Abstract
Okadaic acid (OA) is a protein phosphatase inhibitor which has, among other properties, previously been shown to induce a fragmentation of the cisternae of the Golgi stack [for review, see Lucocq (1992) J. Cell Sci. 103, 875-880]. The effects of OA an reversible and mimic intracellular events which occur during mitosis. To date, due to a lack of endogenous marker proteins, the effects of OA on the trans-Golgi network (TGN) has not been studied. Certain drugs, e.g. Brefeldin A (BFA), have different effects on the morphology of the Golgi stack and the TGN; it is therefore relevant to ask what effect(s) OA has on the TGN. We now present data from a study in which we have used antibodies to TGN38, an integral membrane protein predominantly localized to the TGN of rat NRK cells [Luzio, Brake, Banting, Howell, Braghetta and Stanley (1990) Biochem. J. 270, 97-102], to investigate the effects of OA on this organelle. OA induces a reversible fragmentation of the TGN. This fragmentation occurs with similar kinetics to that observed within the Golgi stack, and is independent of protein synthesis. The sensitivity of the TGN to OA is similar to that of the Golgi stack. The fragmentation of the TGN induced by OA also leads to a 10-fold increase in the level of TGN38 expressed at the plasma membrane.
Full text
PDF


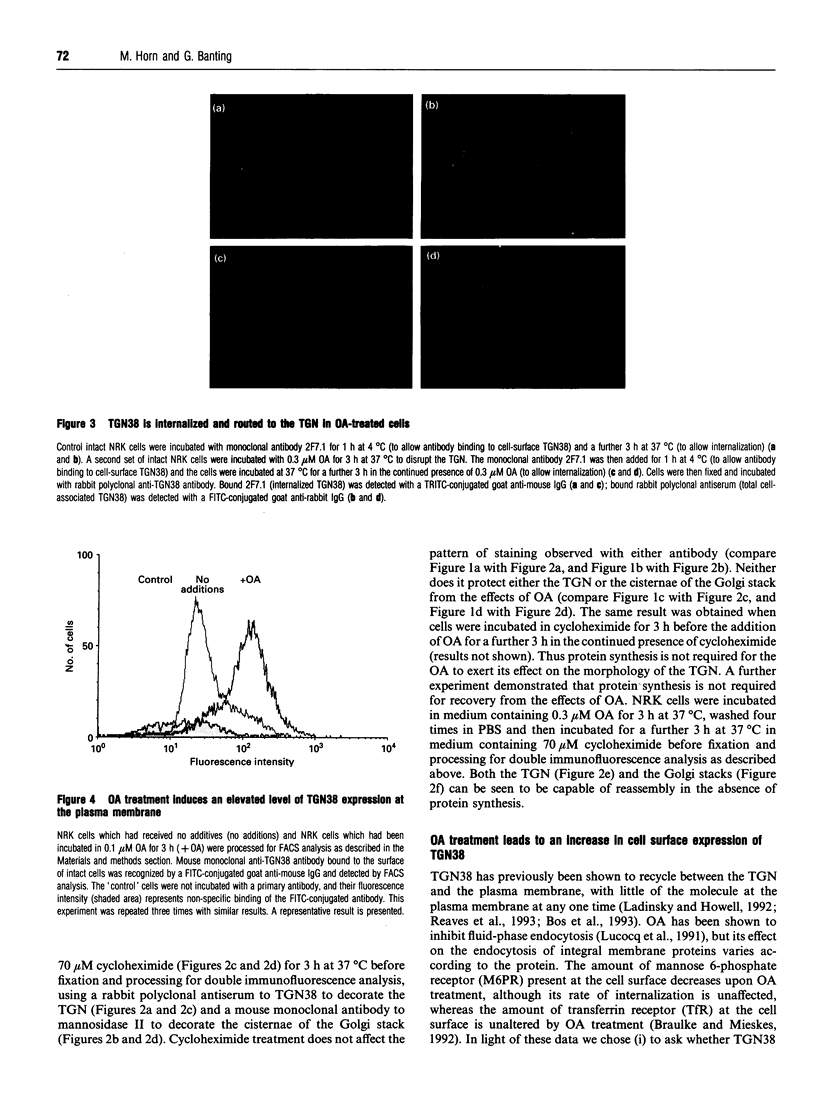

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berlin R. D., Oliver J. M. Surface functions during mitosis. II. Quantitation of pinocytosis and kinetic characterization of the mitotic cycle with a new fluorescence technique. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):660–671. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialojan C., Takai A. Inhibitory effect of a marine-sponge toxin, okadaic acid, on protein phosphatases. Specificity and kinetics. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):283–290. doi: 10.1042/bj2560283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos K., Wraight C., Stanley K. K. TGN38 is maintained in the trans-Golgi network by a tyrosine-containing motif in the cytoplasmic domain. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2219–2228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05870.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braulke T., Mieskes G. Role of protein phosphatases in insulin-like growth factor II (IGF II)-stimulated mannose 6-phosphate/IGF II receptor redistribution. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17347–17353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chege N. W., Pfeffer S. R. Compartmentation of the Golgi complex: brefeldin-A distinguishes trans-Golgi cisternae from the trans-Golgi network. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):893–899. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churcher Y., Kramer K. M., Gomperts B. D. Evidence for protein dephosphorylation as a permissive step in GTP-gamma-S-induced exocytosis from permeabilized mast cells. Cell Regul. 1990 Jun;1(7):523–530. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.7.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson H. W., McGowan C. H., Balch W. E. Evidence for the regulation of exocytic transport by protein phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(6):1343–1355. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.6.1343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Russ G., Yewdell J. W. Brefeldin A redistributes resident and itinerant Golgi proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):61–72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Rothman J. E. Compartmentation of asparagine-linked oligosaccharide processing in the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):270–275. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone C., Griffiths G., Warren G. Newly synthesized G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus is not transported to the Golgi complex in mitotic cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2036–2046. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. E., Kornfeld S. Evidence for extensive subcellular organization of asparagine-linked oligosaccharide processing and lysosomal enzyme phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3159–3165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomperts B. D., Churcher Y., Koffer A., Kramer I. M., Lillie T., Tatham P. E. The role and mechanism of the GTP-binding protein GE in the control of regulated exocytosis. Biochem Soc Symp. 1990;56:85–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Simons K. The trans Golgi network: sorting at the exit site of the Golgi complex. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):438–443. doi: 10.1126/science.2945253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Beaven M. A., Rogers J., Burke B., Warren G. B. Stimulated release of histamine by a rat mast cell line is inhibited during mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):2250–2254. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.2250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. S., Peters P. J., Yuan L. C., Bonifacino J. S. Localization of TGN38 to the trans-Golgi network: involvement of a cytoplasmic tyrosine-containing sequence. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1123–1135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladinsky M. S., Howell K. E. The trans-Golgi network can be dissected structurally and functionally from the cisternae of the Golgi complex by brefeldin A. Eur J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;59(1):92–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Yuan L., Tipper C., Amherdt M., Orci L., Klausner R. D. Brefeldin A's effects on endosomes, lysosomes, and the TGN suggest a general mechanism for regulating organelle structure and membrane traffic. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):601–616. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90534-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucocq J. Mimicking mitotic Golgi disassembly using okadaic acid. J Cell Sci. 1992 Dec;103(Pt 4):875–880. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103.4.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucocq J., Warren G., Pryde J. Okadaic acid induces Golgi apparatus fragmentation and arrest of intracellular transport. J Cell Sci. 1991 Dec;100(Pt 4):753–759. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100.4.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzio J. P., Brake B., Banting G., Howell K. E., Braghetta P., Stanley K. K. Identification, sequencing and expression of an integral membrane protein of the trans-Golgi network (TGN38). Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):97–102. doi: 10.1042/bj2700097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méresse S., Hoflack B. Phosphorylation of the cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor is closely associated with its exit from the trans-Golgi network. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(1):67–75. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaves B., Banting G. Perturbation of the morphology of the trans-Golgi network following Brefeldin A treatment: redistribution of a TGN-specific integral membrane protein, TGN38. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):85–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaves B., Horn M., Banting G. TGN38/41 recycles between the cell surface and the TGN: brefeldin A affects its rate of return to the TGN. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jan;4(1):93–105. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Wilde C. D., Köhler G. A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):269–270. doi: 10.1038/276269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai A., Bialojan C., Troschka M., Rüegg J. C. Smooth muscle myosin phosphatase inhibition and force enhancement by black sponge toxin. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 8;217(1):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81247-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takuma T., Ichida T. Okadaic acid inhibits amylase exocytosis from parotid acini stimulated by cyclic AMP. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 8;285(1):124–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80740-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyberg J., Moskalewski S. Disorganization of the Golgi complex and the cytoplasmic microtubule system in CHO cells exposed to okadaic acid. J Cell Sci. 1992 Dec;103(Pt 4):1167–1175. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103.4.1167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G., Davoust J., Cockcroft A. Recycling of transferrin receptors in A431 cells is inhibited during mitosis. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2217–2225. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02119.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalley T., Crossley I., Whitaker M. Phosphoprotein inhibition of calcium-stimulated exocytosis in sea urchin eggs. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):769–778. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde A., Reaves B., Banting G. Epitope mapping of two isoforms of a trans Golgi network specific integral membrane protein TGN38/41. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 30;313(3):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81199-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. H., Hong W. The SXYQRL sequence in the cytoplasmic domain of TGN38 plays a major role in trans-Golgi network localization. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22853–22862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Yasuda H., Pines J., Yasumoto K., Nishitani H., Ohtsubo M., Hunter T., Sugimura T., Nishimoto T. Okadaic acid, a potent inhibitor of type 1 and type 2A protein phosphatases, activates cdc2/H1 kinase and transiently induces a premature mitosis-like state in BHK21 cells. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4331–4338. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07882.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara N., Toyohira Y., Koda Y., Wada A., Izumi F. Inhibitory effect of okadaic acid on carbachol-evoked secretion of catecholamines in cultured bovine adrenal medullary cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jan 15;174(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90487-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]