Abstract
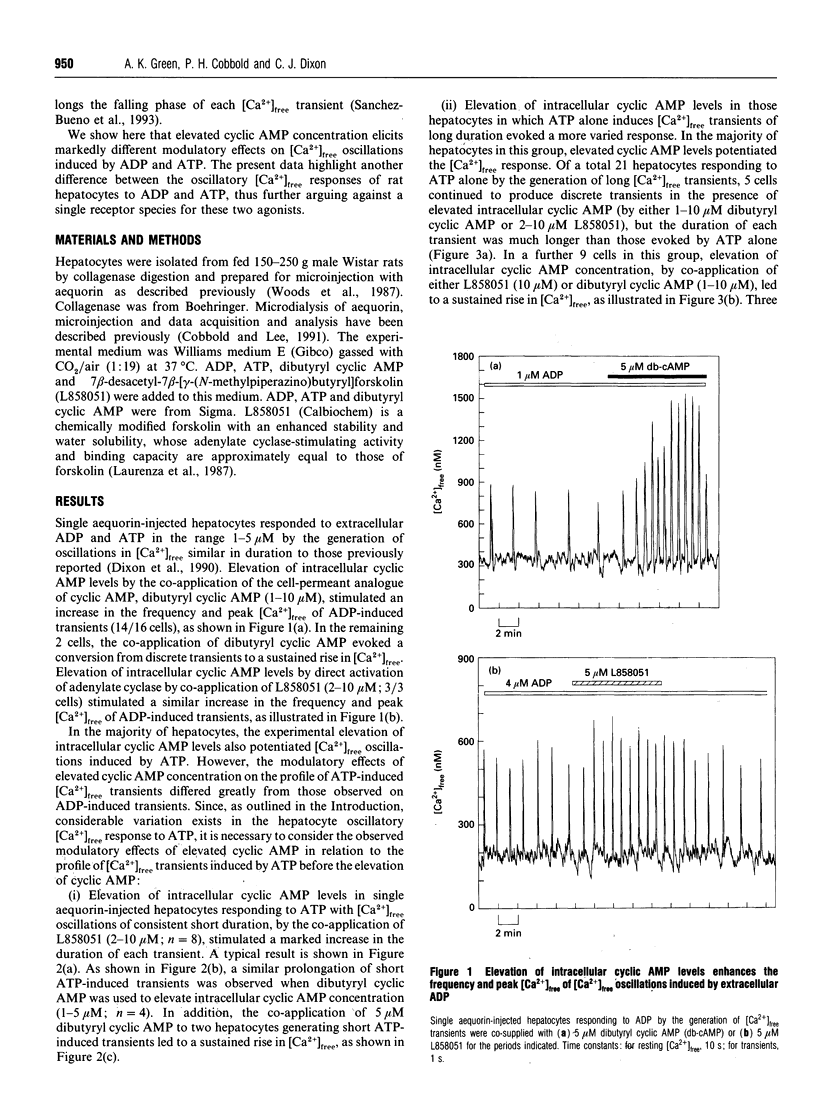
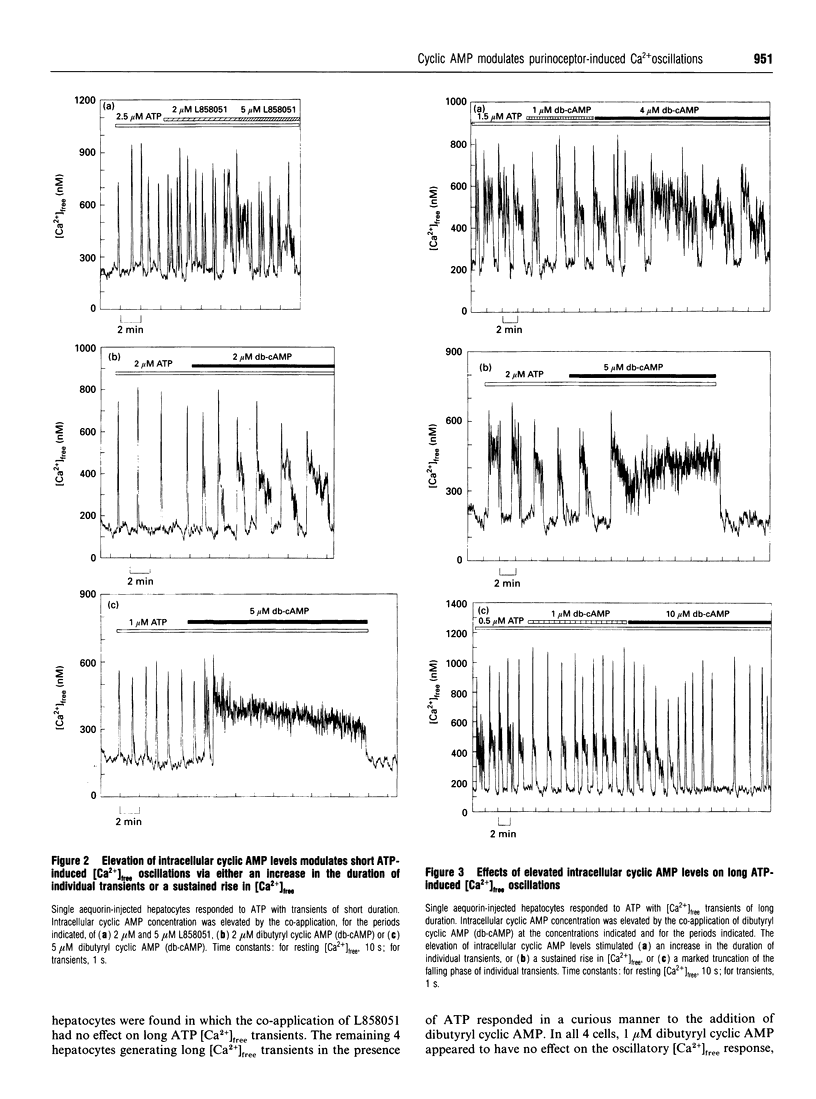
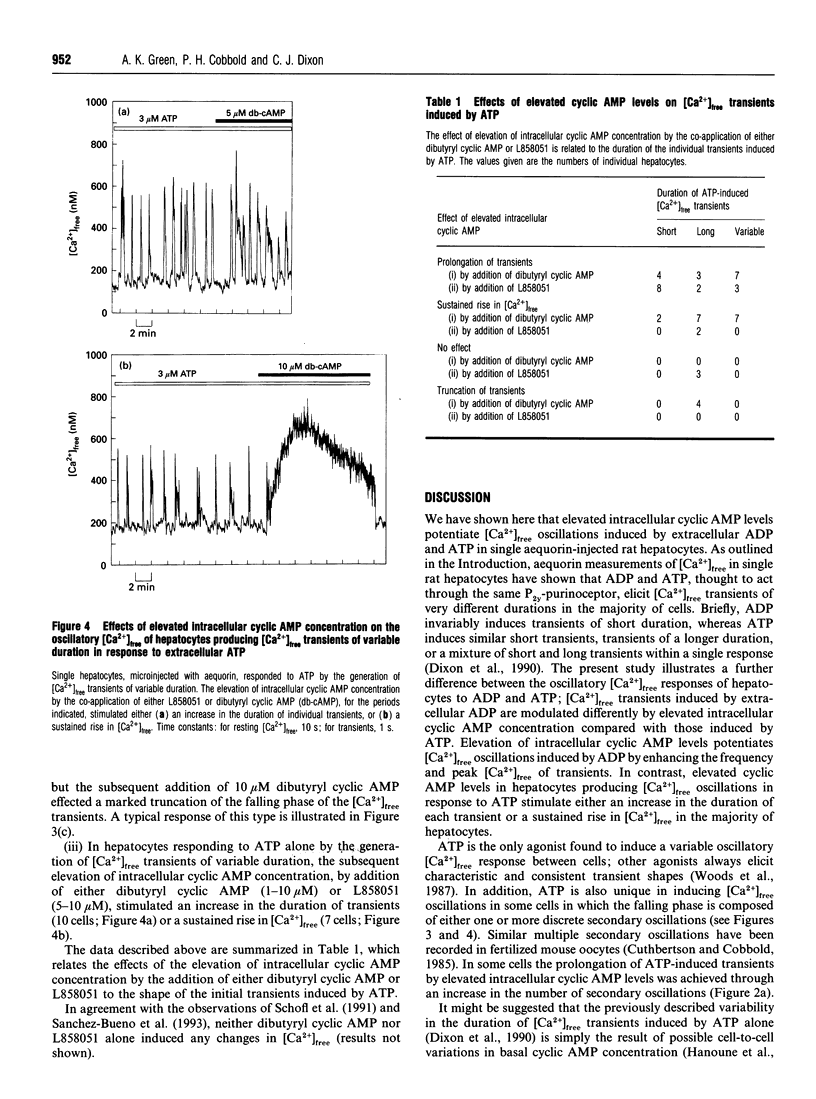
Single aequorin-injected hepatocytes respond to agonists acting via the phosphoinositide signalling pathway by the generation of oscillations in cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]free). The duration of [Ca2+]free transients is characteristic of the stimulating agonist. We have previously reported that ADP and ATP, which are believed to act through a single P(2y)-purinoceptor species, induce very different oscillatory [Ca2+]free responses in the majority of hepatocytes. We have interpreted these data as evidence for two separate Ca(2+)-mobilizing purinoceptors for these nucleotides. We show here that the elevation of intracellular cyclic AMP concentration, by the co-application of either dibutyryl cyclic AMP or 7 beta-desacetyl-7 beta-[gamma-(N-methylpiperazino)butyryl]- forskolin (L858051), exerts different modulatory effects on [Ca2+]free oscillations induced by ADP and ATP in single rat hepatocytes. Elevated intracellular cyclic AMP levels enhance the frequency and peak [Ca2+]free of transients induced by ADP. In contrast, the elevation of intracellular cyclic AMP levels in hepatocytes producing [Ca2+]free oscillations in response to ATP stimulates either an increase in the duration of transients or a sustained rise in [Ca2+]free. The data illustrate a further difference between the oscillatory [Ca2+]free responses of hepatocytes to ADP and ATP, thus further arguing against ADP and ATP acting via a single purinoceptor species.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altin J. G., Bygrave F. L. Synergistic stimulation of Ca2+ uptake by glucagon and Ca2+-mobilizing hormones in the perfused rat liver. A role for mitochondria in long-term Ca2+ homoeostasis. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):653–661. doi: 10.1042/bj2380653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altin J. G., Bygrave F. L. The influx of Ca2+ induced by the administration of glucagon and Ca2+-mobilizing agents to the perfused rat liver could involve at least two separate pathways. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 15;242(1):43–50. doi: 10.1042/bj2420043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Calcium oscillations. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9583–9586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Studies on the hepatic calcium-mobilizing activity of aluminum fluoride and glucagon. Modulation by cAMP and phorbol myristate acetate. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11056–11063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M., Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regulation of adrenergic receptor function by phosphorylation. II. Effects of agonist occupancy on phosphorylation of alpha 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors by protein kinase C and the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3106–3113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. A., Lazarowski E. R., Boucher R. C., Harden T. K. Evidence that UTP and ATP regulate phospholipase C through a common extracellular 5'-nucleotide receptor in human airway epithelial cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;40(5):648–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Bird G. S., Obie J. F., Putney J. W., Jr The mechanism for synergism between phospholipase C- and adenylylcyclase-linked hormones in liver. Cyclic AMP-dependent kinase augments inositol trisphosphate-mediated Ca2+ mobilization without increasing the cellular levels of inositol polyphosphates. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4772–4781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bygrave F. L., Benedetti A. Calcium: its modulation in liver by cross-talk between the actions of glucagon and calcium-mobilizing agonists. Biochem J. 1993 Nov 15;296(Pt 1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj2960001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bygrave F. L., Gamberucci A., Fulceri R., Benedetti A. Evidence that stimulation of plasma-membrane Ca2+ inflow is an early action of glucagon and dibutyryl cyclic AMP in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1993 May 15;292(Pt 1):19–22. doi: 10.1042/bj2920019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest R., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Characterization of responses of isolated rat hepatocytes to ATP and ADP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15789–15794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold P. H., Sanchez-Bueno A., Dixon C. J. The hepatocyte calcium oscillator. Cell Calcium. 1991 Feb-Mar;12(2-3):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(91)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Stutchfield J. The receptors for ATP and fMetLeuPhe are independently coupled to phospholipases C and A2 via G-protein(s). Relationship between phospholipase C and A2 activation and exocytosis in HL60 cells and human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 1;263(3):715–723. doi: 10.1042/bj2630715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane J. K., Campanile C. P., Garrison J. C. The hepatic angiotensin II receptor. II. Effect of guanine nucleotides and interaction with cyclic AMP production. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4959–4965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Phorbol ester and sperm activate mouse oocytes by inducing sustained oscillations in cell Ca2+. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):541–542. doi: 10.1038/316541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon C. J., Cobbold P. H., Green A. K. Adenosine 5'-[alpha beta-methylene]triphosphate potentiates the oscillatory cytosolic Ca2+ responses of hepatocytes to ATP, but not to ADP. Biochem J. 1993 Aug 1;293(Pt 3):757–760. doi: 10.1042/bj2930757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon C. J., Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Evidence for two Ca2(+)-mobilizing purinoceptors on rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):499–502. doi: 10.1042/bj2690499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulon D., Mollard P., Aran J. M. Extracellular ATP elevates cytosolic Ca2+ in cochlear inner hair cells. Neuroreport. 1991 Feb;2(2):69–72. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199102000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Alfonzo R. G., Toro J. R., Heppel L. A. Receptor specific for certain nucleotides stimulates inositol phosphate metabolism and Ca2+ fluxes in A431 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Dec;141(3):606–617. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041410320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Rozengurt E., Heppel L. A. Extracellular ATP induces the release of calcium from intracellular stores without the activation of protein kinase C in Swiss 3T6 mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4530–4534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillon G., Gallo-Payet N., Balestre M. N., Lombard C. Cholera-toxin and corticotropin modulation of inositol phosphate accumulation induced by vasopressin and angiotensin II in rat glomerulosa cells. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):765–775. doi: 10.1042/bj2530765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajnóczky G., Gao E., Nomura T., Hoek J. B., Thomas A. P. Multiple mechanisms by which protein kinase A potentiates inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ mobilization in permeabilized hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 15;293(Pt 2):413–422. doi: 10.1042/bj2930413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanoune J., Stengel D., Lacombe M. L., Feldmann G., Coudrier E. Proteolytic activation of rat liver adenylate cyclase by a contaminant of crude collagenase from Clostridium histolyticum. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2039–2045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., De Wulf H. Characterization of the liver P2-purinoceptor involved in the activation of glycogen phosphorylase. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):367–371. doi: 10.1042/bj2400367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., De Wulf H. P2-purinergic control of liver glycogenolysis. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):797–799. doi: 10.1042/bj2310797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki M., Takeshige K., Minakami S. ATP-induced calcium mobilization in human neutrophils. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jun 15;1012(1):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurenza A., Khandelwal Y., De Souza N. J., Rupp R. H., Metzger H., Seamon K. B. Stimulation of adenylate cyclase by water-soluble analogues of forskolin. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;32(1):133–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig K. D., Shiau A. K., Brake A. J., Julius D. Expression cloning of an ATP receptor from mouse neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5113–5117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauger J. P., Poggioli J., Claret M. Synergistic stimulation of the Ca2+ influx in rat hepatocytes by glucagon and the Ca2+-linked hormones vasopressin and angiotensin II. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11635–11642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan N. G., Charest R., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Potentiation of alpha 1-adrenergic responses in rat liver by a cAMP-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4208–4212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan N. G., Exton J. H., Blackmore P. F. Angiotensin II inhibits hepatic cAMP accumulation induced by glucagon and epinephrine and their metabolic effects. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 7;153(1):77–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murgo A. J., Sistare F. D. K562 leukemia cells express P2T (adenosine diphosphate) purinergic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 May;261(2):580–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Tokumitsu Y., Kondo Y., Ui M. P2-purinergic receptors are coupled to two signal transduction systems leading to inhibition of cAMP generation and to production of inositol trisphosphate in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13483–13490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittner R. A., Fain J. N. Exposure of cultured hepatocytes to cyclic AMP enhances the vasopressin-mediated stimulation of inositol phosphate production. Biochem J. 1989 Jan 15;257(2):455–460. doi: 10.1042/bj2570455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittner R. A., Fain J. N. Vasopressin and norepinephrine stimulation of inositol phosphate accumulation in rat hepatocytes are modified differently by protein f1nase C and protein kinase A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 2;1043(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90298-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggioli J., Mauger J. P., Claret M. Effect of cyclic AMP-dependent hormones and Ca2+-mobilizing hormones on the Ca2+ influx and polyphosphoinositide metabolism in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):663–669. doi: 10.1042/bj2350663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage S. O., Reast R., Rink T. J. ADP evokes biphasic Ca2+ influx in fura-2-loaded human platelets. Evidence for Ca2+ entry regulated by the intracellular Ca2+ store. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):675–680. doi: 10.1042/bj2650675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Bueno A., Cobbold P. H. Agonist-specificity in the role of Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release in hepatocyte Ca2+ oscillations. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 1;291(Pt 1):169–172. doi: 10.1042/bj2910169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Bueno A., Marrero I., Cobbold P. H. Different modulatory effects of elevated cyclic AMP on cytosolic Ca2+ spikes induced by phenylephrine or vasopressin in single rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 1;291(Pt 1):163–168. doi: 10.1042/bj2910163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöfl C., Sanchez-Bueno A., Brabant G., Cobbold P. H., Cuthbertson K. S. Frequency and amplitude enhancement of calcium transients by cyclic AMP in hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):799–802. doi: 10.1042/bj2730799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi R., Zhao M., Stucki J. W. Modulation of cytosolic-[Ca2+] oscillations in hepatocytes results from cross-talk among second messengers. The synergism between the alpha 1-adrenergic response, glucagon and cyclic AMP, and their antagonism by insulin and diacylglycerol manifest themselves in the control of the cytosolic-[Ca2+] oscillations. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 15;286(Pt 3):869–877. doi: 10.1042/bj2860869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb T. E., Simon J., Krishek B. J., Bateson A. N., Smart T. G., King B. F., Burnstock G., Barnard E. A. Cloning and functional expression of a brain G-protein-coupled ATP receptor. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 14;324(2):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81397-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Agonist-induced oscillations in cytoplasmic free calcium concentration in single rat hepatocytes. Cell Calcium. 1987 Feb;8(1):79–100. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(87)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Repetitive transient rises in cytoplasmic free calcium in hormone-stimulated hepatocytes. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):600–602. doi: 10.1038/319600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


