Abstract
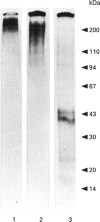
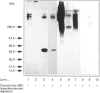
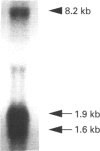
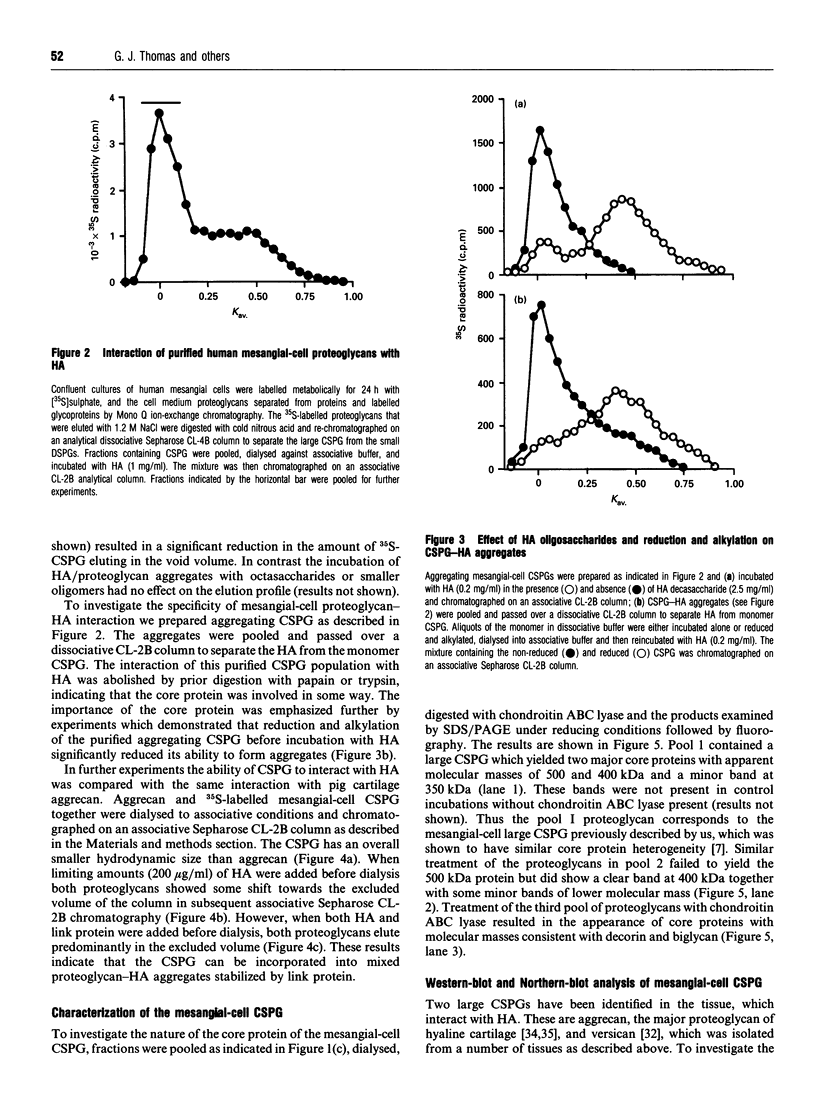
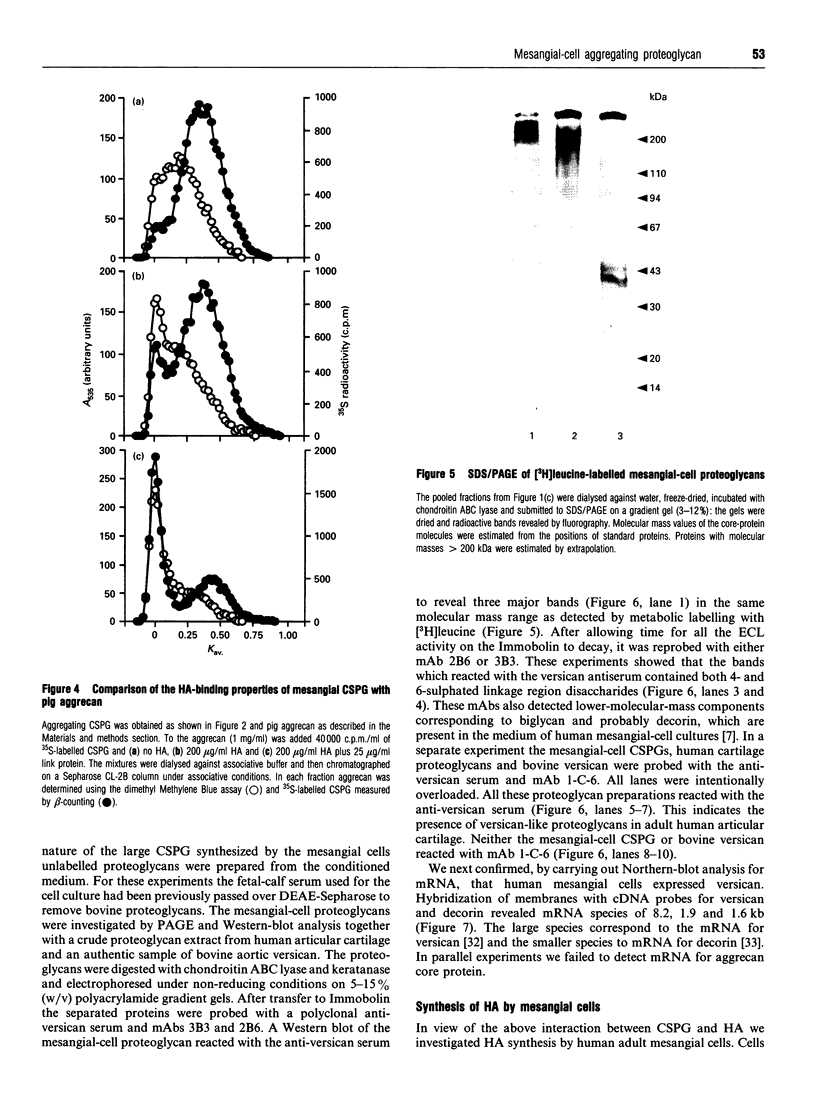
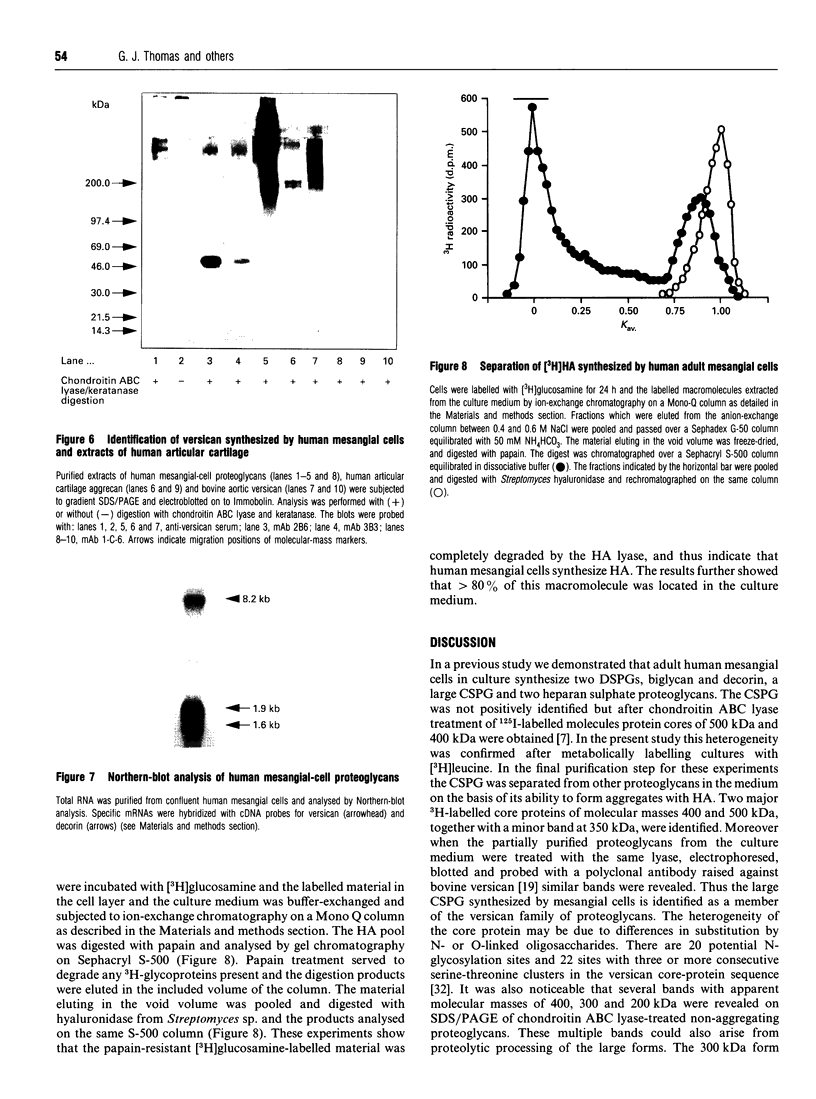
Recent studies have shown that mesangial cells derived from human adult glomeruli synthesize a number of 35S-labelled proteoglycans including a large chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan (CSPG), two dermatan sulphate proteoglycans (biglycan and decorin) and two heparan sulphate proteoglycans [Thomas, Mason and Davies (1991) Biochem. J. 277, 81-88]. In the present study we have examined the interaction of these proteoglycans with hyaluronan (HA) using associative gel chromatography. Only the large CSPG bound to HA, with 60% of those molecules in the medium and 80% of those in the cell layer being able to interact. Reduction and alkylation, or treatment of the monomer CSPG with proteinases, prevented the formation of aggregates, suggesting that the core protein was involved. The aggregates formed between purified CSPG and HA could be dissociated in the presence of HA-oligosaccharides of at least 10 monosaccharides in length. The inclusion of link protein with CSPG and HA promoted the formation of aggregates. Experiments with 3H-labelled mesangial-cell proteoglycans confirmed that only the large CSPG, with core protein molecular masses of 400 kDa and 500 kDa, interacted with HA. After chondroitin ABC lyase treatment of CSPG isolated from conditioned culture medium, several bands similar to those observed with 3H-labelled core proteins were identified using a polyclonal antiserum that recognizes versican. A monoclonal antibody recognizing the 1-C-6 epitope in the G1 and G2 globular regions of aggrecan did not recognize either mesangial-cell CSPG or bovine aortic versican. Northern-blot analysis confirmed that human mesangial cells express versican. Thus human mesangial large CSPG is a member of the versican family of proteoglycans. The interaction of CSPG and HA within the glomerulus may be important in glomerular cell migration and proliferation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aikawa J., Isemura M., Munakata H., Ototani N., Kodama C., Hayashi N., Kurosawa K., Yoshinaga K., Tada K., Yosizawa Z. Isolation and characterization of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans from porcine thoracic aorta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Aug 6;883(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90138-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss M. T., Roughley P. J. The properties of proteoglycan prepared from human articular cartilage by using associative caesium chloride gradients of high and low starting densities. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):111–117. doi: 10.1042/bj2320111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm T., Buluwela L., Williams D., White L., Rabbitts T. H. A cluster of chromosome 11p13 translocations found via distinct D-D and D-D-J rearrangements of the human T cell receptor delta chain gene. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2011–2017. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuer B., Quentin E., Cully Z., Götte M., Kresse H. A novel large dermatan sulfate proteoglycan from human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13224–13232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y., Yanagishita M., Hascall V. C., Wight T. N. Proteoglycans synthesized by smooth muscle cells derived from monkey (Macaca nemestrina) aorta. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5679–5688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christner J. E., Brown M. L., Dziewiatkowski D. D. Interactions of cartilage proteoglycans with hyaluronate. Inhibition of the interaction by modified oligomers of hyaluronate. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4624–4630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couchman J. R., Caterson B., Christner J. E., Baker J. R. Mapping by monoclonal antibody detection of glycosaminoglycans in connective tissues. Nature. 1984 Feb 16;307(5952):650–652. doi: 10.1038/307650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M., Thomas G. J., Shewring L. D., Mason R. M. Mesangial cell proteoglycans: synthesis and metabolism. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992 Apr;2(10 Suppl):S88–S94. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V210s88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher L. W., Termine J. D., Young M. F. Deduced protein sequence of bone small proteoglycan I (biglycan) shows homology with proteoglycan II (decorin) and several nonconnective tissue proteins in a variety of species. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4571–4576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosang A. J., Hardingham T. E. 1-C-6 epitope in cartilage proteoglycan G2 domain is masked by keratan sulphate. Biochem J. 1991 Jan 15;273(Pt 2):369–373. doi: 10.1042/bj2730369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover J., Roughley P. J. Versican gene expression in human articular cartilage and comparison of mRNA splicing variation with aggrecan. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 15;291(Pt 2):361–367. doi: 10.1042/bj2910361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Batchu R. B., Datta K. Purification, partial characterization of rat kidney hyaluronic acid binding protein and its localization on the cell surface. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;56(1):58–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Ewins R. J., Muir H. Cartilage proteoglycans. Structure and heterogeneity of the protein core and the effects of specific protein modifications on the binding to hyaluronate. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):127–143. doi: 10.1042/bj1570127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Heinegård D. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. II. Oligosaccharide competitors of the proteoglycan-hyaluronic acid interaction. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4242–4249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Sajdera S. W. Physical properties and polydispersity of proteoglycan from bovine nasal cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):4920–4930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Björne-Persson A., Cöster L., Franzén A., Gardell S., Malmström A., Paulsson M., Sandfalk R., Vogel K. The core proteins of large and small interstitial proteoglycans from various connective tissues form distinct subgroups. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 15;230(1):181–194. doi: 10.1042/bj2300181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Jakubowski M. L., Rosenzweig L. J. Distribution of sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the glomerular basement membrane and mesangial matrix. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;31(2):290–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Rosenzweig L. J., Jakubowski M. L. Distribution of de novo synthesized sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the glomerular basement membrane and mesangial matrix. Lab Invest. 1983 Aug;49(2):216–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krusius T., Gehlsen K. R., Ruoslahti E. A fibroblast chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan core protein contains lectin-like and growth factor-like sequences. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13120–13125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent T. C., Fraser J. R. Hyaluronan. FASEB J. 1992 Apr;6(7):2397–2404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBaron R. G., Zimmermann D. R., Ruoslahti E. Hyaluronate binding properties of versican. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):10003–10010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mené P., Simonson M. S., Dunn M. J. Physiology of the mesangial cell. Physiol Rev. 1989 Oct;69(4):1347–1424. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.4.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita H., Takeuchi T., Suzuki S., Maeda K., Yamada K., Eguchi G., Kimata K. Aortic endothelial cells synthesize a large chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan capable of binding to hyaluronate. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 1;265(1):61–68. doi: 10.1042/bj2650061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oike Y., Kimata K., Shinomura T., Nakazawa K., Suzuki S. Structural analysis of chick-embryo cartilage proteoglycan by selective degradation with chondroitin lyases (chondroitinases) and endo-beta-D-galactosidase (keratanase). Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):193–207. doi: 10.1042/bj1910193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT J. E. Aliphatic ammonium salts in the assay of acidic polysaccharides from tissues. Methods Biochem Anal. 1960;8:145–197. doi: 10.1002/9780470110249.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio L. de O., Bayliss M. T., Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Dermatan sulphate proteoglycan from human articular cartilage. Variation in its content with age and its structural comparison with a small chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan from pig laryngeal cartilage. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 15;254(3):757–764. doi: 10.1042/bj2540757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Buddecke E. Cell-associated proteoheparan sulfate from bovine arterial smooth muscle cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Oct;178(2):242–253. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90395-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönherr E., Järveläinen H. T., Sandell L. J., Wight T. N. Effects of platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta 1 on the synthesis of a large versican-like chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan by arterial smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17640–17647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomura T., Nishida Y., Ito K., Kimata K. cDNA cloning of PG-M, a large chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan expressed during chondrogenesis in chick limb buds. Alternative spliced multiforms of PG-M and their relationships to versican. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14461–14469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. E., Conrad H. E. Formation of anhydrosugars in the chemical depolymerization of heparin. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 7;15(18):3932–3942. doi: 10.1021/bi00663a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. E., Conrad H. E. Nearest neighbor analysis of heparin: identification and quantitation of the products formed by selective depolymerization procedures. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 7;15(18):3943–3950. doi: 10.1021/bi00663a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan S. R., Vijayagopal P., Eberle K., Radhakrishnamurthy B., Berenson G. S. Low-density lipoprotein binding affinity of arterial wall proteoglycans: characteristics of a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan subfraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 28;1006(2):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. J., Jenner L., Mason R. M., Davies M. Human glomerular epithelial cell proteoglycans. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Apr;278(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90224-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. J., Mason R. M., Davies M. Characterization of proteoglycans synthesized by human adult glomerular mesangial cells in culture. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 1;277(Pt 1):81–88. doi: 10.1042/bj2770081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wight T. N. Cell biology of arterial proteoglycans. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–20. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wight T. N., Hascall V. C. Proteoglycans in primate arteries. III. Characterization of the proteoglycans synthesized by arterial smooth muscle cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):167–176. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wight T. N., Potter-Perigo S., Aulinskas T. Proteoglycans and vascular cell proliferation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Oct;140(4):1132–1135. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.4.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata T., Saito H., Habuchi O., Suzuki S. Purification and properties of bacterial chondroitinases and chondrosulfatases. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1523–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaoita E., Oguri K., Okayama E., Kawasaki K., Kobayashi S., Kihara I., Okayama M. Isolation and characterization of proteoglycans synthesized by cultured mesangial cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):522–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann D. R., Ruoslahti E. Multiple domains of the large fibroblast proteoglycan, versican. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2975–2981. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]