Zur M. Kinetics of the activation of bovine coagulation factor X by components of the extrinsic pathway. Kinetic behavior of two-chain factor VII in the presence and absence of tissue factor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8481–8488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka H., Janssen B., Preissner K. T., Müller-Berghaus G. Purification of glycosylated apoprotein of tissue factor from human brain and inhibition of its procoagulant activity by a specific antibody. Thromb Res. 1985 Dec 15;40(6):745–756. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90312-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tankersley D. L., Alving B. M., Finlayson J. S. Preparation of beta-XIIa (Hageman factor fragment) from human plasma. Thromb Res. 1982 Feb 15;25(4):307–317. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Protein S and the regulation of activated protein C. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1984 Apr;10(2):131–138. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warn-Cramer B. J., Bajaj S. P. Intrinsic versus extrinsic coagulation. Kinetic considerations. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):757–762. doi: 10.1042/bj2390757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zur M., Nemerson Y. Kinetics of factor IX activation via the extrinsic pathway. Dependence of Km on tissue factor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5703–5707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zur M., Nemerson Y. The esterase activity of coagulation factor VII. Evidence for intrinsic activity of the zymogen. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2203–2209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dieijen G., Tans G., Rosing J., Hemker H. C. The role of phospholipid and factor VIIIa in the activation of bovine factor X. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3433–3442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rijn J. L., Govers-Riemslag J. W., Zwaal R. F., Rosing J. Kinetic studies of prothrombin activation: effect of factor Va and phospholipids on the formation of the enzyme-substrate complex. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 25;23(20):4557–4564. doi: 10.1021/bi00315a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


