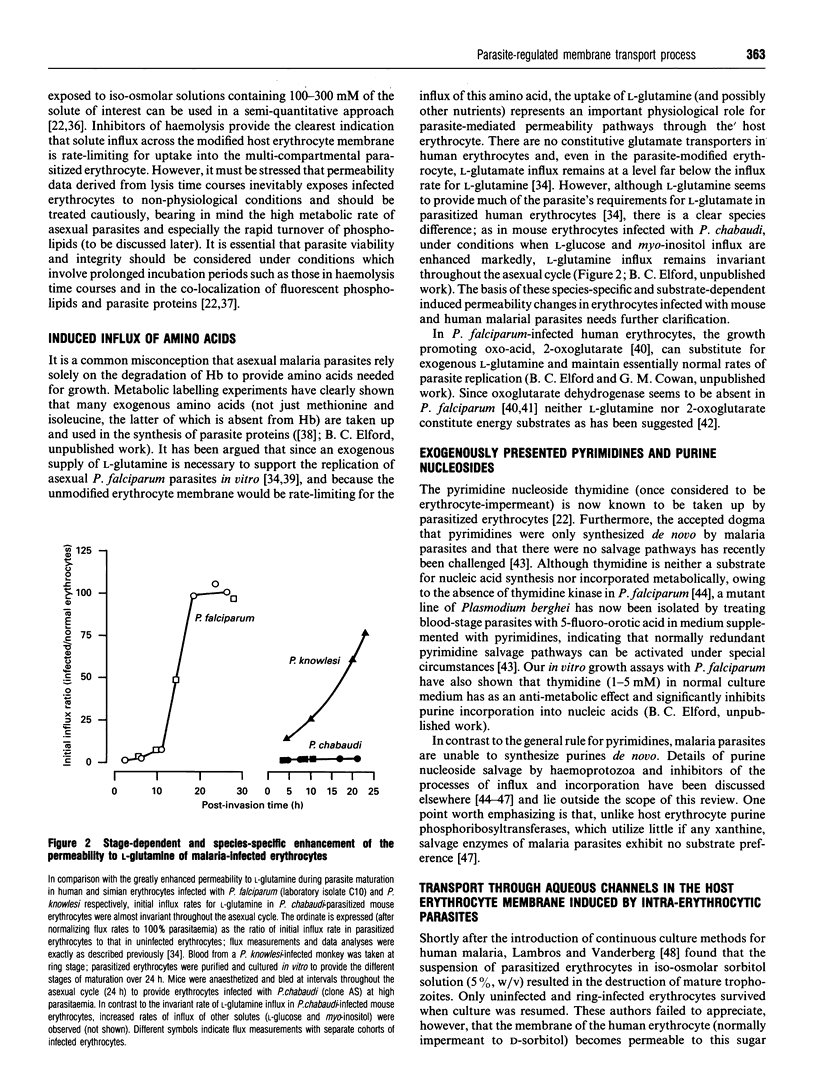
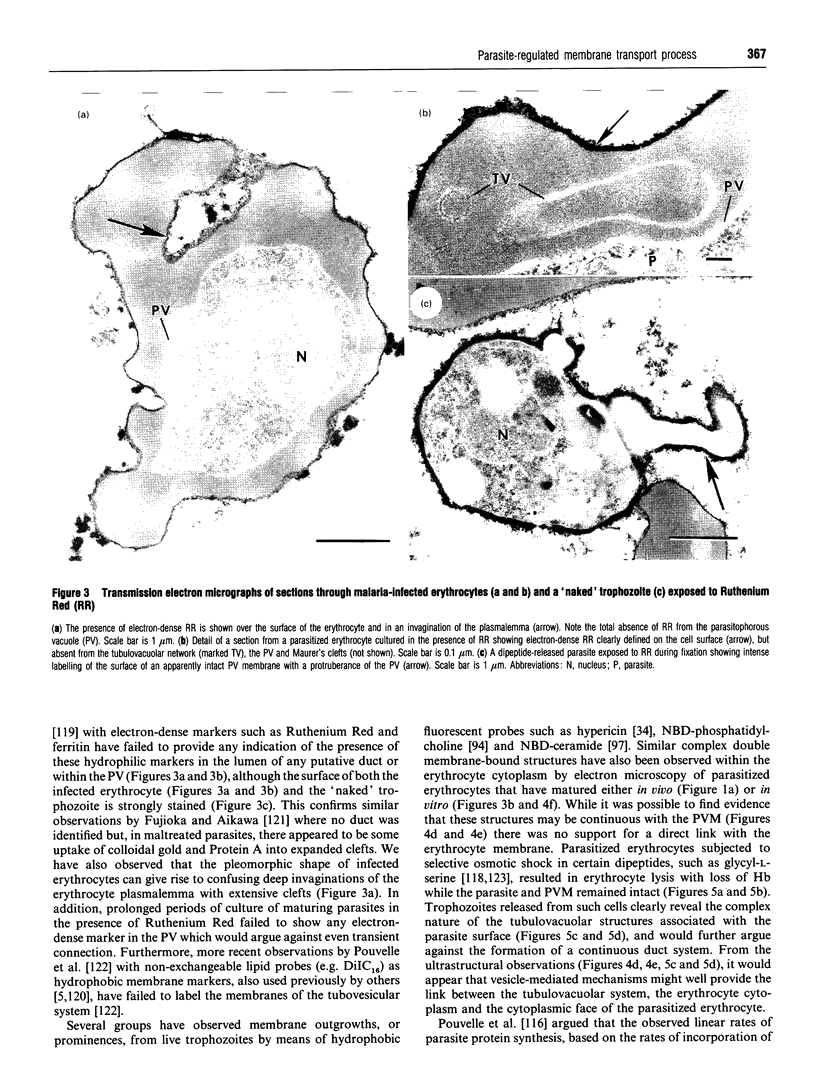
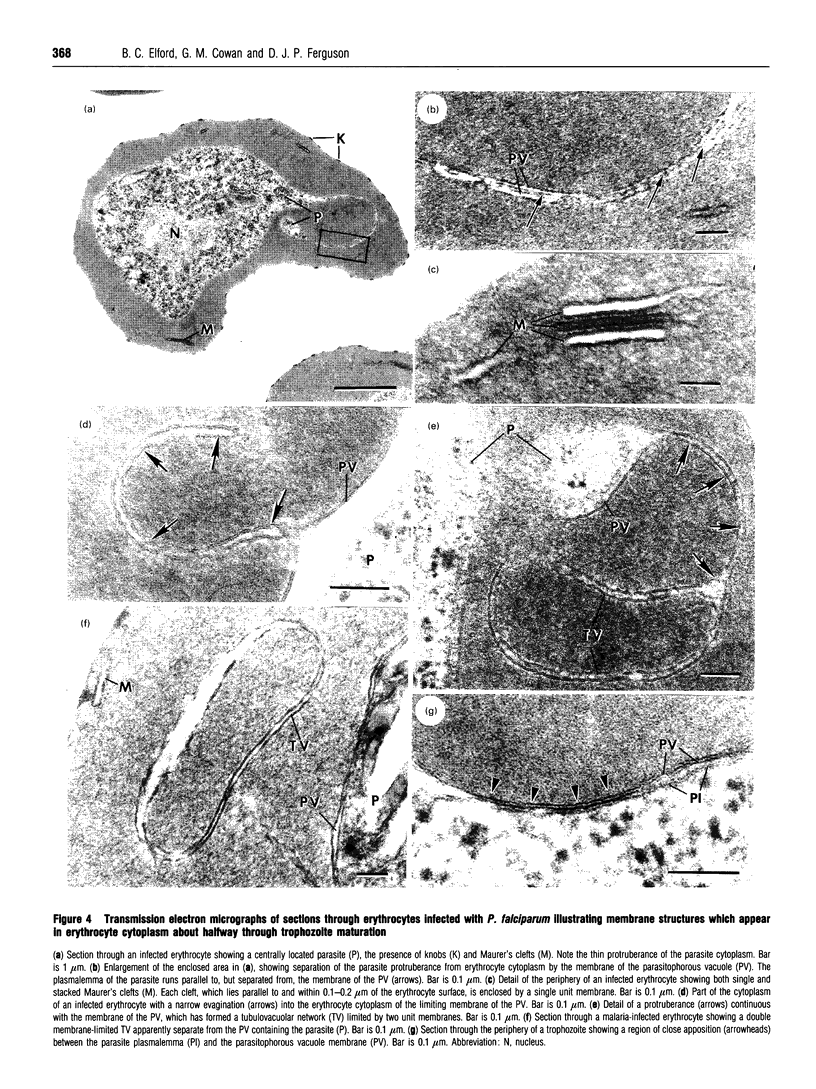
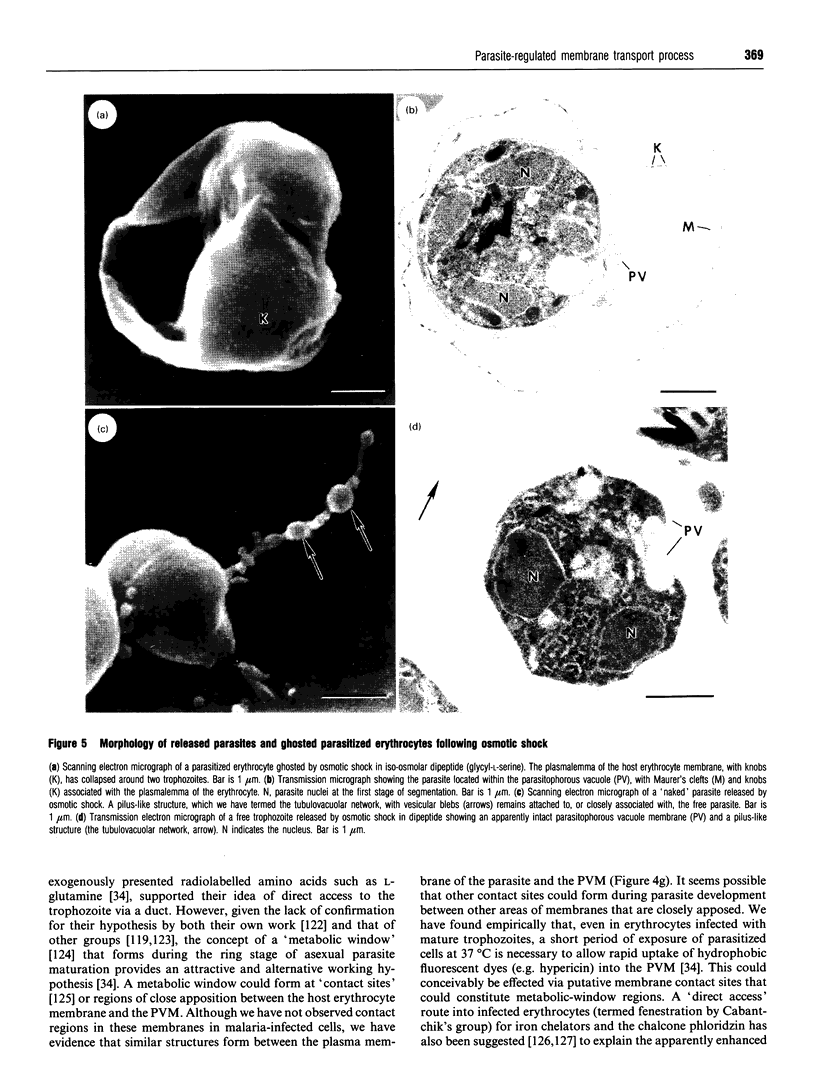
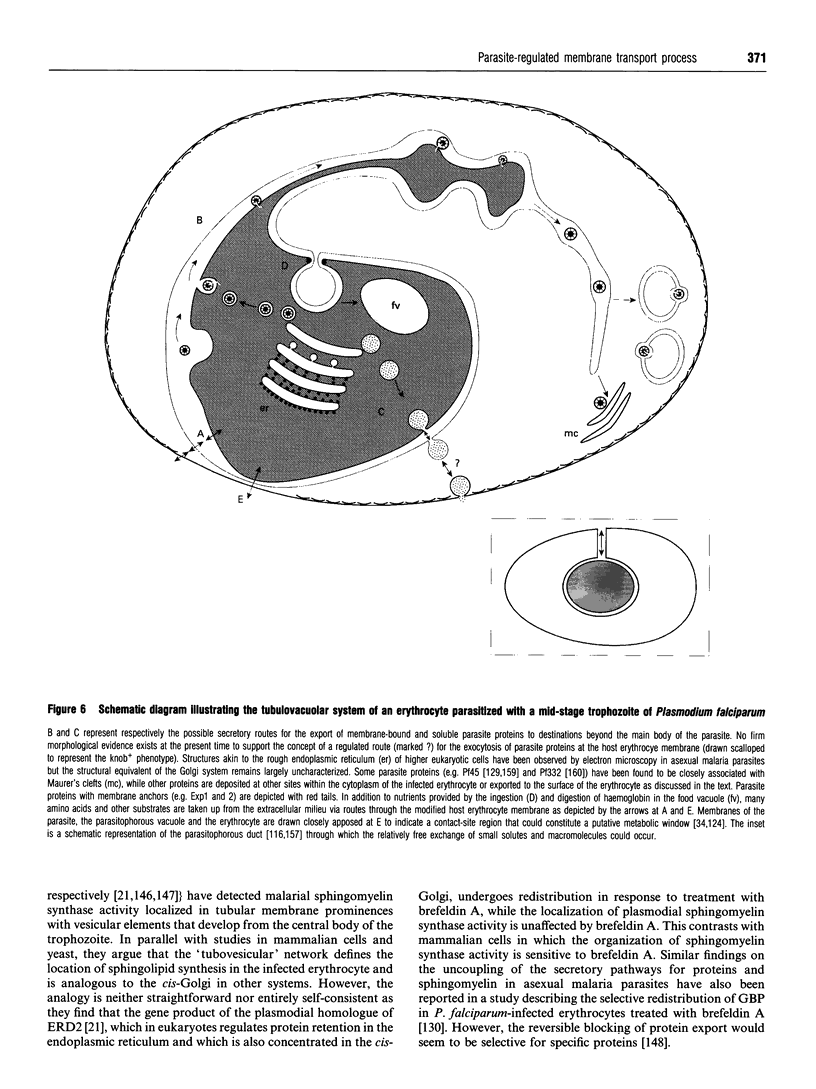
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aikawa M., Miller L. H., Johnson J., Rabbege J. Erythrocyte entry by malarial parasites. A moving junction between erythrocyte and parasite. J Cell Biol. 1978 Apr;77(1):72–82. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aikawa M., Uni Y., Andrutis A. T., Howard R. J. Membrane-associated electron-dense material of the asexual stages of Plasmodium falciparum: evidence for movement from the intracellular parasite to the erythrocyte membrane. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Jan;35(1):30–36. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Hagelberg C., Kallen K. J., Haest C. W. Echinocytosis and microvesiculation of human erythrocytes induced by insertion of merocyanine 540 into the outer membrane leaflet. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 17;986(1):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90279-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ancelin M. L., Parant M., Thuet M. J., Philippot J. R., Vial H. J. Increased permeability to choline in simian erythrocytes after Plasmodium knowlesi infection. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):701–709. doi: 10.1042/bj2730701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ancelin M. L., Vial H. J. Quaternary ammonium compounds efficiently inhibit Plasmodium falciparum growth in vitro by impairment of choline transport. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):814–820. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ancelin M. L., Vial H. J. Regulation of phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis in Plasmodium-infected erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 23;1001(1):82–89. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90310-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ancelin M. L., Vial H. J. Saturable and non-saturable components of choline transport in Plasmodium-infected mammalian erythrocytes: possible role of experimental conditions. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 15;283(Pt 2):619–621. doi: 10.1042/bj2830619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ancelin M. L., Vial H. J. Several lines of evidence demonstrating that Plasmodium falciparum, a parasitic organism, has distinct enzymes for the phosphorylation of choline and ethanolamine. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 7;202(2):217–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80690-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Ashcroft F. M. Properties and functions of ATP-sensitive K-channels. Cell Signal. 1990;2(3):197–214. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90048-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson C. T., Aikawa M., Perry G., Fujino T., Bennett V., Davidson E. A., Howard R. J. Ultrastructural localization of erythrocyte cytoskeletal and integral membrane proteins in Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. Eur J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;45(2):192–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson C. T., Aikawa M. Ultrastructure of malaria-infected erythrocytes. Blood Cells. 1990;16(2-3):351–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister L. H., Dluzewski A. R. The ultrastructure of red cell invasion in malaria infections: a review. Blood Cells. 1990;16(2-3):257–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnwell J. W. Vesicle-mediated transport of membrane and proteins in malaria-infected erythrocytes. Blood Cells. 1990;16(2-3):379–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behari R., Haldar K. Plasmodium falciparum: protein localization along a novel, lipid-rich tubovesicular membrane network in infected erythrocytes. Exp Parasitol. 1994 Nov;79(3):250–259. doi: 10.1006/expr.1994.1088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benting J., Mattei D., Lingelbach K. Brefeldin A inhibits transport of the glycophorin-binding protein from Plasmodium falciparum into the host erythrocyte. Biochem J. 1994 Jun 15;300(Pt 3):821–826. doi: 10.1042/bj3000821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum J. J., Ginsburg H. Absence of alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase activity and presence of CO2-fixing activity in Plasmodium falciparum grown in vitro in human erythrocytes. J Protozool. 1984 Feb;31(1):167–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1984.tb04310.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodammer J. E., Bahr G. F. The initiation of a "metabolic window" in the surface of host erythrocytes by Plasmodium berghei NYU-2. Lab Invest. 1973 Jun;28(6):708–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuer W. V., Kutner S., Sylphen J., Ginsburg H., Cabantchik Z. I. Covalent modification of the permeability pathways induced in the human erythrocyte membrane by the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Oct;133(1):55–63. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Greger R. Chemical probes for anion transporters of mammalian cell membranes. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):C803–C827. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.4.C803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Kutner S., Krugliak M., Ginsburg H. Anion transport inhibitors as suppressors of Plasmodium falciparum growth in in vitro cultures. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 Jan;23(1):92–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I. Properties of permeation pathways induced in the human red cell membrane by malaria parasites. Blood Cells. 1990;16(2-3):421–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crary J. L., Haldar K. Brefeldin A inhibits protein secretion and parasite maturation in the ring stage of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Jul;53(1-2):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90020-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz A., Beverley S. M. Gene replacement in parasitic protozoa. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):171–173. doi: 10.1038/348171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva E., Foley M., Dluzewski A. R., Murray L. J., Anders R. F., Tilley L. The Plasmodium falciparum protein RESA interacts with the erythrocyte cytoskeleton and modifies erythrocyte thermal stability. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1994 Jul;66(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(94)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A., Elmendorf H. G., Li W. I., Haldar K. Biosynthesis, export and processing of a 45 kDa protein detected in membrane clefts of erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium falciparum. Biochem J. 1994 Sep 1;302(Pt 2):487–496. doi: 10.1042/bj3020487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai S. A., Krogstad D. J., McCleskey E. W. A nutrient-permeable channel on the intraerythrocytic malaria parasite. Nature. 1993 Apr 15;362(6421):643–646. doi: 10.1038/362643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divo A. A., Geary T. G., Davis N. L., Jensen J. B. Nutritional requirements of Plasmodium falciparum in culture. I. Exogenously supplied dialyzable components necessary for continuous growth. J Protozool. 1985 Feb;32(1):59–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1985.tb03013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dluzewski A. R., Mitchell G. H., Fryer P. R., Griffiths S., Wilson R. J., Gratzer W. B. Origins of the parasitophorous vacuole membrane of the malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum, in human red blood cells. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jul;102(Pt 3):527–532. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.3.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald R. G., Roos D. S. Stable molecular transformation of Toxoplasma gondii: a selectable dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase marker based on drug-resistance mutations in malaria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11703–11707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elford B. C., Ferguson D. J. Secretory processes in Plasmodium. Parasitol Today. 1993 Mar;9(3):80–81. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(93)90205-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elford B. C., Haynes J. D., Chulay J. D., Wilson R. J. Selective stage-specific changes in the permeability to small hydrophilic solutes of human erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Jun;16(1):43–60. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elford B. C. L-Glutamine influx in malaria-infected erythrocytes: a target for antimalarials? Parasitol Today. 1986 Nov;2(11):309–312. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(86)90126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elford B. C., Pinches R. A. Inducible transport systems in the regulation of parasite growth in malaria-infected red blood cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 Nov;20(4):790–796. doi: 10.1042/bst0200790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elford B. C., Pinches R. A., Newbold C. I., Ellory J. C. Heterogeneous and substrate-specific membrane transport pathways induced in malaria-infected erythrocytes. Blood Cells. 1990;16(2-3):433–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmendorf H. G., Haldar K. Identification and localization of ERD2 in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum: separation from sites of sphingomyelin synthesis and implications for organization of the Golgi. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4763–4773. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06165.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmendorf H. G., Haldar K. Plasmodium falciparum exports the Golgi marker sphingomyelin synthase into a tubovesicular network in the cytoplasm of mature erythrocytes. J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;124(4):449–462. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.4.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmendorf H. G., Haldar K. Plasmodium falciparum exports the Golgi marker sphingomyelin synthase into a tubovesicular network in the cytoplasm of mature erythrocytes. J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;124(4):449–462. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.4.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmendorf H. G., Haldar K. Secretory transport in Plasmodium. Parasitol Today. 1993 Mar;9(3):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(93)90216-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fath M. J., Kolter R. ABC transporters: bacterial exporters. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Dec;57(4):995–1017. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.4.995-1017.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foley M., Tilley L., Sawyer W. H., Anders R. F. The ring-infected erythrocyte surface antigen of Plasmodium falciparum associates with spectrin in the erythrocyte membrane. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 May;46(1):137–147. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90207-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote S. J., Kyle D. E., Martin R. K., Oduola A. M., Forsyth K., Kemp D. J., Cowman A. F. Several alleles of the multidrug-resistance gene are closely linked to chloroquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):255–258. doi: 10.1038/345255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franck P. F., Op den Kamp J. A., Roelofsen B., van Deenen L. L. Does diamide treatment of intact human erythrocytes cause a loss of phospholipid asymmetry? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 May 9;857(1):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch G., Jung A. 14C-desferrioxamine B: uptake into erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium falciparum. Z Parasitenkd. 1986;72(6):709–713. doi: 10.1007/BF00925092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujioka H., Aikawa M. Morphological changes of clefts in Plasmodium-infected erythrocytes under adverse conditions. Exp Parasitol. 1993 May;76(3):302–307. doi: 10.1006/expr.1993.1036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gero A. M., Kirk K. Nutrient transport pathways in Plasmodium-infected erythrocytes: what and where are they? Parasitol Today. 1994 Oct;10(10):395–399. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(94)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gero A. M., O'Sullivan W. J. Purines and pyrimidines in malarial parasites. Blood Cells. 1990;16(2-3):467–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gero A. M., Wood A. M., Hogue D. L., Upston J. M. Effect of diamide on nucleoside and glucose transport in Plasmodium falciparum and Babesia bovis infected erythrocytes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Feb;44(2):195–206. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90005-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg H., Kutner S., Krugliak M., Cabantchik Z. I. Characterization of permeation pathways appearing in the host membrane of Plasmodium falciparum infected red blood cells. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Mar;14(3):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg H. Some reflections concerning host erythrocyte-malarial parasite interrelationships. Blood Cells. 1990;16(2-3):225–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg H., Stein W. D. Biophysical analysis of novel transport pathways induced in red blood cell membranes. J Membr Biol. 1987;96(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01869329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg H., Stein W. D. New permeability pathways induced by the malarial parasite in the membrane of its host erythrocyte: potential routes for targeting of drugs into infected cells. Biosci Rep. 1987 Jun;7(6):455–463. doi: 10.1007/BF01116501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Holman G. D. The glucose transporter family: structure, function and tissue-specific expression. Biochem J. 1993 Oct 15;295(Pt 2):329–341. doi: 10.1042/bj2950329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grellier P., Rigomier D., Clavey V., Fruchart J. C., Schrevel J. Lipid traffic between high density lipoproteins and Plasmodium falciparum-infected red blood cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(2):267–277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta C. M., Mishra G. C. Transbilayer phospholipid asymmetry in Plasmodium knowlesi-infected host cell membrane. Science. 1981 May 29;212(4498):1047–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.7233198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günther K., Tümmler M., Arnold H. H., Ridley R., Goman M., Scaife J. G., Lingelbach K. An exported protein of Plasmodium falciparum is synthesized as an integral membrane protein. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 May;46(1):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90208-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldar K. Ducts, channels and transporters in Plasmodium-infected erythrocytes. Parasitol Today. 1994 Oct;10(10):393–395. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(94)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldar K., Elmendorf H. G., Das A., Li W. L., Ferguson D. J., Elford B. C. In vitro secretory assays with erythrocyte-free malaria parasites. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;45:221–246. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61854-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldar K., Ferguson M. A., Cross G. A. Acylation of a Plasmodium falciparum merozoite surface antigen via sn-1,2-diacyl glycerol. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4969–4974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldar K., Uyetake L., Ghori N., Elmendorf H. G., Li W. L. The accumulation and metabolism of a fluorescent ceramide derivative in Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Nov;49(1):143–156. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90137-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldar K., Uyetake L., Ghori N., Elmendorf H. G., Li W. L. The accumulation and metabolism of a fluorescent ceramide derivative in Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Nov;49(1):143–156. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90137-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldar K., Uyetake L. The movement of fluorescent endocytic tracers in Plasmodium falciparum infected erythrocytes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Jan;50(1):161–177. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90253-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes J. D., Diggs C. L., Hines F. A., Desjardins R. E. Culture of human malaria parasites Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 1976 Oct 28;263(5580):767–769. doi: 10.1038/263767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Coady M. J., Ikeda T. S., Wright E. M. Expression cloning and cDNA sequencing of the Na+/glucose co-transporter. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):379–381. doi: 10.1038/330379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinterberg K., Scherf A., Gysin J., Toyoshima T., Aikawa M., Mazie J. C., da Silva L. P., Mattei D. Plasmodium falciparum: the Pf332 antigen is secreted from the parasite by a brefeldin A-dependent pathway and is translocated to the erythrocyte membrane via the Maurer's clefts. Exp Parasitol. 1994 Nov;79(3):279–291. doi: 10.1006/expr.1994.1091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., Jr Lipids and the malarial parasite. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(2-3):237–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homewood C. A., Neame K. D. Malaria and the permeability of the host erythrocyte. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):718–719. doi: 10.1038/252718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn M., Banting G. Okadaic acid treatment leads to a fragmentation of the trans-Golgi network and an increase in expression of TGN38 at the cell surface. Biochem J. 1994 Jul 1;301(Pt 1):69–73. doi: 10.1042/bj3010069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D., Günther K., Ansorge I., Benting J., Kent A., Bannister L., Ridley R., Lingelbach K. Characterization of membrane proteins exported from Plasmodium falciparum into the host erythrocyte. Parasitology. 1994 Jul;109(Pt 1):1–9. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000077696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaani J., Ginsburg H. Metabolic interconnection between the human malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum and its host erythrocyte. Regulation of ATP levels by means of an adenylate translocator and adenylate kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3194–3199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaani J., Ginsburg H. Transport of lactate in Plasmodium falciparum-infected human erythrocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Dec;149(3):469–476. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041490316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kara U. A., Stenzel D. J., Ingram L. T., Bushell G. R., Lopez J. A., Kidson C. Inhibitory monoclonal antibody against a (myristylated) small-molecular-weight antigen from Plasmodium falciparum associated with the parasitophorous vacuole membrane. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):903–909. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.903-909.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kara U. A., Stenzel D. J., Ingram L. T., Kidson C. The parasitophorous vacuole membrane of Plasmodium falciparum: demonstration of vesicle formation using an immunoprobe. Eur J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;46(1):9–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kara U., Murray B., Pam C., Lahnstein J., Gould H., Kidson C., Saul A. Chemical characterization of the parasitophorous vacuole membrane antigen QF 116 from Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Jan 1;38(1):19–23. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90200-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karcz S. R., Herrmann V. R., Cowman A. F. Cloning and characterization of a vacuolar ATPase A subunit homologue from Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Apr;58(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90056-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karcz S. R., Herrmann V. R., Trottein F., Cowman A. F. Cloning and characterization of the vacuolar ATPase B subunit from Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1994 May;65(1):123–133. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(94)90121-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A. Characterization of a protein correlated with the production of knob-like protrusions on membranes of erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4650–4653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A., Rashid M. A., Aikawa M., Aji T., Yang Y. F. Selective association of a fragment of the knob protein with spectrin, actin and the red cell membrane. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Feb;44(2):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90003-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Soldati D., Boothroyd J. C. Gene replacement in Toxoplasma gondii with chloramphenicol acetyltransferase as selectable marker. Science. 1993 Nov 5;262(5135):911–914. doi: 10.1126/science.8235614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Yamaguchi Y., Takada S., Tanabe K. Cloning of a Ca(2+)-ATPase gene of Plasmodium falciparum and comparison with vertebrate Ca(2+)-ATPases. J Cell Sci. 1993 Apr;104(Pt 4):1129–1136. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.4.1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk K., Ashworth K. J., Elford B. C., Pinches R. A., Ellory J. C. Characteristics of 86Rb+ transport in human erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium falciparum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 30;1061(2):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90296-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk K., Elford B. C., Ellory J. C. The increased K+ leak of malaria-infected erythrocytes is not via a Ca(2+)-activated K+ channel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 30;1135(1):8–12. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90159-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk K., Horner H. A., Elford B. C., Ellory J. C., Newbold C. I. Transport of diverse substrates into malaria-infected erythrocytes via a pathway showing functional characteristics of a chloride channel. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3339–3347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk K., Horner H. A., Spillett D. J., Elford B. C. Glibenclamide and meglitinide block the transport of low molecular weight solutes into malaria-infected erythrocytes. FEBS Lett. 1993 May 24;323(1-2):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81462-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk K., Poli de Figueiredo C. E., Elford B. C., Ellory J. C. Effect of cell age on erythrocyte choline transport: implications for the increased choline permeability of malaria-infected erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 15;283(Pt 2):617–619. doi: 10.1042/bj2830617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk K., Wong H. Y., Elford B. C., Newbold C. I., Ellory J. C. Enhanced choline and Rb+ transport in human erythrocytes infected with the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Biochem J. 1991 Sep 1;278(Pt 2):521–525. doi: 10.1042/bj2780521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan J., Perkins M., Ravetch J. V. A tandemly repeated sequence determines the binding domain for an erythrocyte receptor binding protein of P. falciparum. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90834-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna S., Cowan G. M., Robson K. J., Meade J. C. Plasmodium falciparum: further characterization of putative cation ATPases. Exp Parasitol. 1994 Feb;78(1):113–117. doi: 10.1006/expr.1994.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna S., Cowan G., Meade J. C., Wells R. A., Stringer J. R., Robson K. J. A family of cation ATPase-like molecules from Plasmodium falciparum. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):385–398. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Gluzman I. Y., Kyle D. E., Oduola A. M., Martin S. K., Milhous W. K., Schlesinger P. H. Efflux of chloroquine from Plasmodium falciparum: mechanism of chloroquine resistance. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1283–1285. doi: 10.1126/science.3317830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambros C., Vanderberg J. P. Synchronization of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic stages in culture. J Parasitol. 1979 Jun;65(3):418–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., Coburn C. M., McMahon-Pratt D., Beverley S. M. Development of a stable Leishmania expression vector and application to the study of parasite surface antigen genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9736–9740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P., Ye Z., Van Dyke K., Kirk R. G. X-ray microanalysis of Plasmodium falciparum and infected red blood cells: effects of qinghaosu and chloroquine on potassium, sodium, and phosphorus composition. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Aug;39(2):157–165. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.39.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. L., Das A., Song J. Y., Crary J. L., Haldar K. Stage-specific expression of plasmodial proteins containing an antigenic marker of the intraerythrocytic cisternae. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Nov;49(1):157–168. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90138-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingelbach K. R. Plasmodium falciparum: a molecular view of protein transport from the parasite into the host erythrocyte. Exp Parasitol. 1993 May;76(3):318–327. doi: 10.1006/expr.1993.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loyevsky M., Cabantchik Z. I. Antimalarial action of hydrophilic drugs: involvement of aqueous access routes to intracellular parasites. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Mar;45(3):446–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loyevsky M., Lytton S. D., Mester B., Libman J., Shanzer A., Cabantchik Z. I. The antimalarial action of desferal involves a direct access route to erythrocytic (Plasmodium falciparum) parasites. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):218–224. doi: 10.1172/JCI116174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucocq J. Mimicking mitotic Golgi disassembly using okadaic acid. J Cell Sci. 1992 Dec;103(Pt 4):875–880. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103.4.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire P. A., Sherman I. W. Phospholipid composition, cholesterol content and cholesterol exchange in Plasmodium falciparum-infected red cells. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Jan 1;38(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90210-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConville M. J., Ferguson M. A. The structure, biosynthesis and function of glycosylated phosphatidylinositols in the parasitic protozoa and higher eukaryotes. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 1;294(Pt 2):305–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2940305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick G. J. Amino acid transport and incorporation in red blood cells of normal and Plasmodium knowlesi-infected rhesus monkeys. Exp Parasitol. 1970 Feb;27(1):143–149. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4894(70)80018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGivan J. D., Pastor-Anglada M. Regulatory and molecular aspects of mammalian amino acid transport. Biochem J. 1994 Apr 15;299(Pt 2):321–334. doi: 10.1042/bj2990321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen R. B., Kamber M., Wadwa K. S., Lin P. S., Schmidt-Ullrich R. The role of lipids in Plasmodium falciparum invasion of erythrocytes: a coordinated biochemical and microscopic analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5956–5960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Tanabe K., Takada S. Structure of a Plasmodium yoelii gene-encoded protein homologous to the Ca(2+)-ATPase of rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Sci. 1990 Nov;97(Pt 3):487–495. doi: 10.1242/jcs.97.3.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano R. E., Sleight R. G. Defining lipid transport pathways in animal cells. Science. 1985 Sep 13;229(4718):1051–1057. doi: 10.1126/science.4035344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasloske B. L., Baruch D. I., van Schravendijk M. R., Handunnetti S. M., Aikawa M., Fujioka H., Taraschi T. F., Gormley J. A., Howard R. J. Cloning and characterization of a Plasmodium falciparum gene encoding a novel high-molecular weight host membrane-associated protein, PfEMP3. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 May;59(1):59–72. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90007-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole R. C., Halestrap A. P. Transport of lactate and other monocarboxylates across mammalian plasma membranes. Am J Physiol. 1993 Apr;264(4 Pt 1):C761–C782. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.4.C761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouvelle B., Gormley J. A., Taraschi T. F. Characterization of trafficking pathways and membrane genesis in malaria-infected erythrocytes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1994 Jul;66(1):83–96. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(94)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouvelle B., Spiegel R., Hsiao L., Howard R. J., Morris R. L., Thomas A. P., Taraschi T. F. Direct access to serum macromolecules by intraerythrocytic malaria parasites. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):73–75. doi: 10.1038/353073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes P., Rathod P. K., Sanchez D. J., Mrema J. E., Rieckmann K. H., Heidrich H. G. Enzymes of purine and pyrimidine metabolism from the human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1982 May;5(5):275–290. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(82)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruangjirachuporn W., Udomsangpetch R., Carlsson J., Drenckhahn D., Perlmann P., Berzins K. Plasmodium falciparum: analysis of the interaction of antigen Pf155/RESA with the erythrocyte membrane. Exp Parasitol. 1991 Jul;73(1):62–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(91)90008-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleyer M., Neupert W. Transport of proteins into mitochondria: translocational intermediates spanning contact sites between outer and inner membranes. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):339–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahabuddin M., Günther K., Lingelbach K., Aikawa M., Schreiber M., Ridley R. G., Scaife J. G. Localisation of hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Exp Parasitol. 1992 Feb;74(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(92)90134-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard D. N., Welsh M. J. Effect of ATP-sensitive K+ channel regulators on cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator chloride currents. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Oct;100(4):573–591. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.4.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. W. Biochemistry of Plasmodium (malarial parasites). Microbiol Rev. 1979 Dec;43(4):453–495. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.4.453-495.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. W., Tanigoshi L. Glucose transport in the malarial (Plasmodium lophurae) infected erythrocyte. J Protozool. 1974 Oct;21(4):603–607. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. W., Virkar R. A., Ruble J. A. The accumulation of amino acids by Plasmodium lophurae (avian malaria). Comp Biochem Physiol. 1967 Oct;23(1):43–57. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(67)90471-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman W. R., Stewart M. A., Zinbo M. Mass spectrometric study on the mechanism of D-glucose 6-phosphate-L-myo-inositol 1-phosphate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5703–5708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Messina M., Niesman I. R. Stable DNA transformation in the obligate intracellular parasite Toxoplasma gondii by complementation of tryptophan auxotrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5508–5512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D., Woollett G., Bergin-Cartwright M., Kay D., Scaife J. A malaria protein exported into a new compartment within the host erythrocyte. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):485–491. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04779.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simões A. P., Moll G. N., Beaumelle B., Vial H. J., Roelofsen B., Op den Kamp J. A. Plasmodium knowlesi induces alterations in phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine molecular species composition of parasitized monkey erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Feb 28;1022(2):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90107-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe K. Glucose transport in malaria infected erythrocytes. Parasitol Today. 1990 Jul;6(7):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(90)90199-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraschi T. F., Nicolas E. The parasitophorous duct pathway: new opportunities for antimalarial drug and vaccine development. Parasitol Today. 1994 Oct;10(10):399–401. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(94)90232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraschi T. F., Parashar A., Hooks M., Rubin H. Perturbation of red cell membrane structure during intracellular maturation of Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):102–104. doi: 10.1126/science.3006251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraschi T. F., Pouvelle B. There is no ducking the duct. Parasitol Today. 1994 Jun;10(6):212–213. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(94)90113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Jensen J. B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.781840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vial H. J., Ancelin M. L. Malarial lipids. An overview. Subcell Biochem. 1992;18:259–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vial H. J., Ancelin M. L., Philippot J. R., Thuet M. J. Biosynthesis and dynamics of lipids in Plasmodium-infected mature mammalian erythrocytes. Blood Cells. 1990;16(2-3):531–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vial H. J., Ancelin M. L., Philippot J. R., Thuet M. J. Biosynthesis and dynamics of lipids in Plasmodium-infected mature mammalian erythrocytes. Blood Cells. 1990;16(2-3):531–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vial H. J., Philippot J. R., Wallach D. F. A reevaluation of the status of cholesterol in erythrocytes infected by Plasmodium knowlesi and P. falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Sep;13(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vial H. J., Thuet M. J., Broussal J. L., Philippot J. R. Phospholipid biosynthesis by Plasmodium knowlesi-infected erythrocytes: the incorporation of phospohlipid precursors and the identification of previously undetected metabolic pathways. J Parasitol. 1982 Jun;68(3):379–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vial H. J., Thuet M. J., Philippot J. R. Phospholipid biosynthesis in synchronous Plasmodium falciparum cultures. J Protozool. 1982 May;29(2):258–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1982.tb04023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward G. E., Miller L. H., Dvorak J. A. The origin of parasitophorous vacuole membrane lipids in malaria-infected erythrocytes. J Cell Sci. 1993 Sep;106(Pt 1):237–248. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.1.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellems T. E., Panton L. J., Gluzman I. Y., do Rosario V. E., Gwadz R. W., Walker-Jonah A., Krogstad D. J. Chloroquine resistance not linked to mdr-like genes in a Plasmodium falciparum cross. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):253–255. doi: 10.1038/345253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellems T. E., Walliker D., Smith C. L., do Rosario V. E., Maloy W. L., Howard R. J., Carter R., McCutchan T. F. A histidine-rich protein gene marks a linkage group favored strongly in a genetic cross of Plasmodium falciparum. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):633–642. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90539-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiser M. F. Malarial proteins that interact with the erythrocyte membrane and cytoskeleton. Exp Parasitol. 1991 Nov;73(4):515–523. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(91)90076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachowski A. Phospholipids in animal eukaryotic membranes: transverse asymmetry and movement. Biochem J. 1993 Aug 15;294(Pt 1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj2940001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarchin S., Krugliak M., Ginsburg H. Digestion of the host erythrocyte by malaria parasites is the primary target for quinoline-containing antimalarials. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Jul 15;35(14):2435–2442. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90473-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman M. L., Daleke D. L. Regulation of a candidate aminophospholipid-transporting ATPase by lipid. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 16;32(45):12257–12263. doi: 10.1021/bi00096a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Asbroek A. L., Ouellette M., Borst P. Targeted insertion of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene into the tubulin gene cluster of Trypanosoma brucei. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):174–175. doi: 10.1038/348174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Kuile F. O., Nosten F., Thieren M., Luxemburger C., Edstein M. D., Chongsuphajaisiddhi T., Phaipun L., Webster H. K., White N. J. High-dose mefloquine in the treatment of multidrug-resistant falciparum malaria. J Infect Dis. 1992 Dec;166(6):1393–1400. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.6.1393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Es H. H., Karcz S., Chu F., Cowman A. F., Vidal S., Gros P., Schurr E. Expression of the plasmodial pfmdr1 gene in mammalian cells is associated with increased susceptibility to chloroquine. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2419–2428. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]