Abstract
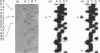
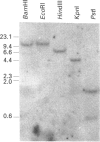
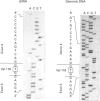
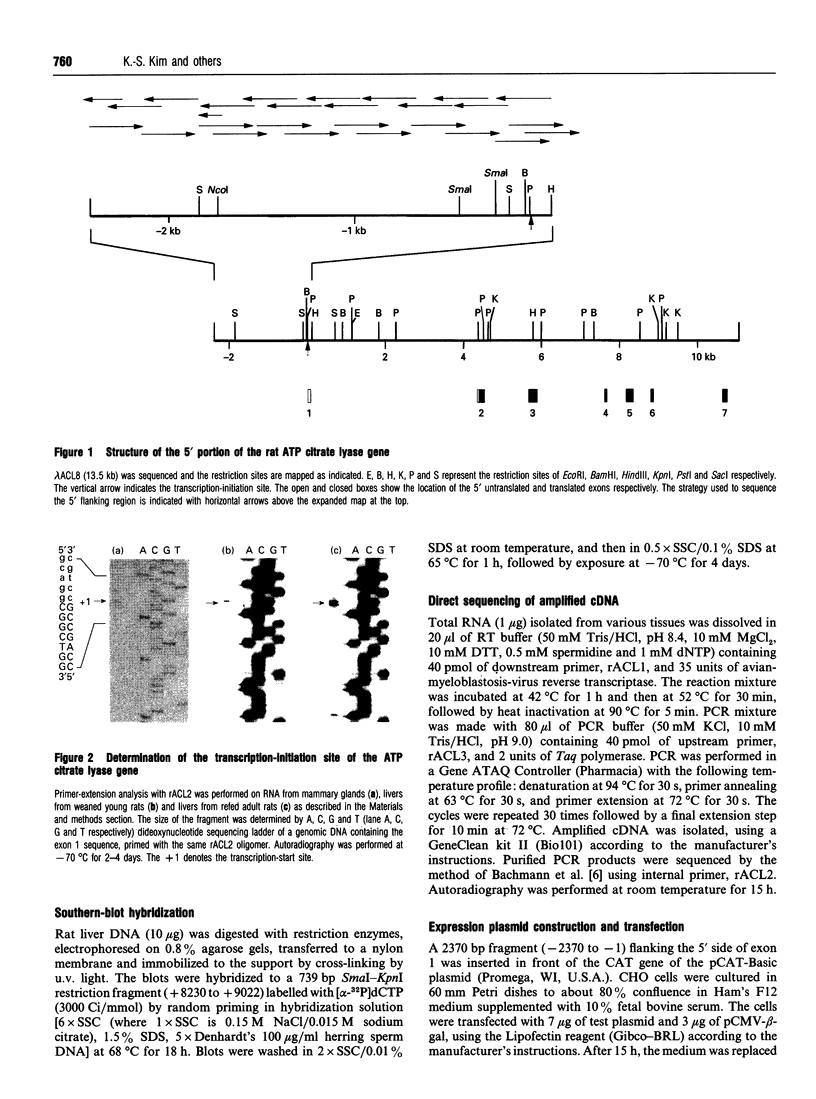
A genomic clone, encompassing the 5' flanking region and the first seven exons of rat ATP citrate lyase gene, was isolated from a rat genomic library and sequenced. Primer-extension analysis showed that mRNA is transcribed at 4407 nucleotides upstream from the translation start site. Primer-extension analysis and sequencing of ATP citrate lyase cDNA amplified by PCR showed that the promoter used for transcription is identical in mammary gland, lung, liver, brain and kidney. Southern-blot analysis showed that the ATP citrate lyase gene exists as a single copy. The 5' flanking region contains several consensus sequences defined as promoter elements. These include a CAAT box and Sp1-binding sites. However, a TATA box lacks this promoter. The expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene was induced by the 5' flanking region (-2370 to -1) in the CHO cell line. The 5' flanking region also contains several sequence elements that may be involved in the transcriptional regulation of the gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M. C., Lomanto M., Nasrin N., Ramaika C. Insulin stimulates glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene expression through cis-acting DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5092–5096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- An G., Hidaka K., Siminovitch L. Expression of bacterial beta-galactosidase in animal cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1628–1632. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B., Lüke W., Hunsmann G. Improvement of PCR amplified DNA sequencing with the aid of detergents. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1309–1309. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back D. W., Wilson S. B., Morris S. M., Jr, Goodridge A. G. Hormonal regulation of lipogenic enzymes in chick embryo hepatocytes in culture. Thyroid hormone and glucagon regulate malic enzyme mRNA level at post-transcriptional steps. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12555–12561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batenburg J. J., Elfring R. H. Pre-translational regulation by glucocorticoid of fatty acid and phosphatidylcholine synthesis in type II cells from fetal rat lung. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 28;307(2):164–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80759-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. T., Davis C. M., Chrapkiewicz N. B., Granner D. K. Reciprocal regulation of gene transcription by insulin. Inhibition of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene and stimulation of gene 33 in a single cell type. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13007–13011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Morgan J. G., Campbell L. A., Fourel G., Crabtree G. R. Interaction of a liver-specific nuclear factor with the fibrinogen and alpha 1-antitrypsin promoters. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):688–692. doi: 10.1126/science.3499668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Near J. C., Kmetz P. J., Sathe G. M., Southan C., Strickler J. E., Gross M., Young J. F., Wells T. N., Groot P. H. Rat ATP citrate-lyase. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of a full-length cDNA and mRNA abundance as a function of diet, organ, and age. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1430–1435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda H., Katsurada A., Iritani N. Effects of nutrients and hormones on gene expression of ATP citrate-lyase in rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Oct 1;209(1):217–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gharbi-Chihi J., Facchinetti T., Bergé-Lefranc J. L., Bonne J., Torresani J. Triiodothyronine control of ATP-citrate lyase and malic enzyme during differentiation of a murine preadipocyte cell line. Horm Metab Res. 1991 Sep;23(9):423–427. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C. R., Ro J. H., Dobson D. E., Min H. Y., Spiegelman B. M. Adipocyte P2 gene: developmental expression and homology of 5'-flanking sequences among fat cell-specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3786–3790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNACKER M. S., LOWENSTEIN J. M. CITRATE AND THE CONVERSION OF CARBOHYDRATE INTO FAT. THE ACTIVITIES OF CITRATE-CLEAVAGE ENZYME AND ACETATE THIOKINASE IN LIVERS OF STARVED AND RE-FED RATS. Biochem J. 1965 Jan;94:209–215. doi: 10.1042/bj0940209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsurada A., Iritani N., Fukuda H., Noguchi T., Tanaka T. Effects of dietary nutrients on lipogenic enzyme and mRNA activities in rat liver during induction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 18;877(3):350–358. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90199-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Park S. W., Kim Y. S. Regulation of ATP-citrate lyase at transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 30;189(1):264–271. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91553-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas P. C., Granner D. K. Hormone response domains in gene transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1131–1173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo X. C., Kim K. H. An enhancer element in the house-keeping promoter for acetyl-CoA carboxylase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3249–3254. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo X. C., Park K., Lopez-Casillas F., Kim K. H. Structural features of the acetyl-CoA carboxylase gene: mechanisms for the generation of mRNAs with 5' end heterogeneity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4042–4046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson M. A., Andreone T. L., Printz R. L., Koch S., Granner D. K. Rat glucokinase gene: structure and regulation by insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4838–4842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micossi L. G., Tomaszewicz M., Bielarczyk H., Luszawska D., Trognoni A., Szutowicz A. Effect of angiotensin II and eledoisin on cholinergic neurons in rat hippocampus. Neuroreport. 1992 Jan;3(1):36–38. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199201000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. M., Lucas P. C., Forest C. D., Magnuson M. A., Granner D. K. Identification of a sequence in the PEPCK gene that mediates a negative effect of insulin on transcription. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):533–537. doi: 10.1126/science.2166335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Rosenberg M. P., Keller S. A., Meisler M. H. Tissue-specific and insulin-dependent expression of a pancreatic amylase gene in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):326–334. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulauskis J. D., Sul H. S. Hormonal regulation of mouse fatty acid synthase gene transcription in liver. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):574–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP and the induction of eukaryotic gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9063–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roncero C., Lorenzo M., Fabregat I., Benito M. Rates of lipogenesis in fetal hepatocytes in suspension and in primary culture: hormonal effects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 15;1012(3):320–324. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90115-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan A. C., Triscari J., Hamilton J. G., Miller O. N., Wheatley V. R. Effect of (-)-hydroxycitrate upon the accumulation of lipid in the rat. I. Lipogenesis. Lipids. 1974 Feb;9(2):121–128. doi: 10.1007/BF02532136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]