Full text
PDF


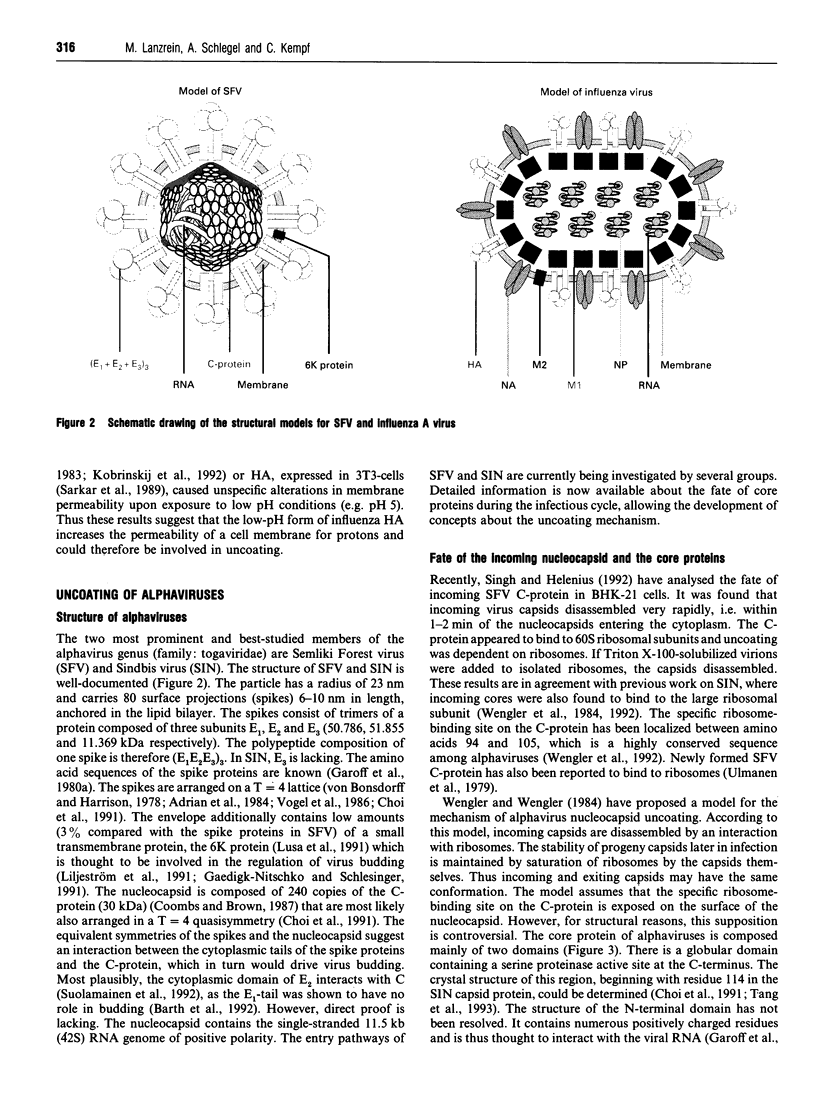




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian M., Dubochet J., Lepault J., McDowall A. W. Cryo-electron microscopy of viruses. Nature. 1984 Mar 1;308(5954):32–36. doi: 10.1038/308032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W. Exocytosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:607–624. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth B. U., Suomalainen M., Liljeström P., Garoff H. Alphavirus assembly and entry: role of the cytoplasmic tail of the E1 spike subunit. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7560–7564. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7560-7564.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashford C. L., Alder G. M., Menestrina G., Micklem K. J., Murphy J. J., Pasternak C. A. Membrane damage by hemolytic viruses, toxins, complement, and other cytotoxic agents. A common mechanism blocked by divalent cations. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9300–9308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bron R., Wahlberg J. M., Garoff H., Wilschut J. Membrane fusion of Semliki Forest virus in a model system: correlation between fusion kinetics and structural changes in the envelope glycoprotein. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):693–701. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05703.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukrinskaya A. G., Vorkunova N. K., Kornilayeva G. V., Narmanbetova R. A., Vorkunova G. K. Influenza virus uncoating in infected cells and effect of rimantadine. J Gen Virol. 1982 May;60(Pt 1):49–59. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-60-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr C. M., Kim P. S. A spring-loaded mechanism for the conformational change of influenza hemagglutinin. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):823–832. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90260-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi H. K., Tong L., Minor W., Dumas P., Boege U., Rossmann M. G., Wengler G. Structure of Sindbis virus core protein reveals a chymotrypsin-like serine proteinase and the organization of the virion. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):37–43. doi: 10.1038/354037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciampor F., Thompson C. A., Grambas S., Hay A. J. Regulation of pH by the M2 protein of influenza A viruses. Virus Res. 1992 Mar;22(3):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90056-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs K., Brown D. T. Organization of the Sindbis virus nucleocapsid as revealed by bifunctional cross-linking agents. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):359–371. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90657-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels R. S., Downie J. C., Hay A. J., Knossow M., Skehel J. J., Wang M. L., Wiley D. C. Fusion mutants of the influenza virus hemagglutinin glycoprotein. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):431–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90157-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGrado W. F., Lear J. D. Conformationally constrained alpha-helical peptide models for protein ion channels. Biopolymers. 1990 Jan;29(1):205–213. doi: 10.1002/bip.360290125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Wileman T. E., Anderson S. J., Stahl P. The use of permeabilized cells to study the ion requirements of receptor-ligand dissociation in endosomes. Biochem J. 1989 May 15;260(1):127–134. doi: 10.1042/bj2600127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaedigk-Nitschko K., Schlesinger M. J. Site-directed mutations in Sindbis virus E2 glycoprotein's cytoplasmic domain and the 6K protein lead to similar defects in virus assembly and budding. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):206–214. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90133-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Frischauf A. M., Simons K., Lehrach H., Delius H. Nucleotide sequence of cdna coding for Semliki Forest virus membrane glycoproteins. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):236–241. doi: 10.1038/288236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Frischauf A. M., Simons K., Lehrach H., Delius H. The capsid protein of Semliki Forest virus has clusters of basic amino acids and prolines in its amino-terminal region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6376–6380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geigenmüller-Gnirke U., Nitschko H., Schlesinger S. Deletion analysis of the capsid protein of Sindbis virus: identification of the RNA binding region. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1620–1626. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1620-1626.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Doms R. W., York D., White J. Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: site-specific mutagenesis of the hemagglutinin of influenza virus. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):11–23. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grambas S., Bennett M. S., Hay A. J. Influence of amantadine resistance mutations on the pH regulatory function of the M2 protein of influenza A viruses. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):541–549. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90229-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grambas S., Hay A. J. Maturation of influenza A virus hemagglutinin--estimates of the pH encountered during transport and its regulation by the M2 protein. Virology. 1992 Sep;190(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)91187-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter C., Bächi T., Semenza G., Brunner J. Hydrophobic photolabeling identifies BHA2 as the subunit mediating the interaction of bromelain-solubilized influenza virus hemagglutinin with liposomes at low pH. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):1856–1864. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter C., James P., Bächi T., Semenza G., Brunner J. Hydrophobic binding of the ectodomain of influenza hemagglutinin to membranes occurs through the "fusion peptide". J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6459–6464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay A. J., Wolstenholme A. J., Skehel J. J., Smith M. H. The molecular basis of the specific anti-influenza action of amantadine. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):3021–3024. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04038.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A. Unpacking the incoming influenza virus. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):577–578. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemble G. W., Bodian D. L., Rosé J., Wilson I. A., White J. M. Intermonomer disulfide bonds impair the fusion activity of influenza virus hemagglutinin. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4940–4950. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4940-4950.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemble G. W., Danieli T., White J. M. Lipid-anchored influenza hemagglutinin promotes hemifusion, not complete fusion. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempf C., Michel M. R., Kohler U., Koblet H. Can viral envelope proteins act as or induce proton channels? Biosci Rep. 1987 Oct;7(10):761–769. doi: 10.1007/BF01116748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempf C., Michel M. R., Omar A., Jentsch P., Morell A. Semliki Forest virus induced cell-cell fusion at neutral extracellular pH. Biosci Rep. 1990 Aug;10(4):363–374. doi: 10.1007/BF01117236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielian M., Helenius A. pH-induced alterations in the fusogenic spike protein of Semliki Forest virus. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2284–2291. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koblet H. The "merry-go-round": alphaviruses between vertebrate and invertebrate cells. Adv Virus Res. 1990;38:343–402. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60866-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. The gene structure and replication of influenza virus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:467–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzrein M., Käsermann N., Kempf C. Changes in membrane permeability during Semliki Forest virus induced cell fusion. Biosci Rep. 1992 Jun;12(3):221–236. doi: 10.1007/BF01121792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzrein M., Käsermann N., Weingart R., Kempf C. Early events of Semliki Forest virus-induced cell-cell fusion. Virology. 1993 Oct;196(2):541–547. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzrein M., Weingart R., Kempf C. pH-dependent pore formation in Semliki forest virus-infected Aedes albopictus cells. Virology. 1993 Mar;193(1):296–302. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lear J. D., Wasserman Z. R., DeGrado W. F. Synthetic amphiphilic peptide models for protein ion channels. Science. 1988 May 27;240(4856):1177–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.2453923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy-Mintz P., Kielian M. Mutagenesis of the putative fusion domain of the Semliki Forest virus spike protein. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4292–4300. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4292-4300.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeström P., Lusa S., Huylebroeck D., Garoff H. In vitro mutagenesis of a full-length cDNA clone of Semliki Forest virus: the small 6,000-molecular-weight membrane protein modulates virus release. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4107–4113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4107-4113.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusa S., Garoff H., Liljeström P. Fate of the 6K membrane protein of Semliki Forest virus during virus assembly. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):843–846. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90556-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Virus entry into animal cells. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:107–151. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60583-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K., Helenius A. Nuclear transport of influenza virus ribonucleoproteins: the viral matrix protein (M1) promotes export and inhibits import. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90576-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K., Helenius A. Transport of incoming influenza virus nucleocapsids into the nucleus. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):232–244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.232-244.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauracher C. A., Gillam S., Shukin R., Tingle A. J. pH-dependent solubility shift of rubella virus capsid protein. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):773–777. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90916-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monck J. R., Fernandez J. M. The exocytotic fusion pore. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1395–1404. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojcius D. M., Young J. D. Cytolytic pore-forming proteins and peptides: is there a common structural motif? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90090-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omar A., Koblet H. Semliki Forest virus particles containing only the E1 envelope glycoprotein are infectious and can induce cell-cell fusion. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90141-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K., Pasternak C. A. Ca2+-sensitive permeability changes caused by influenza virus. Biosci Rep. 1983 Aug;3(8):749–755. doi: 10.1007/BF01120986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto L. H., Holsinger L. J., Lamb R. A. Influenza virus M2 protein has ion channel activity. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90452-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P. Interacting phospholipid bilayers: measured forces and induced structural changes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1981;10:277–314. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.10.060181.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P., Parsegian V. A. Mimicry and mechanism in phospholipid models of membrane fusion. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:201–212. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruigrok R. W., Hirst E. M., Hay A. J. The specific inhibition of influenza A virus maturation by amantadine: an electron microscopic examination. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jan;72(Pt 1):191–194. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-1-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen A., Wahlberg J. M., Lobigs M., Liljeström P., Garoff H. Membrane fusion process of Semliki Forest virus. II: Cleavage-dependent reorganization of the spike protein complex controls virus entry. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):349–357. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar D. P., Morris S. J., Eidelman O., Zimmerberg J., Blumenthal R. Initial stages of influenza hemagglutinin-induced cell fusion monitored simultaneously by two fluorescent events: cytoplasmic continuity and lipid mixing. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):113–122. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel A., Omar A., Jentsch P., Morell A., Kempf C. Semliki Forest virus envelope proteins function as proton channels. Biosci Rep. 1991 Oct;11(5):243–255. doi: 10.1007/BF01127500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel A., Schaller J., Jentsch P., Kempf C. Semliki Forest virus core protein fragmentation: its possible role in nucleocapsid disassembly. Biosci Rep. 1993 Dec;13(6):333–347. doi: 10.1007/BF01150478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh I., Helenius A. Role of ribosomes in Semliki Forest virus nucleocapsid uncoating. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7049–7058. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7049-7058.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Bayley P. M., Brown E. B., Martin S. R., Waterfield M. D., White J. M., Wilson I. A., Wiley D. C. Changes in the conformation of influenza virus hemagglutinin at the pH optimum of virus-mediated membrane fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):968–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruce A. E., Iwata A., Almers W. The first milliseconds of the pore formed by a fusogenic viral envelope protein during membrane fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruce A. E., Iwata A., White J. M., Almers W. Patch clamp studies of single cell-fusion events mediated by a viral fusion protein. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):555–558. doi: 10.1038/342555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., Delfino J. M., Richards F. M., Helenius A. The HA2 subunit of influenza hemagglutinin inserts into the target membrane prior to fusion. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18404–18410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., Doms R. W., Helenius A. Protein-mediated membrane fusion. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:187–211. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhauer D. A., Wharton S. A., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C., Hay A. J. Amantadine selection of a mutant influenza virus containing an acid-stable hemagglutinin glycoprotein: evidence for virus-specific regulation of the pH of glycoprotein transport vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11525–11529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong R. K., Harrison S. C. Proteolytic dissection of Sindbis virus core protein. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3992–3994. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3992-3994.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs M. J., Miller A., Sizer P. J., Stephenson J. R., Crooks A. J. X-ray solution scattering of Sindbis virus. Changes in conformation induced at low pH. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 5;221(1):39–42. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80200-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugrue R. J., Bahadur G., Zambon M. C., Hall-Smith M., Douglas A. R., Hay A. J. Specific structural alteration of the influenza haemagglutinin by amantadine. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3469–3476. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07555.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugrue R. J., Hay A. J. Structural characteristics of the M2 protein of influenza A viruses: evidence that it forms a tetrameric channel. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):617–624. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90075-M. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen M., Liljeström P., Garoff H. Spike protein-nucleocapsid interactions drive the budding of alphaviruses. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4737–4747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4737-4747.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund H., Käriänen L., Von Bonsdorff C. H., Weckström P. Properties of Semliki forest virus nucleocapsid. II. An irreversible contraction by acid pH. Virology. 1972 Mar;47(3):753–760. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90565-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong L., Wengler G., Rossmann M. G. Refined structure of Sindbis virus core protein and comparison with other chymotrypsin-like serine proteinase structures. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 5;230(1):228–247. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse F. W., Iwata A., Almers W. Membrane flux through the pore formed by a fusogenic viral envelope protein during cell fusion. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(3):543–552. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.3.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurudome M., Glück R., Graf R., Falchetto R., Schaller U., Brunner J. Lipid interactions of the hemagglutinin HA2 NH2-terminal segment during influenza virus-induced membrane fusion. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20225–20232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmanen I., Söderlund H., Käriäinen L. Role of protein synthesis in the assembly of Semliki forest virus nucleocapsid. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):265–276. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel R. H., Provencher S. W., von Bonsdorff C. H., Adrian M., Dubochet J. Envelope structure of Semliki Forest virus reconstructed from cryo-electron micrographs. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):533–535. doi: 10.1038/320533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlberg J. M., Bron R., Wilschut J., Garoff H. Membrane fusion of Semliki Forest virus involves homotrimers of the fusion protein. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7309–7318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7309-7318.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlberg J. M., Garoff H. Membrane fusion process of Semliki Forest virus. I: Low pH-induced rearrangement in spike protein quaternary structure precedes virus penetration into cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):339–348. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G., Boege U., Wahn K. Establishment and analysis of a system which allows assembly and disassembly of alphavirus core-like particles under physiological conditions in vitro. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G. Identification of a transfer of viral core protein to cellular ribosomes during the early stages of alphavirus infection. Virology. 1984 Apr 30;134(2):435–442. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Würkner D., Wengler G. Identification of a sequence element in the alphavirus core protein which mediates interaction of cores with ribosomes and the disassembly of cores. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):880–888. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90263-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M. Membrane fusion. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):917–924. doi: 10.1126/science.1439803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M. Viral and cellular membrane fusion proteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:675–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Helenius A. pH-dependent fusion between the Semliki Forest virus membrane and liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3273–3277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kartenbeck J., Helenius A. Fusion of Semliki forest virus with the plasma membrane can be induced by low pH. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):264–272. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kielian M., Helenius A. Membrane fusion proteins of enveloped animal viruses. Q Rev Biophys. 1983 May;16(2):151–195. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the haemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus at 3 A resolution. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):366–373. doi: 10.1038/289366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Young G. P., Cohn Z. A., Lenard J. Interaction of enveloped viruses with planar bilayer membranes: observations on Sendai, influenza, vesicular stomatitis, and Semliki Forest viruses. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):186–194. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90329-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zebedee S. L., Lamb R. A. Influenza A virus M2 protein: monoclonal antibody restriction of virus growth and detection of M2 in virions. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2762–2772. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2762-2772.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhirnov O. P. Solubilization of matrix protein M1/M from virions occurs at different pH for orthomyxo- and paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1990 May;176(1):274–279. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90253-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bonsdorff C. H., Harrison S. C. Hexagonal glycoprotein arrays from Sindbis virus membranes. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):578–583. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.578-583.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]