Abstract
The polycation protamine impedes the catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and this has been suggested to be due to intravascular inactivation of lipoprotein lipase. We have made intravenous injections of protamine to rats and found that both lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase activities were released to plasma. The effect of protamine was more short-lived than that obtained by injection of heparin. The release of hepatic lipase by protamine was as effective as the release by heparin, while the amount of lipoprotein lipase released by protamine was only about one-tenth of that released by heparin. This was not due to inactivation of lipoprotein lipase, since injection of an excess of heparin 10 min after injection of protamine released as much lipoprotein lipase activity to plasma as in controls. The results in vivo differed from those obtained in model experiments in vitro. Protamine was able to almost quantitatively release both lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase from columns of heparin-agarose. The displacement was dependent on the total amount of protamine that had passed over the column, indicating that it was due to occupation by protamine of all available binding sites. Our results in vivo showed that the binding sites for lipoprotein lipase were not blocked as efficiently as those for hepatic lipase, indicating that the binding structures were not identical. It was concluded that the impaired turnover of lipoproteins by protamine probably was due to prevention of binding of the lipoproteins to endothelial cell surfaces rather than to impaired lipase function.
Full text
PDF

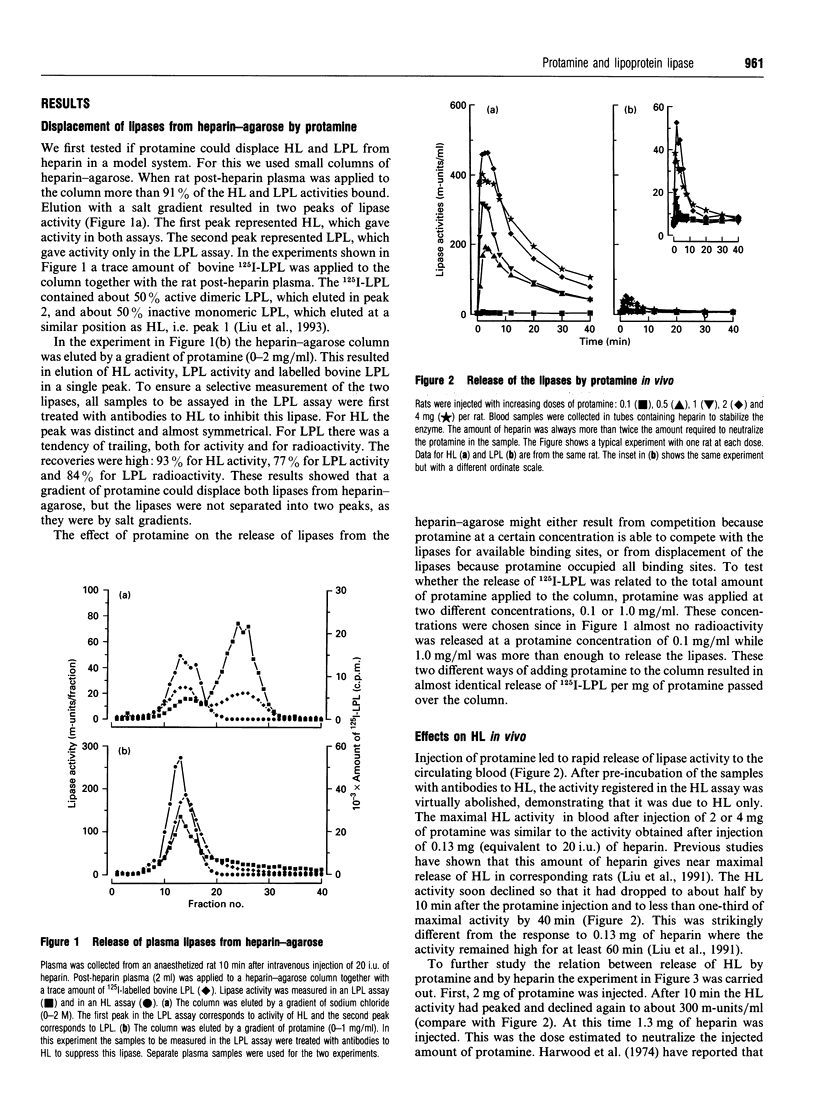
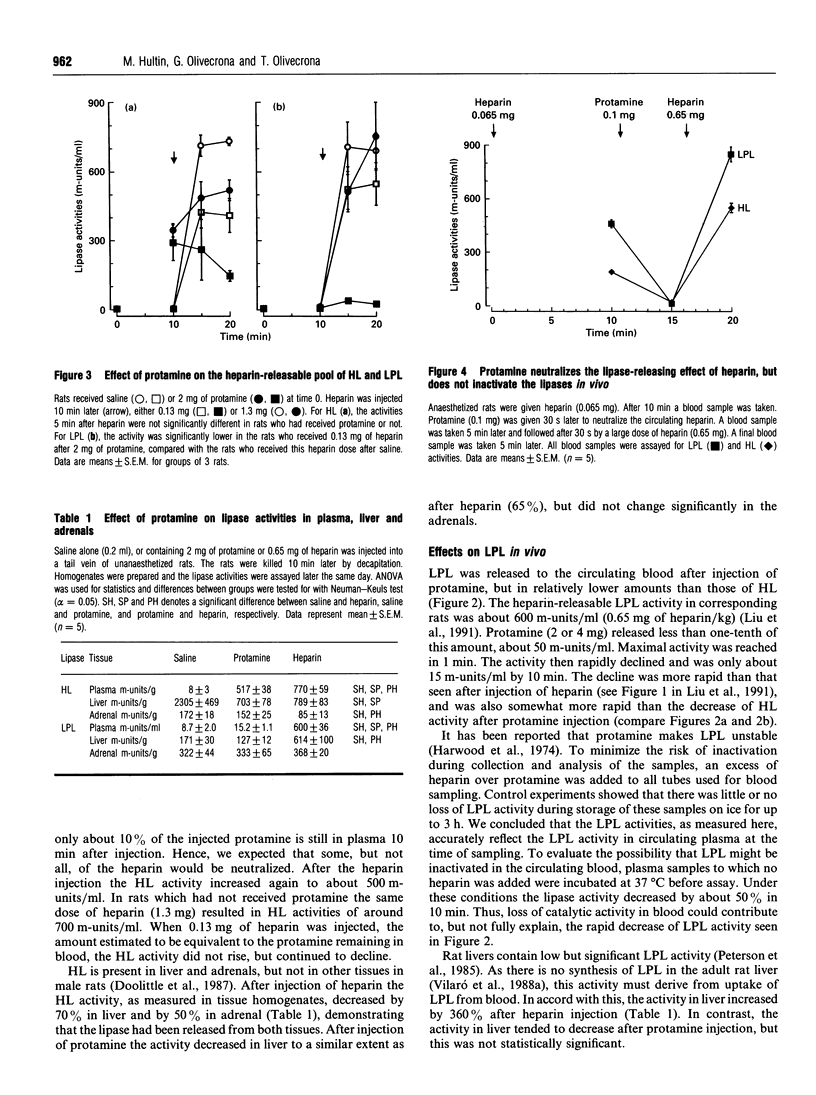
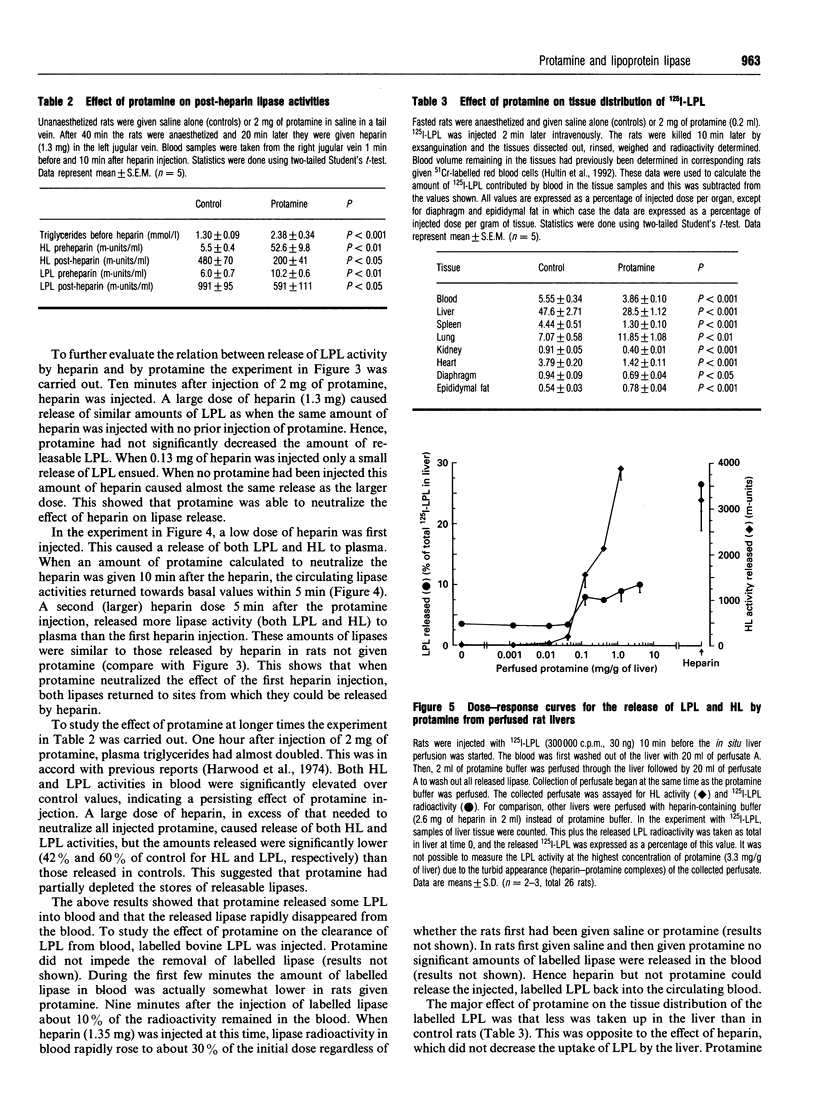
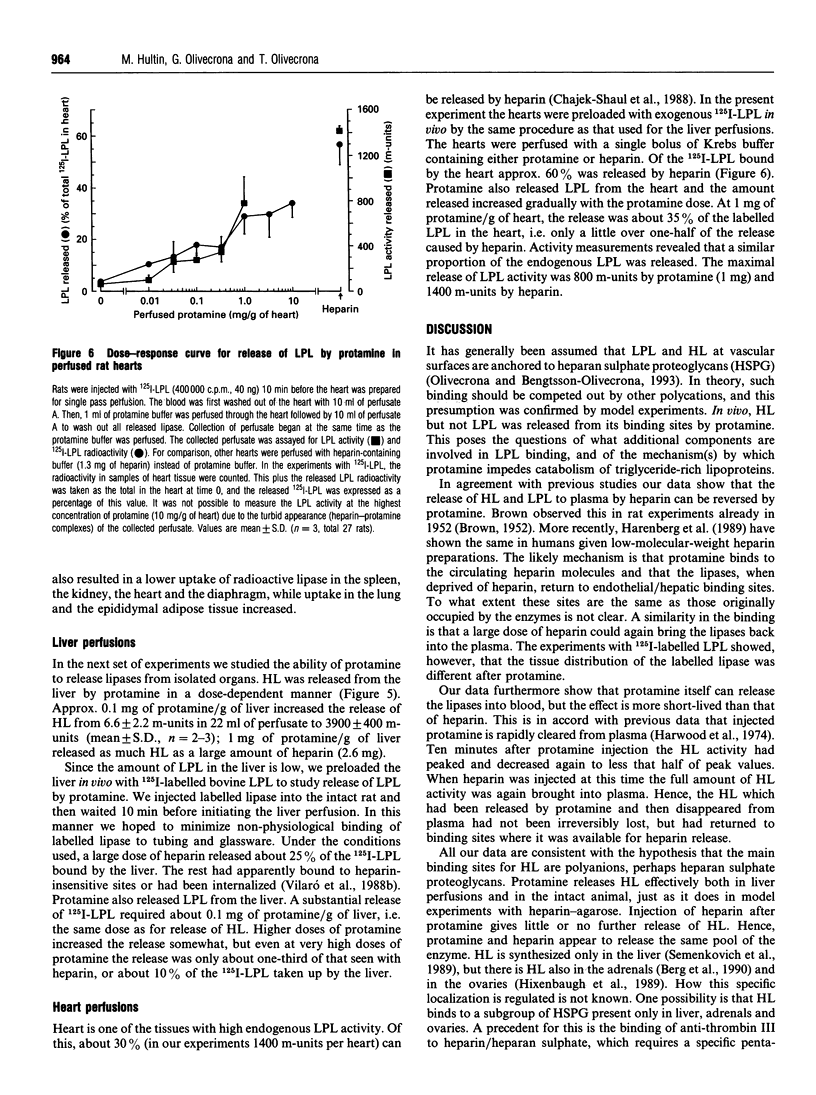


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beisiegel U., Weber W., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G. Lipoprotein lipase enhances the binding of chylomicrons to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8342–8346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Olivecrona T. Phospholipase activity of milk lipoprotein lipase. Methods Enzymol. 1991;197:345–356. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)97160-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson G., Olivecrona T., Hök M., Riesenfeld J., Lindahl U. Interaction of lipoprotein lipase with native and modified heparin-like polysaccharides. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 1;189(3):625–633. doi: 10.1042/bj1890625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg A. L., Hansson P., Nilsson-Ehle P. Salt resistant lipase activity in human adrenal gland is increased in Cushing's disease. J Intern Med. 1990 Sep;228(3):257–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1990.tb00228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chajek-Shaul T., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Peterson J., Olivecrona T. Metabolic fate of rat heart endothelial lipoprotein lipase. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 1):E247–E254. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.3.E247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L. Apolipoprotein B, the major protein component of triglyceride-rich and low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25621–25624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckelbaum R. J., Ramakrishnan R., Eisenberg S., Olivecrona T., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G. Triacylglycerol and phospholipid hydrolysis in human plasma lipoproteins: role of lipoprotein and hepatic lipase. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 15;31(36):8544–8551. doi: 10.1021/bi00151a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle M. H., Wong H., Davis R. C., Schotz M. C. Synthesis of hepatic lipase in liver and extrahepatic tissues. J Lipid Res. 1987 Nov;28(11):1326–1334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harenberg J., Stehle G., Dempfle C. E., von Hodenberg E., Heene D. L. The pharmacological profile of the low molecular weight heparin 21-23 in man: anticoagulant, lipolytic and protamine reversible effects. Folia Haematol Int Mag Klin Morphol Blutforsch. 1989;116(6):967–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood J. L., Riley S. E., Robinson D. S. The action of protamine on clearing factor lipase and on plasma triglyceride metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Feb 25;337(2):225–238. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hide W. A., Chan L., Li W. H. Structure and evolution of the lipase superfamily. J Lipid Res. 1992 Feb;33(2):167–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M. H., Oliveira H. C., Quintão E. C., Redgrave T. G., Maranhão R. C. The effects of Triton WR-1339, protamine sulfate and heparin on the plasma removal of emulsion models of chylomicrons and remnants in rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Feb 14;917(2):344–346. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixenbaugh E. A., Sullivan T. R., Jr, Strauss J. F., 3rd, Laposata E. A., Komaromy M., Paavola L. G. Hepatic lipase in the rat ovary. Ovaries cannot synthesize hepatic lipase but accumulate it from the circulation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4222–4230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultin M., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Olivecrona T. Release of lipoprotein lipase to plasma by triacylglycerol emulsions. Comparison to the effect of heparin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 8;1125(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(92)90161-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl U. Store nordiske Jahre-prisen 1993. Hur "kodas" heparansulfat? Nord Med. 1994;109(1):4–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu G. Q., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Ostergaard P., Olivecrona T. Low-Mr heparin is as potent as conventional heparin in releasing lipoprotein lipase, but is less effective in preventing hepatic clearance of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):747–752. doi: 10.1042/bj2730747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu G., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Olivecrona T. Assembly of lipoprotein lipase in perfused guinea-pig hearts. Biochem J. 1993 May 15;292(Pt 1):277–282. doi: 10.1042/bj2920277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu G., Olivecrona T. Synthesis and transport of lipoprotein lipase in perfused guinea pig hearts. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 2):H438–H446. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.263.2.H438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nykjaer A., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Lookene A., Moestrup S. K., Petersen C. M., Weber W., Beisiegel U., Gliemann J. The alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein binds lipoprotein lipase and beta-migrating very low density lipoprotein associated with the lipase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):15048–15055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J., Olivecrona T., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G. Distribution of lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase between plasma and tissues: effect of hypertriglyceridemia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 4;837(3):262–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenkovich C. F., Chen S. H., Wims M., Luo C. C., Li W. H., Chan L. Lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase mRNA tissue specific expression, developmental regulation, and evolution. J Lipid Res. 1989 Mar;30(3):423–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Gill P. J., Silbert J. E., Douglas W. H., Fanburg B. L. Involvement of cell surface heparin sulfate in the binding of lipoprotein lipase to cultured bovine endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):995–1002. doi: 10.1172/JCI110354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimano H., Yamada N., Katsuki M., Yamamoto K., Gotoda T., Harada K., Shimada M., Yazaki Y. Plasma lipoprotein metabolism in transgenic mice overexpressing apolipoprotein E. Accelerated clearance of lipoproteins containing apolipoprotein B. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):2084–2091. doi: 10.1172/JCI116091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivaram P., Klein M. G., Goldberg I. J. Identification of a heparin-releasable lipoprotein lipase binding protein from endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16517–16522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stins M. F., Maxfield F. R., Goldberg I. J. Polarized binding of lipoprotein lipase to endothelial cells. Implications for its physiological actions. Arterioscler Thromb. 1992 Dec;12(12):1437–1446. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.12.12.1437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilaró S., Llobera M., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Olivecrona T. Lipoprotein lipase uptake by the liver: localization, turnover, and metabolic role. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 1):G711–G722. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.5.G711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilaró S., Llobera M., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Olivecrona T. Synthesis of lipoprotein lipase in the liver of newborn rats and localization of the enzyme by immunofluorescence. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 15;249(2):549–556. doi: 10.1042/bj2490549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallinder L., Peterson J., Olivecrona T., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G. Hepatic and extrahepatic uptake of intravenously injected lipoprotein lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 4;795(3):513–524. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


