Abstract
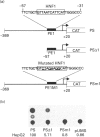
C4b-binding protein (C4BP) is an abundant oligomeric plasma glycoprotein which controls the activation of the complement cascade through the classical pathway. In humans, the majority form of C4BP is composed of seven alpha-chains and one beta-chain, covalently linked by their C-termini. C4BP is mainly expressed in the liver. We have previously cloned and characterized the structure of the genes encoding the alpha and beta chains, C4BPA and C4BPB, respectively. Here we addressed the characterization of the mechanisms controlling the hepatic restricted expression of the C4BPA gene. We found that the C4BPA promoter is contained within the first 369 bp upstream of the transcription start site. The activity of this promoter is restricted to hepatic cells in transfection experiments. The hepatic transcription factor HNF1 interacts with a region of this promoter at -38 bp. This region is absolutely required for the activity of this promoter, suggesting that HNF1 is essential for the hepatic activity of the C4BPA promoter. We speculate that this extreme requirement of HNF1 for the activity of the human C4BPA promoter is related to the fact that this promoter lacks a TATA box.
Full text
PDF

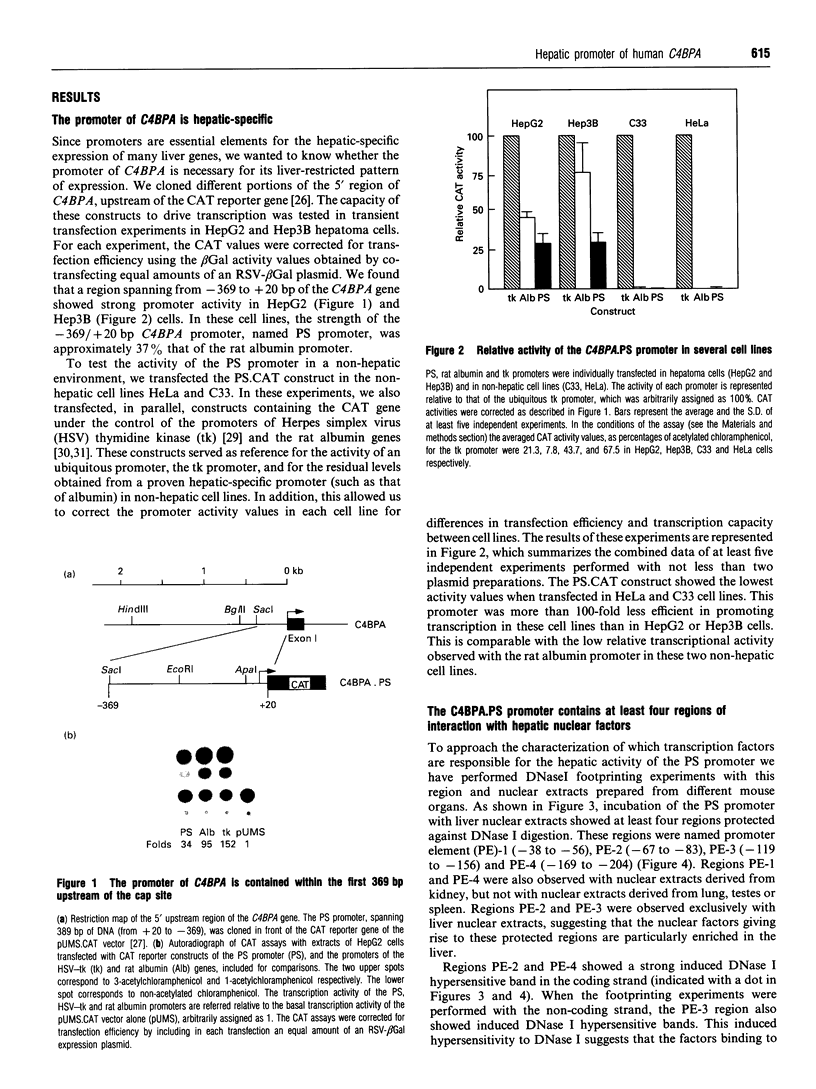


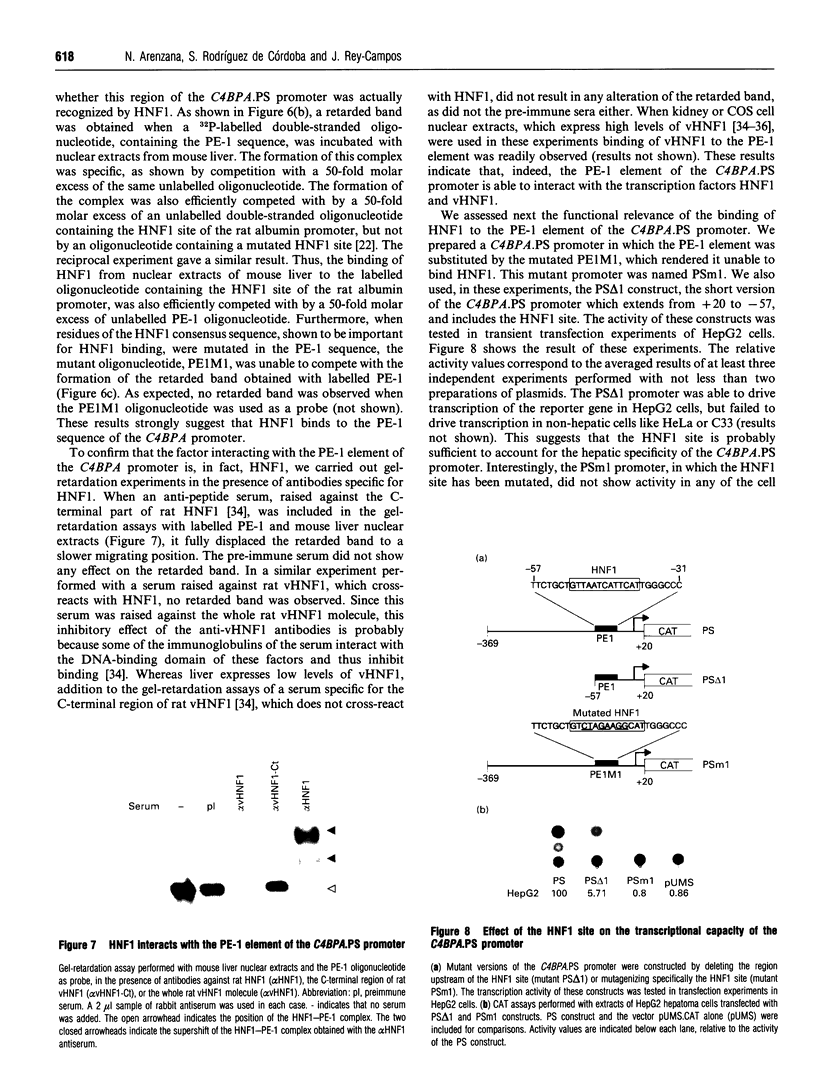



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach I., Galcheva-Gargova Z., Mattei M. G., Simon-Chazottes D., Guénet J. L., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. Cloning of human hepatic nuclear factor 1 (HNF1) and chromosomal localization of its gene in man and mouse. Genomics. 1990 Sep;8(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90238-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartkowski S., Zapp D., Weber H., Eberle G., Zoidl C., Senkel S., Klein-Hitpass L., Ryffel G. U. Developmental regulation and tissue distribution of the liver transcription factor LFB1 (HNF1) in Xenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):421–431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumhueter S., Mendel D. B., Conley P. B., Kuo C. J., Turk C., Graves M. K., Edwards C. A., Courtois G., Crabtree G. R. HNF-1 shares three sequence motifs with the POU domain proteins and is identical to LF-B1 and APF. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):372–379. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bora N. S., Lublin D. M., Kumar B. V., Hockett R. D., Holers V. M., Atkinson J. P. Structural gene for human membrane cofactor protein (MCP) of complement maps to within 100 kb of the 3' end of the C3b/C4b receptor gene. J Exp Med. 1989 Feb 1;169(2):597–602. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.2.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Blumenfeld M., Yaniv M. A liver-specific factor essential for albumin transcription differs between differentiated and dedifferentiated rat hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):957–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Raymondjean M., Carranca A. G., Herbomel P., Yaniv M. Factors involved in control of tissue-specific expression of albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouard T., Blumenfeld M., Bach I., Vandekerckhove J., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. A distal dimerization domain is essential for DNA-binding by the atypical HNF1 homeodomain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5853–5863. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung L. P., Bentley D. R., Reid K. B. Molecular cloning and characterization of the cDNA coding for C4b-binding protein, a regulatory protein of the classical pathway of the human complement system. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 15;230(1):133–141. doi: 10.1042/bj2300133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Xanthopoulos K. G., Darnell J. E., Jr A liver-specific DNA-binding protein recognizes multiple nucleotide sites in regulatory regions of transthyretin, alpha 1-antitrypsin, albumin, and simian virus 40 genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3840–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Simone V., Cortese R. Transcriptional regulation of liver-specific gene expression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;3(6):960–965. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90114-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frain M., Swart G., Monaci P., Nicosia A., Stämpfli S., Frank R., Cortese R. The liver-specific transcription factor LF-B1 contains a highly diverged homeobox DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90877-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Gigli I., Nussenzweig V. Human C4-binding protein. II. Role in proteolysis of C4b by C3b-inactivator. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1044–1051. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heard J. M., Herbomel P., Ott M. O., Mottura-Rollier A., Weiss M., Yaniv M. Determinants of rat albumin promoter tissue specificity analyzed by an improved transient expression system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2425–2434. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillarp A., Dahlbäck B. Cloning of cDNA coding for the beta chain of human complement component C4b-binding protein: sequence homology with the alpha chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1183–1187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillarp A., Dahlbäck B. Novel subunit in C4b-binding protein required for protein S binding. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12759–12764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourcade D., Garcia A. D., Post T. W., Taillon-Miller P., Holers V. M., Wagner L. M., Bora N. S., Atkinson J. P. Analysis of the human regulators of complement activation (RCA) gene cluster with yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs). Genomics. 1992 Feb;12(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90376-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourcade D., Miesner D. R., Bee C., Zeldes W., Atkinson J. P. Duplication and divergence of the amino-terminal coding region of the complement receptor 1 (CR1) gene. An example of concerted (horizontal) evolution within a gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):974–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Smith E., Litvin O., Costa R. H., Darnell J. E., Jr HNF-3A, a hepatocyte-enriched transcription factor of novel structure is regulated transcriptionally. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1427–1436. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Tao W. F., Chen W. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 alpha belongs to a gene family in mammals that is homologous to the Drosophila homeotic gene fork head. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):416–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel D. B., Hansen L. P., Graves M. K., Conley P. B., Crabtree G. R. HNF-1 alpha and HNF-1 beta (vHNF-1) share dimerization and homeo domains, but not activation domains, and form heterodimers in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1042–1056. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksicek R., Heber A., Schmid W., Danesch U., Posseckert G., Beato M., Schütz G. Glucocorticoid responsiveness of the transcriptional enhancer of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90745-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffat G. J., Tack B. F. Regulation of C4b-binding protein gene expression by the acute-phase mediators tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, and interleukin-1. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 15;31(49):12376–12384. doi: 10.1021/bi00164a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffat G. J., Vik D. P., Noack D., Tack B. F. Complete structure of the murine C4b-binding protein gene and regulation of its expression by dexamethasone. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20400–20406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardo-Manuel F., Rey-Campos J., Hillarp A., Dahlbäck B., Rodriguez de Cordoba S. Human genes for the alpha and beta chains of complement C4b-binding protein are closely linked in a head-to-tail arrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4529–4532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkert C. A., Ornitz D. M., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. An albumin enhancer located 10 kb upstream functions along with its promoter to direct efficient, liver-specific expression in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):268–276. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pothier F., Ouellet M., Julien J. P., Guérin S. L. An improved CAT assay for promoter analysis in either transgenic mice or tissue culture cells. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Jan-Feb;11(1):83–90. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey-Campos J., Baeza-Sanz D., Rodriguez de Cordoba S. Physical linkage of the human genes coding for complement factor H and coagulation factor XIII B subunit. Genomics. 1990 Aug;7(4):644–646. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90213-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey-Campos J., Rubinstein P., Rodriguez de Cordoba S. A physical map of the human regulator of complement activation gene cluster linking the complement genes CR1, CR2, DAF, and C4BP. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):664–669. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey-Campos J., Rubinstein P., Rodriguez de Cordoba S. A physical map of the human regulator of complement activation gene cluster linking the complement genes CR1, CR2, DAF, and C4BP. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):664–669. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez de Cordoba S., Sanchez-Corral P., Rey-Campos J. Structure of the gene coding for the alpha polypeptide chain of the human complement component C4b-binding protein. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1073–1082. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeki T., Hirose S., Nukatsuka M., Kusunoki Y., Nagasawa S. Evidence that C4b-binding protein is an acute phase protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 15;164(3):1446–1451. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91832-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe R., Dahlbäck B., Hillarp A., Nelsestuen G. Assembly of protein S and C4b-binding protein on membranes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16074–16081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Corral P., Pardo-Manuel de Villena F., Rey-Campos J., Rodríguez de Córdoba S. C4BPAL1, a member of the human regulator of complement activation (RCA) gene cluster that resulted from the duplication of the gene coding for the alpha-chain of C4b-binding protein. Genomics. 1993 Jul;17(1):185–193. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasset D., Tora L., Fromental C., Scheer E., Chambon P. Distinct classes of transcriptional activating domains function by different mechanisms. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1177–1187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90394-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronche F., Rollier A., Bach I., Weiss M. C., Yaniv M. The rat albumin promoter: cooperation with upstream elements is required when binding of APF/HNF1 to the proximal element is partially impaired by mutation or bacterial methylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4759–4766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronche F., Rollier A., Herbomel P., Bach I., Cereghini S., Weiss M., Yaniv M. Anatomy of the rat albumin promoter. Mol Biol Med. 1990 Apr;7(2):173–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Jackson S. P. The TATA-binding protein: a central role in transcription by RNA polymerases I, II and III. Trends Genet. 1992 Aug;8(8):284–288. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90255-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Liu J. K., DiPersio C. M. Site-directed mutagenesis reveals a liver transcription factor essential for the albumin transcriptional enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5469–5473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]