Abstract
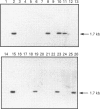
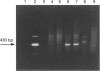
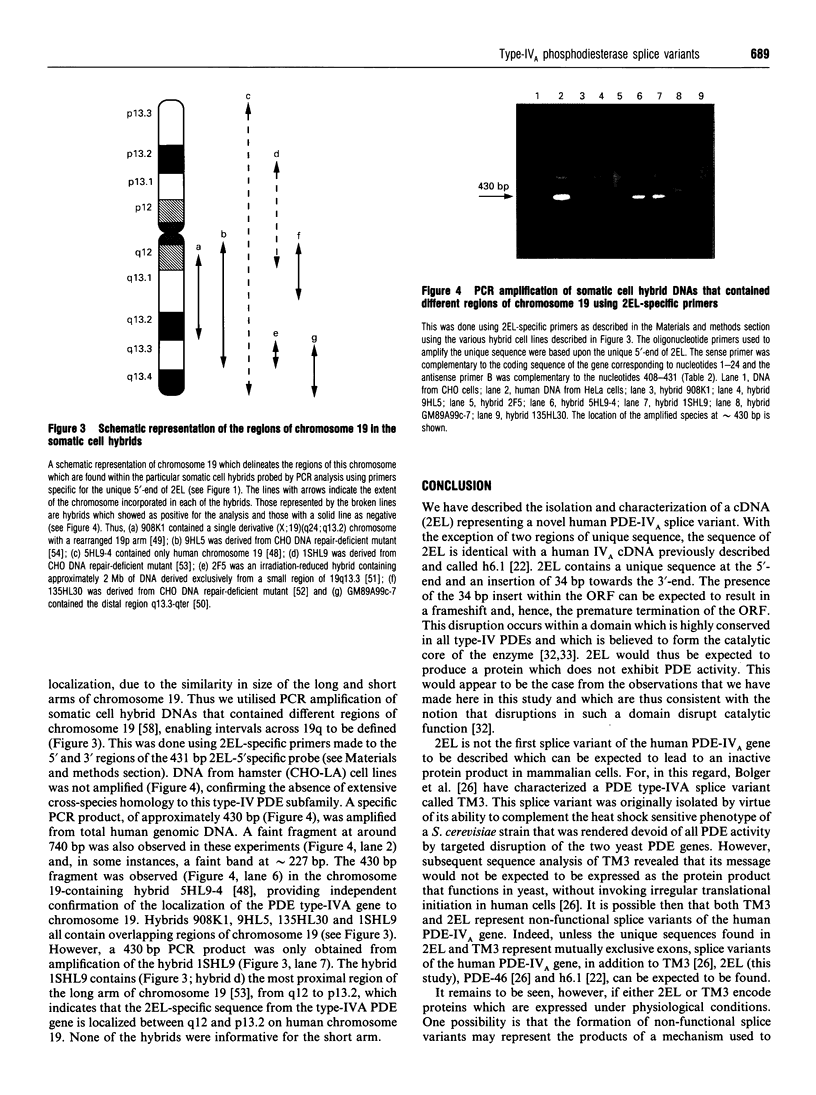
We have isolated from a human T-cell Jurkat cDNA library a novel human cDNA (2EL) that is closely related to the human type-IV PDE splice variant family 'A' (PDE-IVA) cDNA characterized previously by us [Sullivan, Egerton, Shakur, Marquardsen and Houslay (1994) Cell. Signalling 6, 793-812]; (h6.1, PDE-IVA/h6.1; HSPDE4A7). (PDE stands for cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase). The novel cDNA 2EL (PDE-IVA/2EL; HSPDE4A8) contains two regions of unique sequence not found in PDE-IVA/h6.1. These are a distinct 5'-end and a 34 bp insert which occurs within a domain thought to encode the type-IV PDE catalytic site and which can be expected to result in premature truncation of any expressed protein. HSPDE4A8 appeared to be catalytically inactive. Isolation and characterization of a human genomic cosmid clone revealed that 2EL and h6.1 represent alternative splice variants of the human PDE-IVA gene. Using a unique sequence found at the 5'-end of the 2EL cDNA, a probe was generated which was used to screen the DNA of human-hamster hybrids. This located the human gene for PDE-IVA to human chromosome 19. Through both the analysis of genomic DNAs from a human-hamster somatic cell hybrid panel and also using fluorescent in situ hybridization, it was shown that the human PDE-IVA gene is located on human chromosome 19, between p13.2 [corrected] and q12. This region on chromosome 19 has been shown to be related to genetic diseases such as the autosomal dominant cerebrovascular disease CADASIL, susceptibility to late-onset Alzheimer's disease and changes seen in benign pituitary and thyroid adenomas.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehr W., Champagne M. S., Lee A. K., Pittler S. J. Complete cDNA sequences of mouse rod photoreceptor cGMP phosphodiesterase alpha- and beta-subunits, and identification of beta'-, a putative beta-subunit isozyme produced by alternative splicing of the beta-subunit gene. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jan 14;278(1):107–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80095-k. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. S. Sex in flies: the splice of life. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):521–524. doi: 10.1038/340521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Conti M., Heaslip R. J. Multiple cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Sep;46(3):399–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belge G., Thode B., Bullerdiek J., Bartnitzke S. Aberrations of chromosome 19. Do they characterize a subtype of benign thyroid adenomas? Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1992 May;60(1):23–26. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(92)90227-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley J. K., Kadlecek A., Sherbert C. H., Seger D., Sonnenburg W. K., Charbonneau H., Novack J. P., Beavo J. A. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding a "63"-kDa calmodulin-stimulated phosphodiesterase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18676–18682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolger G. B. Molecular biology of the cyclic AMP-specific cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: a diverse family of regulatory enzymes. Cell Signal. 1994 Nov;6(8):851–859. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(94)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolger G., Michaeli T., Martins T., St John T., Steiner B., Rodgers L., Riggs M., Wigler M., Ferguson K. A family of human phosphodiesterases homologous to the dunce learning and memory gene product of Drosophila melanogaster are potential targets for antidepressant drugs. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6558–6571. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook J. D., Zemelman B. V., Hadingham K., Siciliano M. J., Crow S., Harley H. G., Rundle S. A., Buxton J., Johnson K., Almond J. W. Radiation-reduced hybrids for the myotonic dystrophy locus. Genomics. 1992 Jun;13(2):243–250. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90238-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter N. P., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Perryman M. T., Telenius H., Pelmear A. H., Leversha M. A., Glancy M. T., Wood S. L., Cook K., Dyson H. M. Reverse chromosome painting: a method for the rapid analysis of aberrant chromosomes in clinical cytogenetics. J Med Genet. 1992 May;29(5):299–307. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.5.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Kumar S., Novack J. P., Blumenthal D. K., Griffin P. R., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Beavo J. A., Walsh K. A. Evidence for domain organization within the 61-kDa calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase from bovine brain. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 13;30(32):7931–7940. doi: 10.1021/bi00246a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colicelli J., Birchmeier C., Michaeli T., O'Neill K., Riggs M., Wigler M. Isolation and characterization of a mammalian gene encoding a high-affinity cAMP phosphodiesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3599–3603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. J., McCormick F. Inhibition by cAMP of Ras-dependent activation of Raf. Science. 1993 Nov 12;262(5136):1069–1072. doi: 10.1126/science.7694367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Takayasu H., Eberwine M., Myres J. Cloning and characterization of mammalian homologs of the Drosophila dunce+ gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3604–3608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. E., Jauniaux J. C., Roger P. P. The cyclic AMP-mediated stimulation of cell proliferation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):67–71. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer L. A., Stice L. Susceptibility genes for familial Alzheimer's disease on chromosomes 19 and 21: a reality check. Genet Epidemiol. 1993;10(6):425–430. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370100616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller L. F., Painter R. B. A Chinese hamster ovary cell line hypersensitive to ionizing radiation and deficient in repair replication. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar;193(2):109–121. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(88)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garson J. A., van den Berghe J. A., Kemshead J. T. Novel non-isotopic in situ hybridization technique detects small (1 Kb) unique sequences in routinely G-banded human chromosomes: fine mapping of N-myc and beta-NGF genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4761–4770. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebenstreit G. F., Fellerer K., Fichte K., Fischer G., Geyer N., Meya U., Sastre-y-Hernández M., Schöny W., Schratzer M., Soukop W. Rolipram in major depressive disorder: results of a double-blind comparative study with imipramine. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1989 Jul;22(4):156–160. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1014599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms C., Graham M. Y., Dutchik J. E., Olson M. V. A new method for purifying lambda DNA from phage lysates. DNA. 1985 Feb;4(1):39–49. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulsebos T., Wieringa B., Hochstenbach R., Smeets D., Schepens J., Oerlemans F., Zimmer J., Ropers H. H. Toward early diagnosis of myotonic dystrophy: construction and characterization of a somatic cell hybrid with a single human der(19) chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;43(1-2):47–56. doi: 10.1159/000132297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S. L., Swinnen J. V., Conti M. Characterization of the structure of a low Km, rolipram-sensitive cAMP phosphodiesterase. Mapping of the catalytic domain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18929–18939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joutel A., Bousser M. G., Biousse V., Labauge P., Chabriat H., Nibbio A., Maciazek J., Meyer B., Bach M. A., Weissenbach J. Migraine hémiplégique familiale. Localisation d'un gène responsable sur le chromosome 19. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1994;150(5):340–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley D. M. Encyclopedia of the mouse genome III. October 1993. Mouse chromosome 9. Mamm Genome. 1993;4(Spec No):S136–S153. doi: 10.1007/BF00360835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landis C. A., Masters S. B., Spada A., Pace A. M., Bourne H. R., Vallar L. GTPase inhibiting mutations activate the alpha chain of Gs and stimulate adenylyl cyclase in human pituitary tumours. Nature. 1989 Aug 31;340(6236):692–696. doi: 10.1038/340692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavan B. E., Lakey T., Houslay M. D. Resolution of soluble cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isoenzymes, from liver and hepatocytes, identifies a novel IBMX-insensitive form. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Nov 15;38(22):4123–4136. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90694-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li T. S., Volpp K., Applebury M. L. Bovine cone photoreceptor cGMP phosphodiesterase structure deduced from a cDNA clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):293–297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livi G. P., Kmetz P., McHale M. M., Cieslinski L. B., Sathe G. M., Taylor D. P., Davis R. L., Torphy T. J., Balcarek J. M. Cloning and expression of cDNA for a human low-Km, rolipram-sensitive cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2678–2686. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobban M., Shakur Y., Beattie J., Houslay M. D. Identification of two splice variant forms of type-IVB cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase, DPD (rPDE-IVB1) and PDE-4 (rPDE-IVB2) in brain: selective localization in membrane and cytosolic compartments and differential expression in various brain regions. Biochem J. 1994 Dec 1;304(Pt 2):399–406. doi: 10.1042/bj3040399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin M. M., Cieslinski L. B., Burman M., Torphy T. J., Livi G. P. A low-Km, rolipram-sensitive, cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase from human brain. Cloning and expression of cDNA, biochemical characterization of recombinant protein, and tissue distribution of mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6470–6476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meacci E., Taira M., Moos M., Jr, Smith C. J., Movsesian M. A., Degerman E., Belfrage P., Manganiello V. Molecular cloning and expression of human myocardial cGMP-inhibited cAMP phosphodiesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3721–3725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaeli T., Bloom T. J., Martins T., Loughney K., Ferguson K., Riggs M., Rodgers L., Beavo J. A., Wigler M. Isolation and characterization of a previously undetected human cAMP phosphodiesterase by complementation of cAMP phosphodiesterase-deficient Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12925–12932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milatovich A., Bolger G., Michaeli T., Francke U. Chromosome localizations of genes for five cAMP-specific phosphodiesterases in man and mouse. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1994 Mar;20(2):75–86. doi: 10.1007/BF02290677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Sparkes R. S., Hellkuhl B., Grzeschik K. H., Shapiro L. J. Expression of an X-linked gene from an inactive human X chromosome in mouse-human hybrid cells: further evidence for the noninactivation of the steroid sulfatase locus in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6759–6763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco L., Vicini E., Conti M. Structure of two rat genes coding for closely related rolipram-sensitive cAMP phosphodiesterases. Multiple mRNA variants originate from alternative splicing and multiple start sites. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):347–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura A., Morita M., Nishimura Y., Sugino Y. A rapid and highly efficient method for preparation of competent Escherichia coli cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6169–6169. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novack J. P., Charbonneau H., Bentley J. K., Walsh K. A., Beavo J. A. Sequence comparison of the 63-, 61-, and 59-kDa calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 13;30(32):7940–7947. doi: 10.1021/bi00246a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obernolte R., Bhakta S., Alvarez R., Bach C., Zuppan P., Mulkins M., Jarnagin K., Shelton E. R. The cDNA of a human lymphocyte cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase (PDE IV) reveals a multigene family. Gene. 1993 Jul 30;129(2):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ophoff R. A., van Eijk R., Sandkuijl L. A., Terwindt G. M., Grubben C. P., Haan J., Lindhout D., Ferrari M. D., Frants R. R. Genetic heterogeneity of familial hemiplegic migraine. Genomics. 1994 Jul 1;22(1):21–26. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittler S. J., Baehr W., Wasmuth J. J., McConnell D. G., Champagne M. S., vanTuinen P., Ledbetter D., Davis R. L. Molecular characterization of human and bovine rod photoreceptor cGMP phosphodiesterase alpha-subunit and chromosomal localization of the human gene. Genomics. 1990 Feb;6(2):272–283. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90567-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polli J. W., Kincaid R. L. Molecular cloning of DNA encoding a calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase enriched in striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):11079–11083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.11079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyne N. J., Cooper M. E., Houslay M. D. Identification and characterization of both the cytosolic and particulate forms of cyclic GMP-stimulated cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase from rat liver. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 1;234(2):325–334. doi: 10.1042/bj2340325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock J. P., Babu V. R., Drumheller T., Chason J. Cytogenetic findings in pituitary adenoma: results of a pilot study. Surg Neurol. 1993 Sep;40(3):224–229. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(93)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonk D., Coerwinkel-Driessen M., van Dalen I., Oerlemans F., Smeets B., Schepens J., Hulsebos T., Cockburn D., Boyd Y., Davis M. Definition of subchromosomal intervals around the myotonic dystrophy gene region at 19q. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):384–396. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90346-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwengel D. A., Nouri N., Meyers D. A., Levitt R. C. Linkage mapping of the human thromboxane A2 receptor (TBXA2R) to chromosome 19p13.3 using transcribed 3' untranslated DNA sequence polymorphisms. Genomics. 1993 Nov;18(2):212–215. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakur Y., Pryde J. G., Houslay M. D. Engineered deletion of the unique N-terminal domain of the cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase RD1 prevents plasma membrane association and the attainment of enhanced thermostability without altering its sensitivity to inhibition by rolipram. Biochem J. 1993 Jun 15;292(Pt 3):677–686. doi: 10.1042/bj2920677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakur Y., Wilson M., Pooley L., Lobban M., Griffiths S. L., Campbell A. M., Beattie J., Daly C., Houslay M. D. Identification and characterization of the type-IVA cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase RD1 as a membrane-bound protein expressed in cerebellum. Biochem J. 1995 Mar 15;306(Pt 3):801–809. doi: 10.1042/bj3060801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siciliano M. J., Carrano A. V., Thompson L. H. Assignment of a human DNA-repair gene associated with sister-chromatid exchange to chromosome 19. Mutat Res. 1986 Aug;174(4):303–308. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(86)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenburg W. K., Seger D., Beavo J. A. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding the "61-kDa" calmodulin-stimulated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Tissue-specific expression of structurally related isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):645–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan M., Egerton M., Shakur Y., Marquardsen A., Houslay M. D. Molecular cloning and expression, in both COS-1 cells and S. cerevisiae, of a human cytosolic type-IVA, cyclic AMP specific phosphodiesterase (hPDE-IVA-h6.1). Cell Signal. 1994 Sep;6(7):793–812. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(94)00039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinnen J. V., Joseph D. R., Conti M. Molecular cloning of rat homologues of the Drosophila melanogaster dunce cAMP phosphodiesterase: evidence for a family of genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5325–5329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira M., Hockman S. C., Calvo J. C., Taira M., Belfrage P., Manganiello V. C. Molecular cloning of the rat adipocyte hormone-sensitive cyclic GMP-inhibited cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18573–18579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Bachinski L. L., Stallings R. L., Dolf G., Weber C. A., Westerveld A., Siciliano M. J. Complementation of repair gene mutations on the hemizygous chromosome 9 in CHO: a third repair gene on human chromosome 19. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):670–679. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Carrano A. V., Sato K., Salazar E. P., White B. F., Stewart S. A., Minkler J. L., Siciliano M. J. Identification of nucleotide-excision-repair genes on human chromosomes 2 and 13 by functional complementation in hamster-human hybrids. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 Sep;13(5):539–551. doi: 10.1007/BF01534495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerveld A., Naylor S. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of Chromosomes 18, 19, 20, 21, and 22. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;37(1-4):155–175. doi: 10.1159/000132008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander L. A simple method to recover intact high molecular weight RNA and DNA after electrophoretic separation in low gelling temperature agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M., Sullivan M., Brown N., Houslay M. D. Purification, characterization and analysis of rolipram inhibition of a human type-IVA cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase expressed in yeast. Biochem J. 1994 Dec 1;304(Pt 2):407–415. doi: 10.1042/bj3040407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]