Abstract
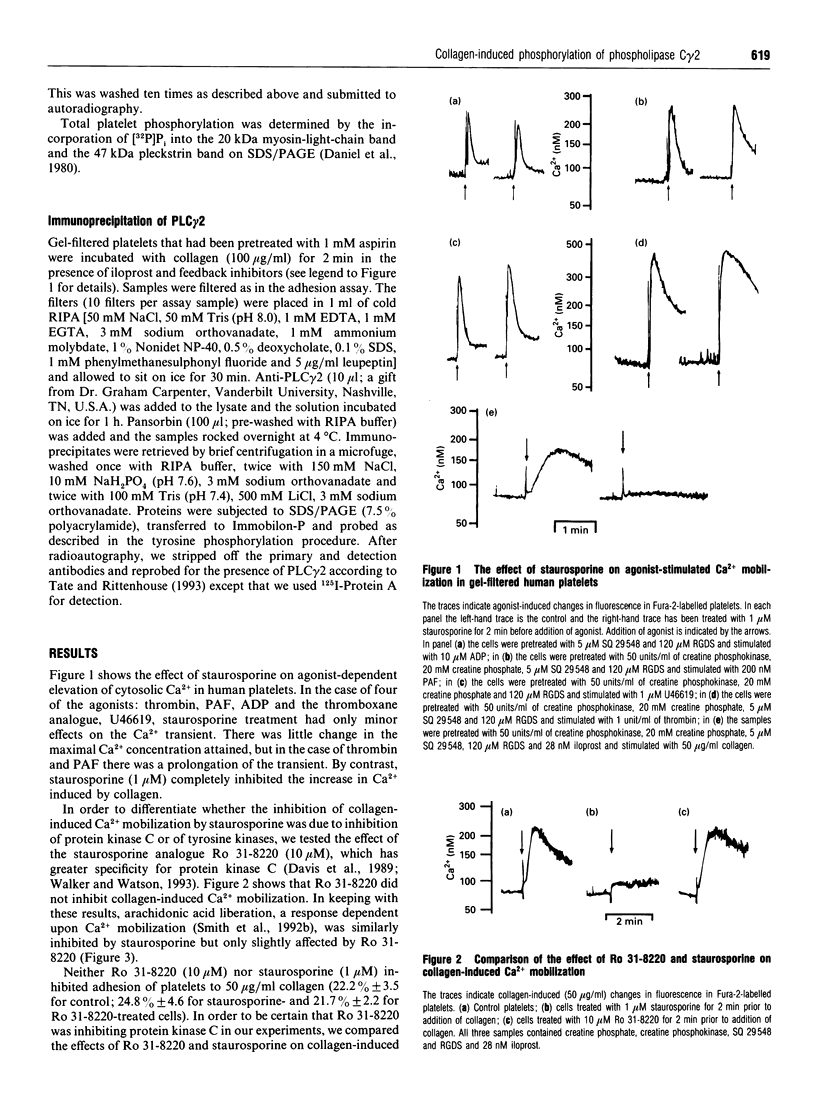
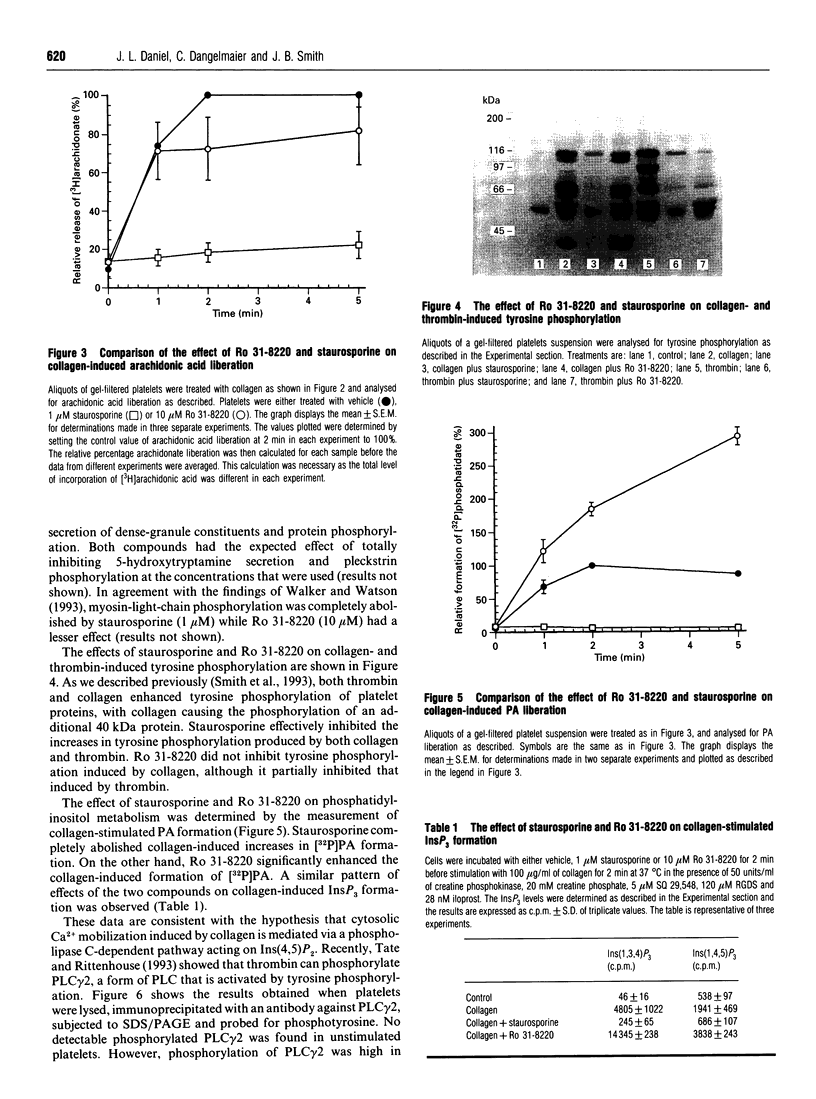
(1) The non-specific protein kinase C inhibitor, staurosporine, inhibited collagen-induced increases in cytosolic free Ca2+ while having no effect on Ca2+ mobilization by other platelet agonists. A more specific inhibitor of protein kinase C, Ro 31-8220, did not inhibit collagen-induced Ca2+ mobilization. Neither drug had an effect on platelet adhesion to collagen. (2) Staurosporine inhibited collagen-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation, while Ro 31-8220 had no effect. (3) It also inhibited collagen-induced phosphatidic acid formation, inositol trisphosphate formation and arachidonic acid liberation. (4) Ro 31-8220 did not inhibit collagen-stimulated arachidonic acid formation, but it enhanced collagen-stimulated phosphatidic acid and inositol trisphosphate formation. (5) Immunoprecipitation of phospholipase C gamma 2 (PLC gamma 2) with a specific antibody demonstrated that PLC gamma 2 was phosphorylated on tyrosine after stimulation by collagen. (6) The phosphorylation of PLC gamma 2 was inhibited by staurosporine but not by Ro 31-8220. These results provide additional evidence that the mechanism of signal transduction for collagen is different from other platelet agonists and indicate that it involves activation of PLC gamma through a tyrosine kinase-dependent mechanism.
Full text
PDF



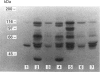
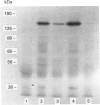
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake R. A., Walker T. R., Watson S. P. Activation of human platelets by peroxovanadate is associated with tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C gamma and formation of inositol phosphates. Biochem J. 1993 Mar 1;290(Pt 2):471–475. doi: 10.1042/bj2900471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cichowski K., McCormick F., Brugge J. S. p21rasGAP association with Fyn, Lyn, and Yes in thrombin-activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5025–5028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa J. L., Murphy D. L. Platelet 5-HT uptake and release stopped rapidly by formaldehyde. Nature. 1975 May 29;255(5507):407–408. doi: 10.1038/255407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J. L., Dangelmaier C. A., Smith J. B. Formation and metabolism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in human platelets. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 15;246(1):109–114. doi: 10.1042/bj2460109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J. L., Molish I. R., Holmsen H. Myosin phosphorylation in intact platelets. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7510–7514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. D., Hill C. H., Keech E., Lawton G., Nixon J. S., Sedgwick A. D., Wadsworth J., Westmacott D., Wilkinson S. E. Potent selective inhibitors of protein kinase C. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):61–63. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81494-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Platelet tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation is regulated by thrombin. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3603–3610. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation is regulated by glycoprotein IIb-IIIa in platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2234–2238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Brugge J. S., Shattil S. J. Role of platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa in agonist-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of platelet proteins. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3117–3127. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Brugge J. S. Thrombin treatment induces rapid changes in tyrosine phosphorylation in platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):901–905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Nemeth S. P., Brugge J. S. Blood platelets express high levels of the pp60c-src-specific tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):852–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak I. D., Corcoran M. L., Thompson P. A., Wahl L. M., Bolen J. B. Expression of p60fyn in human platelets. Oncogene. 1990 Apr;5(4):597–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. M., Bolen J. B., Barnwell J. W., Shattil S. J., Brugge J. S. Membrane glycoprotein IV (CD36) is physically associated with the Fyn, Lyn, and Yes protein-tyrosine kinases in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7844–7848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang R., Kucera G. L., Rittenhouse S. E. Elevated cytosolic Ca2+ activates phospholipase D in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1652–1655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg L. J., Earp H. S., Turner C. E., Prockop C., Juliano R. L. Signal transduction by integrins: increased protein tyrosine phosphorylation caused by clustering of beta 1 integrins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8392–8396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre D. E., McNicol A., Drummond A. H. Tumour-promoting phorbol esters inhibit agonist-induced phosphatidate formation and Ca2+ flux in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 28;180(2):160–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. R., Brass L. F. The role of GTP-binding proteins in platelet activation. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Oct 1;66(4):393–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi M., Jung S. M., Okuma M., Shinmyozu K. A patient with platelets deficient in glycoprotein VI that lack both collagen-induced aggregation and adhesion. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1440–1445. doi: 10.1172/JCI114318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta S., Taniguchi T., Asahi M., Kato Y., Nakagawara G., Yamamura H. Protein-tyrosine kinase p72syk is activated by wheat germ agglutinin in platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 30;185(3):1128–1132. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91743-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa K., Yamada K., Kazanietz M. G., Blumberg P. M., Beaven M. A. Different isozymes of protein kinase C mediate feedback inhibition of phospholipase C and stimulatory signals for exocytosis in rat RBL-2H3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2280–2283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulcinelli F. M., Gazzaniga P. P., Salganicoff L. Use of Zn-pyrophosphatase in the high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of cell extracts containing 32P-labelled inositol phosphates. J Chromatogr. 1992 Mar 13;575(1):51–55. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(92)80502-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumiglia K. M., Lau L. F., Huang C. K., Burroughs S., Feinstein M. B. Activation of signal transduction in platelets by the tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor pervanadate (vanadyl hydroperoxide). Biochem J. 1992 Sep 1;286(Pt 2):441–449. doi: 10.1042/bj2860441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rendu F., Eldor A., Grelac F., Bachelot C., Gazit A., Gilon C., Levy-Toledano S., Levitzki A. Inhibition of platelet activation by tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Sep 1;44(5):881–888. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samelson L. E., Phillips A. F., Luong E. T., Klausner R. D. Association of the fyn protein-tyrosine kinase with the T-cell antigen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4358–4362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro S. A., Rajpara S. M., Staatz W. D., Woods V. L., Jr Isolation and characterization of a platelet surface collagen binding complex related to VLA-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 31;153(1):217–223. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81211-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenker A., Goldsmith P., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M. The G protein coupled to the thromboxane A2 receptor in human platelets is a member of the novel Gq family. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9309–9313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Dangelmaier C., Daniel J. L. Elevation of cAMP in human platelets inhibits thrombin- but not collagen-induced tyrosine phosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Mar 15;191(2):695–700. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Dangelmaier C. Determination of platelet adhesion to collagen and the associated formation of phosphatidic acid and calcium mobilization. Anal Biochem. 1990 May 15;187(1):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90437-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Dangelmaier C., Mauco G. Measurement of arachidonic acid liberation in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Use of agents that inhibit both the cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 9;835(2):344–351. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90290-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Dangelmaier C., Selak M. A., Ashby B., Daniel J. Cyclic AMP does not inhibit collagen-induced platelet signal transduction. Biochem J. 1992 May 1;283(Pt 3):889–892. doi: 10.1042/bj2830889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Dangelmaier C., Selak M. A., Daniel J. L. Facile platelet adhesion to collagen requires metabolic energy and actin polymerization and evokes intracellular free calcium mobilization. J Cell Biochem. 1991 Sep;47(1):54–61. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240470108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Selak M. A., Dangelmaier C., Daniel J. L. Cytosolic calcium as a second messenger for collagen-induced platelet responses. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 15;288(Pt 3):925–929. doi: 10.1042/bj2880925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandon N. N., Kralisz U., Jamieson G. A. Identification of glycoprotein IV (CD36) as a primary receptor for platelet-collagen adhesion. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7576–7583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate B. F., Rittenhouse S. E. Thrombin activation of human platelets causes tyrosine phosphorylation of PLC-gamma 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Sep 13;1178(3):281–285. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90205-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Bolen J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhallen P. F., Bevers E. M., Comfurius P., Zwaal R. F. Fluoride-dependent calcium-induced platelet procoagulant activity shows that calpain is involved in increased phospholipid transbilayer movement. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jul 7;942(1):150–158. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90284-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. R., Watson S. P. Synergy between Ca2+ and protein kinase C is the major factor in determining the level of secretion from human platelets. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 1;289(Pt 1):277–282. doi: 10.1042/bj2890277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Kakiuchi T., Mizuguchi J., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Association of B cell antigen receptor with protein tyrosine kinase Lyn. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):192–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1702903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberman Y., Gutman Y. Multiple effects of staurosporine, a kinase inhibitor, on thymocyte functions. Comparison with the effect of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Oct 20;44(8):1563–1568. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90473-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]