Abstract
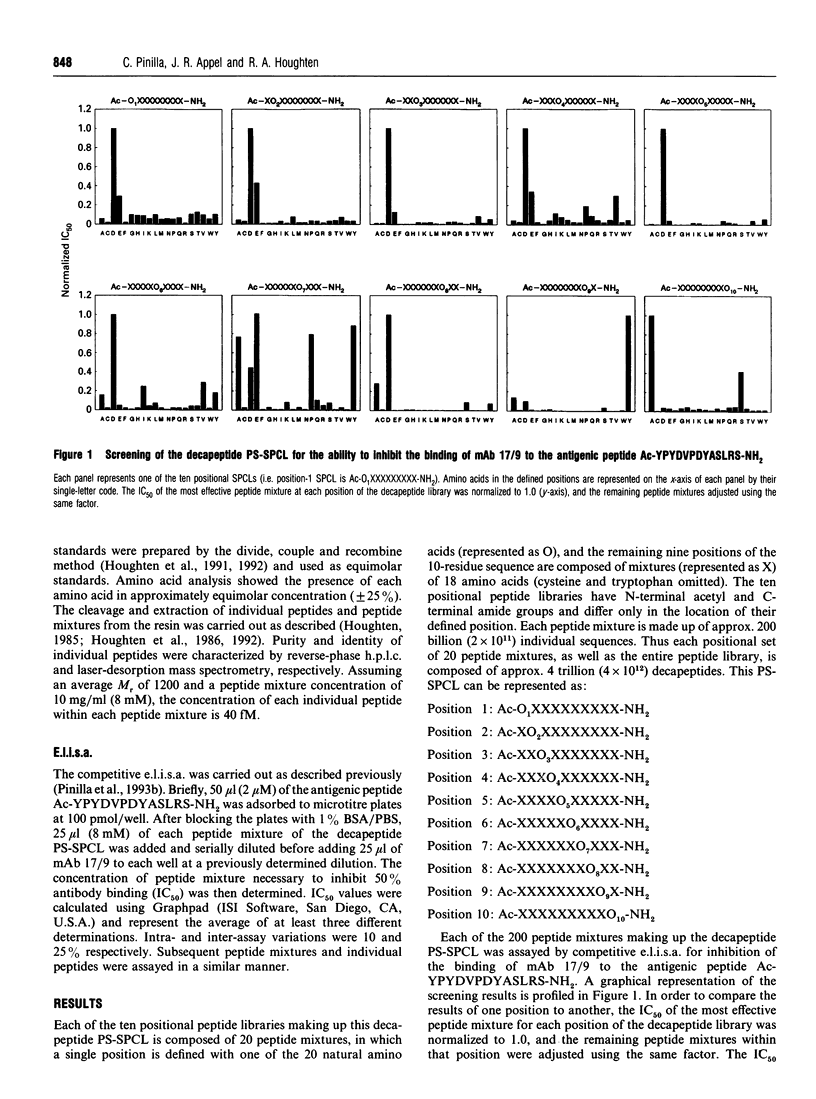
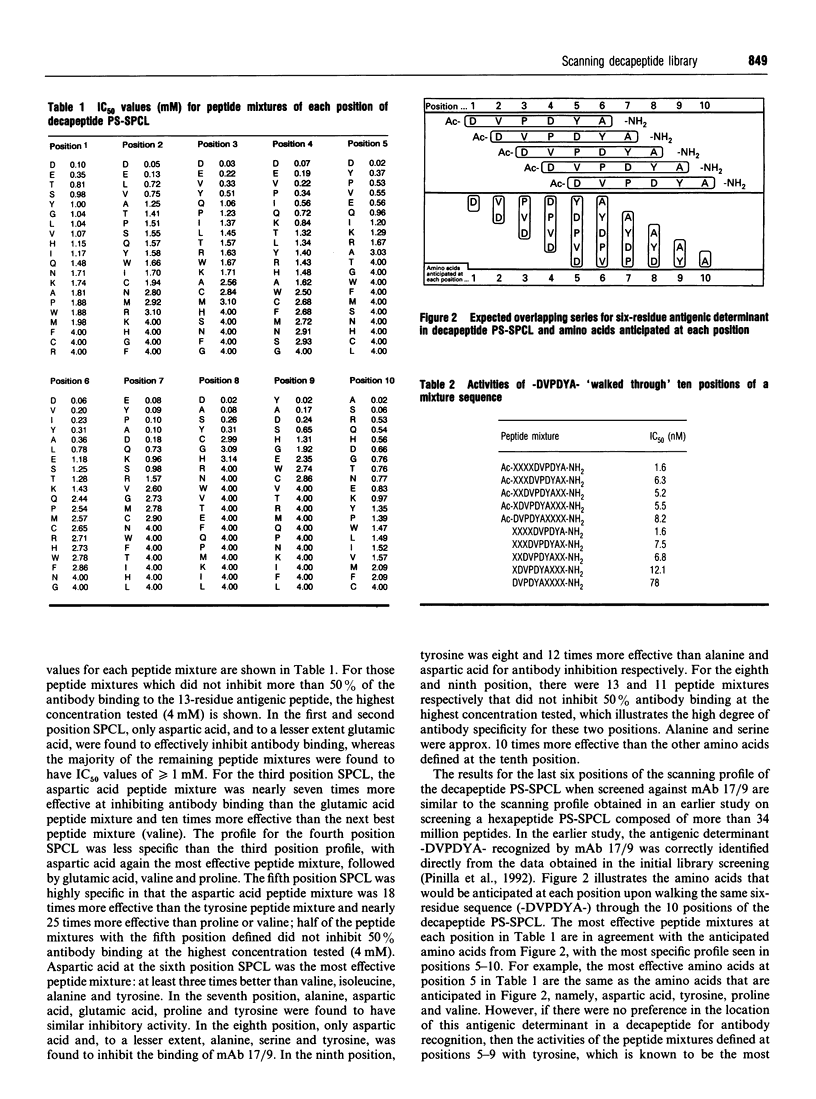
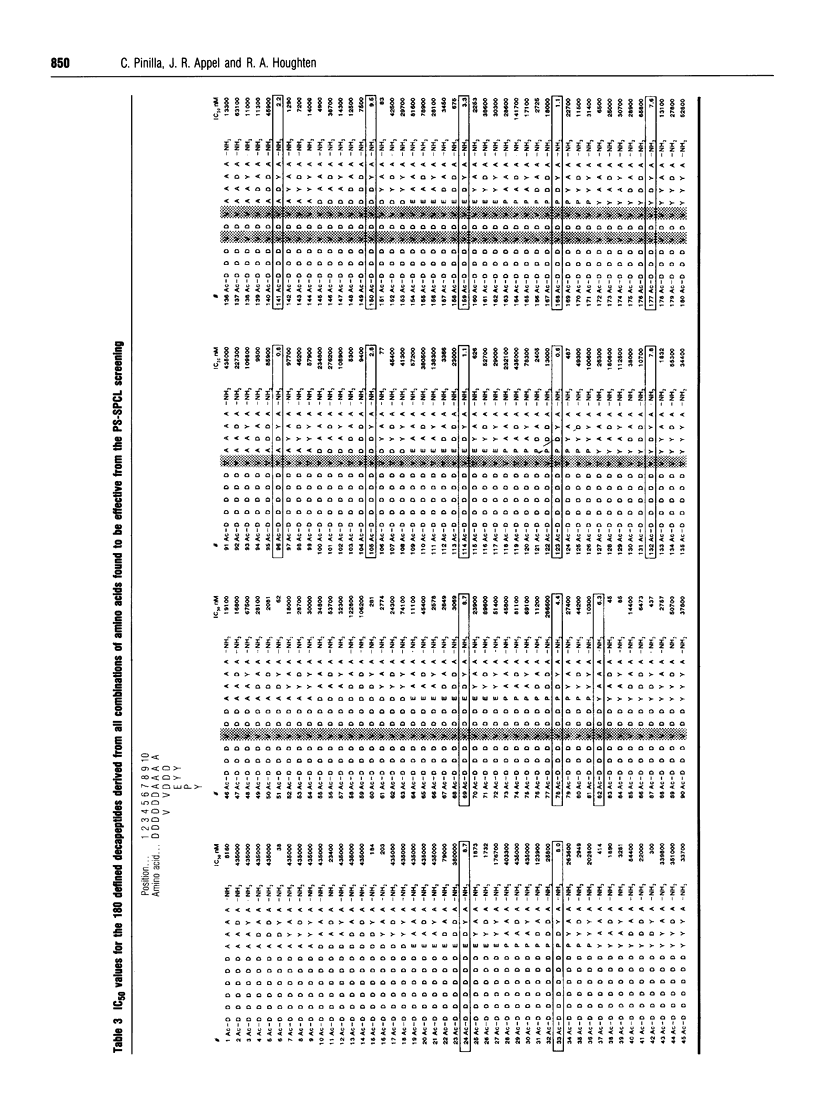
A decapeptide positional-scanning synthetic-peptide combinatorial library (PS-SPCL) made up of four trillion (4 x 10(12) decapeptides was synthesized; its use is illustrated here for the study of a peptide-antibody interaction. This library was prepared by a chemical-mixture approach using a specific ratio of amino acids empirically determined to give approximately equimolar incorporation of each amino acid during each coupling step. Despite the immense number of decapeptides making up each peptide mixture [approx. 200 billion (2 x 10(11)], specific sequences having nanomolar affinities for a peptide-antibody interaction could be readily identified. Upon screening this decapeptide PS-SPCL in this well characterized system, the known six-residue antigenic-determinant sequence was found, with the most specific residues appearing to 'walk through' the ten positions of the peptide library. More importantly, it appears that antibody recognition in this system is stronger when the antigenic determinant is located at the C-terminus of the decapeptide library. Individual decapeptides corresponding to sequences derived from the most active peptide mixtures at each position were synthesized to confirm the results of the screening; 15 peptides were found to have IC50 values between 0.6 and 9.5 nM, four of which were found to be 5-10 times more active than the known six- and 13-residue control peptides. These results further illustrate the power of the positional-scanning peptide library concept, and extend its practical range to a decamer library composed of four trillion (4 x 10(12) decapeptides.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cull M. G., Miller J. F., Schatz P. J. Screening for receptor ligands using large libraries of peptides linked to the C terminus of the lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1865–1869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cwirla S. E., Peters E. A., Barrett R. W., Dower W. J. Peptides on phage: a vast library of peptides for identifying ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6378–6382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin J. J., Panganiban L. C., Devlin P. E. Random peptide libraries: a source of specific protein binding molecules. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):404–406. doi: 10.1126/science.2143033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley C. T., Chung N. N., Schiller P. W., Houghten R. A. Acetalins: opioid receptor antagonists determined through the use of synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10811–10815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley C. T., Houghten R. A. The use of positional scanning synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries for the rapid determination of opioid receptor ligands. Life Sci. 1993;52(18):1509–1517. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90113-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichler J., Houghten R. A. Identification of substrate-analog trypsin inhibitors through the screening of synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 19;32(41):11035–11041. doi: 10.1021/bi00092a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J. A priori delineation of a peptide which mimics a discontinuous antigenic determinant. Mol Immunol. 1986 Jul;23(7):709–715. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Appel J. R., Blondelle S. E., Cuervo J. H., Dooley C. T., Pinilla C. The use of synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries for the identification of bioactive peptides. Biotechniques. 1992 Sep;13(3):412–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Bray M. K., Degraw S. T., Kirby C. J. Simplified procedure for carrying out simultaneous multiple hydrogen fluoride cleavages of protected peptide resins. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1986 Jun;27(6):673–678. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1986.tb01064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A. General method for the rapid solid-phase synthesis of large numbers of peptides: specificity of antigen-antibody interaction at the level of individual amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5131–5135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Pinilla C., Blondelle S. E., Appel J. R., Dooley C. T., Cuervo J. H. Generation and use of synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries for basic research and drug discovery. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):84–86. doi: 10.1038/354084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K. S., Salmon S. E., Hersh E. M., Hruby V. J., Kazmierski W. M., Knapp R. J. A new type of synthetic peptide library for identifying ligand-binding activity. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):82–84. doi: 10.1038/354082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowman H. B., Bass S. H., Simpson N., Wells J. A. Selecting high-affinity binding proteins by monovalent phage display. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 12;30(45):10832–10838. doi: 10.1021/bi00109a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinilla C., Appel J. R., Blanc P., Houghten R. A. Rapid identification of high affinity peptide ligands using positional scanning synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries. Biotechniques. 1992 Dec;13(6):901–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinilla C., Appel J. R., Houghten R. A. Functional importance of amino acid residues making up peptide antigenic determinants. Mol Immunol. 1993 Apr;30(6):577–585. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(93)90032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinilla C., Appel J. R., Houghten R. A. Synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries (SPCLs): identification of the antigenic determinant of beta-endorphin recognized by monoclonal antibody 3E7. Gene. 1993 Jun 15;128(1):71–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90155-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rini J. M., Schulze-Gahmen U., Wilson I. A. Structural evidence for induced fit as a mechanism for antibody-antigen recognition. Science. 1992 Feb 21;255(5047):959–965. doi: 10.1126/science.1546293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Niman H. L., Houghten R. A., Cherenson A. R., Connolly M. L., Lerner R. A. The structure of an antigenic determinant in a protein. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


