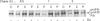Abstract
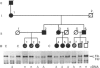
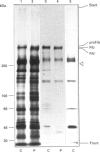
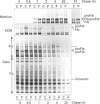
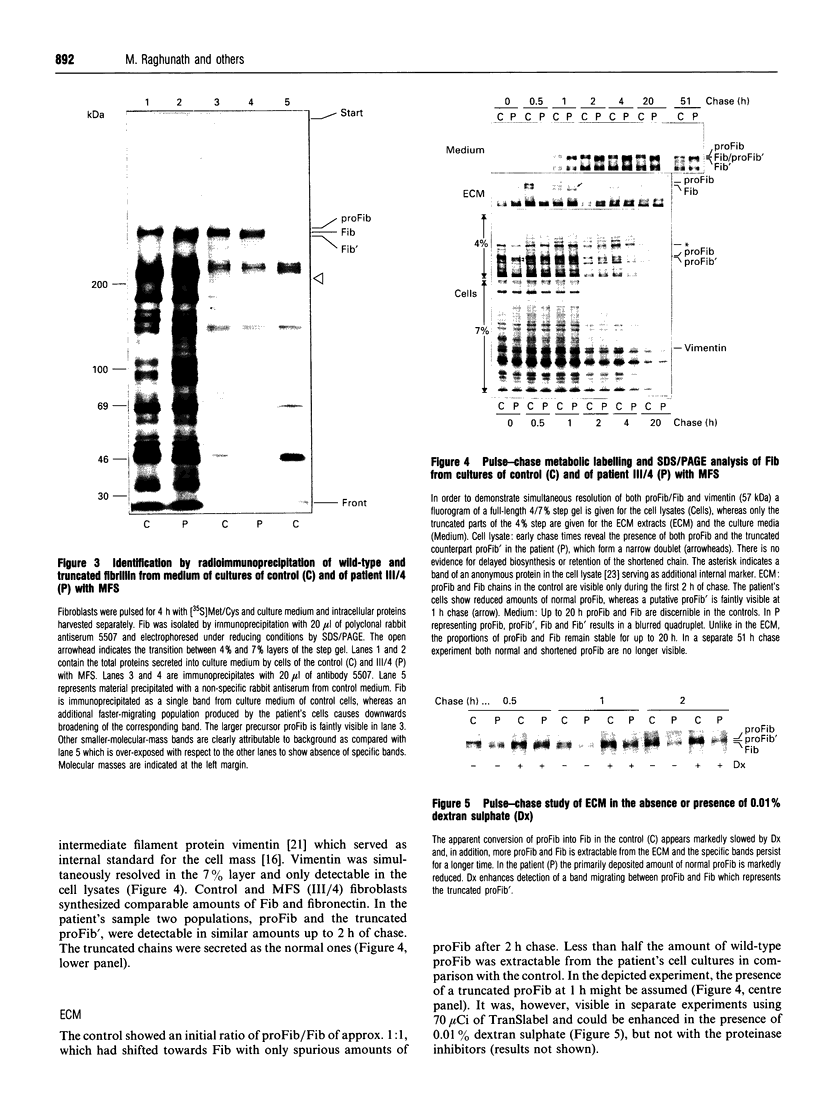
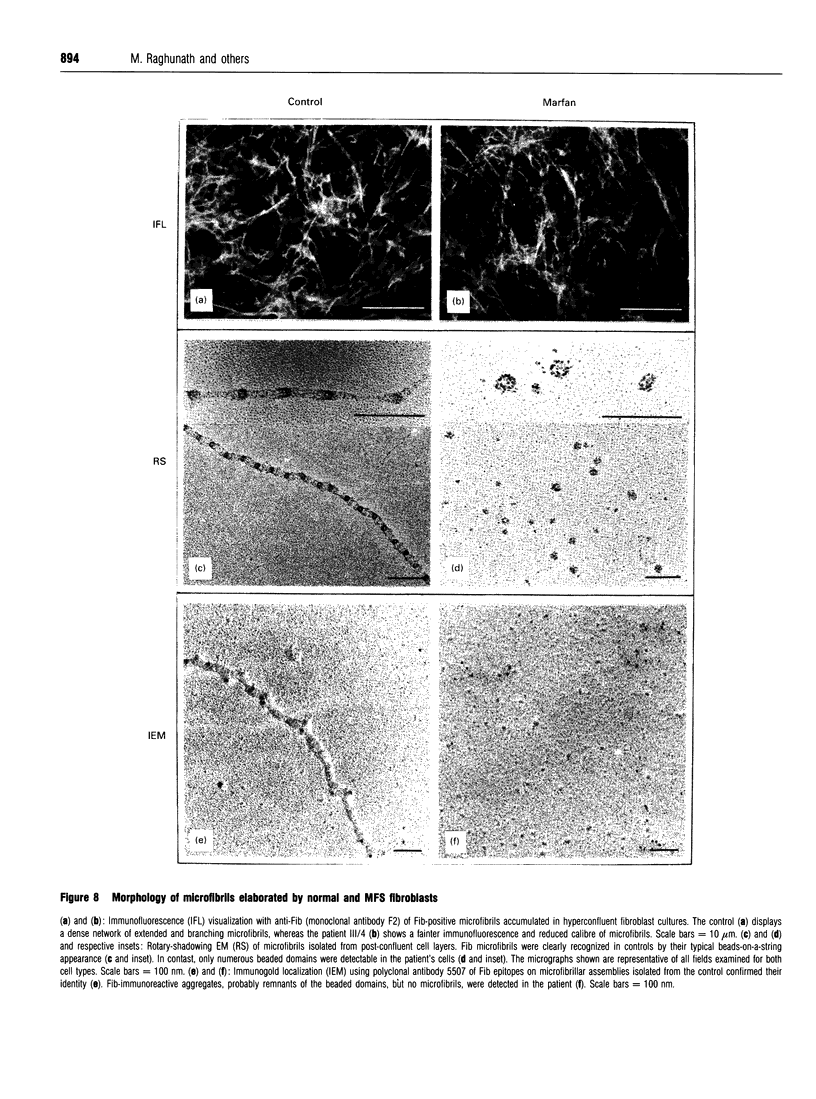
We studied fibrillin synthesis in cultured fibroblasts from 11 members of a three-generation family with Marfan syndrome, caused by a large in-frame deletion in FBN1 (the fibrillin gene) leading to a loss of 366 bases in the corresponding fibrillin mRNA. Metabolic labelling with [35S]Met/Cys and SDS/PAGE allowed unequivocal identification of normal and truncated fibrillin in all cell strains harbouring the deletion. In culture medium, fibrillin and its truncated counterpart were predominant, whereas their respective larger precursors were found only in traces. This proportion, however, was markedly shifted towards the normal and truncated precursors by EGTA and reversed by the addition of calcium, which confirmed the existence of profibrillin and its probably calcium-dependent conversion into fibrillin. Tunicamycin caused increased electrophoretic mobility of normal and truncated molecules without changing their apparent size differences. Intracellularly, only profibrillin was found; in the mutant cells truncated and normal profibrillin molecules were present in similar amounts and both populations were secreted and deposited simultaneously into the extracellular matrix; there, however, truncated profibrillin only became easily detectable after treatment of cells with dextran sulphate, which increased the amount of extractable profibrillin. Immunofluorescence microscopy in patients' cultures identified fibrillin-containing microfibrils which appeared to be moderately reduced both in amount and diameter. Ultrastructural analysis by rotary-shadowing and immunogold electron microscopy demonstrated the presence of numerous beaded domains reacting with fibrillin antibodies, but no intact fibrillin microfibrils in patient's cell-layer extracts, in contrast with the extensive microfibrils elaborated by control cultures. Our findings suggest, that in the patients' cell cultures all microfibrils contained the truncated fibrillin molecules.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corson G. M., Chalberg S. C., Dietz H. C., Charbonneau N. L., Sakai L. Y. Fibrillin binds calcium and is coded by cDNAs that reveal a multidomain structure and alternatively spliced exons at the 5' end. Genomics. 1993 Aug;17(2):476–484. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Cutting G. R., Pyeritz R. E., Maslen C. L., Sakai L. Y., Corson G. M., Puffenberger E. G., Hamosh A., Nanthakumar E. J., Curristin S. M. Marfan syndrome caused by a recurrent de novo missense mutation in the fibrillin gene. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):337–339. doi: 10.1038/352337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Valle D., Francomano C. A., Kendzior R. J., Jr, Pyeritz R. E., Cutting G. R. The skipping of constitutive exons in vivo induced by nonsense mutations. Science. 1993 Jan 29;259(5095):680–683. doi: 10.1126/science.8430317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey M., Vandemark N., Wang M., Velinov M., Wargowski D., Tsipouras P., Han J., Becker J., Robertson W., Droste S. Prenatal diagnosis and a donor splice site mutation in fibrillin in a family with Marfan syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Aug;53(2):472–480. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. M., Bers D. M. The effect of temperature and ionic strength on the apparent Ca-affinity of EGTA and the analogous Ca-chelators BAPTA and dibromo-BAPTA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Aug 13;925(2):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(87)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollister D. W., Godfrey M., Sakai L. Y., Pyeritz R. E. Immunohistologic abnormalities of the microfibrillar-fiber system in the Marfan syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 19;323(3):152–159. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007193230303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kainulainen K., Karttunen L., Puhakka L., Sakai L., Peltonen L. Mutations in the fibrillin gene responsible for dominant ectopia lentis and neonatal Marfan syndrome. Nat Genet. 1994 Jan;6(1):64–69. doi: 10.1038/ng0194-64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kainulainen K., Pulkkinen L., Savolainen A., Kaitila I., Peltonen L. Location on chromosome 15 of the gene defect causing Marfan syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 4;323(14):935–939. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010043231402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kainulainen K., Sakai L. Y., Child A., Pope F. M., Puhakka L., Ryhänen L., Palotie A., Kaitila I., Peltonen L. Two mutations in Marfan syndrome resulting in truncated fibrillin polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5917–5921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielty C. M., Berry L., Whittaker S. P., Grant M. E., Shuttleworth C. A. Microfibrillar assemblies of foetal bovine skin. Developmental expression and relative abundance of type VI collagen and fibrillin. Matrix. 1993 Mar;13(2):103–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielty C. M., Cummings C., Whittaker S. P., Shuttleworth C. A., Grant M. E. Isolation and ultrastructural analysis of microfibrillar structures from foetal bovine elastic tissues. Relative abundance and supramolecular architecture of type VI collagen assemblies and fibrillin. J Cell Sci. 1991 Aug;99(Pt 4):797–807. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.4.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielty C. M., Shuttleworth C. A. Synthesis and assembly of fibrillin by fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. J Cell Sci. 1993 Sep;106(Pt 1):167–173. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.1.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Granger B. L. Preparation and assay of the intermediate filament proteins desmin and vimentin. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):488–508. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Godfrey M., Vitale E., Hori H., Mattei M. G., Sarfarazi M., Tsipouras P., Ramirez F., Hollister D. W. Linkage of Marfan syndrome and a phenotypically related disorder to two different fibrillin genes. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):330–334. doi: 10.1038/352330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magenis R. E., Maslen C. L., Smith L., Allen L., Sakai L. Y. Localization of the fibrillin (FBN) gene to chromosome 15, band q21.1. Genomics. 1991 Oct;11(2):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milewicz D. M., Pyeritz R. E., Crawford E. S., Byers P. H. Marfan syndrome: defective synthesis, secretion, and extracellular matrix formation of fibrillin by cultured dermal fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):79–86. doi: 10.1172/JCI115589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., D'Alessio M., Ramirez F., Lynch J. R., Sykes B., Pangilinan T., Bonadio J. Genomic organization of the sequence coding for fibrillin, the defective gene product in Marfan syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2(7):961–968. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.7.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghunath M., Superti-Furga A., Godfrey M., Steinmann B. Decreased extracellular deposition of fibrillin and decorin in neonatal Marfan syndrome fibroblasts. Hum Genet. 1993 Jan;90(5):511–515. doi: 10.1007/BF00217450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai L. Y., Keene D. R., Engvall E. Fibrillin, a new 350-kD glycoprotein, is a component of extracellular microfibrils. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2499–2509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggett A. D., Kielty C. M., Shuttleworth C. A. Microfibrillar elements in the synovial joint: presence of type VI collagen and fibrillin-containing microfibrils. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Jun;52(6):449–453. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.6.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]