Abstract
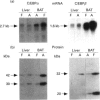
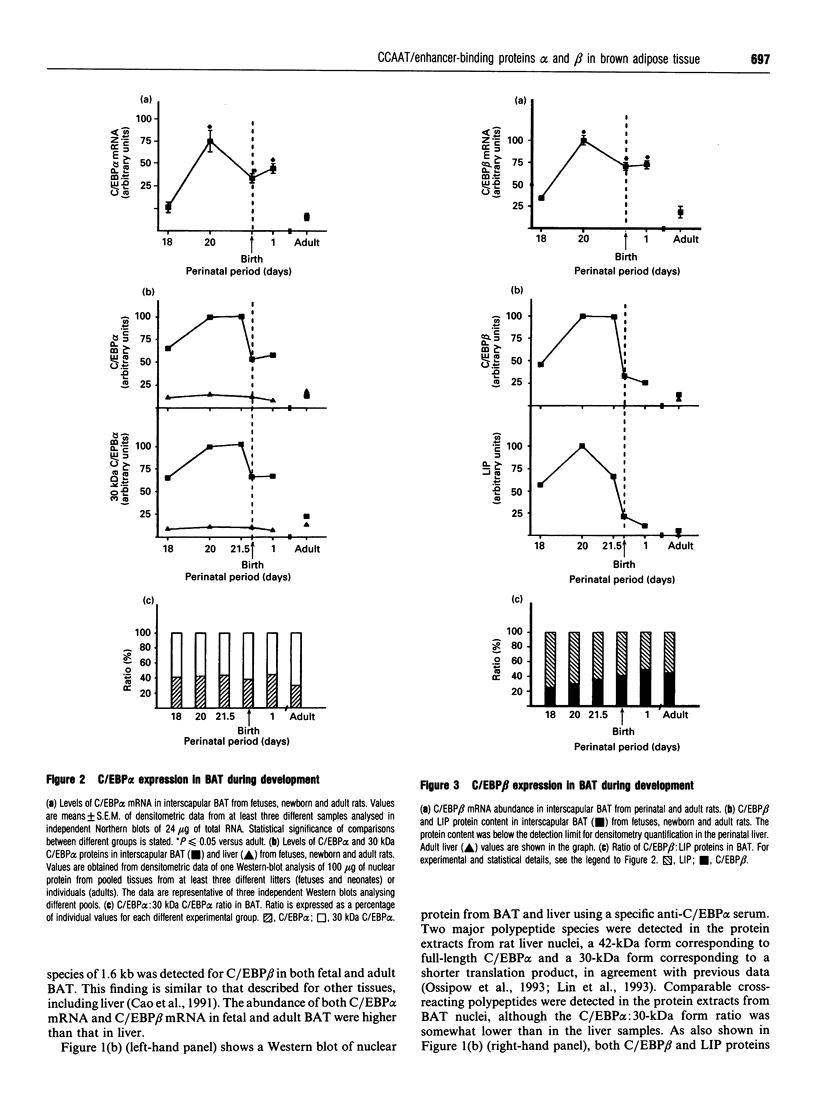
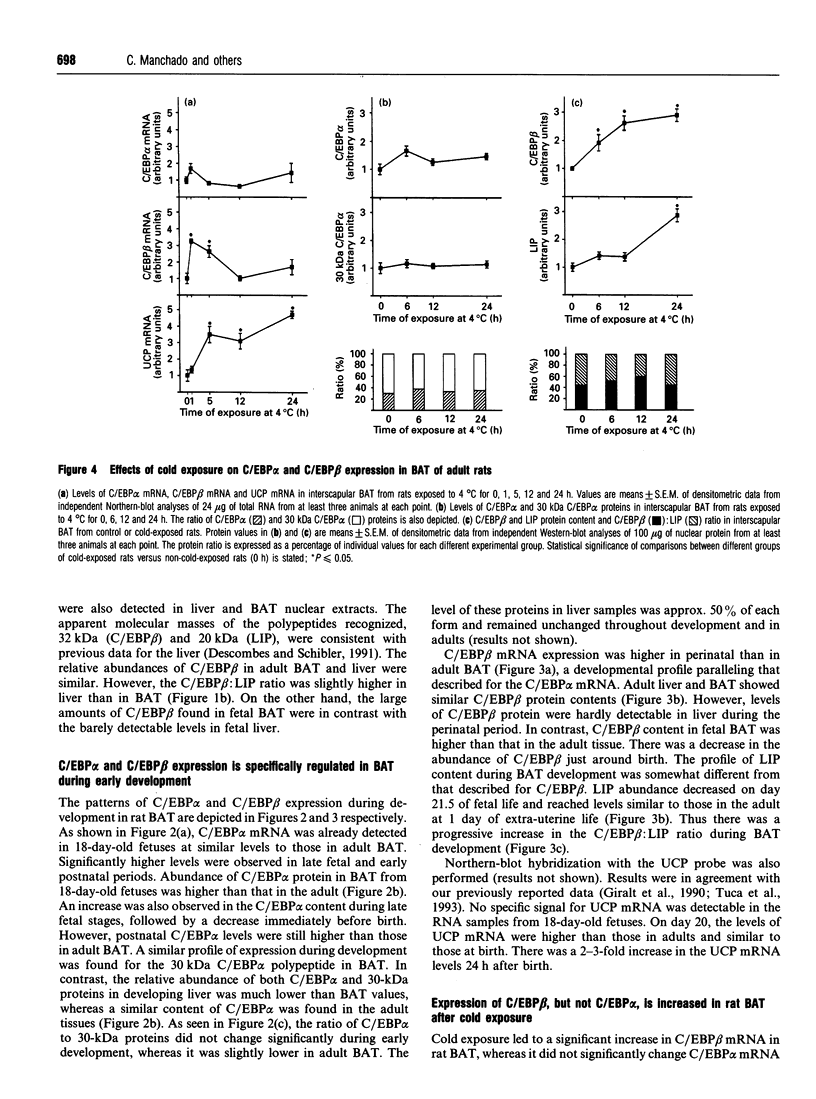
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) alpha mRNA and its protein products C/EBP alpha and 30 kDa C/EBP alpha are expressed in rat brown-adipose tissue. Results also demonstrate the expression of C/EBP beta mRNA and its protein products C/EBP beta and liver inhibitory protein (LIP) in the tissue. The abundance of C/EBP alpha and C/EBP beta proteins in adult brown fat is similar to that found in adult liver. However, the expression of C/EBP alpha and C/EBP beta is specifically regulated in brown fat during development. C/EBP alpha, 30 kDa C/EBP alpha, C/EBP beta and LIP content is several-fold higher in fetal brown fat than in the adult tissue, or liver at any stage of development. Peak values are attained in late fetal life, in concurrence with the onset of transcription of the uncoupling protein (UCP) gene, the molecular marker of terminal brown-adipocyte differentiation. When adult rats are exposed to a cold environment, which is a physiological stimulus of brown-adipose tissue hyperplasia and UCP gene expression, a specific rise in C/EBP beta expression with respect to C/EBP alpha, 30 kDa C/EBP alpha and LIP is observed. Present data suggest that the C/EBP family of transcription factors has an important role in the development and terminal differentiation of brown-adipose tissue.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco A. C., Kieffer J. D., Silva J. E. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and thyroid hormone control of uncoupling protein messenger ribonucleic acid in freshly dispersed brown adipocytes. Endocrinology. 1992 May;130(5):2625–2633. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.5.1374009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco A. C., Sheng X. Y., Silva J. E. Triiodothyronine amplifies norepinephrine stimulation of uncoupling protein gene transcription by a mechanism not requiring protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18168–18175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Gwynn B., Howard S., Jerry J., Gordon J. I., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and genetic mapping of the gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1146–1156. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouillaud F., Ricquier D., Mory G., Thibault J. Increased level of mRNA for the uncoupling protein in brown adipose tissue of rats during thermogenesis induced by cold exposure or norepinephrine infusion. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11583–11586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouillaud F., Ricquier D., Thibault J., Weissenbach J. Molecular approach to thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue: cDNA cloning of the mitochondrial uncoupling protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):445–448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowiecki L. J., Géloën A., Collet A. J. Proliferation and differentiation of brown adipocytes from interstitial cells during cold acclimation. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 1):C880–C887. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.6.C880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Z., Umek R. M., McKnight S. L. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1538–1552. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. J., Chen T. T., Lei H. Y., Chen D. S., Lee S. C. Molecular cloning of a transcription factor, AGP/EBP, that belongs to members of the C/EBP family. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6642–6653. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy R. J., Yang V. W., Ntambi J. M., Geiman D. E., Landschulz W. H., Friedman A. D., Nakabeppu Y., Kelly T. J., Lane M. D. Differentiation-induced gene expression in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein interacts with and activates the promoters of two adipocyte-specific genes. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1323–1335. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Schibler U. A liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein, LAP, and a transcriptional inhibitory protein, LIP, are translated from the same mRNA. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):569–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein activates the promoter of the serum albumin gene in cultured hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1314–1322. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giralt M., Martin I., Iglesias R., Viñas O., Villarroya F., Mampel T. Ontogeny and perinatal modulation of gene expression in rat brown adipose tissue. Unaltered iodothyronine 5'-deiodinase activity is necessary for the response to environmental temperature at birth. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Oct 5;193(1):297–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19336.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giralt M., Martin I., Mampel T., Villarroya F., Iglesias R., Viñas O. Evidence for a differential physiological modulation of brown fat iodothyronine 5'-deiodinase activity in the perinatal period. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):493–499. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80868-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giralt M., Park E. A., Gurney A. L., Liu J. S., Hakimi P., Hanson R. W. Identification of a thyroid hormone response element in the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene. Evidence for synergistic interaction between thyroid hormone and cAMP cis-regulatory elements. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21991–21996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Strube M., Mueckler M. Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):83–87. doi: 10.1038/338083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Christy R. J., Lane M. D. Mouse insulin-responsive glucose transporter gene: characterization of the gene and trans-activation by the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):251–255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb P., McKnight S. L. Diversity and specificity in transcriptional regulation: the benefits of heterotypic dimerization. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):417–422. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90167-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. T., Lane M. D. Antisense CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein RNA suppresses coordinate gene expression and triglyceride accumulation during differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):533–544. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. T., MacDougald O. A., Diehl A. M., Lane M. D. A 30-kDa alternative translation product of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha message: transcriptional activator lacking antimitotic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9606–9610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mory G., Bouillaud F., Combes-George M., Ricquier D. Noradrenaline controls the concentration of the uncoupling protein in brown adipose tissue. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 30;166(2):393–396. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikami H., Shimizu Y., Endoh D., Yano H., Saito M. Cold exposure increases glucose utilization and glucose transporter expression in brown adipose tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 30;185(3):1078–1082. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91736-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossipow V., Descombes P., Schibler U. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein mRNA is translated into multiple proteins with different transcription activation potentials. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8219–8223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park E. A., Gurney A. L., Nizielski S. E., Hakimi P., Cao Z., Moorman A., Hanson R. W. Relative roles of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta and cAMP regulatory element-binding protein in controlling transcription of the gene for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):613–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park E. A., Roesler W. J., Liu J., Klemm D. J., Gurney A. L., Thatcher J. D., Shuman J., Friedman A., Hanson R. W. The role of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein in the transcriptional regulation of the gene for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6264–6272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Mancini F. P., Cortese R. IL-6DBP, a nuclear protein involved in interleukin-6 signal transduction, defines a new family of leucine zipper proteins related to C/EBP. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90459-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehnmark S., Antonson P., Xanthopoulos K. G., Jacobsson A. Differential adrenergic regulation of C/EBP alpha and C/EBP beta in brown adipose tissue. FEBS Lett. 1993 Mar 8;318(3):235–241. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80519-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricquier D., Bouillaud F., Toumelin P., Mory G., Bazin R., Arch J., Pénicaud L. Expression of uncoupling protein mRNA in thermogenic or weakly thermogenic brown adipose tissue. Evidence for a rapid beta-adrenoreceptor-mediated and transcriptionally regulated step during activation of thermogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):13905–13910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricquier D., Raimbault S., Champigny O., Miroux B., Bouillaud F. Comment to Shinohara et al. (1991) FEBS Letters 293, 173-174. The uncoupling protein is not expressed in rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1992 May 25;303(1):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Habener J. F. CHOP, a novel developmentally regulated nuclear protein that dimerizes with transcription factors C/EBP and LAP and functions as a dominant-negative inhibitor of gene transcription. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):439–453. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson L., Strömberg K., Vikman K., Bjursell G., Enerbäck S. The CCAAT/enhancer binding protein and its role in adipocyte differentiation: evidence for direct involvement in terminal adipocyte development. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3787–3793. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04948.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santalucía T., Camps M., Castelló A., Muñoz P., Nuel A., Testar X., Palacin M., Zorzano A. Developmental regulation of GLUT-1 (erythroid/Hep G2) and GLUT-4 (muscle/fat) glucose transporter expression in rat heart, skeletal muscle, and brown adipose tissue. Endocrinology. 1992 Feb;130(2):837–846. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.2.1370797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuca A., Giralt M., Villarroya F., Viñas O., Mampel T., Iglesias R. Ontogeny of thyroid hormone receptors and c-erbA expression during brown adipose tissue development: evidence of fetal acquisition of the mature thyroid status. Endocrinology. 1993 May;132(5):1913–1920. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.5.8386604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umek R. M., Friedman A. D., McKnight S. L. CCAAT-enhancer binding protein: a component of a differentiation switch. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):288–292. doi: 10.1126/science.1987644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. C., Cantwell C. A., Johnson P. F. A family of C/EBP-related proteins capable of forming covalently linked leucine zipper dimers in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1553–1567. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yubero P., Manchado C., Cassard-Doulcier A. M., Mampel T., Viñas O., Iglesias R., Giralt M., Villarroya F. CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins alpha and beta are transcriptional activators of the brown fat uncoupling protein gene promoter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jan 28;198(2):653–659. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer D. B., Magnuson M. A. Immunohistochemical localization of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase in adult and developing mouse tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1990 Feb;38(2):171–178. doi: 10.1177/38.2.1688895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]