Abstract
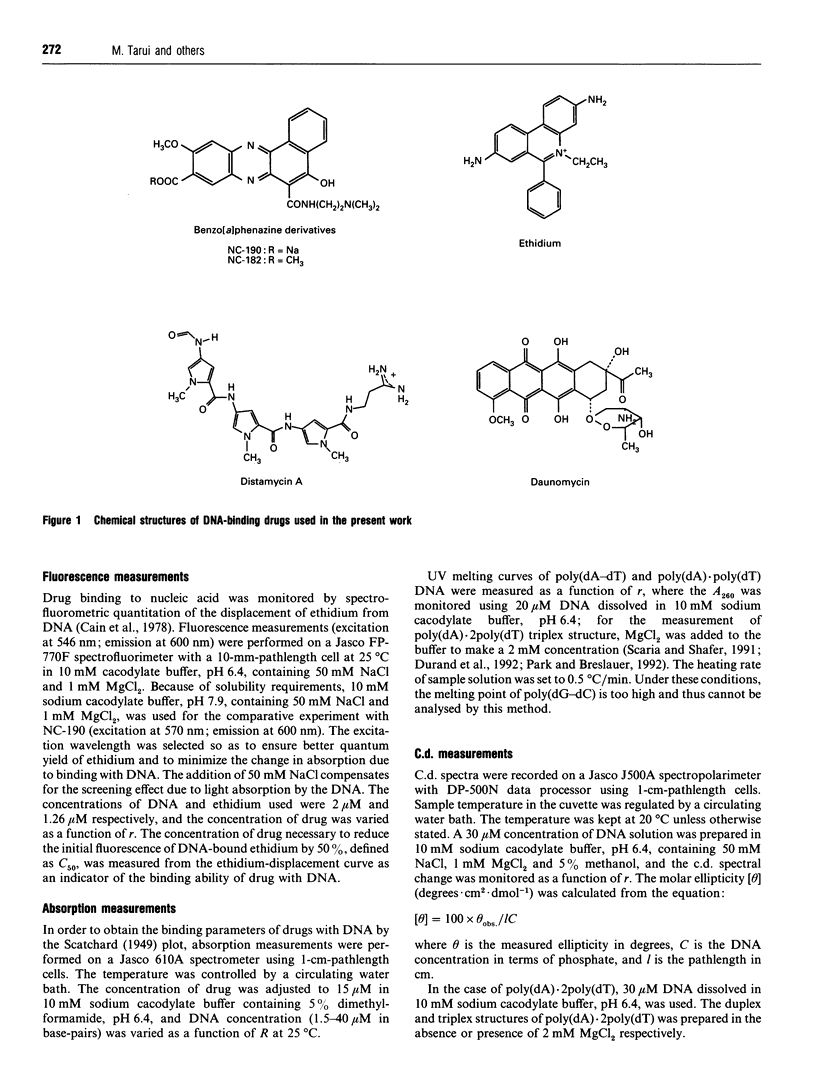
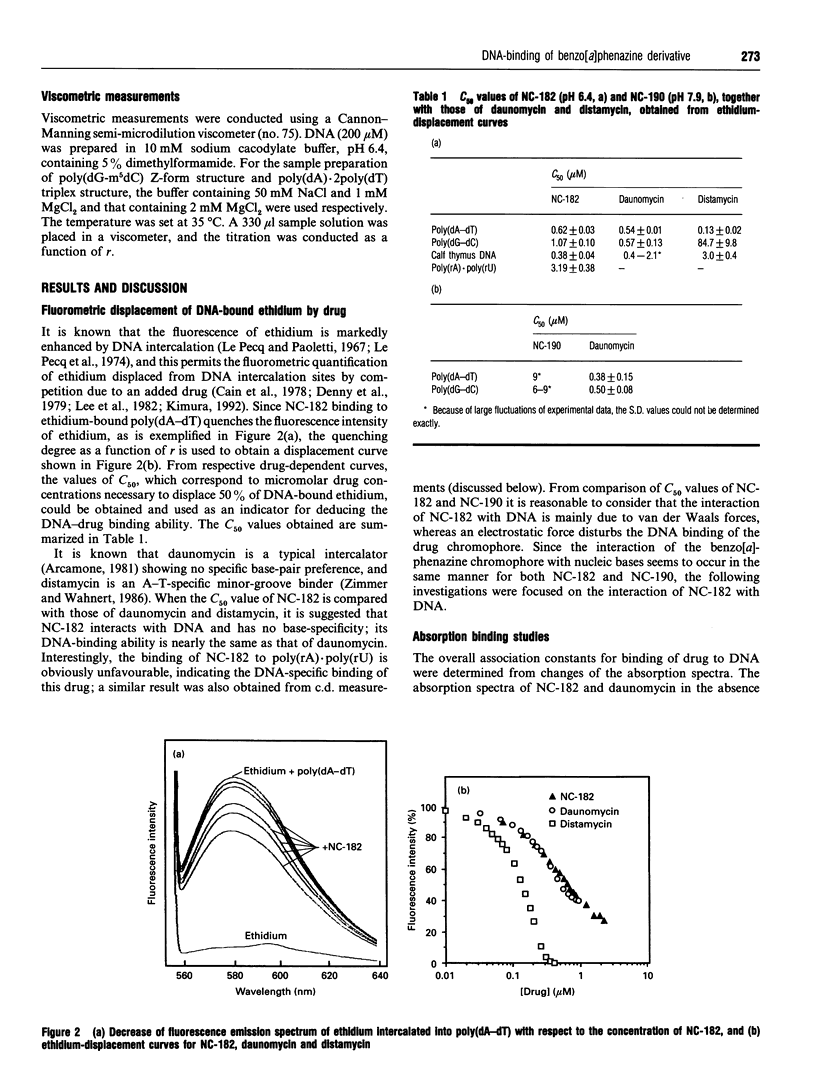
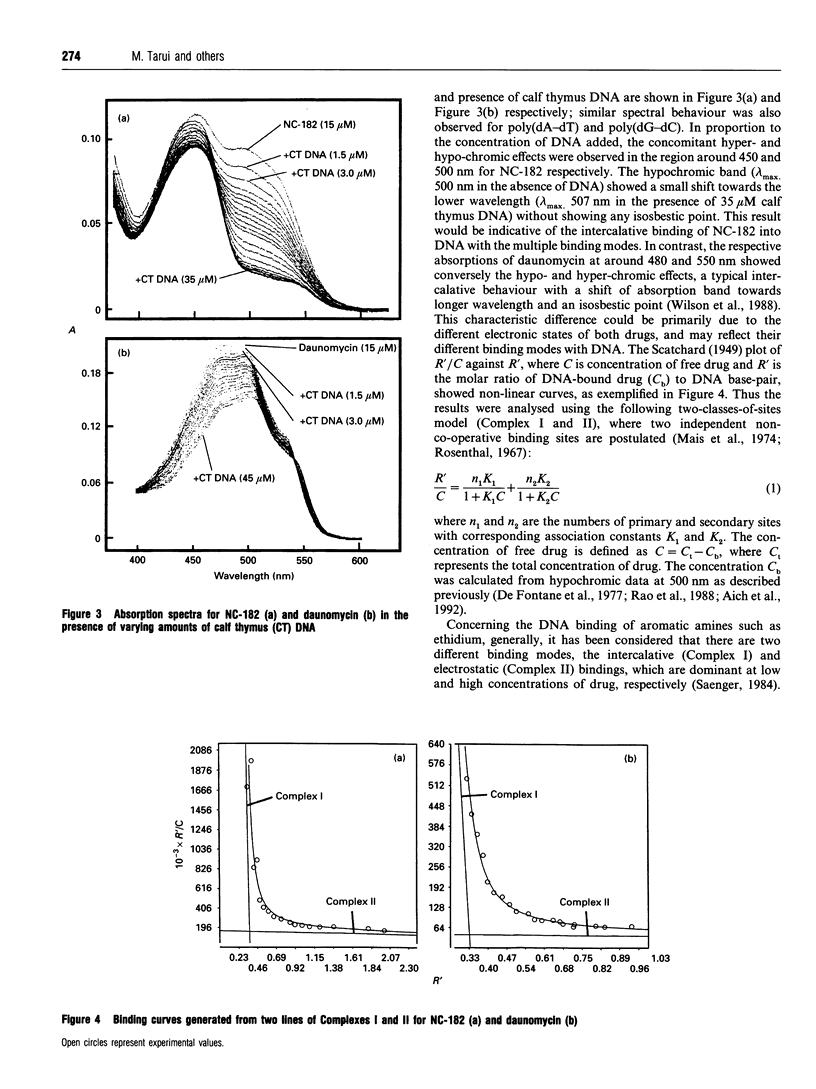
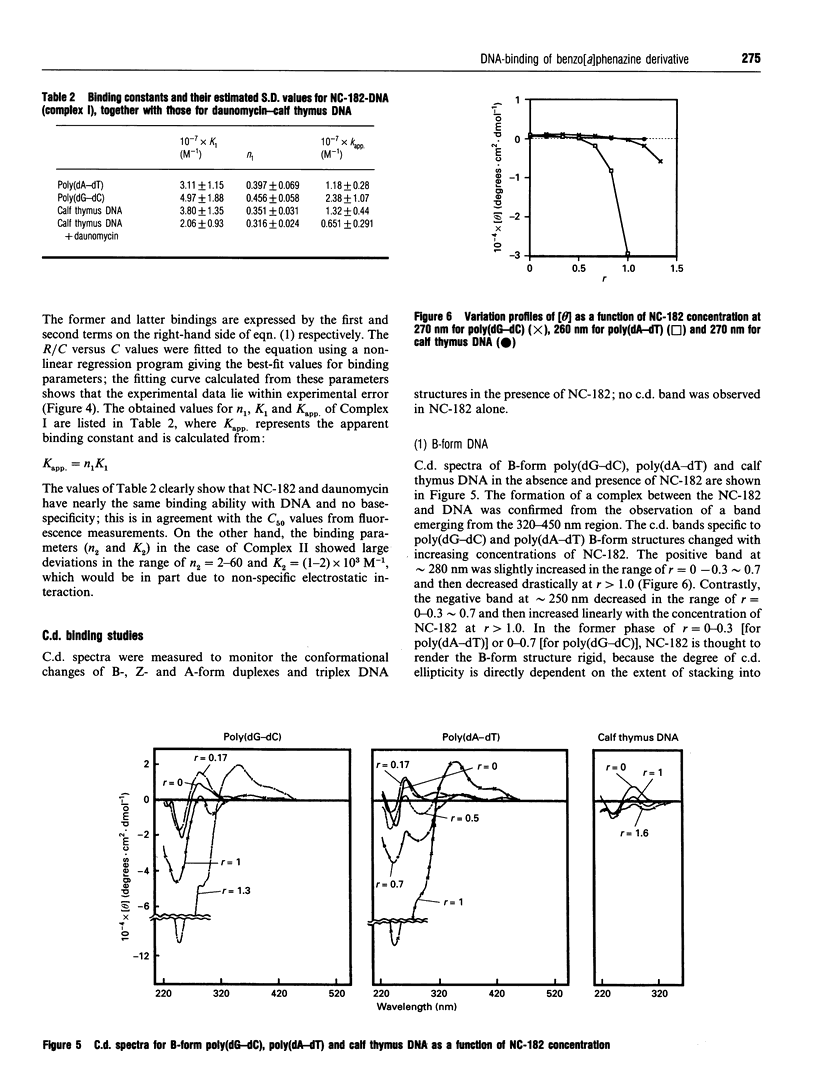
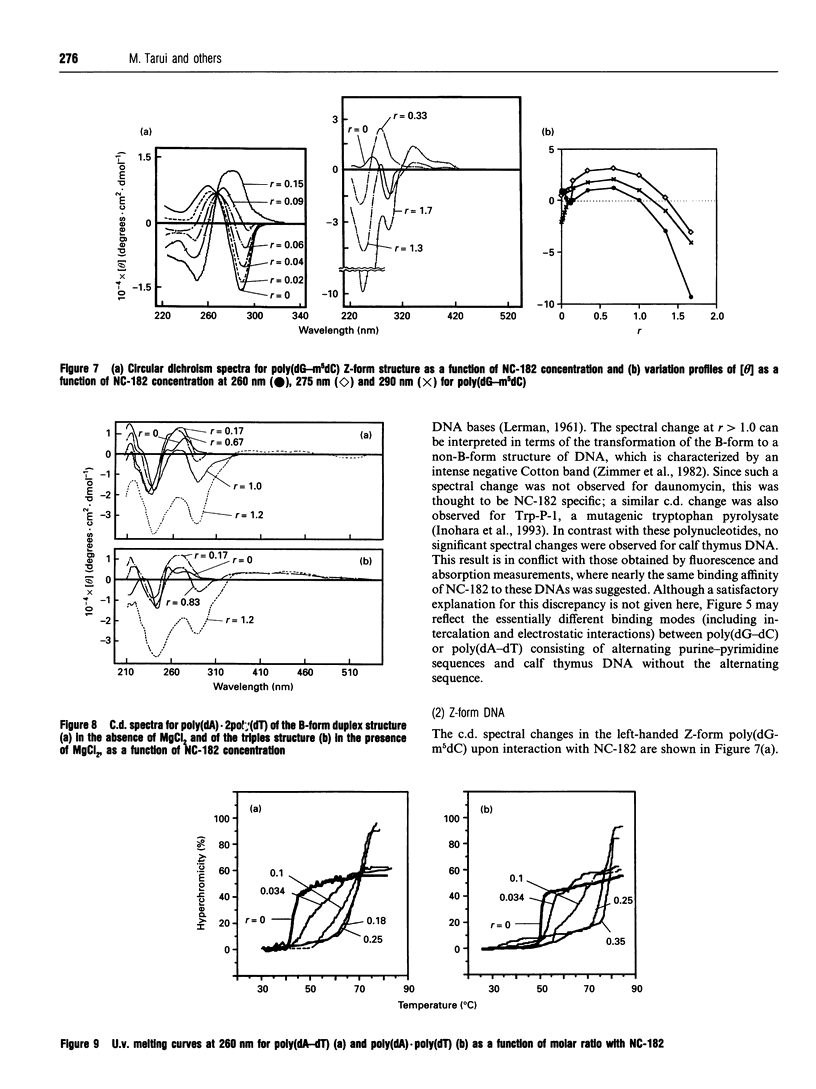
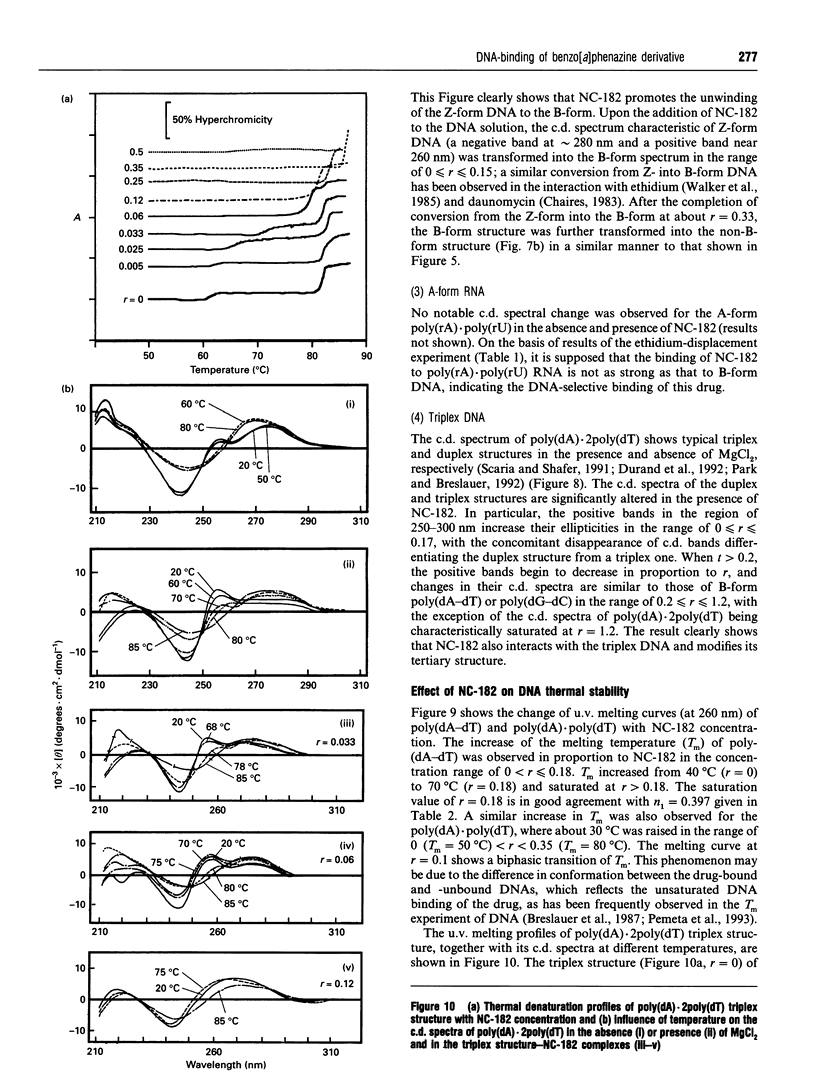
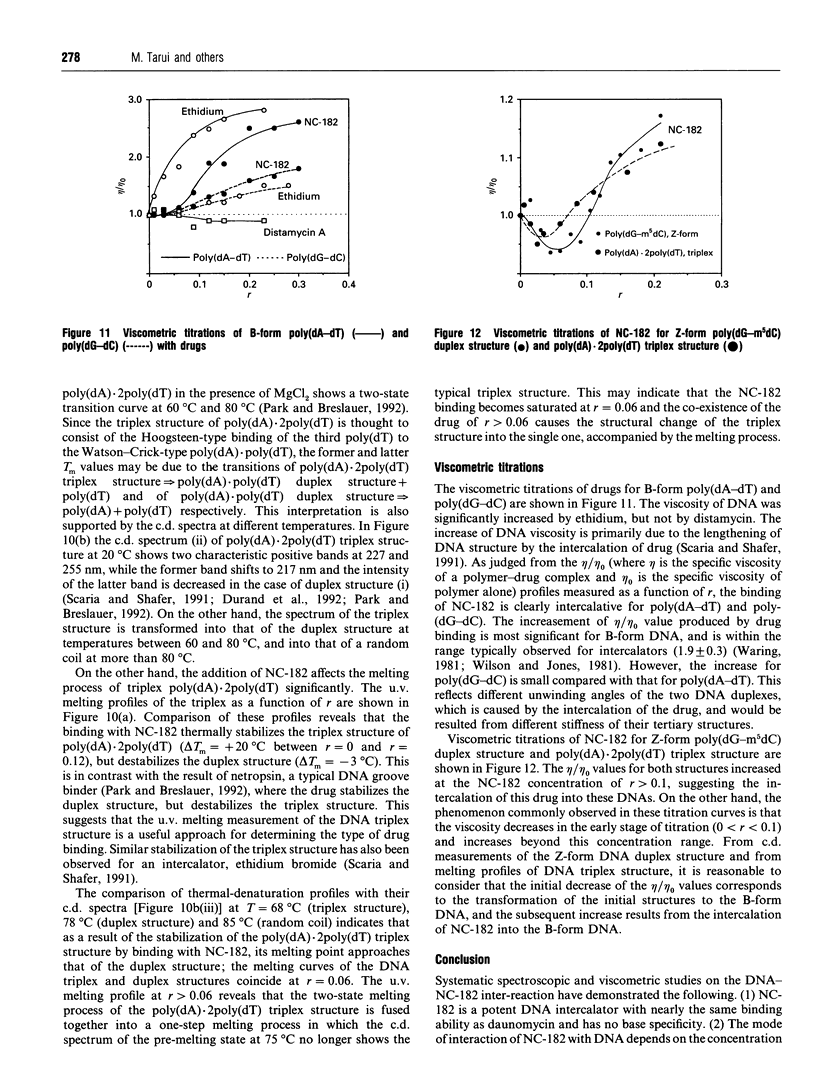
NC-182 is a novel anti-tumour compound having a benzo[a]phenazine ring. Fluorescence, absorption and c.d. spectroscopy, as well as viscometric titrations, were systematically performed to investigate the interaction mode of this drug with DNA and its effect on DNA conformation, based on comparative measurements with distamycin (DNA minor-groove binder) and daunomycin (DNA-base intercalator). NC-182 was found to be a potent intercalator of DNA, especially the B-form DNA, although no specificity was observed against the base-pair. The binding of NC-182 to B-DNA behaves biphasically, depending on the molar ratio (r) of drug to DNA: NC-182 acts to render the B-form structure rigid at relatively low r value and to promote the transformation of B- to non-B forms at high r values. It was also shown that NC-182 promotes the unwinding of Z-form DNA to B-form. Viscometric, u.v. 'melting' and c.d. experiments further showed that (1) the DNA duplex structure is thermally stabilized by intercalation with NC-182 and (2) the intercalation of NC-182 into a poly(dA).2poly(dT) DNA structure thermally stabilizes the triplex structure, resulting in a melting point close to that of the duplex structure; the melting curves of triplex and duplex structures coincide at r > 0.06. These observations make a significant contribution to our understanding of the biological properties of this novel benzo[a]phenazine derivative, a new anti-tumour tumour agent against multidrug-resistant and sensitive tumours.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aich P., Sen R., Dasgupta D. Role of magnesium ion in the interaction between chromomycin A3 and DNA: binding of chromomycin A3-Mg2+ complexes with DNA. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 24;31(11):2988–2997. doi: 10.1021/bi00126a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslauer K. J., Remeta D. P., Chou W. Y., Ferrante R., Curry J., Zaunczkowski D., Snyder J. G., Marky L. A. Enthalpy-entropy compensations in drug-DNA binding studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8922–8926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain B. F., Baguley B. C., Denny W. A. Potenial antitumor agents. 28. Deoxyribonucleic acid polyintercalating agents. J Med Chem. 1978 Jul;21(7):658–668. doi: 10.1021/jm00205a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaires J. B. Equilibrium studies on the interaction of daunomycin with deoxypolynucleotides. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 30;22(18):4204–4211. doi: 10.1021/bi00287a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen F. M., Jones C. M., Johnson Q. L. Dissociation kinetics of actinomycin D from oligonucleotides with hairpin motifs. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 1;32(21):5554–5559. doi: 10.1021/bi00072a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny W. A., Atwell G. J., Baguley B. C., Cain B. F. Potential antitumor agents. 29. Quantitative structure-activity relationships for the antileukemic bisquaternary ammonium heterocycles. J Med Chem. 1979 Feb;22(2):134–150. doi: 10.1021/jm00188a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inohara T., Tarui M., Doi M., Inoue M., Ishida T. Interaction of mutagenic tryptophan pyrolysate with DNA. CD spectral study on the binding specificity. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 21;324(3):301–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80139-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M. [Quenching of ethidium-DNA fluorescence by novel acridines with antitumor activities]. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1992 Dec;112(12):914–918. doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.112.12_914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERMAN L. S. Structural considerations in the interaction of DNA and acridines. J Mol Biol. 1961 Feb;3:18–30. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Pecq J. B., Nguyen-Dat-Xuong, Gosse C., Paoletti C. A new antitumoral agent: 9-hydroxyellipticine. Possibility of a rational design of anticancerous drugs in the series of DNA intercalating drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):5078–5082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.5078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LePecq J. B., Paoletti C. A fluorescent complex between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. Physical-chemical characterization. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):87–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90353-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. S., Hashimoto Y., Ohta T., Shudo K., Okamoto T. New dimeric analogs of 2-aminodipyrido[1,2-a:3',2'-d]imidazole: synthesis and interaction with DNA. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1982 Aug;30(8):3046–3049. doi: 10.1248/cpb.30.3046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mais R. F., Keresztes-Nagy S., Zaroslinski J. F., Oester Y. T. Interpretation of protein-drug interaction through fraction bound and relative contribution of secondary sites. J Pharm Sci. 1974 Sep;63(9):1423–1427. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600630919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaike S., Yamagishi T., Nanaumi K., Otomo S., Tsukagoshi S. Cell-killing activity and kinetic analysis of a novel antitumor compound NC-190, a benzo[a]phenazine derivative. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1992 Apr;83(4):402–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1992.tb00122.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaike S., Yamagishi T., Samata K., Nishida K., Inazuki K., Ichihara T., Migita Y., Otomo S., Aihara H., Tsukagoshi S. In vivo activity on murine tumors of a novel antitumor compound, N-beta-dimethylaminoethyl 9-carboxy-5-hydroxy-10-methoxybenzo[a]phenazine-6-carboxamide sodium salt (NC-190). Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1989;23(3):135–139. doi: 10.1007/BF00267943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park Y. W., Breslauer K. J. Drug binding to higher ordered DNA structures: netropsin complexation with a nucleic acid triple helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6653–6657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao K. E., Dasgupta D., Sasisekharan V. Interaction of synthetic analogues of distamycin and netropsin with nucleic acids. Does curvature of ligand play a role in distamycin-DNA interactions? Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):3018–3024. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remeta D. P., Mudd C. P., Berger R. L., Breslauer K. J. Thermodynamic characterization of daunomycin-DNA interactions: comparison of complete binding profiles for a series of DNA host duplexes. Biochemistry. 1993 May 18;32(19):5064–5073. doi: 10.1021/bi00070a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remeta D. P., Mudd C. P., Berger R. L., Breslauer K. J. Thermodynamic characterization of daunomycin-DNA interactions: comparison of complete binding profiles for a series of DNA host duplexes. Biochemistry. 1993 May 18;32(19):5064–5073. doi: 10.1021/bi00070a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal H. E. A graphic method for the determination and presentation of binding parameters in a complex system. Anal Biochem. 1967 Sep;20(3):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaria P. V., Shafer R. H. Binding of ethidium bromide to a DNA triple helix. Evidence for intercalation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5417–5423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuruo T., Naito M., Takamori R., Tsukahara S., Yamabe-Mitsuhashi J., Yamazaki A., Oh-hara T., Sudo Y., Nakaike S., Yamagishi T. A benzophenazine derivative, N-beta-dimethylaminoethyl 9-carboxy-5-hydroxy-10-methoxy-benzo[a]phenazine-6-carboxamide, as a new antitumor agent against multidrug-resistant and sensitive tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1990;26(2):83–87. doi: 10.1007/BF02897249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. T., Stone M. P., Krugh T. R. Ethidium binding to left-handed (Z) DNAs results in regions of right-handed DNA at the intercalation site. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7462–7471. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. D., Jones R. L. Intercalating drugs: DNA binding and molecular pharmacology. Adv Pharmacol Chemother. 1981;18:177–222. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60255-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer C., Tymen S., Marck C., Guschlbauer W. Conformational transitions of poly(dA-dC).poly(dG-dT) induced by high salt or in ethanolic solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):1081–1091. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer C., Wähnert U. Nonintercalating DNA-binding ligands: specificity of the interaction and their use as tools in biophysical, biochemical and biological investigations of the genetic material. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1986;47(1):31–112. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(86)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



