Abstract
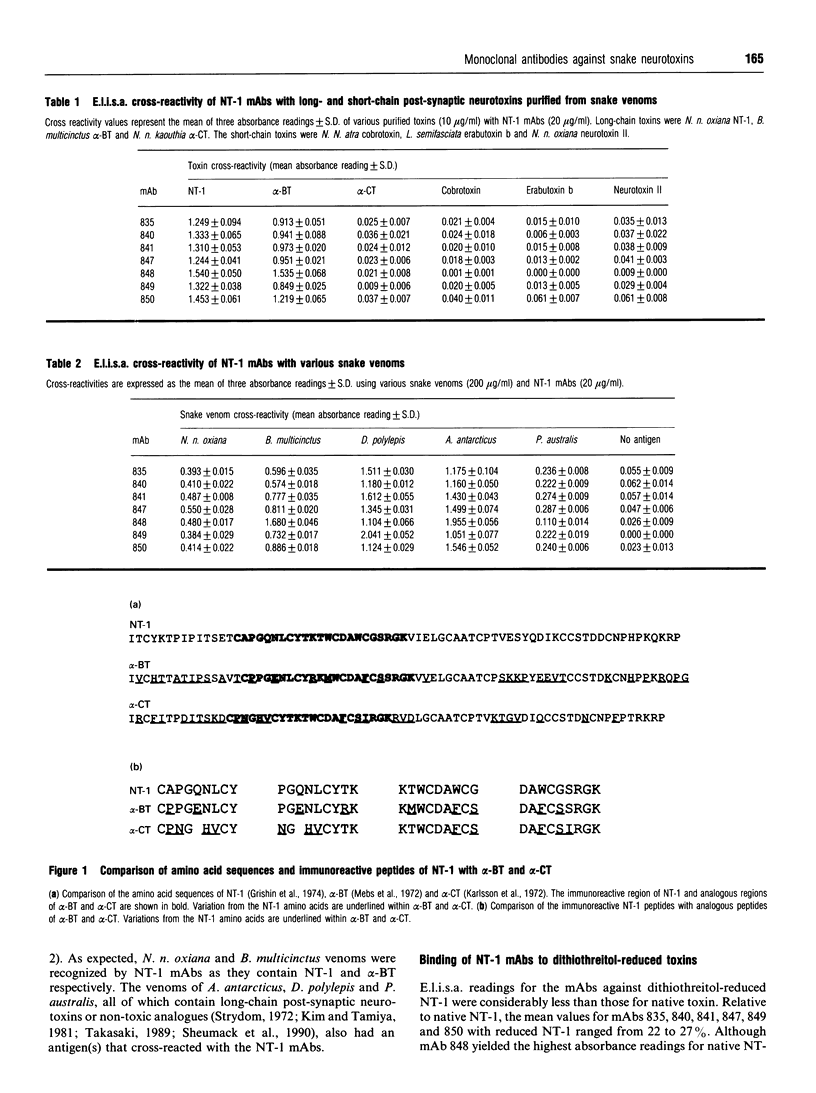
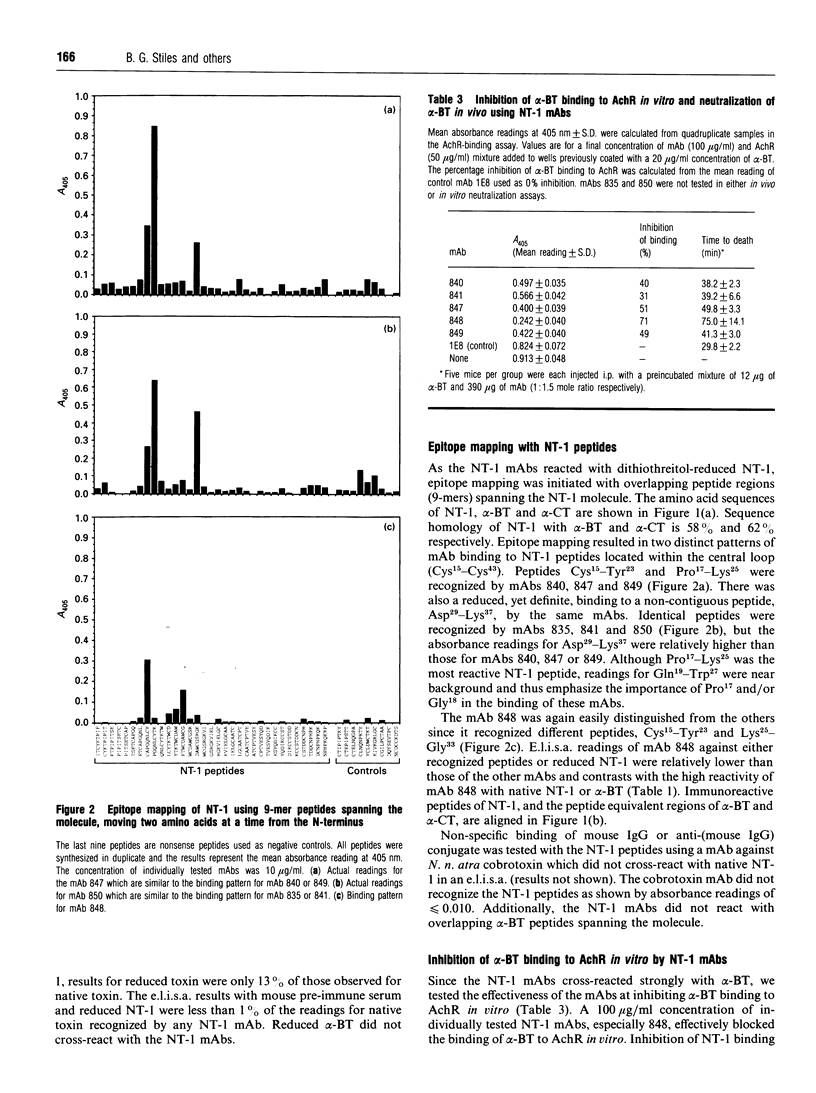
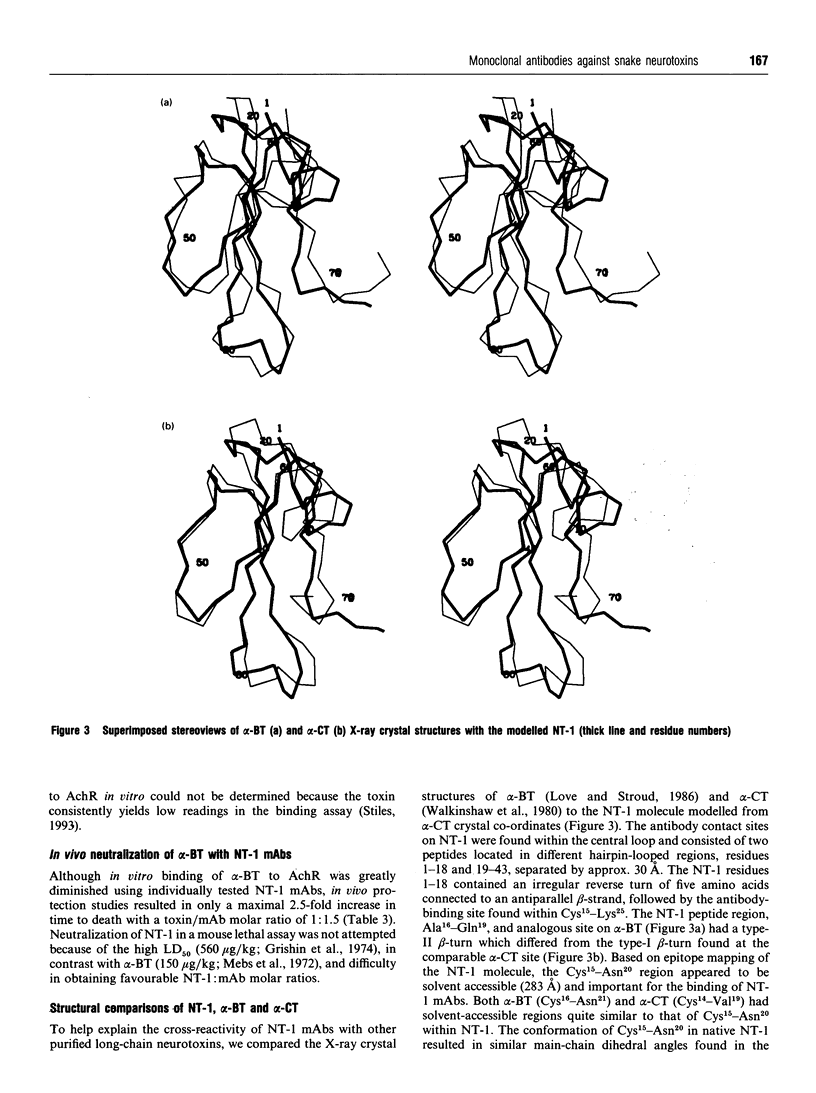
Seven monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) were developed against neurotoxin I (NT-1), a protein from central Asian cobra (Naja naja oxiana) venom which binds specifically to nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AchR). All of the mAbs cross-reacted with another long-chain post-synaptic neurotoxin, Bungarus multicinctus alpha-bungarotoxin (alpha-BT), but not Naja naja kaouthia alpha-cobratoxin, in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (e.l.i.s.a.). Short-chain post-synaptic neurotoxins like Naja naja atra cobrotoxin, Laticauda semifasciata erabutoxin b, or N. n. oxiana neurotoxin II did not cross-react with the NT-1 mAbs, but an antigen(s) found in Dendroaspis polylepis, Acanthophis antarcticus and Pseudechis australis venoms was immunoreactive. The e.l.i.s.a. readings for dithiothreitol-reduced NT-1 and NT-1 mAbs ranged from 13 to 27% of those for native toxin but reduced alpha-BT was not immunoreactive. Synthetic NT-1 peptides were used in epitope-mapping studies and two, non-contiguous regions (Cys15-Tyr23 and Lys25-Gly33 or Pro17-Lys25 and Asp29-Lys37) were recognized by the NT-1 mAbs. The NT-1 mAbs individually inhibited 31-71% of alpha-BT binding to AchR in vitro and afforded a slight protective effect in vivo with a toxin: antibody mole ratio of 1:1.5. This report is the first to describe mAbs which recognize and protect against a heterologous, long-chain, post-synaptic neurotoxin from snake venom.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amit A. G., Mariuzza R. A., Phillips S. E., Poljak R. J. Three-dimensional structure of an antigen-antibody complex at 2.8 A resolution. Science. 1986 Aug 15;233(4765):747–753. doi: 10.1126/science.2426778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betzel C., Lange G., Pal G. P., Wilson K. S., Maelicke A., Saenger W. The refined crystal structure of alpha-cobratoxin from Naja naja siamensis at 2.4-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21530–21536. doi: 10.2210/pdb2ctx/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boquet P., Poilleux G., Dumarey C., Izard Y., Ronsseray A. M. An attempt to classify the toxic proteins of Elapidae and Hydrophiidae venoms. Toxicon. 1973 Jul;11(4):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(73)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Yang C. C. Immunochemical studies on cobrotoxin. J Immunol. 1969 Jun;102(6):1437–1444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charpentier I., Pillet L., Karlsson E., Couderc J., Ménez A. Recognition of the acetylcholine receptor binding site of a long-chain neurotoxin by toxin-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Mol Recognit. 1990 Apr;3(2):74–81. doi: 10.1002/jmr.300030204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang L. Y., Lin S. R., Chang S. F., Chang C. C. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibody specific for alpha-bungarotoxin and localization of the epitope. Toxicon. 1989;27(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(89)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danse J. M., Toussaint J. L., Kempf J. Neutralization of alpha-bungarotoxin by monoclonal antibodies. Toxicon. 1986;24(2):141–151. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(86)90116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufton M. J., Hider R. C. Conformational properties of the neurotoxins and cytotoxins isolated from Elapid snake venoms. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1983;14(2):113–171. doi: 10.3109/10409238309102792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Meloen R. H., Barteling S. J. Use of peptide synthesis to probe viral antigens for epitopes to a resolution of a single amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3998–4002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J. A priori delineation of a peptide which mimics a discontinuous antigenic determinant. Mol Immunol. 1986 Jul;23(7):709–715. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grishin E. V., Sukhikh A. P., Slobodyan L. N., Ovchinnikov YuA, Sorokin V. M. Amino acid sequence of neurotoxin I from Naja naja oxiana venom. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 1;45(1):118–121. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80825-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa Y., Menez A., Hori H., Yoshida H., Tamiya N. Structure of snake toxins and their affinity to the acetylcholine receptor of fish electric organ. Toxicon. 1977;15(6):477–488. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(77)90098-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson E., Eaker D., Ponterius G. Modification of amino groups in Naja naja neurotoxins and the preparation of radioactive derivatives. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 29;257(2):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90275-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kase R., Kitagawa H., Hayashi K., Tanoue K., Inagaki F. Neutralizing monoclonal antibody specific for alpha-bungarotoxin: preparation and characterization of the antibody, and localization of antigenic region of alpha-bungarotoxin. FEBS Lett. 1989 Aug 28;254(1-2):106–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. S., Tamiya N. Isolation, properties and amino acid sequence of a long-chain neurotoxin, Acanthophis antarcticus b, from the venom of an Australian snake (the common death adder, Acanthophis antarcticus). Biochem J. 1981 Mar 1;193(3):899–906. doi: 10.1042/bj1930899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Goas R., LaPlante S. R., Mikou A., Delsuc M. A., Guittet E., Robin M., Charpentier I., Lallemand J. Y. Alpha-cobratoxin: proton NMR assignments and solution structure. Biochemistry. 1992 May 26;31(20):4867–4875. doi: 10.1021/bi00135a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love R. A., Stroud R. M. The crystal structure of alpha-bungarotoxin at 2.5 A resolution: relation to solution structure and binding to acetylcholine receptor. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):37–46. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mebs D., Narita K., Iwanaga S., Samejima Y., Lee C. Y. Purification, properties and amino acid sequence of -bungarotoxin from the venom of Bungarus multicinctus. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Feb;353(2):243–262. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1972.353.1.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikhailov A. M., Nickitenko A. V., Trakhanov S. D., Vainshtein B. K., Chetverina E. V. Crystallization and preliminary x-ray diffraction study of neurotoxin-I from Naja naja oxiana venom. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 20;269(1):255–257. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81167-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickitenko A. V., Michailov A. M., Betzel C., Wilson K. S. Three-dimensional structure of neurotoxin-1 from Naja naja oxiana venom at 1.9 A resolution. FEBS Lett. 1993 Apr 5;320(2):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachner A. R., Ricalton N. In vitro neutralization by monoclonal antibodies of alpha-bungarotoxin binding to acetylcholine receptor. Toxicon. 1989;27(12):1263–1268. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(89)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poljak R. J. X-ray diffraction studies of immunoglobulins. Adv Immunol. 1975;21:1–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruan K. H., Spurlino J., Quiocho F. A., Atassi M. Z. Acetylcholine receptor-alpha-bungarotoxin interactions: determination of the region-to-region contacts by peptide-peptide interactions and molecular modeling of the receptor cavity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6156–6160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheriff S., Silverton E. W., Padlan E. A., Cohen G. H., Smith-Gill S. J., Finzel B. C., Davies D. R. Three-dimensional structure of an antibody-antigen complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8075–8079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheumack D. D., Spence I., Tyler M. I., Howden M. E. The complete amino acid sequence of a post-synaptic neurotoxin isolated from the venom of the Australian death adder snake Acanthophis antarcticus. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1990;95(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(90)90246-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles B. G. A non-radioactive receptor assay for snake venom postsynaptic neurotoxins. Toxicon. 1991;29(4-5):503–510. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(91)90024-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles B. G. Acetylcholine receptor binding characteristics of snake and cone snail venom postsynaptic neurotoxins: further studies with a non-radioactive assay. Toxicon. 1993 Jul;31(7):825–834. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(93)90217-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles B. G., Lidgerding B. C., Sexton F. W., Guest S. B. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Naja naja atra cobrotoxin. Toxicon. 1991;29(10):1195–1204. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(91)90192-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles B. G., Middlebrook J. L. Epitope mapping of snake venom phospholipases A2 with pseudexin monoclonal antibodies. J Protein Chem. 1991 Apr;10(2):193–204. doi: 10.1007/BF01024784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom D. J. Snake venom toxins. The amino acid sequences of two toxins from Dendroaspis polylepis polylepis (black mamba) venom. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):4029–4042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasaki C. Amino acid sequence of a long-chain neurotoxin homologue, Pa ID, from the venom of an Australian elapid snake, Pseudechis australis. J Biochem. 1989 Jul;106(1):11–16. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trémeau O., Boulain J. C., Couderc J., Fromageot P., Ménez A. A monoclonal antibody which recognized the functional site of snake neurotoxins and which neutralizes all short-chain variants. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 24;208(2):236–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu A. T. Neurotoxins of animal venoms: snakes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:235–258. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.001315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Regenmortel M. H. Structural and functional approaches to the study of protein antigenicity. Immunol Today. 1989 Aug;10(8):266–272. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90140-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walkinshaw M. D., Saenger W., Maelicke A. Three-dimensional structure of the "long" neurotoxin from cobra venom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2400–2404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M., Changeux J. P. Binding of Naja nigricollis (3H)alpha-toxin to membrane fragments from Electrophorus and Torpedo electric organs. II. Effect of cholinergic agonists and antagonists on the binding of the tritiated alpha-neurotoxin. Mol Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;10(1):15–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



