Abstract
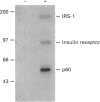
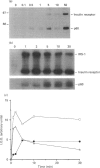
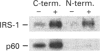
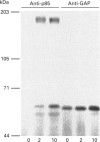
Activation of the tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor by autophosphorylation leads to phosphorylation of cellular substrates on tyrosine. Thus far, the best characterized is the insulin receptor substrate (IRS) 1, which has been proposed to serve as a docking protein for other molecules involved in signal transduction. A number of other proteins that become phosphorylated in response to insulin have been identified, some of which are reported to be tissue-specific. A 60 kDa phosphoprotein has been detected in adipocytes after insulin stimulation [Lavan and Lienhard (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268, 5921-5928]. We have identified a protein of similar molecular mass in rat hepatoma cells transfected with the human insulin receptor. The 60 kDa protein in hepatoma cells is tyrosine-phosphorylated in response to insulin in a dose-dependent manner, with maximal phosphorylation occurring at 50 nM insulin. Although the dose-response of p60 phosphorylation mirrors that of IRS-1, the time course is slightly slower, with maximal phosphorylation observed 5 min after addition of insulin. Like the adipocyte protein, the 60 kDa protein detected in liver cells binds to the SH2 domain of the p85 regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, but not to other SH2 domains. Binding of p60 to p85 is similar to the interaction between p85 and IRS-1 in that a tyrosine-phosphorylated peptide containing the YVXM motif can inhibit the association. The presence of this 60 kDa tyrosine-phosphorylated protein in adipocytes and hepatoma cells suggests that it represents another important intermediate in the insulin-receptor signal-transduction pathway.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backer J. M., Myers M. G., Jr, Shoelson S. E., Chin D. J., Sun X. J., Miralpeix M., Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Schlessinger J. Phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase is activated by association with IRS-1 during insulin stimulation. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3469–3479. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. J., Ellis C., Pawson T., Velu T. Effects of substitution of threonine 654 of the epidermal growth factor receptor on epidermal growth factor-mediated activation of phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):7009–7015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domchek S. M., Auger K. R., Chatterjee S., Burke T. R., Jr, Shoelson S. E. Inhibition of SH2 domain/phosphoprotein association by a nonhydrolyzable phosphonopeptide. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 20;31(41):9865–9870. doi: 10.1021/bi00156a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Kaplan D. R., Kavanaugh W. M., Turck C. W., Williams L. T. A phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase binds to platelet-derived growth factor receptors through a specific receptor sequence containing phosphotyrosine. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1125–1132. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Escobedo J. A., Martin G. A., Turck C. W., del Rosario M., McCormick F., Williams L. T. Distinct phosphotyrosines on a growth factor receptor bind to specific molecules that mediate different signaling pathways. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90444-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosomi Y., Shii K., Ogawa W., Matsuba H., Yoshida M., Okada Y., Yokono K., Kasuga M., Baba S., Roth R. A. Characterization of a 60-kilodalton substrate of the insulin receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11498–11502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly M., Kazlauskas A., Fay F. S., Corvera S. Disruption of PDGF receptor trafficking by mutation of its PI-3 kinase binding sites. Science. 1994 Feb 4;263(5147):684–687. doi: 10.1126/science.8303278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Autophosphorylation of the PDGF receptor in the kinase insert region regulates interactions with cell proteins. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1121–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhné M. R., Pawson T., Lienhard G. E., Feng G. S. The insulin receptor substrate 1 associates with the SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase Syp. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11479–11481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavan B. E., Lienhard G. E. The insulin-elicited 60-kDa phosphotyrosine protein in rat adipocytes is associated with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5921–5928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Li W., Nishimura R., Zhou M., Batzer A. G., Myers M. G., Jr, White M. F., Schlessinger J., Skolnik E. Y. Nck associates with the SH2 domain-docking protein IRS-1 in insulin-stimulated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11713–11717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein E. J., Daly R. J., Batzer A. G., Li W., Margolis B., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Skolnik E. Y., Bar-Sagi D., Schlessinger J. The SH2 and SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 links receptor tyrosine kinases to ras signaling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):431–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90167-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maa M. C., Leu T. H., Trandel B. J., Chang J. H., Parsons S. J. A protein that is highly related to GTPase-activating protein-associated p62 complexes with phospholipase C gamma. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;14(8):5466–5473. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Li N., Koch A., Mohammadi M., Hurwitz D. R., Zilberstein A., Ullrich A., Pawson T., Schlessinger J. The tyrosine phosphorylated carboxyterminus of the EGF receptor is a binding site for GAP and PLC-gamma. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4375–4380. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07887.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Baltimore D. Signalling through SH2 and SH3 domains. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;3(1):8–13. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmichi M., Decker S. J., Pang L., Saltiel A. R. Nerve growth factor binds to the 140 kd trk proto-oncogene product and stimulates its association with the src homology domain of phospholipase C gamma 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):217–223. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91357-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmichi M., Matuoka K., Takenawa T., Saltiel A. R. Growth factors differentially stimulate the phosphorylation of Shc proteins and their association with Grb2 in PC-12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1143–1148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmichi M., Pang L., Ribon V., Saltiel A. R. Divergence of signaling pathways for insulin in PC-12 pheochromocytoma cells. Endocrinology. 1993 Jul;133(1):46–56. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.1.7686484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada T., Kawano Y., Sakakibara T., Hazeki O., Ui M. Essential role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in insulin-induced glucose transport and antilipolysis in rat adipocytes. Studies with a selective inhibitor wortmannin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3568–3573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotou G., Waterfield M. D. Phosphatidyl-inositol 3-kinase: a key enzyme in diverse signalling processes. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;2(12):358–360. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90042-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Gish G. D. SH2 and SH3 domains: from structure to function. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):359–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccione E., Case R. D., Domchek S. M., Hu P., Chaudhuri M., Backer J. M., Schlessinger J., Shoelson S. E. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase p85 SH2 domain specificity defined by direct phosphopeptide/SH2 domain binding. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 6;32(13):3197–3202. doi: 10.1021/bi00064a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Dodson G. S., Rubin G. M. An SH3-SH2-SH3 protein is required for p21Ras1 activation and binds to sevenless and Sos proteins in vitro. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90169-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Lee C. H., Batzer A., Vicentini L. M., Zhou M., Daly R., Myers M. J., Jr, Backer J. M., Ullrich A., White M. F. The SH2/SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 interacts with tyrosine-phosphorylated IRS1 and Shc: implications for insulin control of ras signalling. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1929–1936. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto S., Lechleider R. J., Shoelson S. E., Neel B. G., Walsh C. T. Expression, purification, and characterization of SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase, SH-PTP2. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22771–22776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. J., Crimmins D. L., Myers M. G., Jr, Miralpeix M., White M. F. Pleiotropic insulin signals are engaged by multisite phosphorylation of IRS-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7418–7428. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. J., Rothenberg P., Kahn C. R., Backer J. M., Araki E., Wilden P. A., Cahill D. A., Goldstein B. J., White M. F. Structure of the insulin receptor substrate IRS-1 defines a unique signal transduction protein. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):73–77. doi: 10.1038/352073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung C. K., Goldfine I. D. Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase is a non-tyrosine phosphorylated member of the insulin receptor signalling complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):1024–1030. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92306-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung C. K., Sánchez-Margalet V., Goldfine I. D. Role of p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase as an adaptor molecule linking the insulin receptor, p62, and GTPase-activating protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 29;269(17):12503–12507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobe K., Matuoka K., Tamemoto H., Ueki K., Kaburagi Y., Asai S., Noguchi T., Matsuda M., Tanaka S., Hattori S. Insulin stimulates association of insulin receptor substrate-1 with the protein abundant Src homology/growth factor receptor-bound protein 2. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11167–11171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Kahn C. R. The insulin signaling system. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Altschuler D., Wood E., Horlick K., Jacobs S., Lapetina E. G. Association of phosphorylated insulin-like growth factor-I receptor with the SH2 domains of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase p85. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11337–11343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu G., Decker S. J., Saltiel A. R. Direct analysis of the binding of Src-homology 2 domains of phospholipase C to the activated epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9559–9563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]