Abstract
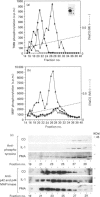
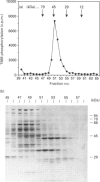
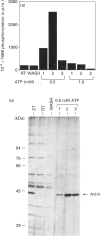
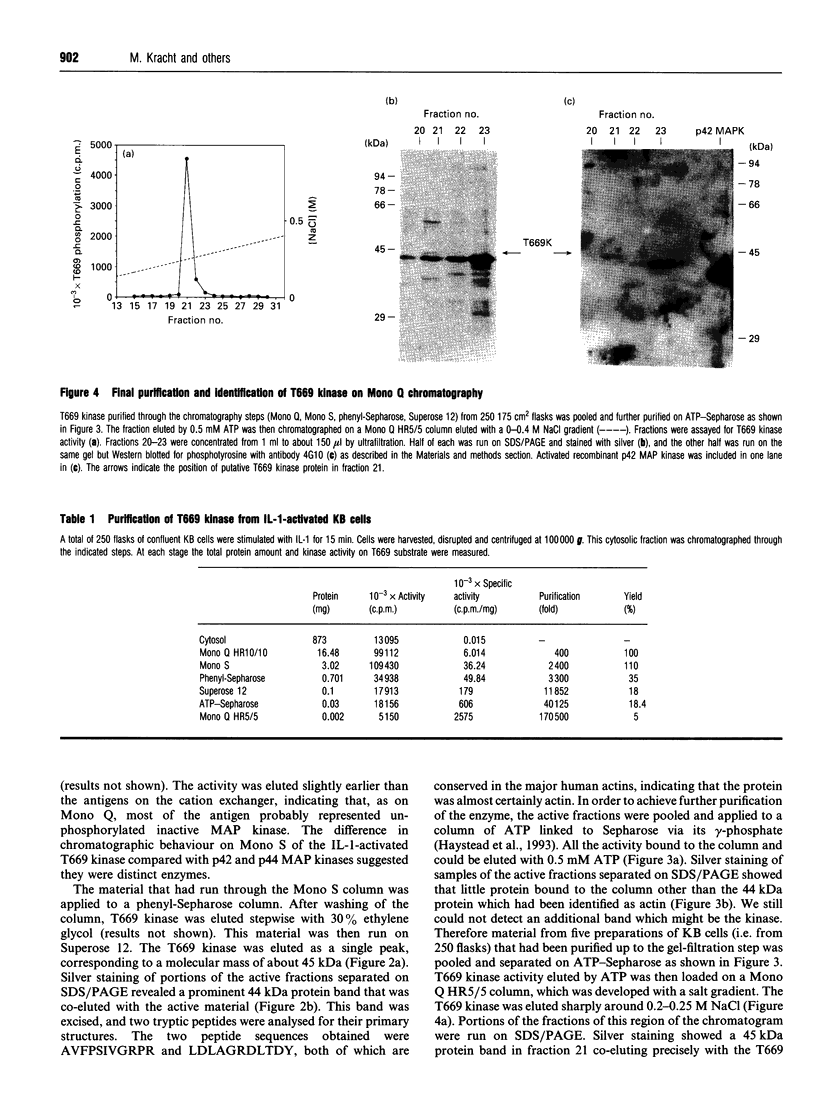
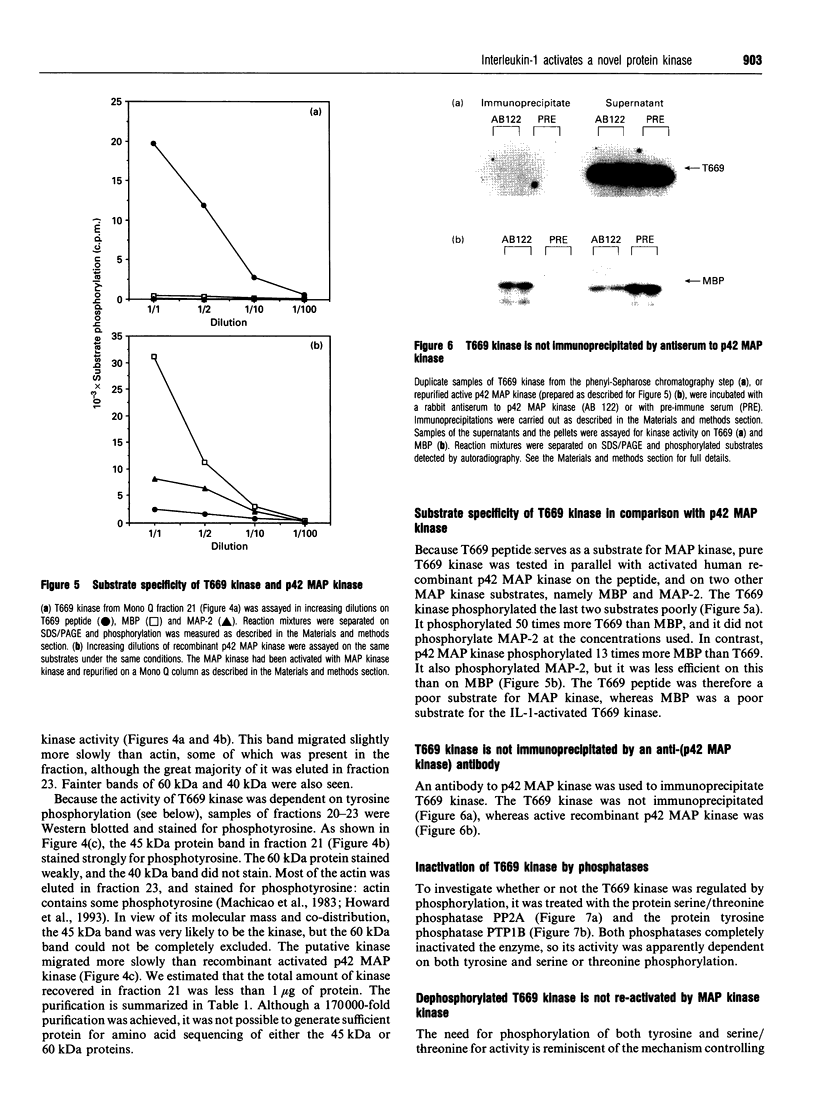
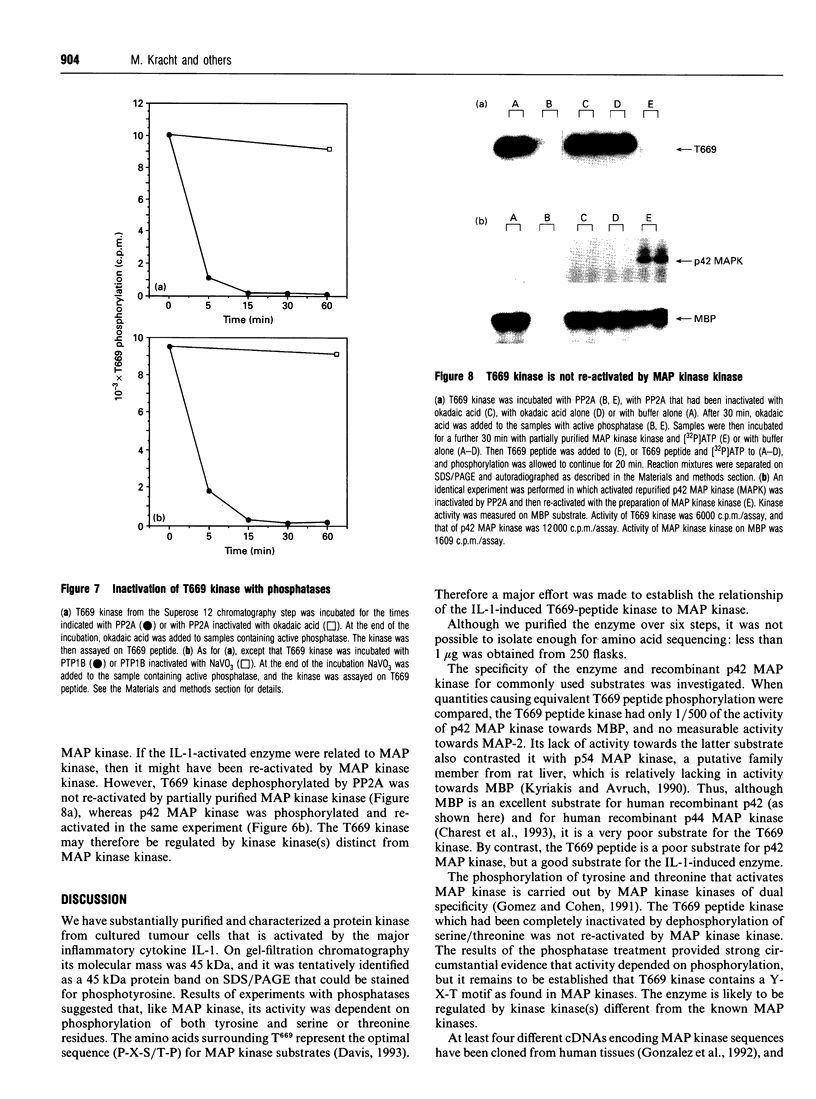
We have isolated from KB cells stimulated with interleukin-1 (IL-1) a protein kinase that phosphorylates a peptide (T669) based on the sequence around T669 of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor. The enzyme, which had an apparent molecular mass of 45 kDa on gel-filtration chromatography, was purified 170,000-fold from cytosolic extracts by sequential chromatography on Mono Q, Mono S, phenyl-Sepharose, Superose 12, ATP-Sepharose and Mono Q. The enzyme activity co-chromatographed at the last step with a 45 kDa protein band that stained for phosphotyrosine. This peak fraction also contained some actin and a 60 kDa protein that stained weakly for phosphotyrosine. The T669 peptide is a substrate for mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase. Amounts of IL-1-induced T669 kinase and activated recombinant p42 MAP kinase having equal activity on T669 peptide were compared on commonly used MAP kinase substrates. T669 kinase was two or three orders of magnitude less active on myelin basic protein or microtubule-associated protein-2 than was MAP kinase. The IL-1-induced T669 kinase did not react with antiserum to p42/p44 MAP kinase. It was inactivated by treatment with protein phosphatase 2A or protein phosphotyrosine phosphatase 1B, so it may be regulated by dual phosphorylation in similar fashion to MAP kinase. The dephosphorylated enzyme was not re-activated by MAP kinase kinase. This novel enzyme could lie on a kinase cascade induced by IL-1. It may be responsible for phosphorylating T669 of the EGF receptor.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn N. G., Seger R., Krebs E. G. The mitogen-activated protein kinase activator. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;4(6):992–999. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90131-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. A., Saklatvala J. Down-modulation of epidermal growth factor receptor affinity in fibroblasts treated with interleukin 1 or tumor necrosis factor is associated with phosphorylation at a site other than threonine 654. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):235–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. A., Saklatvala J. IL-1 and TNF transmodulate epidermal growth factor receptors by a protein kinase C-independent mechanism. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):126–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. A., Sleath P. R., deRoos P. C., Dower S. K., Virca G. D. Interleukin-1 represents a new modality for the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases/microtubule-associated protein-2 kinases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22661–22670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest D. L., Mordret G., Harder K. W., Jirik F., Pelech S. L. Molecular cloning, expression, and characterization of the human mitogen-activated protein kinase p44erk1. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4679–4690. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid M., Shirakawa F., Naylor P., Mizel S. B. Signal transduction pathway for IL-1. Involvement of a pertussis toxin-sensitive GTP-binding protein in the activation of adenylate cyclase. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4301–4306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Alemany S., Hemmings B. A., Resink T. J., Strålfors P., Tung H. Y. Protein phosphatase-1 and protein phosphatase-2A from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:390–408. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J. The mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14553–14556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood. 1991 Apr 15;77(8):1627–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G. Cell cycle control in eukaryotes: molecular mechanisms of cdc2 activation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Oct;15(10):378–383. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler K. A., Mathias S., Kolesnick R. N. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha activates the sphingomyelin signal transduction pathway in a cell-free system. Science. 1992 Mar 27;255(5052):1715–1718. doi: 10.1126/science.1313189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Raden D. L., Davis R. J. Identification of substrate recognition determinants for human ERK1 and ERK2 protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22159–22163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Raden D. L., Rigby M. R., Davis R. J. Heterogeneous expression of four MAP kinase isoforms in human tissues. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 15;304(2-3):170–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80612-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy G. R., Chua S. P., Wong N. S., Ng S. B., Tan Y. H. Interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor activate common multiple protein kinases in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14343–14352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez N., Cohen P. Dissection of the protein kinase cascade by which nerve growth factor activates MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):170–173. doi: 10.1038/353170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead C. M., Gregory P., Sturgill T. W., Haystead T. A. Gamma-phosphate-linked ATP-sepharose for the affinity purification of protein kinases. Rapid purification to homogeneity of skeletal muscle mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jun 1;214(2):459–467. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17942.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard P. K., Sefton B. M., Firtel R. A. Tyrosine phosphorylation of actin in Dictyostelium associated with cell-shape changes. Science. 1993 Jan 8;259(5092):241–244. doi: 10.1126/science.7678470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Identification of multiple novel polypeptide substrates of the v-src, v-yes, v-fps, v-ros, and v-erb-B oncogenic tyrosine protein kinases utilizing antisera against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur P., Saklatvala J. Interleukin 1 and tumour necrosis factor increase phosphorylation of fibroblast proteins. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 5;241(1-2):6–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur P., Welch W. J., Saklatvala J. Interleukin 1 and tumour necrosis factor increase phosphorylation of the small heat shock protein. Effects in fibroblasts, Hep G2 and U937 cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 4;258(2):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81671-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Binder L. I., Rosenbaum J. L. The periodic association of MAP2 with brain microtubules in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):266–276. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kracht M., Heiner A., Resch K., Szamel M. Interleukin-1-induced signaling in T-cells. Evidence for the involvement of phosphatases PP1 and PP2A in regulating protein kinase C-mediated protein phosphorylation and interleukin-2 synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21066–21072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J. pp54 microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. A novel serine/threonine protein kinase regulated by phosphorylation and stimulated by poly-L-lysine. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17355–17363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J. Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, ERK2, by p21ras oncoprotein. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):569–574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machicao F., Urumow T., Wieland O. H. Evidence for phosphorylation of actin by the insulin receptor-associated protein kinase from human placenta. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 31;163(1):76–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias S., Younes A., Kan C. C., Orlow I., Joseph C., Kolesnick R. N. Activation of the sphingomyelin signaling pathway in intact EL4 cells and in a cell-free system by IL-1 beta. Science. 1993 Jan 22;259(5094):519–522. doi: 10.1126/science.8424175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida E., Gotoh Y. The MAP kinase cascade is essential for diverse signal transduction pathways. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Apr;18(4):128–131. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90019-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northwood I. C., Gonzalez F. A., Wartmann M., Raden D. L., Davis R. J. Isolation and characterization of two growth factor-stimulated protein kinases that phosphorylate the epidermal growth factor receptor at threonine 669. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15266–15276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S. Mitogen-activated protein kinases: versatile transducers for cell signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jun;17(6):233–238. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)80005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosoff P. M., Savage N., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 stimulates diacylglycerol production in T lymphocytes by a novel mechanism. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90181-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saklatvala J., Rawlinson L. M., Marshall C. J., Kracht M. Interleukin 1 and tumour necrosis factor activate the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase in cultured cells. FEBS Lett. 1993 Nov 15;334(2):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81709-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroo M., Matsushima K. Enhanced phosphorylation of 65 and 74 kDa proteins by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Cytokine. 1990 Jan;2(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(90)90038-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims J. E., Gayle M. A., Slack J. L., Alderson M. R., Bird T. A., Giri J. G., Colotta F., Re F., Mantovani A., Shanebeck K. Interleukin 1 signaling occurs exclusively via the type I receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6155–6159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokoe D., Campbell D. G., Nakielny S., Hidaka H., Leevers S. J., Marshall C., Cohen P. MAPKAP kinase-2; a novel protein kinase activated by mitogen-activated protein kinase. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3985–3994. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05492.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totty N. F., Waterfield M. D., Hsuan J. J. Accelerated high-sensitivity microsequencing of proteins and peptides using a miniature reaction cartridge. Protein Sci. 1992 Sep;1(9):1215–1224. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]