Abstract
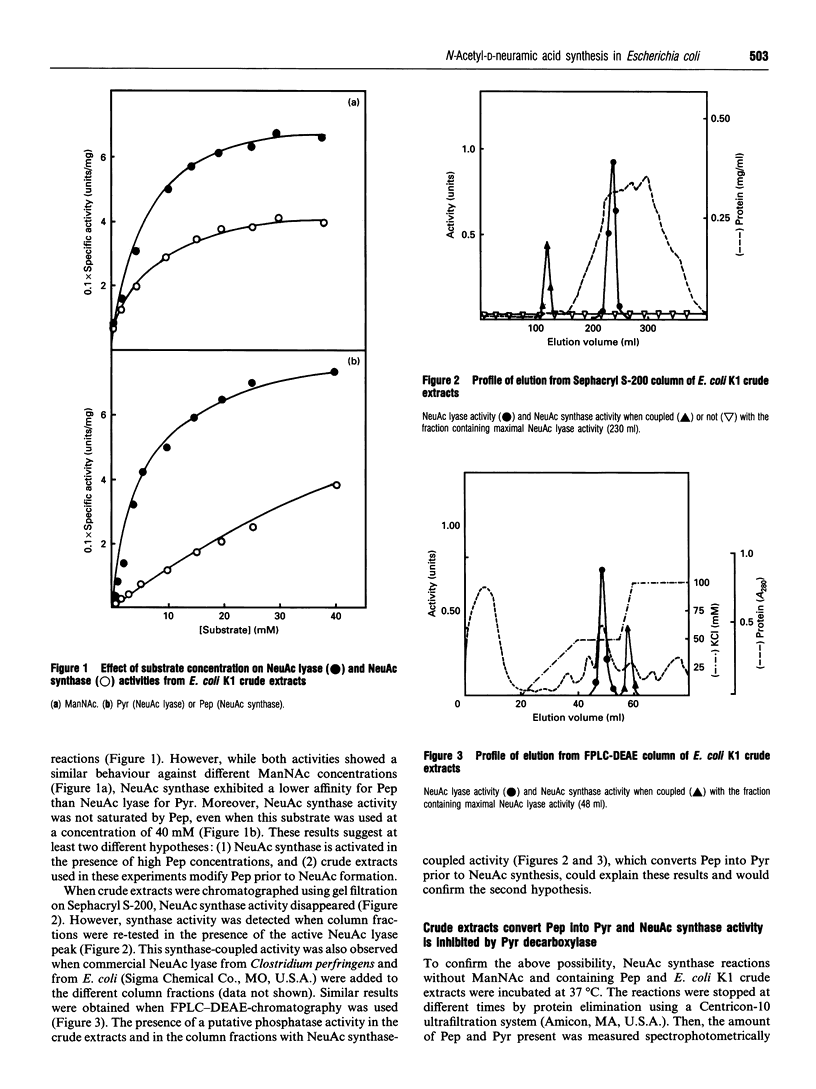
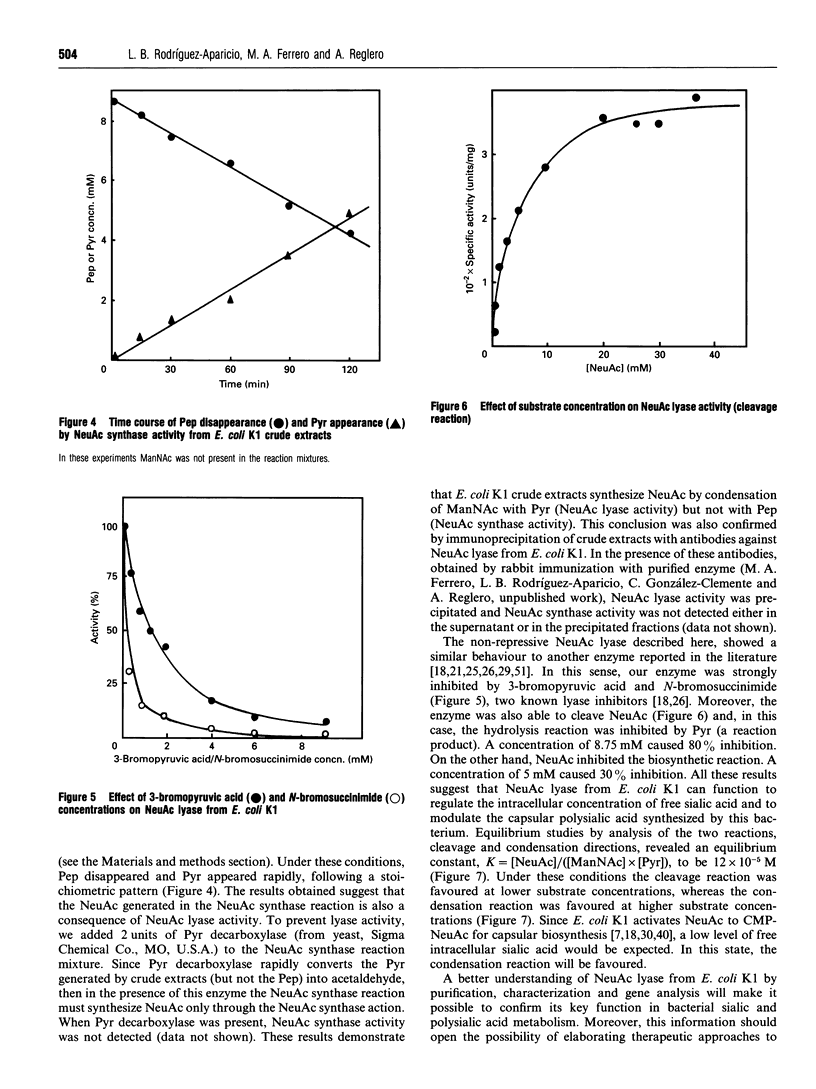
Two enzymes have been found to be involved in bacterial N-acetyl-D-neuraminic acid (NeuAc) synthesis: NeuAc synthase, which condenses N-acetyl-L,D-mannosamine and phosphoenolpyruvate, and NeuAc lyase or NeuAc aldolase, which condenses N-acetyl-D-mannosamine and pyruvate. When we used Escherichia coli K1 crude extracts, we observed the generation of NeuAc in the presence of N-acetylmannosamine and both phosphoenolpyruvate (NeuAc synthase activity) or pyruvate (NeuAc lyase activity). However, when crude extracts were fractionated by Sephacryl S-200 chromatography, NeuAc synthase activity disappeared. A chromatographic peak of NeuAc synthase activity was detected when column fractions were re-tested in the presence of the active NeuAc lyase peak. Furthermore, crude extracts converted phosphoenolpyruvate into pyruvate. Pyruvate depletion, due to the addition of pyruvate decarboxylase to the NeuAc synthase reaction mixture, blocked NeuAc formation. Moreover, after NeuAc lyase immunoprecipitation no NeuAc synthase was detected. These findings suggest that NeuAc synthase is not present in E. coli K1 and therefore that NeuAc lyase is the only enzyme responsible for NeuAc synthesis in this bacterium.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arden S. B., Chang W. H., Barksdale L. Distribution of neuraminidase and n-acetylneuraminate lyase activities among corynebacteria, mycobacteria, and nocardias. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1206–1212. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1206-1212.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY G. T., GOEBEL W. F. Colominic acid, a substance of bacterial origin related to sialic acid. Nature. 1957 Jan 26;179(4552):206–206. doi: 10.1038/179206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACKLOW R. S., WARREN L. Biosynthesis of sialic acids by Neisseria meningitidis. J Biol Chem. 1962 Nov;237:3520–3526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUNETTI P., JOURDIAN G. W., ROSEMAN S. The sialic acids. III. Distribution and properties of animal N-acetylneuraminic aldolase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2447–2453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee A. K., Jennings H. J., Kenny C. P., Martin A., Smith I. C. Structural determination of the polysaccharide antigens of Neisseria meningitidis serogroups Y, W-135, and BO1. Can J Biochem. 1976 Jan;54(1):1–8. doi: 10.1139/o76-001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee A. K., Jennings H. J., Kenny C. P., Martin A., Smith I. C. Structural determination of the sialic acid polysaccharide antigens of Neisseria meningitidis serogroups B and C with carbon 13 nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1926–1932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brossmer R., Rose U., Kaspar D., Smith T. L., Grasmuk H., Unger F. M. Enzymic synthesis of 5-acetamido-9-azido-3,5,9-trideoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-2-nonulosonic acid, a 9-azido-9-deoxy derivative of N-acetylneuraminic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Oct 16;96(3):1282–1289. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90090-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMB D. G., ROSEMAN S. The sialic acids. I. The structure and enzymatic synthesis of N-acetylneuraminic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2529–2537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drzeniek R., Scharmann W., Balke E. Neuraminidase and N-acetylneuraminate pyruvate-lyase of Pasteurella multocida. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Sep;72(2):357–368. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-2-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero-García M. A., Trombetta S. E., Sánchez D. O., Reglero A., Frasch A. C., Parodi A. J. The action of Trypanosoma cruzi trans-sialidase on glycolipids and glycoproteins. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Apr 15;213(2):765–771. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Clemente C., Luengo J. M., Rodríguez-Aparicio L. B., Ferrero M. A., Reglero A. High production of polysialic acid [Neu5Ac alpha(2-8)-Neu5Ac alpha(2-9)]n by Escherichia coli K92 grown in a chemically defined medium. Regulation of temperature. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1990 Nov;371(11):1101–1106. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1990.371.2.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Clemente C., Luengo J. M., Rodríguez-Aparicio L. B., Reglero A. Regulation of colominic acid biosynthesis by temperature: role of cytidine 5'-monophosphate N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):429–432. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80770-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimer R., Meyer K. STUDIES ON SIALIC ACID OF SUBMAXILLARY MUCOID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Oct;42(10):728–734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.10.728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann K., Jann B. The K antigens of Escherichia coli. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:53–79. doi: 10.1159/000407421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaijser B., Hanson L. A., Jodal U., Lidin-Janson G., Robbins J. B. Frequency of E. coli K antigens in urinary-tract infections in children. Lancet. 1977 Mar 26;1(8013):663–666. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean E. L., Roseman S. The sialic acids. X. Purification and properties of cytidine 5'-monophosphosialic acid synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 10;241(23):5643–5650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. Y., Gotschlich E. C., Dunne F. T., Jonssen E. K. Studies on the meningococcal polysaccharides. II. Composition and chemical properties of the group B and group C polysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4703–4712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr, Sarff L. D., Glode M. P., Mize S. G., Schiffer M. S., Robbins J. B., Gotschlich E. C., Orskov I., Orskov F. Relation between Escherichia coli K1 capsular polysaccharide antigen and clinical outcome in neonatal meningitis. Lancet. 1974 Aug 3;2(7875):246–250. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91413-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merker R. I., Troy F. A. Biosynthesis of the polysialic acid capsule in Escherichia coli K1. Cold inactivation of sialic acid synthase regulates capsule expression below 20 degrees C. Glycobiology. 1990 Sep;1(1):93–100. doi: 10.1093/glycob/1.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montreuil J. Primary structure of glycoprotein glycans: basis for the molecular biology of glycoproteins. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1980;37:157–223. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nees S., Schauer R., Mayer F. Purification and characterization of N-acetylneuraminate lyase from Clostridium perfringens. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Jun;357(6):839–853. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1976.357.1.839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz A. I., Reglero A., Rodríguez-Aparicio L. B., Luengo J. M. In vitro synthesis of colominic acid by membrane-bound sialyltransferase of Escherichia coli K-235. Kinetic properties of this enzyme and inhibition by CMP and other cytidine nucleotides. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 2;178(3):741–749. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reglero A., Rodríguez-Aparicio L. B., Luengo J. M. Polysialic acids. Int J Biochem. 1993 Nov;25(11):1517–1527. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(93)90507-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Aparicio L. B., Luengo J. M., Ferrero M. A., Reglero A. Comparative analysis of the antibodies against capsular polysaccharides of Escherichia coli K-92 and K-235: an immunochemical method for the identification of polysialic acids. Int J Biochem. 1993 Mar;25(3):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(93)90635-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Aparicio L. B., Luengo J. M., González-Clemente C., Reglero A. Purification and characterization of the nuclear cytidine 5'-monophosphate N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9257–9263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Aparicio L. B., Reglero A., Martínez-Blanco H., Luengo J. M. Fluorometric determination of phenylacetyl-CoA ligase from Pseudomonas putida: a very sensitive assay for a newly described enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 4;1073(2):431–433. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(91)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Aparicio L. B., Reglero A., Ortiz A. I., Luengo J. M. A protein-sialyl polymer complex involved in colominic acid biosynthesis. Effect of tunicamycin. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 15;251(2):589–596. doi: 10.1042/bj2510589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarff L. D., McCracken G. H., Schiffer M. S., Glode M. P., Robbins J. B., Orskov I., Orskov F. Epidemiology of Escherichia coli K1 in healthy and diseased newborns. Lancet. 1975 May 17;1(7916):1099–1104. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. P., Finn C. W., Vann W. F., Aaronson W., Schneerson R., Kretschmer P. J., Garon C. F. Molecular cloning of the K1 capsular polysaccharide genes of E. coli. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):696–698. doi: 10.1038/289696b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., 2nd Polysialylation: from bacteria to brains. Glycobiology. 1992 Feb;2(1):5–23. doi: 10.1093/glycob/2.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., 2nd The chemistry and biosynthesis of selected bacterial capsular polymers. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:519–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., McCloskey M. A. Role of a membranous sialyltransferase complex in the synthesis of surface polymers containing polysialic acid in Escherichia coli. Temperature-induced alteration in the assembly process. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7377–7387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., Vijay I. K., McCloskey M. A., Rohr T. E. Synthesis of capsular polymers containing polysialic acid in Escherichia coli 07-K1. Methods Enzymol. 1982;83:540–548. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)83050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., Vijay I. K., Tesche N. Role of undecaprenyl phosphate in synthesis of polymers containing sialic acid in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):156–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida Y., Tsukada Y., Sugimori T. Purification and properties of N-acetylneuraminate lyase from Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1984 Aug;96(2):507–522. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rinsum J., Van Dijk W., Hooghwinkel G. J., Ferwerda W. Subcellular localization and tissue distribution of sialic acid precursor-forming enzymes. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 15;210(1):21–28. doi: 10.1042/bj2100021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vann W. F., Silver R. P., Abeijon C., Chang K., Aaronson W., Sutton A., Finn C. W., Lindner W., Kotsatos M. Purification, properties, and genetic location of Escherichia coli cytidine 5'-monophosphate N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17556–17562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimr E. R., Troy F. A. Identification of an inducible catabolic system for sialic acids (nan) in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):845–853. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.845-853.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimr E. R., Troy F. A. Regulation of sialic acid metabolism in Escherichia coli: role of N-acylneuraminate pyruvate-lyase. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):854–860. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.854-860.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L., FELSENFELD H. The biosynthesis of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1421–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


