Abstract
A protein segment consisting of the C-terminal 87 residues of the biotin carboxy carrier protein from Escherichia coli acetyl-CoA carboxylase was overexpressed in E. coli. The expressed biotin-domain peptide can be fully biotinylated by coexpression with a plasmid that overproduces E. coli biotin ligase. The extent of biotinylation was limited in vivo, but could be taken to completion in cell lysates on addition of ATP and biotin. We used the coexpression of biotin ligase and acceptor protein to label the biotin-domain peptide in vitro with [3H]biotin, which greatly facilitated development of a purification procedure. The apo (unbiotinylated) form of the protein was prepared by induction of biotin-domain expression in a strain lacking the biotin-ligase-overproduction plasmid. The apo domain could be separated from the biotinylated protein by ion-exchange chromatography or non-denaturing PAGE, and was converted into the biotinylated form of the peptide on addition of purified biotin ligase. The identify of the purified biotin-domain peptide was confirmed by N-terminal sequence analysis, amino acid analysis and m.s. The domain was readily produced and purified in sufficient quantities for n.m.r. structural analysis.
Full text
PDF


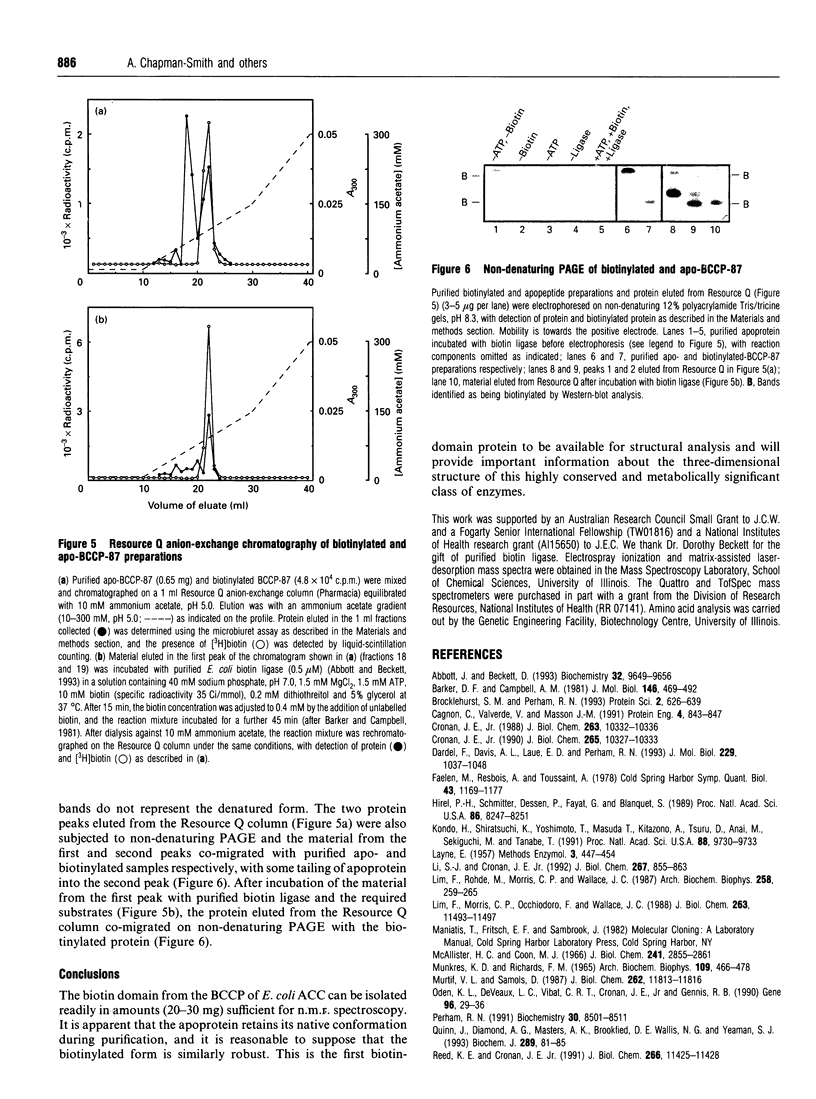

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott J., Beckett D. Cooperative binding of the Escherichia coli repressor of biotin biosynthesis to the biotin operator sequence. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 21;32(37):9649–9656. doi: 10.1021/bi00088a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. F., Campbell A. M. Genetic and biochemical characterization of the birA gene and its product: evidence for a direct role of biotin holoenzyme synthetase in repression of the biotin operon in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 15;146(4):469–492. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst S. M., Perham R. N. Prediction of the three-dimensional structures of the biotinylated domain from yeast pyruvate carboxylase and of the lipoylated H-protein from the pea leaf glycine cleavage system: a new automated method for the prediction of protein tertiary structure. Protein Sci. 1993 Apr;2(4):626–639. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cagnon C., Valverde V., Masson J. M. A new family of sugar-inducible expression vectors for Escherichia coli. Protein Eng. 1991 Oct;4(7):843–847. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.7.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronan J. E., Jr Biotination of proteins in vivo. A post-translational modification to label, purify, and study proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10327–10333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronan J. E., Jr Expression of the biotin biosynthetic operon of Escherichia coli is regulated by the rate of protein biotination. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10332–10336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dardel F., Davis A. L., Laue E. D., Perham R. N. Three-dimensional structure of the lipoyl domain from Bacillus stearothermophilus pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex. J Mol Biol. 1993 Feb 20;229(4):1037–1048. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faelen M., Resibois A., Toussaint A. Mini-mu: an insertion element derived from temperate phage mu-1. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1169–1177. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirel P. H., Schmitter M. J., Dessen P., Fayat G., Blanquet S. Extent of N-terminal methionine excision from Escherichia coli proteins is governed by the side-chain length of the penultimate amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8247–8251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo H., Shiratsuchi K., Yoshimoto T., Masuda T., Kitazono A., Tsuru D., Anai M., Sekiguchi M., Tanabe T. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase from Escherichia coli: gene organization and nucleotide sequence of the biotin carboxylase subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9730–9733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. J., Cronan J. E., Jr The gene encoding the biotin carboxylase subunit of Escherichia coli acetyl-CoA carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):855–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim F., Morris C. P., Occhiodoro F., Wallace J. C. Sequence and domain structure of yeast pyruvate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11493–11497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim F., Rohde M., Morris C. P., Wallace J. C. Pyruvate carboxylase in the yeast pyc mutant. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Oct;258(1):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90343-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNKRES K. D., RICHARDS F. M. THE PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF NEUROSPORA MALATE DEHYDROGENASE. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Mar;109:466–479. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90391-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister H. C., Coon M. J. Further studies on the properties of liver propionyl coenzyme A holocarboxylase synthetase and the specificity of holocarboxylase formation. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jun 25;241(12):2855–2861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murtif V. L., Samols D. Mutagenesis affecting the carboxyl terminus of the biotinyl subunit of transcarboxylase. Effects on biotination. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11813–11816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oden K. L., DeVeaux L. C., Vibat C. R., Cronan J. E., Jr, Gennis R. B. Genomic replacement in Escherichia coli K-12 using covalently closed circular plasmid DNA. Gene. 1990 Nov 30;96(1):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90337-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N. Domains, motifs, and linkers in 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes: a paradigm in the design of a multifunctional protein. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 3;30(35):8501–8512. doi: 10.1021/bi00099a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J., Diamond A. G., Masters A. K., Brookfield D. E., Wallis N. G., Yeaman S. J. Expression and lipoylation in Escherichia coli of the inner lipoyl domain of the E2 component of the human pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 1;289(Pt 1):81–85. doi: 10.1042/bj2890081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. E., Cronan J. E., Jr Escherichia coli exports previously folded and biotinated protein domains. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11425–11428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock C. O., Cronan J. E., Jr Improved purification of acyl carrier protein. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):362–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90168-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samols D., Thornton C. G., Murtif V. L., Kumar G. K., Haase F. C., Wood H. G. Evolutionary conservation among biotin enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6461–6464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenoy B. C., Wood H. G. Purification and properties of the synthetase catalyzing the biotination of the aposubunit of transcarboxylase from Propionibacterium shermanii. FASEB J. 1988 May;2(8):2396–2401. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.8.3360240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenoy B. C., Xie Y., Park V. L., Kumar G. K., Beegen H., Wood H. G., Samols D. The importance of methionine residues for the catalysis of the biotin enzyme, transcarboxylase. Analysis by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18407–18412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]