Abstract
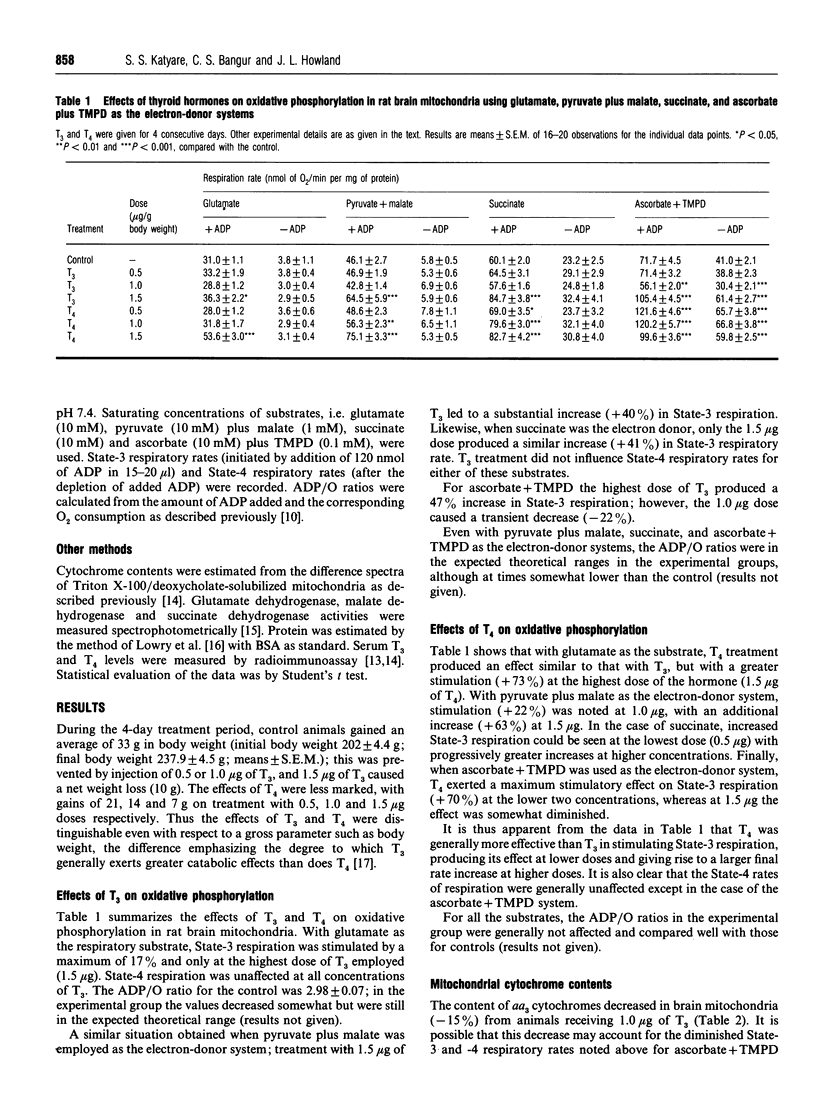
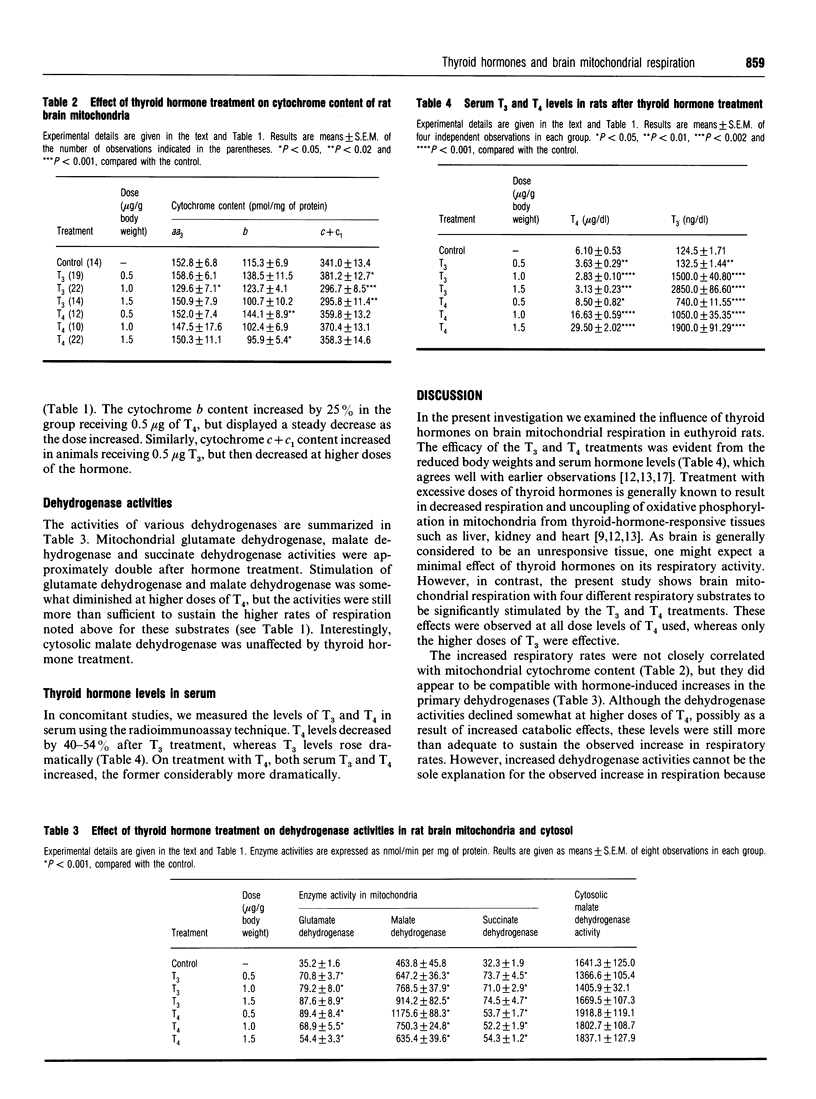
The effects of in vivo treatment with graded doses (0.5-1.5 micrograms/g body weight) of thyroid hormones, tri-iodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), for 4 consecutive days to euthyroid rats on the respiratory activity of isolated brain mitochondria were examined. T4 stimulated coupled State-3 respiration with glutamate, pyruvate + malate, ascorbate + tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine and succinate, in a dose-dependent manner; T3 was effective only at the highest (1.5 micrograms) dose employed. T4 was more effective than T3 in stimulating respiratory activity. State-4 respiratory rates were in general not influenced except in the case of the ascorbate + tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine system. Primary dehydrogenase activities, i.e. glutamate dehydrogenase, malate dehydrogenase and succinate dehydrogenase, were stimulated about 2-fold; interestingly mitochondrial but not cytosolic malate dehydrogenase activity was influenced under these conditions. The hormone treatments did not greatly influence the mitochondrial cytochrome content. The results therefore suggest that thyroid hormone treatment not only stimulates primary dehydrogenase activities but may also directly influence the process of mitochondrial electron transfer.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Daum G. Lipids of mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 12;822(1):1–42. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dussault J. H., Ruel J. Thyroid hormones and brain development. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:321–334. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAZEKAS J. F., GRAVES F. B., ALMAN R. W. The influence of the thyroid on cerebral metabolism. Endocrinology. 1951 Feb;48(2):169–174. doi: 10.1210/endo-48-2-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemon P. Malate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) (NADP) and alpha-glycerophosphate oxidase in the developing rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 25;151(3):681–683. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katyare S. S., Fatterpaker P., Sreenivasan A. Heterogeneity of rat liver mitochondrial fractions and the effect of tri-iodothyronine on their protein turnover. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(1):111–121. doi: 10.1042/bj1180111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katyare S. S., Joshi M. V., Fatterpaker P., Sreenivasan A. Effect of thyroid deficiency on oxidative phosphorylation in rat liver, kidney, and brain mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jul;182(1):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90294-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katyare S. S., Satav J. G. Impaired mitochondrial oxidative energy metabolism following paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan;96(1):51–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11783.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE Y. P., LARDY H. A. INFLUENCE OF THYROID HORMONES ON L-ALPHA-GLYCEROPHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASES AND OTHER DEHYDROGENASES IN VARIOUS ORGANS OF THE RAT. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1427–1436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H. Thyroid hormone action at the cellular level. Science. 1979 Mar 9;203(4384):971–979. doi: 10.1126/science.218285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puymirat J. Thyroid receptors in the rat brain. Prog Neurobiol. 1992 Sep;39(3):281–294. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(92)90019-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISS J. M., REISS M., WYATT A. Action of thyroid hormones on brain metabolism of newborn rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Oct;93(1):19–22. doi: 10.3181/00379727-93-22650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajan R. R., Katyare S. S. Effect of 3,5,3'-tri-iodothyronine on cellular growth and oxygen consumption in neonatal rat brain. Experientia. 1982 Sep 15;38(9):1110–1114. doi: 10.1007/BF01955395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajan R. R., Katyare S. S. Is the first site of phosphorylation operative in rat brain mitochondria in early neonatal life? A critical re-evaluation. Mech Ageing Dev. 1991 Dec 2;61(2):149–161. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(91)90013-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satav J. G., Katyare S. S. Effect of experimental thyrotoxicosis on oxidative phosphorylation in rat liver, kidney and brain mitochondria. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1982 Oct;28(2):173–189. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(82)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satav J. G., Katyare S. S. Thyroid hormones and cathepsin D activity in the rat liver, kidney and brain. Experientia. 1981 Jan 15;37(1):100–102. doi: 10.1007/BF01965594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz H. L., Oppenheimer J. H. Nuclear triiodothyronine receptor sites in brain: probable identity with hepatic receptors and regional distribution. Endocrinology. 1978 Jul;103(1):267–273. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-1-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S., Percin C. J. Thyroid hormone induction of alpha-glycerophosphate dehydrogenase in rats of different ages. Endocrinology. 1966 Dec;79(6):1075–1078. doi: 10.1210/endo-79-6-1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs C. D., Smith A. D. The modification of mammalian membrane polyunsaturated fatty acid composition in relation to membrane fluidity and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 27;779(1):89–137. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(84)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timiras P. S., Nzekwe E. U. Thyroid hormones and nervous system development. Biol Neonate. 1989;55(6):376–385. doi: 10.1159/000242941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


