Abstract
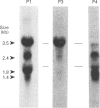
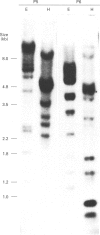
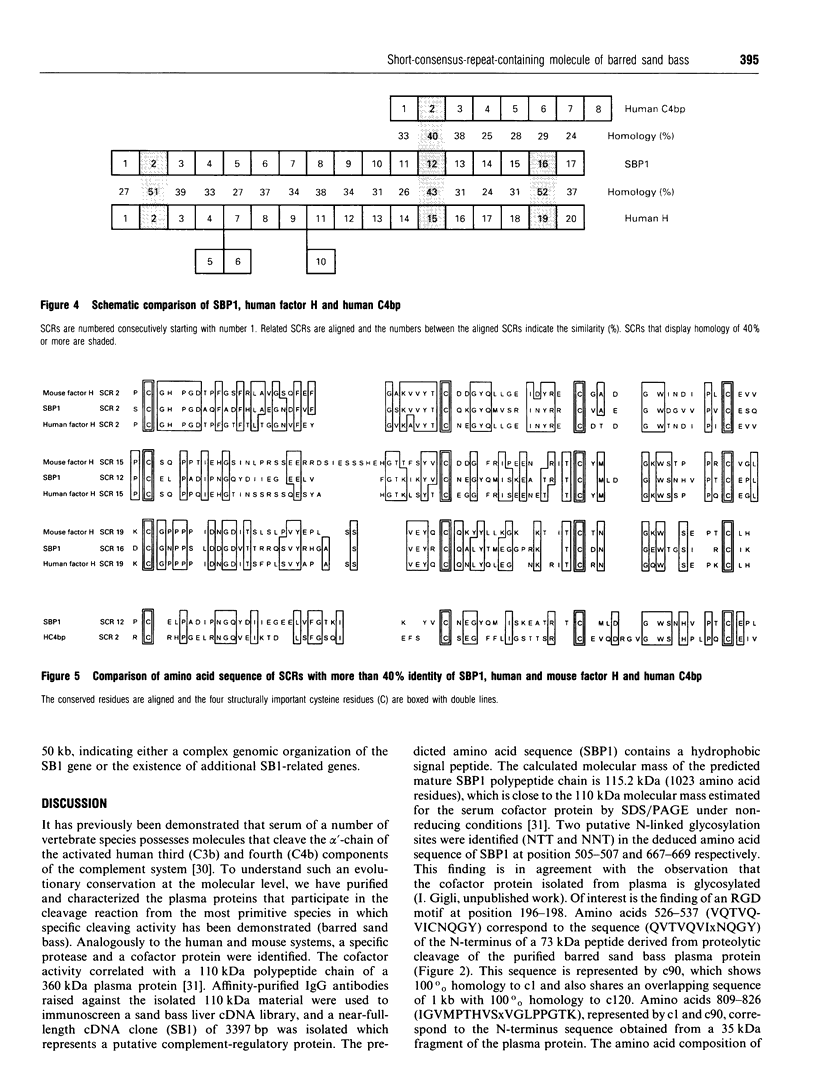
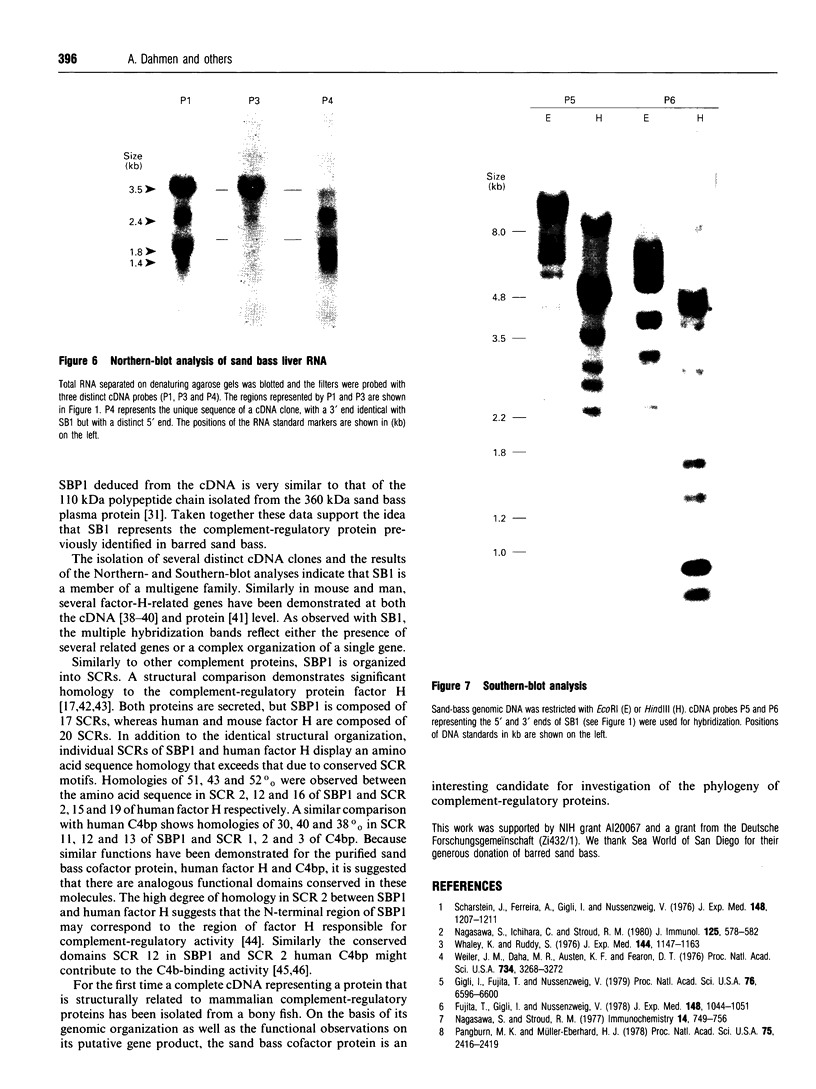
It has been demonstrated previously that plasma from a number of vertebrate species including the phylogenetically old barred sand bass possesses molecules that cleave the alpha'-chain of the activated third (C3b) and fourth (C4b) components of the human complement system. A specific protease and a cofactor protein were identified to be responsible for this cleavage. The cofactor activity in sand bass correlated with a 110 kDa polypeptide chain of a 360 kDa plasma protein. The evolutionary conservation was probed at the cDNA level and subsequently a cDNA clone of barred sand bass was isolated that represents a protein with structural similarity to mammalian complement-regulatory proteins. The cDNA (SB1) was identified by immunoscreening of a sand bass liver expression library using affinity-purified IgG antibodies raised against the isolated 110 kDa material. The cDNA is 3397 bp in size and the open reading frame represents a protein of 1053 amino acid residues with a hydrophobic signal peptide indicative of a secreted protein. The calculated mass of the mature protein (SBP1) is 115.2 kDa which is in good agreement with the molecular mass of 110 kDa determined for the sand bass serum protein. Similarly to mammalian complement-regulatory proteins, the protein deduced from the sand bass cDNA is organized into short consensus repeats (SCR). It consists of 17 SCRs, of which SCRs 2, 12 and 16 exhibit significant homology to SCRs 2, 15 and 19 of human factor H, and SCRs 11, 12 and 13 have homology to SCRs 1, 2 and 3 of human C4b-binding protein. For the first time a complete cDNA representing a putative complement-regulatory protein which is structurally related to mammalian complement proteins has been isolated from a bony fish.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alsenz J., Avila D., Huemer H. P., Esparza I., Becherer J. D., Kinoshita T., Wang Y., Oppermann S., Lambris J. D. Phylogeny of the third component of complement, C3: analysis of the conservation of human CR1, CR2, H, and B binding sites, concanavalin A binding sites, and thiolester bond in the C3 from different species. Dev Comp Immunol. 1992 Jan-Feb;16(1):63–76. doi: 10.1016/0145-305x(92)90052-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alsenz J., Lambris J. D., Schulz T. F., Dierich M. P. Localization of the complement-component-C3b-binding site and the cofactor activity for factor I in the 38kDa tryptic fragment of factor H. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):389–398. doi: 10.1042/bj2240389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burge J., Nicholson-Weller A., Austen K. F. Isolation of C4-binding protein from guinea pig plasma and demonstration of its function as a control protein of the classical complement pathway C3 convertase. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung L. P., Bentley D. R., Reid K. B. Molecular cloning and characterization of the cDNA coding for C4b-binding protein, a regulatory protein of the classical pathway of the human complement system. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 15;230(1):133–141. doi: 10.1042/bj2300133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B. Purification of human C4b-binding protein and formation of its complex with vitamin K-dependent protein S. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):847–856. doi: 10.1042/bj2090847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Smith C. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Visualization of human C4b-binding protein and its complexes with vitamin K-dependent protein S and complement protein C4b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3461–3465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day N. K., Gewurz H., Johannsen R., Finstad J., Good R. A. Complement and complement-like activity in lower vertebrates and invertebrates. J Exp Med. 1970 Nov;132(5):941–950. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.5.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farries T. C., Atkinson J. P. Evolution of the complement system. Immunol Today. 1991 Sep;12(9):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90002-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii T., Nakamura T., Sekizawa A., Tomonaga S. Isolation and characterization of a protein from hagfish serum that is homologous to the third component of the mammalian complement system. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):117–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Gigli I., Nussenzweig V. Human C4-binding protein. II. Role in proteolysis of C4b by C3b-inactivator. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1044–1051. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Fujita T., Nussenzweig V. Modulation of the classical pathway C3 convertase by plasma proteins C4 binding protein and C3b inactivator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6596–6600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossberger D., Marcuz A., Du Pasquier L., Lambris J. D. Conservation of structural and functional domains in complement component C3 of Xenopus and mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1323–1327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillarp A., Dahlbäck B. Cloning of cDNA coding for the beta chain of human complement component C4b-binding protein: sequence homology with the alpha chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1183–1187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro H., Kobayashi K., Suzuki M., Titani K., Tomonaga S., Kurosawa Y. Isolation of a hagfish gene that encodes a complement component. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):829–837. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05120.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai S., Fujita T., Gigli I., Nussenzweig V. Mouse C3b/C4b inactivator: purification and properties. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2409–2415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaidoh T., Fujita T., Takata Y., Natsuume-Sakai S., Takahashi M. Simplified method for purification of mouse beta 1H. Complement. 1984;1(1):44–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaidoh T., Gigli I. Phylogeny of C4b-C3b cleaving activity: similar fragmentation patterns of human C4b and C3b produced by lower animals. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):194–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaidoh T., Gigli I. Phylogeny of regulatory proteins of the complement system. Isolation and characterization of a C4b/C3b inhibitor and a cofactor from sand bass plasma. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1605–1613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen T., D'Eustachio P., Ogata R. T., Chung L. P., Reid K. B., Tack B. F. The superfamily of C3b/C4b-binding proteins. Fed Proc. 1987 May 15;46(7):2463–2469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen T., Tack B. F. Murine protein H is comprised of 20 repeating units, 61 amino acids in length. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3963–3967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen T., Wetsel R. A., Tack B. F. Structural analysis of human complement protein H: homology with C4b binding protein, beta 2-glycoprotein I, and the Ba fragment of B2. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3407–3411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lintin S. J., Lewin A. R., Reid K. B. Derivation of the sequence of the signal peptide in human C4b-binding protein and interspecies cross-hybridisation of the C4bp cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 23;232(2):328–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80763-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa S., Ichihara C., Stroud R. M. Cleavage of C4b by C3b inactivator: production of a nicked form of C4b, C4b', as an intermediate cleavage product of C4b by C3b inactivator. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):578–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa S., Mizuguchi K., Ichihara C., Koyama J. Limited chymotryptic cleavage of human C4-binding protein: isolation of a carbohydrate-containing core domain and an active fragment. J Biochem. 1982 Oct;92(4):1329–1332. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa S., Stroud R. M. Mechanism of action of the C3b inactivator: requirement for a high molecular weight cofactor (C3b-C4bINA cofactor) and production of a new C3b derivative (C3b'). Immunochemistry. 1977 Nov-Dec;14(11-12):749–756. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(77)90345-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Fujii T., Kaidoh T., Natsuume-Sakai S., Nonaka M., Yamaguchi N., Takahashi M. Purification of a lamprey complement protein homologous to the third component of the mammalian complement system. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3242–3249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Iwaki M., Nakai C., Nozaki M., Kaidoh T., Nonaka M., Natsuume-Sakai S., Takahashi M. Purification of a major serum protein of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) homologous to the third component of mammalian complement. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6327–6333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata R. T., Mathias P., Bradt B. M., Cooper N. R. Murine C4b-binding protein. Mapping of the ligand binding site and the N-terminus of the pre-protein. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2273–2280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement C3 convertase: cell surface restriction of beta1H control and generation of restriction on neuraminidase-treated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2416–2420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Day A. J. Structure-function relationships of the complement components. Immunol Today. 1989 Jun;10(6):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90317-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripoche J., Day A. J., Harris T. J., Sim R. B. The complete amino acid sequence of human complement factor H. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 15;249(2):593–602. doi: 10.1042/bj2490593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez de Cordoba S., Lublin D. M., Rubinstein P., Atkinson J. P. Human genes for three complement components that regulate the activation of C3 are tightly linked. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):1189–1195. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. Arg-Gly-Asp: a versatile cell recognition signal. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):517–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., DiScipio R. G. Purification and structural studies on the complement-system control protein beta 1H (Factor H). Biochem J. 1982 Aug 1;205(2):285–293. doi: 10.1042/bj2050285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerka C., Horstmann R. D., Zipfel P. F. Molecular cloning of a human serum protein structurally related to complement factor H. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):12015–12020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerka C., Kühn S., Günther K., Lingelbach K., Zipfel P. F. A novel short consensus repeat-containing molecule is related to human complement factor H. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2904–2908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vik D. P., Muñoz-Cánoves P., Kozono H., Martin L. G., Tack B. F., Chaplin D. D. Identification and sequence analysis of four complement factor H-related transcripts in mouse liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3193–3201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler J. M., Daha M. R., Austen K. F., Fearon D. T. Control of the amplification convertase of complement by the plasma protein beta1H. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3268–3272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whaley K., Ruddy S. Modulation of the alternative complement pathways by beta 1 H globulin. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1147–1163. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]