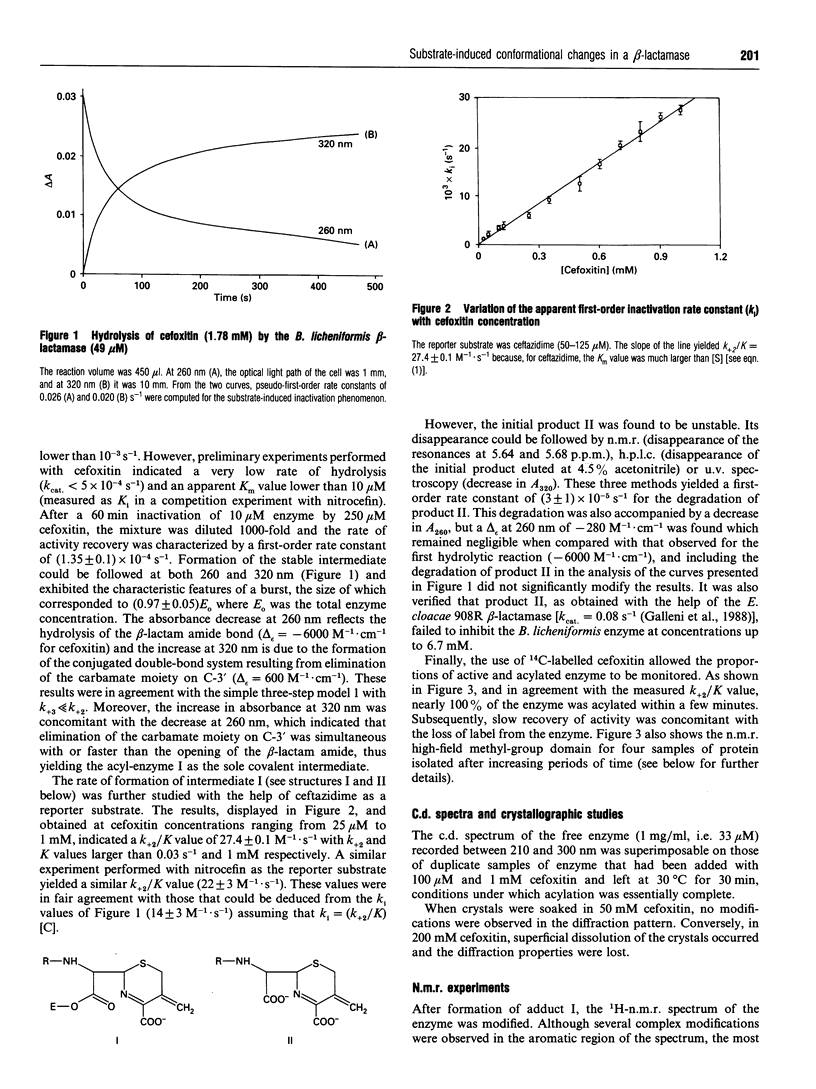
Abstract
Cefoxitin and other beta-lactam antibiotics with a methoxy group on the alpha-face behave as very poor substrates of the Bacillus licheniformis beta-lactamase. The kinetic properties of the enzyme-cefoxitin system made it theoretically suitable for a detailed structural study of the acyl-enzyme. Unfortunately, soaking the crystals in cefoxitin solution did not allow detection of a crystalline acyl-enzyme complex. In contrast, direct observation by n.m.r. of the stable acyl-enzyme formed with cefoxitin and moxalactam indicated clear modifications of the enzyme structure, which were reflected in the aromatic and high-field methyl regions of the spectrum. The return to the initial free enzyme spectrum was concomitant with the hydrolysis of the acyl-enzyme, the process being slow enough to allow multidimensional n.m.r. experiments.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell I. D., Lindskog S., White A. I. A study of the histidine residues of human carbonic anhydrase B using 270 MHz proton magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 15;90(3):469–489. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citri N., Kalkstein A., Samuni A., Zyk N. Conformational adaptation of RTEM beta-lactamase to cefoxitin. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 15;144(2):333–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Meester F., Joris B., Reckinger G., Bellefroid-Bourguignon C., Frère J. M., Waley S. G. Automated analysis of enzyme inactivation phenomena. Application to beta-lactamases and DD-peptidases. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Jul 15;36(14):2393–2403. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90609-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dideberg O., Libert M., Frère J. M., Charlier P., Zhao H., Knox J. R. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray data for the exocellular beta-lactamase of Bacillus licheniformis 749/C. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):145–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90333-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faraci W. S., Pratt R. F. Mechanism of inhibition of RTEM-2 beta-lactamase by cephamycins: relative importance of the 7 alpha-methoxy group and the 3' leaving group. Biochemistry. 1986 May 20;25(10):2934–2941. doi: 10.1021/bi00358a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faraci W. S., Pratt R. F. Mechanism of inhibition of the PC1 beta-lactamase of Staphylococcus aureus by cephalosporins: importance of the 3'-leaving group. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 12;24(4):903–910. doi: 10.1021/bi00325a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J., Belasco J. G., Khosla S., Knowles J. R. beta-Lactamase proceeds via an acyl-enzyme intermediate. Interaction of the Escherichia coli RTEM enzyme with cefoxitin. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 24;19(13):2895–2901. doi: 10.1021/bi00554a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galleni M., Amicosante G., Frère J. M. A survey of the kinetic parameters of class C beta-lactamases. Cephalosporins and other beta-lactam compounds. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):123–129. doi: 10.1042/bj2550123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzhütter H. G., Colosimo A. SIMFIT: a microcomputer software-toolkit for modelistic studies in biochemistry. Comput Appl Biosci. 1990 Jan;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/6.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matagne A., Lamotte-Brasseur J., Dive G., Knox J. R., Frère J. M. Interactions between active-site-serine beta-lactamases and compounds bearing a methoxy side chain on the alpha-face of the beta-lactam ring: kinetic and molecular modelling studies. Biochem J. 1993 Aug 1;293(Pt 3):607–611. doi: 10.1042/bj2930607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matagne A., Misselyn-Bauduin A. M., Joris B., Erpicum T., Granier B., Frère J. M. The diversity of the catalytic properties of class A beta-lactamases. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 1;265(1):131–146. doi: 10.1042/bj2650131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


