Abstract
The ether lipid analogue 1-octadecyl-2-methyl-rac-glycero-3-phosphocholine (ET-18-OCH3) has been recently shown to induce apoptosis in the human leukaemic HL-60 and U937 myeloid cell lines [Mollinedo, Martinez-Dalmau and Modolell (1993) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 192, 603-609]. We have found that ET-18-OCH3 is also able to promote apoptosis in the human leukaemic Jurkat T lymphoid cell line. This lymphoid cell line as well as the two myeloid HL-60 and U937 cell lines incorporated significant amounts of exogenously added radiolabelled ET-18-OCH3. Addition of ET-18-OCH3 to these human leukaemic cells induced an increase in the steady-state mRNA levels of fos and jun proto-oncogenes, components of the transcription factor AP-1. These increases in fos and jun mRNA levels were associated with the activation of the AP-1 transcription factor after addition of ET-18-OCH3 to human leukaemic cells, as assessed by an enhanced binding activity of transcription factor AP-1 to its cognate DNA sequence as well as by stimulation of transcription from an AP-1 enhancer element. These data demonstrate that the ether lipid ET-18-OCH3 can affect gene expression by inducing expression of fos and jun proto-oncogenes and by modulating the activity of transcription factor AP-1.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreesen R., Modolell M., Weltzien H. U., Eibl H., Common H. H., Löhr G. W., Munder P. G. Selective destruction of human leukemic cells by alkyl-lysophospholipids. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 1):3894–3899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 10;1072(2-3):129–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auwerx J., Staels B., Sassone-Corsi P. Coupled and uncoupled induction of fos and jun transcription by different second messengers in cells of hematopoietic origin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 25;18(2):221–228. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
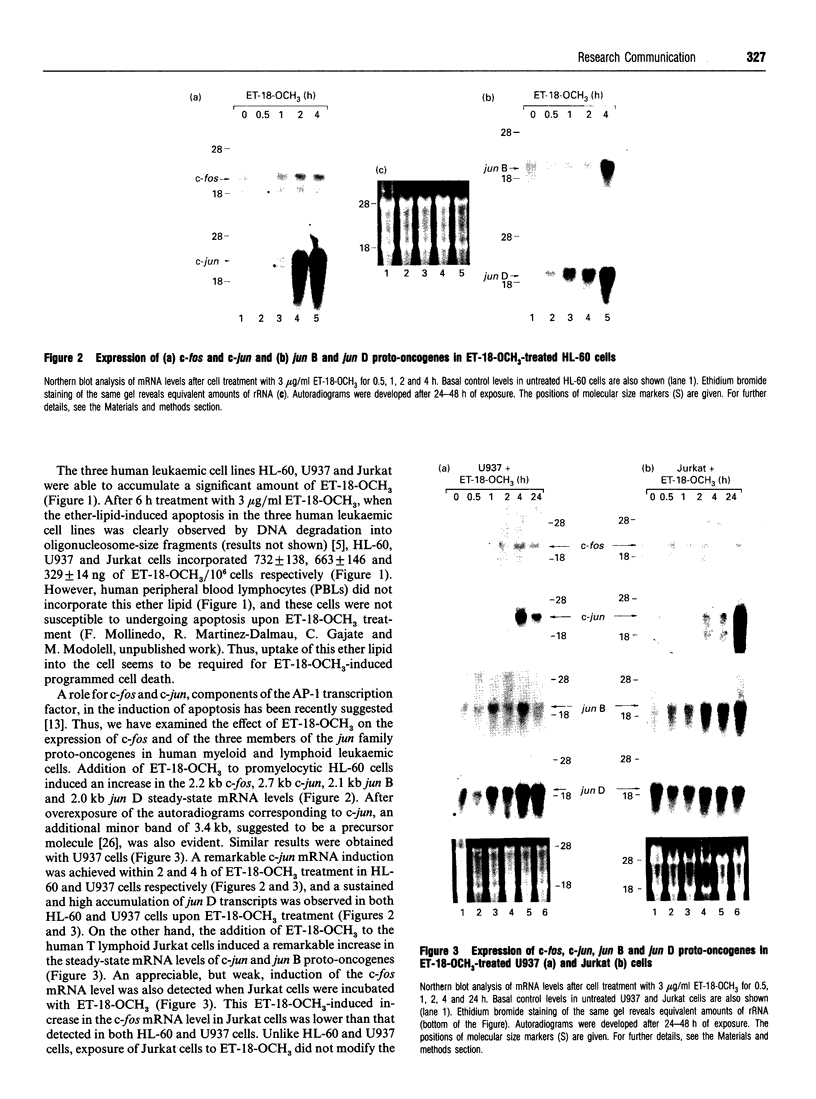
- Colotta F., Polentarutti N., Sironi M., Mantovani A. Expression and involvement of c-fos and c-jun protooncogenes in programmed cell death induced by growth factor deprivation in lymphoid cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18278–18283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins are complexed with a 39,000-dalton cellular protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):167–172. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel L. W., Small G. W., Schmitt J. D., Marasco C. J., Ishaq K., Piantadosi C. Alkyl-linked diglycerides inhibit protein kinase C activation by diacylglycerols. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 29;151(1):291–297. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90592-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dell' Albani P., Condorelli D. F., Mudò G., Amico C., Bindoni M., Belluardo N. Platelet-activating factor and its methoxy-analogue ET-18-OCH3 stimulate immediate early gene expression in rat astroglial cultures. Neurochem Int. 1993 Jun;22(6):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0197-0186(93)90031-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzfelbinger H. F., Kühn D., Zafferani M., Hanauske A. R., Rastetter J. W., Berdel W. E. Removal of breast cancer cells from bone marrow by in vitro purging with ether lipids and cryopreservation. Cancer Res. 1993 Aug 15;53(16):3747–3751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzfelbinger H. F., Lang A., Oberberg D., Rastetter J. W., Berdel W. E. Differential cytotoxicity of an ether lipid on lymphoma and bone marrow cells and its role in purging malignant lymphoid cells from remission bone marrow contaminated with tumor cells. Exp Hematol. 1992 Feb;20(2):178–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diomede L., Colotta F., Piovani B., Re F., Modest E. J., Salmona M. Induction of apoptosis in human leukemic cells by the ether lipid 1-octadecyl-2-methyl-rac-glycero-3-phosphocholine. A possible basis for its selective action. Int J Cancer. 1993 Jan 2;53(1):124–130. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910530123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesbeen E. C., Verdonck L. F., Hermans S. W., van Heugten H. G., Staal G. E., Rijksen G. Alkyllysophospholipid ET-18-OCH3 acts as an activator of protein kinase C in HL-60 cells. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 23;290(1-2):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81267-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann D. B., Neumann H. A. Cytotoxic ether phospholipids. Different affinities to lysophosphocholine acyltransferases in sensitive and resistant cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7742–7747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman D. R., Thomas V. L., Snyder F. Inhibition of cellular transport systems by alkyl phospholipid analogs in HL-60 human leukemia cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jul 9;1127(1):74–80. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modolell M., Andreesen R., Pahlke W., Brugger U., Munder P. G. Disturbance of phospholipid metabolism during the selective destruction of tumor cells induced by alkyl-lysophospholipids. Cancer Res. 1979 Nov;39(11):4681–4686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollinedo F., Gajate C., Tugores A., Flores I., Naranjo J. R. Differences in expression of transcription factor AP-1 in human promyelocytic HL-60 cells during differentiation towards macrophages versus granulocytes. Biochem J. 1993 Aug 15;294(Pt 1):137–144. doi: 10.1042/bj2940137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollinedo F., Martínez-Dalmau R., Modolell M. Early and selective induction of apoptosis in human leukemic cells by the alkyl-lysophospholipid ET-18-OCH3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Apr 30;192(2):603–609. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollinedo F., Naranjo J. R. Uncoupled changes in the expression of the jun family members during myeloid cell differentiation. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Sep 1;200(2):483–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munder P. G., Westphal O. Antitumoral and other biomedical activities of synthetic ether lysophospholipids. Chem Immunol. 1990;49:206–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powis G., Seewald M. J., Gratas C., Melder D., Riebow J., Modest E. J. Selective inhibition of phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C by cytotoxic ether lipid analogues. Cancer Res. 1992 May 15;52(10):2835–2840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated by growth factors is related to the oncogene v-jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1487–1491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Hirai S. I., Yaniv M., Bravo R. Transcriptional activation of c-jun during the G0/G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):535–537. doi: 10.1038/334535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]