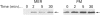Abstract
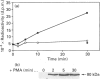
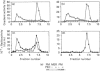
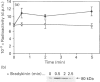
Phosphatidylalcohol accumulates as a product of a phospholipase D (PLD)-catalysed transphosphatidylation reaction in cells incubated in the presence of a primary alcohol. In the presence of ethanol the phorbol ester, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), stimulated the accumulation of [3H]phosphatidylethanol (PEth) in HeLa cells prelabelled with [3H]palmitic acid. Radioactivity associated with PEth increased linearly during a 30 min incubation, indicating that a sustained activation of PLD is caused by PMA in these cells. This was accompanied by the membrane association of protein kinase C-alpha (PKC-alpha), the PKC isoform that recent studies indicate is involved in the activation of PLD. In similar experiments, the neuropeptide bradykinin stimulated an accumulation of PEth in 3T3 Li cells. The radioactivity associated with PEth increased to a maximal level at 30 s and plateaued after this time, suggesting that bradykinin induces only a transient activation of PLD in these cells. This is consistent with the effects of bradykinin on PKC-alpha, which underwent a rapid and transient association with cell membranes. The subcellular localization of PEth was examined using the technique of subcellular fractionation on Percoll density gradients to isolate organelle-enriched fractions from HeLa and 3T3 Li cells. An accumulation of [3H]PEth was measured in the plasma-membrane (PM)-enriched fractions of both HeLa and 3T3 Li cells after incubation with PMA and bradykinin respectively. This was accompanied by a time-dependent accumulation of [3H]PEth in the combined mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum (MER)-enriched fractions of both cell lines. PMA was also found to cause translocation of PKC-alpha to both the PM- and MER-enriched fractions in HeLa cells. However, bradykinin stimulated the translocation of PKC-alpha to the PM-enriched fractions only of 3T3 Li cells. The results show that PLD activation leads to the accumulation of PEth in both the PM and MER fractions. We therefore propose that either bradykinin activates a PM-associated PLD and the PLD reaction product is rapidly translocated to other membrane systems or it activates an MER-associated PLD by a mechanism that does not involve PKC-alpha.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balboa M. A., Firestein B. L., Godson C., Bell K. S., Insel P. A. Protein kinase C alpha mediates phospholipase D activation by nucleotides and phorbol ester in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Stimulation of phospholipase D is independent of activation of polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C and phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10511–10516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baykov A. A., Evtushenko O. A., Avaeva S. M. A malachite green procedure for orthophosphate determination and its use in alkaline phosphatase-based enzyme immunoassay. Anal Biochem. 1988 Jun;171(2):266–270. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90484-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Anthes J. C. The regulation and cellular functions of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):281–291. doi: 10.1042/bj2690281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. A., Gutowski S., Moomaw C. R., Slaughter C., Sternweis P. C. ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-dependent regulatory protein, stimulates phospholipase D activity. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1137–1144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90323-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Thomas G. M., Fensome A., Geny B., Cunningham E., Gout I., Hiles I., Totty N. F., Truong O., Hsuan J. J. Phospholipase D: a downstream effector of ARF in granulocytes. Science. 1994 Jan 28;263(5146):523–526. doi: 10.1126/science.8290961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conricode K. M., Smith J. L., Burns D. J., Exton J. H. Phospholipase D activation in fibroblast membranes by the alpha and beta isoforms of protein kinase C. FEBS Lett. 1994 Apr 4;342(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80490-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. J., Palmer S., Plevin R., Wakelam M. J. Mass measurement of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and sn-1,2-diacylglycerol in bombesin-stimulated Swiss 3T3 mouse fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):617–620. doi: 10.1042/bj2650617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekker L. V., Parker P. J. Protein kinase C--a question of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Feb;19(2):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divecha N., Banfić H., Irvine R. F. The polyphosphoinositide cycle exists in the nuclei of Swiss 3T3 cells under the control of a receptor (for IGF-I) in the plasma membrane, and stimulation of the cycle increases nuclear diacylglycerol and apparently induces translocation of protein kinase C to the nucleus. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3207–3214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04883.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu T., Okano Y., Nozawa Y. Differential pathways (phospholipase C and phospholipase D) of bradykinin-induced biphasic 1,2-diacylglycerol formation in non-transformed and K-ras-transformed NIH-3T3 fibroblasts. Involvement of intracellular Ca2+ oscillations in phosphatidylcholine breakdown. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 15;283(Pt 2):347–354. doi: 10.1042/bj2830347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelas P., Ribbes G., Record M., Terce F., Chap H. Differential activation by fMet-Leu-Phe and phorbol ester of a plasma membrane phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase D in human neutrophil. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81457-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geny B., Fensome A., Cockcroft S. Rat brain cytosol contains a factor which reconstitutes guanine-nucleotide-binding-protein-regulated phospholipase-D activation in HL60 cells previously permeabilized with streptolysin O. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jul 15;215(2):389–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hii C. S., Edwards Y. S., Murray A. W. Basal and phorbol-ester-stimulated turnover of phosphatidylcholine in HeLa cells involve different pathways. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 15;288(Pt 3):983–985. doi: 10.1042/bj2880983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz J., Davis L. L. The substrate specificity of brain microsomal phospholipase D. Biochem J. 1993 Nov 1;295(Pt 3):793–798. doi: 10.1042/bj2950793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Yucel J. K., Malhotra V. ARF signaling: a potential role for phospholipase D in membrane traffic. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1045–1048. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90314-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanoh H., Sakane F., Imai S., Wada I. Diacylglycerol kinase and phosphatidic acid phosphatase--enzymes metabolizing lipid second messengers. Cell Signal. 1993 Sep;5(5):495–503. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(93)90045-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
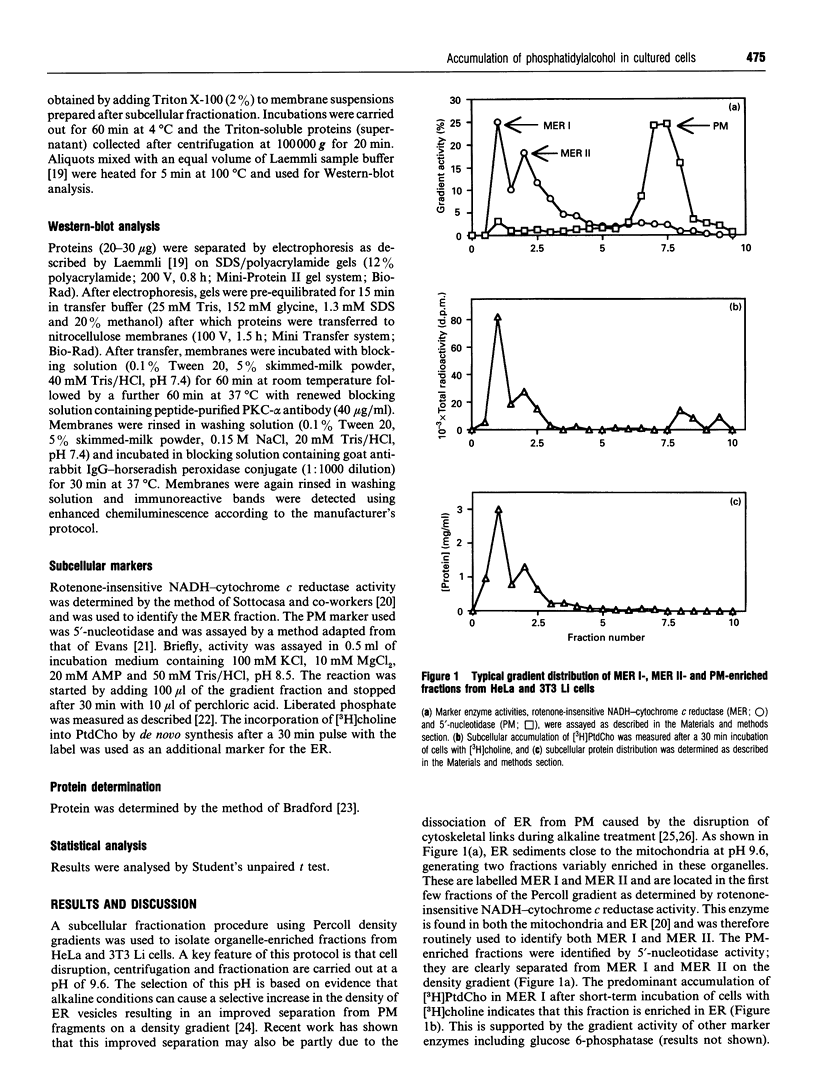
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauter C. J., Solyom A., Trams E. G. Comparative studies on enzyme markers of liver plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 9;266(2):511–523. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M., Cantley L. C. Lipid second messengers. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):329–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
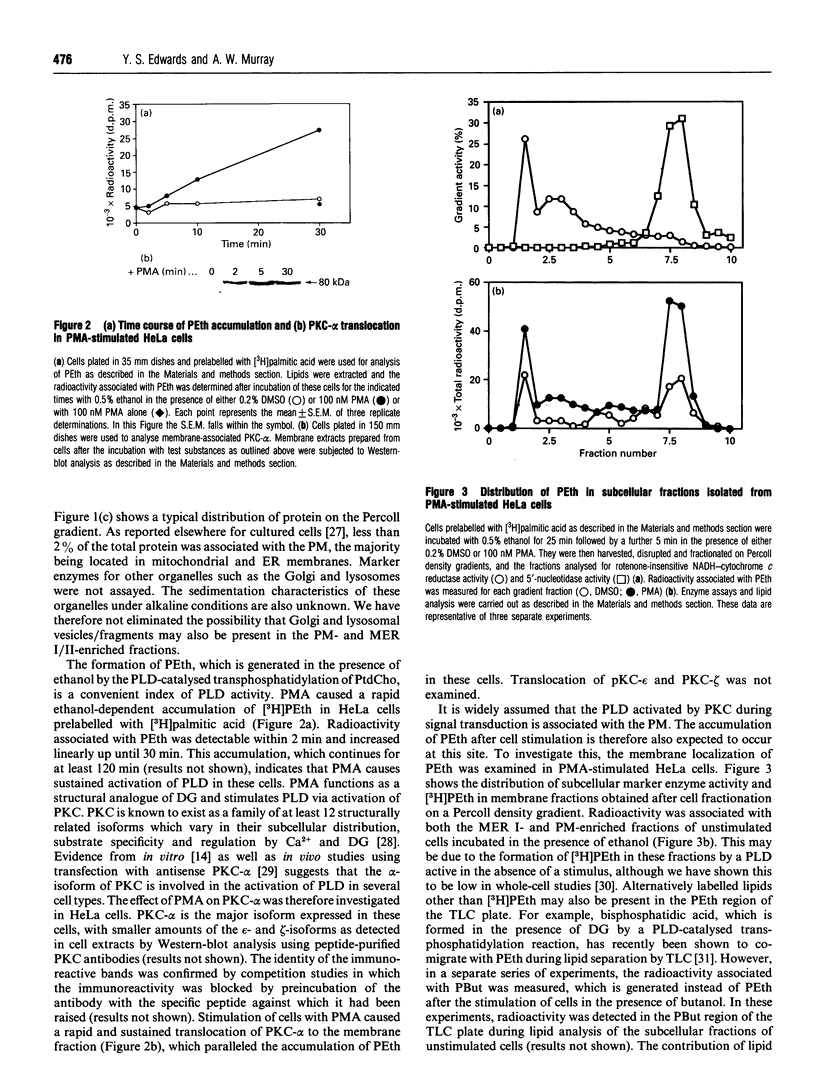
- Liscovitch M. Phosphatidylethanol biosynthesis in ethanol-exposed NG108-15 neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid cells. Evidence for activation of a phospholipase D phosphatidyl transferase activity by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1450–1456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lièvremont J. P., Hill A. M., Hilly M., Mauger J. P. The inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor is localized on specialized sub-regions of the endoplasmic reticulum in rat liver. Biochem J. 1994 Jun 1;300(Pt 2):419–427. doi: 10.1042/bj3000419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostermann J., Orci L., Tani K., Amherdt M., Ravazzola M., Elazar Z., Rothman J. E. Stepwise assembly of functionally active transport vesicles. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):1015–1025. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90545-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano R. E., Longmuir K. J. Phosphorylation, transbilayer movement, and facilitated intracellular transport of diacylglycerol are involved in the uptake of a fluorescent analog of phosphatidic acid by cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1909–1916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
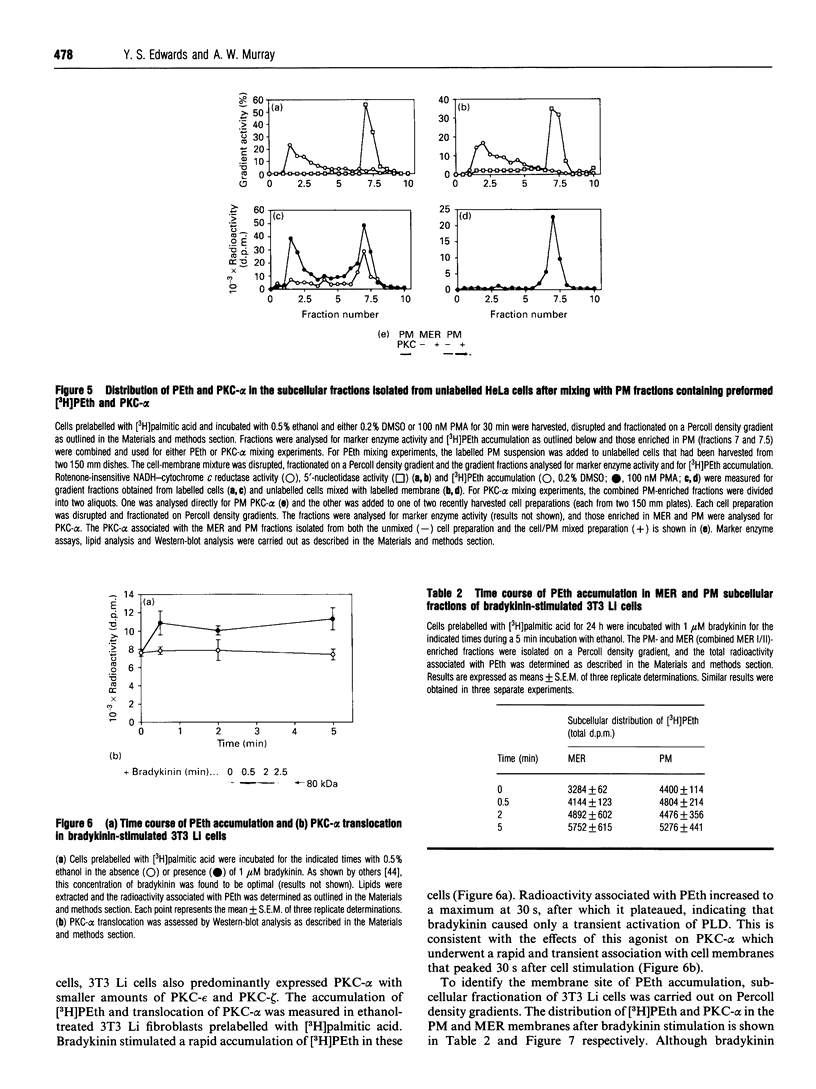
- Randazzo P. A., Kahn R. A. GTP hydrolysis by ADP-ribosylation factor is dependent on both an ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase-activating protein and acid phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10758–10763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M., Bes J. C., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Isolation and characterization of plasma membranes from krebs II ascite cells using Percoll gradient. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 21;688(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90578-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M., Laharrague P., Fillola G., Thomas J., Ribes G., Fontan P., Chap H., Corberand J., Douste-Blazy L. A rapid isolation procedure of plasma membranes from human neutrophils using self-generating Percoll gradients. Importance of pH in avoiding contamination by intracellular membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 25;819(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90188-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier M. F., Bird G. S., Putney J. W., Jr Subcellular distribution of the calcium-storing inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive organelle in rat liver. Possible linkage to the plasma membrane through the actin microfilaments. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 15;274(Pt 3):643–650. doi: 10.1042/bj2740643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebaldt R. J., Adams D. O., Uhing R. J. Quantification of contributions of phospholipid precursors to diradylglycerols in stimulated mononuclear phagocytes. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 1;284(Pt 2):367–375. doi: 10.1042/bj2840367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottocasa G. L., Kuylenstierna B., Ernster L., Bergstrand A. An electron-transport system associated with the outer membrane of liver mitochondria. A biochemical and morphological study. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):415–438. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigawa G., Orci L., Amherdt M., Ravazzola M., Helms J. B., Rothman J. E. Hydrolysis of bound GTP by ARF protein triggers uncoating of Golgi-derived COP-coated vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(6 Pt 1):1365–1371. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly B. C., van Paridon P. A., Verlaan I., Wirtz K. W., de Laat S. W., Moolenaar W. H. Inositol phosphate metabolism in bradykinin-stimulated human A431 carcinoma cells. Relationship to calcium signalling. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):129–135. doi: 10.1042/bj2440129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utal A. K., Jamil H., Vance D. E. Diacylglycerol signals the translocation of CTP:choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase in HeLa cells treated with 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):24084–24091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh C. J., Schmeichel K. Assays for investigations of signal transduction mechanisms involving phospholipase D: mass measurements of phosphatidate, phosphatidylethanol, and diacylglycerol in cultured cells. Anal Biochem. 1991 Feb 1;192(2):281–292. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90537-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R., Snyder F. Quantitative determination of alk-1-enyl- and alkyl-glyceryl ethers in neutral lipids and phospholipids. Lipids. 1968 Mar;3(2):129–135. doi: 10.1007/BF02531729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Blitterswijk W. J., Hilkmann H. Rapid attenuation of receptor-induced diacylglycerol and phosphatidic acid by phospholipase D-mediated transphosphatidylation: formation of bisphosphatidic acid. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2655–2662. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Blitterswijk W. J., Hilkmann H., de Widt J., van der Bend R. L. Phospholipid metabolism in bradykinin-stimulated human fibroblasts. I. Biphasic formation of diacylglycerol from phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylcholine, controlled by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10337–10343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Blitterswijk W. J., Hilkmann H., de Widt J., van der Bend R. L. Phospholipid metabolism in bradykinin-stimulated human fibroblasts. II. Phosphatidylcholine breakdown by phospholipases C and D; involvement of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10344–10350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]