Abstract
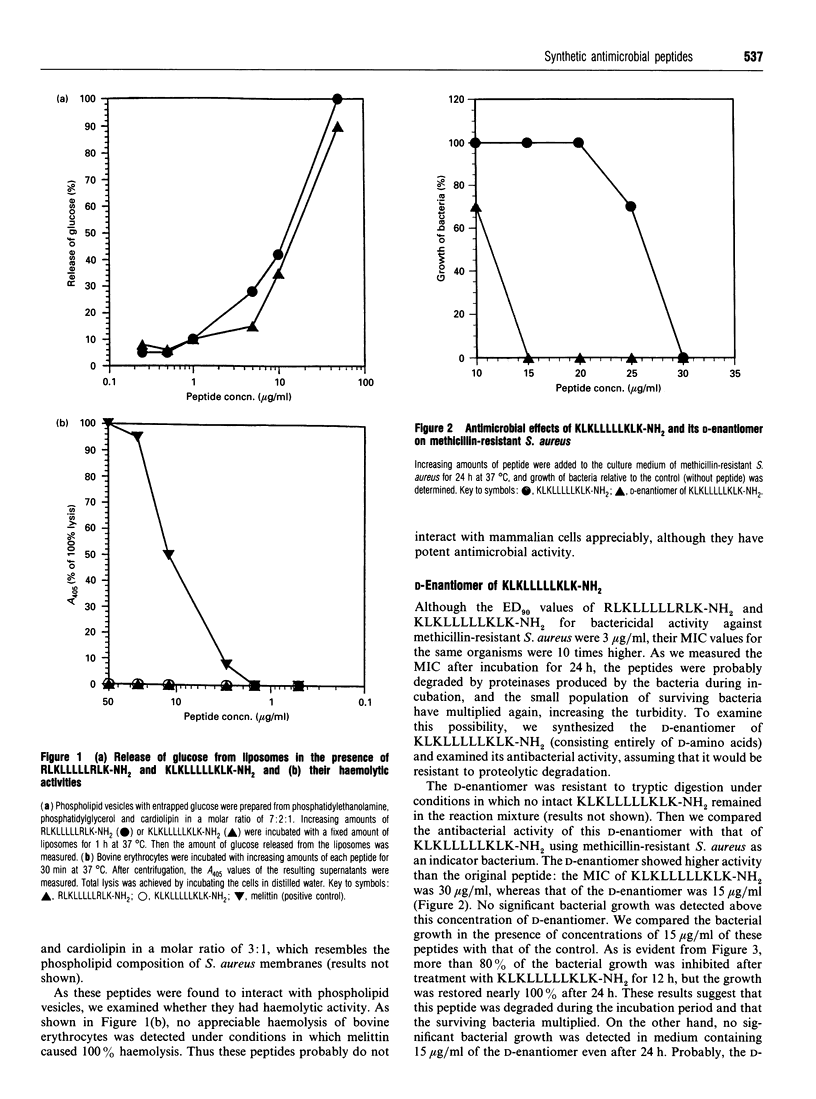
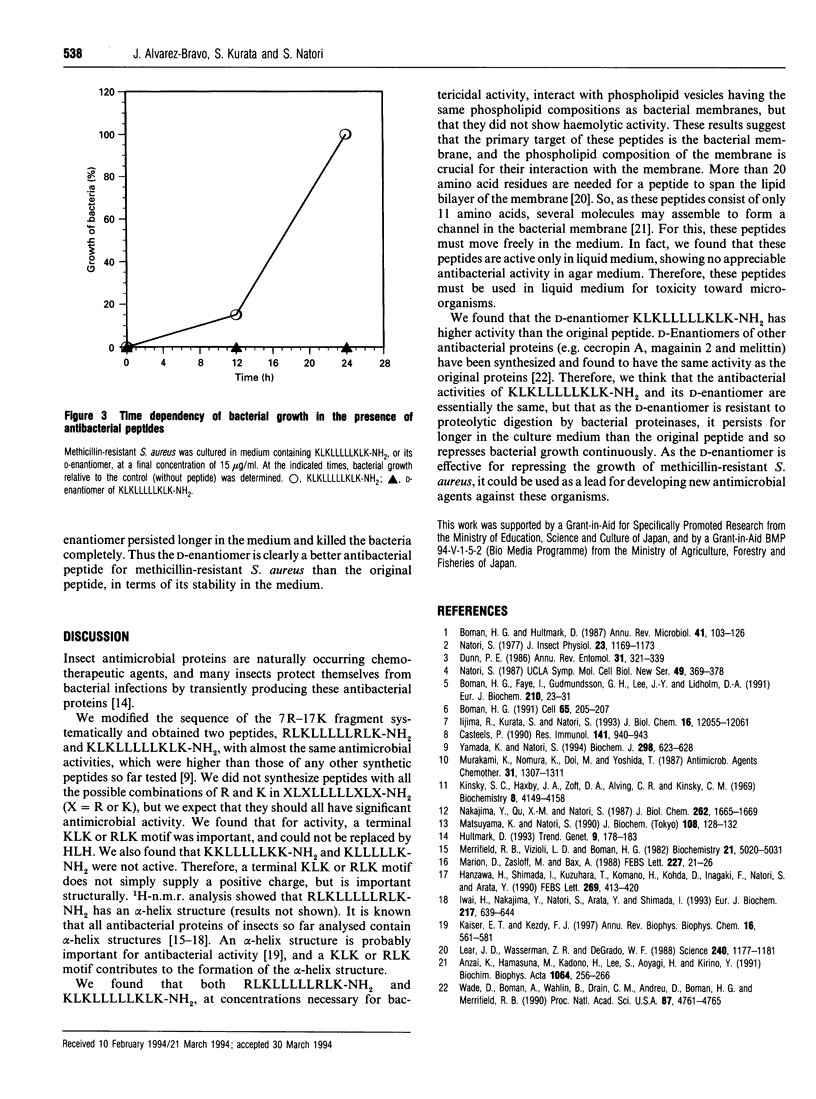
Previously, we identified a core undecapeptide of sapecin B having antimicrobial activity. Based on the structure of this peptide, we systematically synthesized peptides consisting of terminal basic motifs and internal oligo-leucine sequences and examined their antimicrobial activities. Of these peptides, RLKLLLLLRLK-NH2 and KLKLLLLLKLK-NH2 were found to have potent microbicidal activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, methicillin-resistant S. aureus and Candida albicans in liquid medium. We also synthesized the D-enantiomer of KLKLLLLLKLK-NH2. This enantiomer was resistant to tryptic digestion and persisted longer in the culture medium, showing greater antimicrobial activity than the original peptide.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anzai K., Hamasuna M., Kadono H., Lee S., Aoyagi H., Kirino Y. Formation of ion channels in planar lipid bilayer membranes by synthetic basic peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 7;1064(2):256–266. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G. Antibacterial peptides: key components needed in immunity. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):205–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90154-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Faye I., Gudmundsson G. H., Lee J. Y., Lidholm D. A. Cell-free immunity in Cecropia. A model system for antibacterial proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Oct 1;201(1):23–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G., Hultmark D. Cell-free immunity in insects. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:103–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casteels P. Possible applications of insect antibacterial peptides. Res Immunol. 1990 Nov-Dec;141(9):940–942. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(90)90199-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanzawa H., Shimada I., Kuzuhara T., Komano H., Kohda D., Inagaki F., Natori S., Arata Y. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance study of the solution conformation of an antibacterial protein, sapecin. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 3;269(2):413–420. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81206-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D. Immune reactions in Drosophila and other insects: a model for innate immunity. Trends Genet. 1993 May;9(5):178–183. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90165-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iijima R., Kurata S., Natori S. Purification, characterization, and cDNA cloning of an antifungal protein from the hemolymph of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly) larvae. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):12055–12061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwai H., Nakajima Y., Natori S., Arata Y., Shimada I. Solution conformation of an antibacterial peptide, sarcotoxin IA, as determined by 1H-NMR. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Oct 15;217(2):639–644. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser E. T., Kézdy F. J. Peptides with affinity for membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1987;16:561–581. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.16.060187.003021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C., Haxby J. A., Zopf D. A., Alving C. R., Kinsky C. B. Complement-dependent damage to liposomes prepared from pure lipids and Forssman hapten. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):4149–4158. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lear J. D., Wasserman Z. R., DeGrado W. F. Synthetic amphiphilic peptide models for protein ion channels. Science. 1988 May 27;240(4856):1177–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.2453923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion D., Zasloff M., Bax A. A two-dimensional NMR study of the antimicrobial peptide magainin 2. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 18;227(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81405-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama K., Natori S. Mode of action of sapecin, a novel antibacterial protein of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly). J Biochem. 1990 Jul;108(1):128–132. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield R. B., Vizioli L. D., Boman H. G. Synthesis of the antibacterial peptide cecropin A (1-33). Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 28;21(20):5020–5031. doi: 10.1021/bi00263a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Nomura K., Doi M., Yoshida T. Production of low-affinity penicillin-binding protein by low- and high-resistance groups of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1307–1311. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima Y., Qu X. M., Natori S. Interaction between liposomes and sarcotoxin IA, a potent antibacterial protein of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly). J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1665–1669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade D., Boman A., Wåhlin B., Drain C. M., Andreu D., Boman H. G., Merrifield R. B. All-D amino acid-containing channel-forming antibiotic peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4761–4765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Natori S. Characterization of the antimicrobial peptide derived from sapecin B, an antibacterial protein of Sarcophaga peregrina (flesh fly). Biochem J. 1994 Mar 15;298(Pt 3):623–628. doi: 10.1042/bj2980623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


