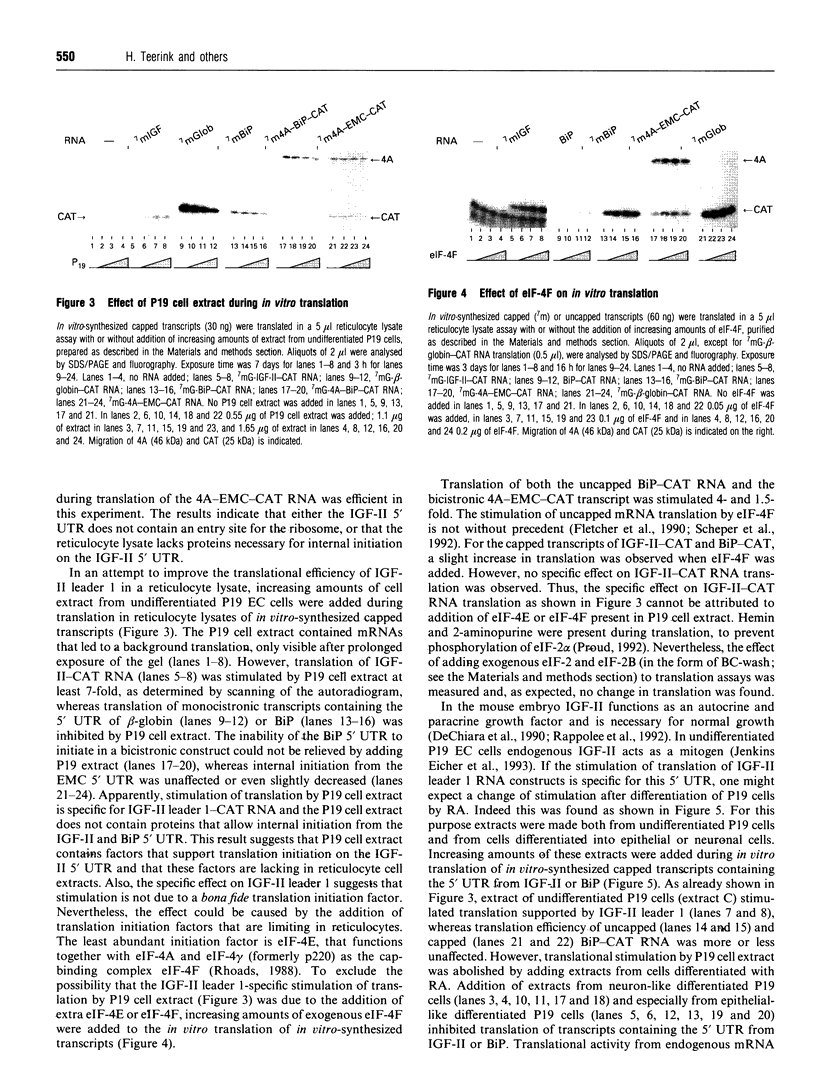
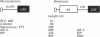Abstract
The majority of cellular mRNAs have relatively short and unstructured 5' untranslated regions (UTRs) that allow efficient translation, such as the beta-globin mRNA. An exception to this rule is the group of growth factor mRNAs which, in general, have long 5' UTRs with a high G + C content. An example is insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II), which is encoded by four mRNAs, arising from four different promoters. Transcripts having the human IGF-II leader 1 are only expressed in adult liver where IGF-II protein synthesis is solely under direction of this 5' UTR. We investigated the translational efficiency in vitro of this 5' UTR, linked to the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) encoding region. As expected from the primary structure of IGF-II leader 1, translational efficiency was very low compared with beta-globin 5' UTR-CAT mRNA. Addition of cell extract from undifferentiated P19 embryonal carcinoma (EC) cells preferentially stimulated translation of an IGF-II 5' UTR RNA construct. No translational stimulation was found when cell extract from differentiated P19 EC cells was added. In contrast with the beta-globin 5' UTR, translation initiation on the IGF-II 5' UTR was not dependent on the presence of a cap structure. The results imply that only in undifferentiated P19 EC cells and not in their differentiated derivatives is a factor present that specifically stimulates IGF-II RNA translation, thereby suggesting translational regulation of IGF-II production during early embryonic development. A mechanism for translation initiation on the 5' UTR of IGF-II is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrick B. A., Lee A. L., Grendell R. L., Derynck R. Inhibition of translation of transforming growth factor-beta 3 mRNA by its 5' untranslated region. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4306–4313. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berben-Bloemheuvel G., Kasperaitis M. A., van Heugten H., Thomas A. A., van Steeg H., Voorma H. O. Interaction of initiation factors with the cap structure of chimaeric mRNA containing the 5'-untranslated regions of Semliki Forest virus RNA is related to translational efficiency. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Sep 15;208(3):581–587. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. W., McBurney M. W. Cell density and cell cycle effects on retinoic acid-induced embryonal carcinoma cell differentiation. Dev Biol. 1990 Mar;138(1):123–135. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90182-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley B., Ehrenfeld E. The cap-binding protein complex in uninfected and poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13599–13606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Benedetti A., Joshi-Barve S., Rinker-Schaeffer C., Rhoads R. E. Expression of antisense RNA against initiation factor eIF-4E mRNA in HeLa cells results in lengthened cell division times, diminished translation rates, and reduced levels of both eIF-4E and the p220 component of eIF-4F. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5435–5445. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChiara T. M., Efstratiadis A., Robertson E. J. A growth-deficiency phenotype in heterozygous mice carrying an insulin-like growth factor II gene disrupted by targeting. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):78–80. doi: 10.1038/345078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eicher D. J., Moats-Staats B. M., Stiles A. D., D'Ercole A. J. Possible autocrine/paracrine actions of insulin-like growth factors during embryonic development: expression and action of IGFs in undifferentiated P19 cells. Dev Genet. 1993;14(3):194–203. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020140306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher L., Corbin S. D., Browning K. S., Ravel J. M. The absence of a m7G cap on beta-globin mRNA and alfalfa mosaic virus RNA 4 increases the amounts of initiation factor 4F required for translation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19582–19587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Schmid C., Schwander J., Zapf J. Actions of insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:443–467. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray A., Tam A. W., Dull T. J., Hayflick J., Pintar J., Cavenee W. K., Koufos A., Ullrich A. Tissue-specific and developmentally regulated transcription of the insulin-like growth factor 2 gene. DNA. 1987 Aug;6(4):283–295. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikejiri K., Furuichi M., Ueno T., Matsuguchi T., Takahashi K., Endo H., Yamamoto M. The presence and active transcription of three independent leader exons in the mouse insulin-like growth factor II gene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 2;1089(1):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C., Wimmer E. A segment of the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA directs internal entry of ribosomes during in vitro translation. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2636–2643. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2636-2643.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Wimmer E. Cap-independent translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA: structural elements of the internal ribosomal entry site and involvement of a cellular 57-kD RNA-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1560–1572. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. J., Park K., Koeller D., Kim K. Y., Wakefield L. M., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Post-transcriptional regulation of the human transforming growth factor-beta 1 gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13702–13707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koromilas A. E., Lazaris-Karatzas A., Sonenberg N. mRNAs containing extensive secondary structure in their 5' non-coding region translate efficiently in cells overexpressing initiation factor eIF-4E. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4153–4158. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05508.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Regulation of translation in eukaryotic systems. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:197–225. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson T. G., Lee K. A., Maimone M. M., Abramson R. D., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. Dissociation of double-stranded polynucleotide helical structures by eukaryotic initiation factors, as revealed by a novel assay. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4729–4734. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macejak D. G., Sarnow P. Internal initiation of translation mediated by the 5' leader of a cellular mRNA. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):90–94. doi: 10.1038/353090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R. Teratocarcinomas as a model system for the study of embryogenesis and neoplasia. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):229–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuguchi T., Takahashi K., Ikejiri K., Ueno T., Endo H., Yamamoto M. Functional analysis of multiple promoters of the rat insulin-like factor II gene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 6;1048(2-3):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meerovitch K., Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. A cellular protein that binds to the 5'-noncoding region of poliovirus RNA: implications for internal translation initiation. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1026–1034. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mummery C. L., Feijen A., van der Saag P. T., van den Brink C. E., de Laat S. W. Clonal variants of differentiated P19 embryonal carcinoma cells exhibit epidermal growth factor receptor kinase activity. Dev Biol. 1985 Jun;109(2):402–410. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90466-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mummery C. L., van den Brink C. E., van der Saag P. T., de Laat S. W. The cell cycle, cell death, and cell morphology during retinoic acid-induced differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Dev Biol. 1984 Aug;104(2):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen F. C., Gammeltoft S., Christiansen J. Translational discrimination of mRNAs coding for human insulin-like growth factor II. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13431–13434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh S. K., Scott M. P., Sarnow P. Homeotic gene Antennapedia mRNA contains 5'-noncoding sequences that confer translational initiation by internal ribosome binding. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1643–1653. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Insertion mutagenesis to increase secondary structure within the 5' noncoding region of a eukaryotic mRNA reduces translational efficiency. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):515–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Internal initiation of translation of eukaryotic mRNA directed by a sequence derived from poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):320–325. doi: 10.1038/334320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud C. G. Protein phosphorylation in translational control. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1992;32:243–369. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152832-4.50008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao C. D., Pech M., Robbins K. C., Aaronson S. A. The 5' untranslated sequence of the c-sis/platelet-derived growth factor 2 transcript is a potent translational inhibitor. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):284–292. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappolee D. A., Sturm K. S., Behrendtsen O., Schultz G. A., Pedersen R. A., Werb Z. Insulin-like growth factor II acts through an endogenous growth pathway regulated by imprinting in early mouse embryos. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):939–952. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E. Cap recognition and the entry of mRNA into the protein synthesis initiation cycle. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E. Regulation of eukaryotic protein synthesis by initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3017–3020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Primary structure of human insulin-like growth factor II. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 15;89(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2769–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheper G. C., Voorma H. O., Thomas A. A. Eukaryotic initiation factors-4E and -4F stimulate 5' cap-dependent as well as internal initiation of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7269–7274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussenbach J. S., Steenbergh P. H., Holthuizen P. Structure and expression of the human insulin-like growth factor genes. Growth Regul. 1992 Mar;2(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. A., Scheper G. C., Kleijn M., De Boer M., Voorma H. O. Dependence of the adenovirus tripartite leader on the p220 subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F during in vitro translation. Effect of p220 cleavage by foot-and-mouth-disease-virus L-protease on in vitro translation. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jul 15;207(2):471–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17073.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting J., Lee A. S. Human gene encoding the 78,000-dalton glucose-regulated protein and its pseudogene: structure, conservation, and regulation. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):275–286. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorma H. O., Thomas A., Goumans H., Amesz H., van der Mast C. Isolation and purification of initiation factors of protein synthesis from rabbit reticulocyte lysate. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:124–135. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Stiles C. D. Regulation of platelet-derived growth factor A messenger RNA translation in differentiating F9 teratocarcinoma cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Oct;4(10):871–877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pagter-Holthuizen P., Jansen M., van Schaik F. M., van der Kammen R., Oosterwijk C., Van den Brande J. L., Sussenbach J. S. The human insulin-like growth factor II gene contains two development-specific promoters. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 20;214(2):259–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pagter-Holthuizen P., Jansen M., van der Kammen R. A., van Schaik F. M., Sussenbach J. S. Differential expression of the human insulin-like growth factor II gene. Characterization of the IGF-II mRNAs and an mRNA encoding a putative IGF-II-associated protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 7;950(3):282–295. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90124-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pagter-Holthuizen P., van Schaik F. M., Verduijn G. M., van Ommen G. J., Bouma B. N., Jansen M., Sussenbach J. S. Organization of the human genes for insulin-like growth factors I and II. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijk M. A., van Schaik F. M., Bootsma H. J., Holthuizen P., Sussenbach J. S. Initial characterization of the four promoters of the human insulin-like growth factor II gene. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1991 Oct;81(1-3):81–94. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(91)90207-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]