Abstract
The gene encoding an alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (abfA) was homologously cloned in Streptomyces lividans and its DNA sequence was determined. The enzyme was purified from the cytoplasm of the hyperproducing clone S. lividans IAF116. Its M(r) was estimated by gel filtration and found to be approx. 380,000. Since SDS/PAGE indicated a native protein of M(r) 69,000, it can be concluded that the native protein consists of several subunits of that size. The pI value was 4.6. The kinetic constants determined with p-nitrophenyl alpha-L-arabinofuranoside as substrate were a Vmax of 180 units/mg of protein and a Km of 0.6 mM. The specific activity of the purified enzyme on this substrate was 153 units/mg of protein. Optimal enzyme activity was obtained at 60 degrees C and pH 6.0. The enzyme cleaved p-nitrophenyl alpha-L-arabinofuranoside, but had no activity on a variety of other p-nitrophenyl glycosides, except on p-nitrophenyl beta-D-xylopyranoside. The enzyme showed no activity on oat-spelts (Avena sativa) xylan or arabinogalactan, but acted on beet (Beta) arabinan or arabinoxylan. Hydrolysis occurred on arabino-oligoxylosides obtained from oat-splets xylan after digestion with xylanases. Since S. lividans normally does not secrete arabinofuranosidase, this enzyme may play a role in the assimilation of arabinose moieties from arabinose-containing xylo-oligosaccharides generated by beta-xylosidases or xylanases.
Full text
PDF

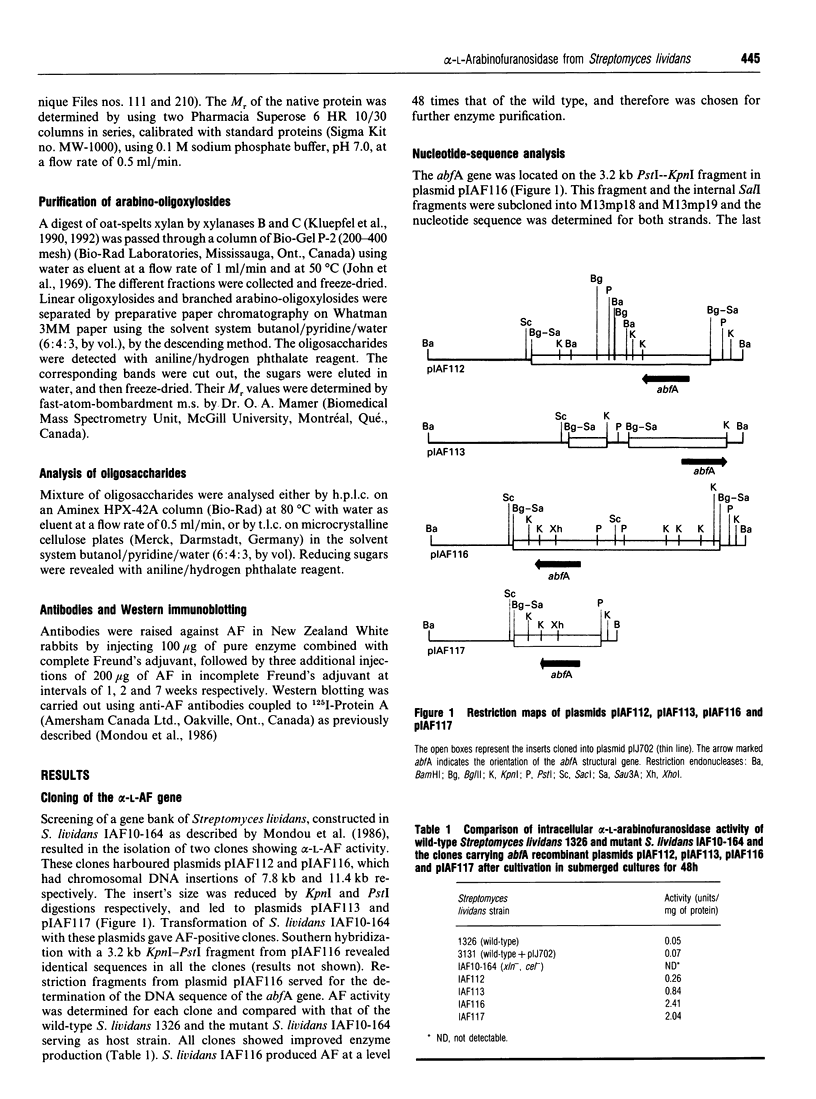
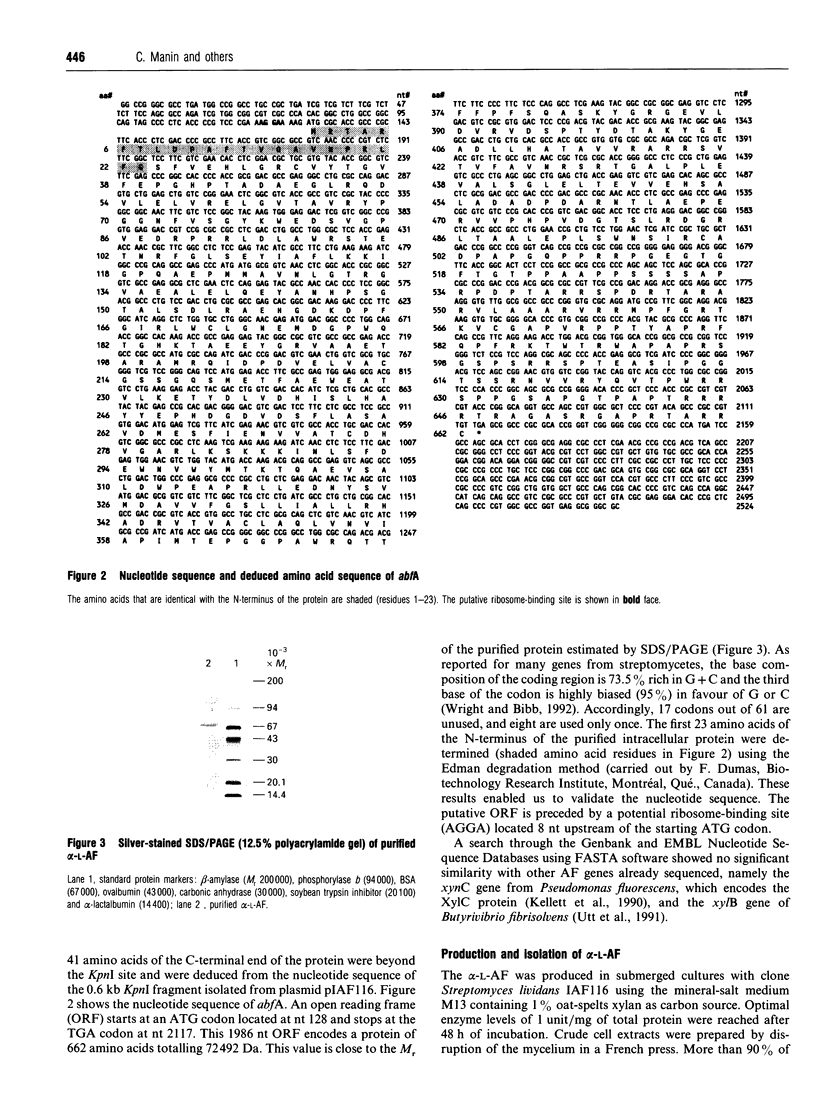
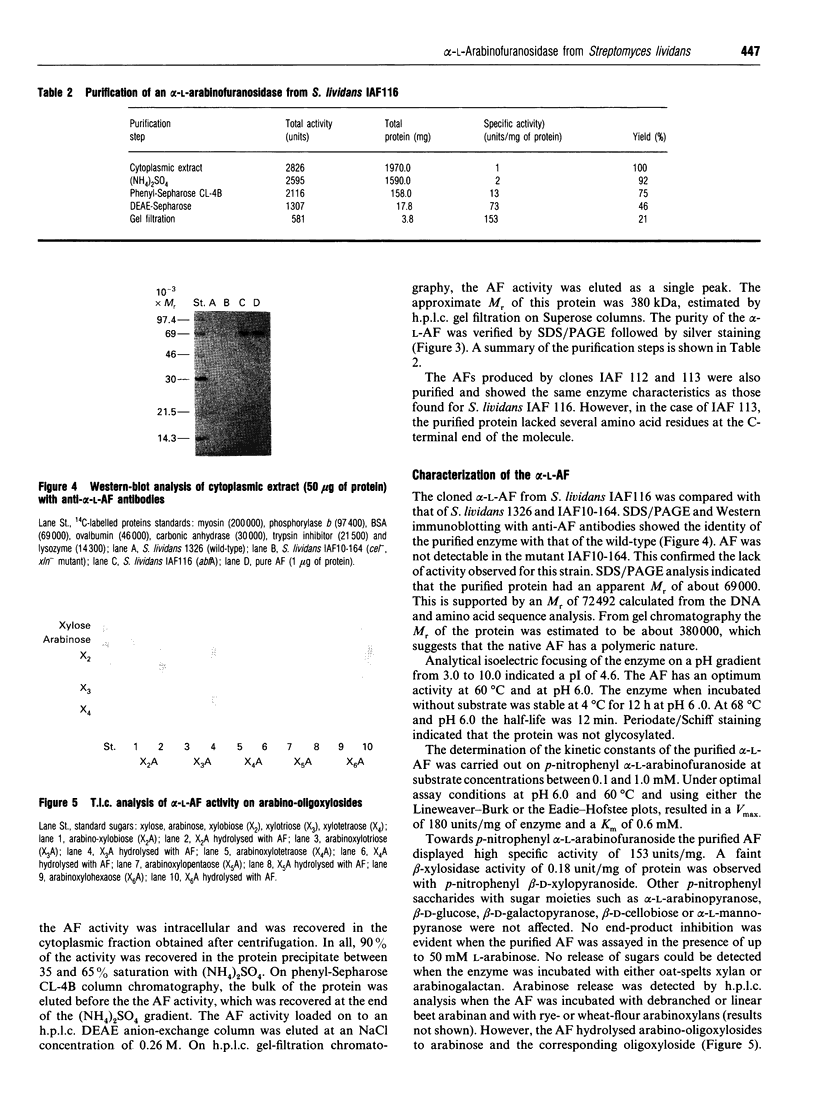


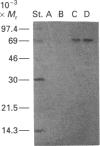
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcand N., Kluepfel D., Paradis F. W., Morosoli R., Shareck F. Beta-mannanase of Streptomyces lividans 66: cloning and DNA sequence of the manA gene and characterization of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1993 Mar 15;290(Pt 3):857–863. doi: 10.1042/bj2900857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekker R. F., Richards G. N. Hemicellulases: their occurrence, purification, properties, and mode of action. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1976;32:277–352. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60339-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flipphi M. J., Visser J., van der Veen P., de Graaff L. H. Cloning of the Aspergillus niger gene encoding alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase A. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1993 Jun;39(3):335–340. doi: 10.1007/BF00192088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve L. C., Labavitch J. M., Hungate R. E. alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase from Ruminococcus albus 8: purification and possible role in hydrolysis of alfalfa cell wall. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):1135–1140. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.1135-1140.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hespell R. B., O'bryan P. J. Purification and Characterization of an alpha-l-Arabinofuranosidase from Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens GS113. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Apr;58(4):1082–1088. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.4.1082-1088.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji A., Talawa K., Ichimi T. Properties of purified alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase from Aspergillus niger. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 7;171(1):186–188. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E., Thompson C. J., Hopwood D. A. Cloning and expression of the tyrosinase gene from Streptomyces antibioticus in Streptomyces lividans. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2703–2714. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellett L. E., Poole D. M., Ferreira L. M., Durrant A. J., Hazlewood G. P., Gilbert H. J. Xylanase B and an arabinofuranosidase from Pseudomonas fluorescens subsp. cellulosa contain identical cellulose-binding domains and are encoded by adjacent genes. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 1;272(2):369–376. doi: 10.1042/bj2720369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluepfel D., Vats-Mehta S., Aumont F., Shareck F., Morosoli R. Purification and characterization of a new xylanase (xylanase B) produced by Streptomyces lividans 66. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 1;267(1):45–50. doi: 10.1042/bj2670045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondou F., Shareck F., Morosoli R., Kluepfel D. Cloning of the xylanase gene of Streptomyces lividans. Gene. 1986;49(3):323–329. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90368-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz W. H., Adelsberger H., Jauris S., Hertel C., Funk B., Staudenbauer W. L. Xylan degradation by the thermophile Clostridium stercorarium: cloning and expression of xylanase, beta-D-xylosidase, and alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase genes in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):368–374. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91283-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shareck F., Roy C., Yaguchi M., Morosoli R., Kluepfel D. Sequences of three genes specifying xylanases in Streptomyces lividans. Gene. 1991 Oct 30;107(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90299-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajana E., Fiechter A., Zimmermann W. Purification and characterization of two alpha-L-arabinofuranosidases from Streptomyces diastaticus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 May;58(5):1447–1450. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.5.1447-1450.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Théberge M., Lacaze P., Shareck F., Morosoli R., Kluepfel D. Purification and characterization of an endoglucanase from Streptomyces lividans 66 and DNA sequence of the gene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Mar;58(3):815–820. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.3.815-820.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utt E. A., Eddy C. K., Keshav K. F., Ingram L. O. Sequencing and expression of the Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens xylB gene encoding a novel bifunctional protein with beta-D-xylosidase and alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase activities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):1227–1234. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1227-1234.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward O. P., Moo-Young M. Enzymatic degradation of cell wall and related plant polysaccharides. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 1989;8(4):237–274. doi: 10.3109/07388558909148194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein L., Albersheim P. Structure of Plant Cell Walls: IX. Purification and Partial Characterization of a Wall-degrading Endo-Arabanase and an Arabinosidase from Bacillus subtilis. Plant Physiol. 1979 Mar;63(3):425–432. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.3.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann S., Shareck F., Kluepfel D., Morosoli R. Purification and characterization of the CelB endoglucanase from Streptomyces lividans 66 and DNA sequence of the encoding gene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 May;60(5):1701–1703. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.5.1701-1703.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. K., Tan L. U., Saddler J. N. Multiplicity of beta-1,4-xylanase in microorganisms: functions and applications. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Sep;52(3):305–317. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.3.305-317.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright F., Bibb M. J. Codon usage in the G+C-rich Streptomyces genome. Gene. 1992 Apr 1;113(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90669-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]