Abstract
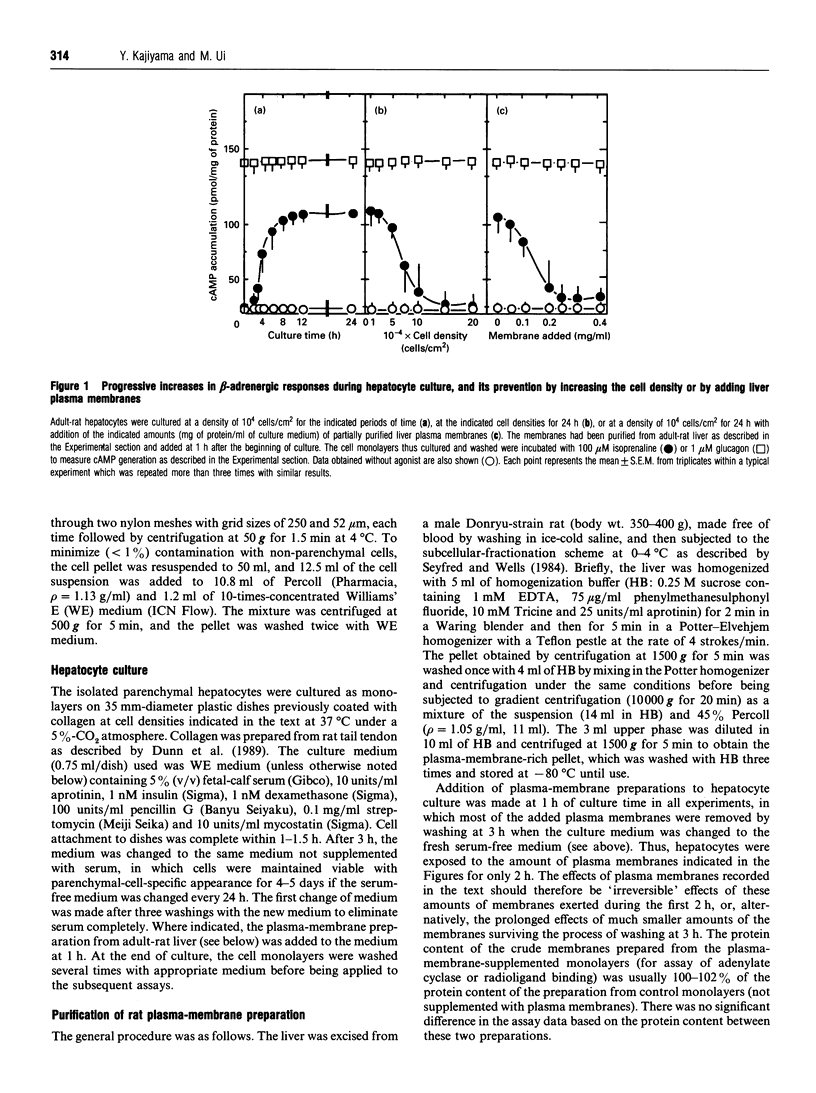
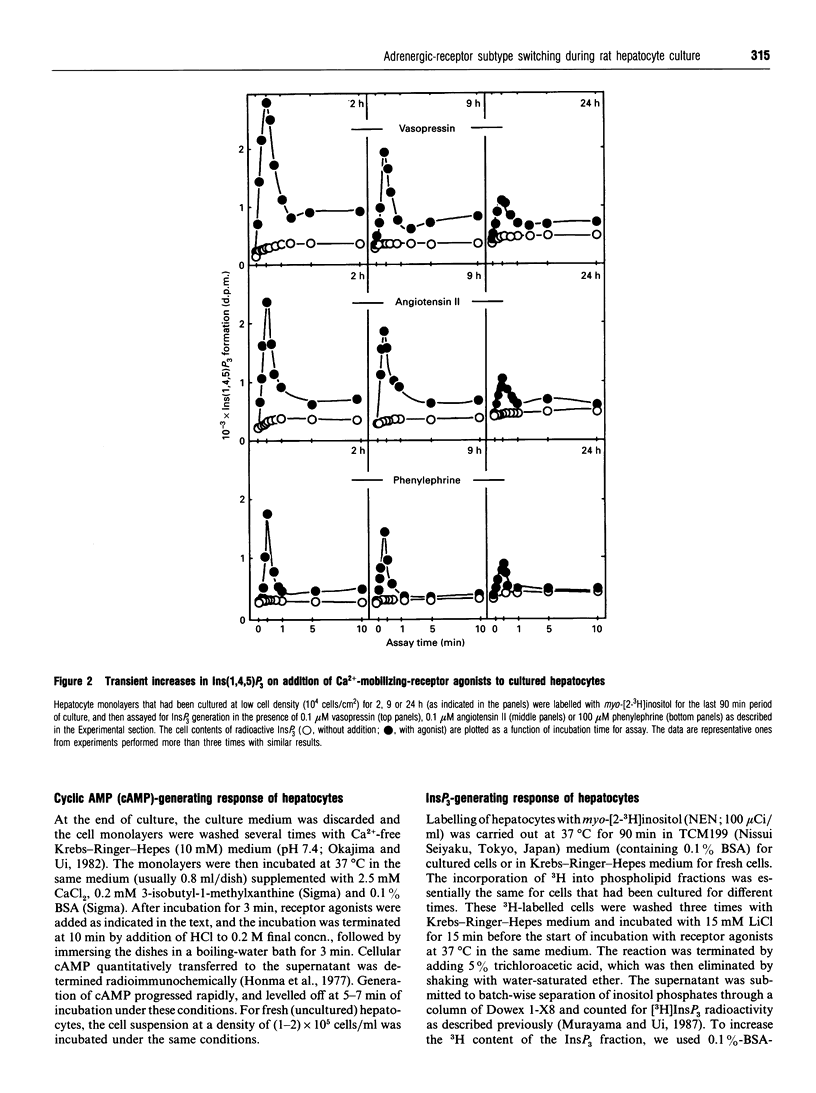
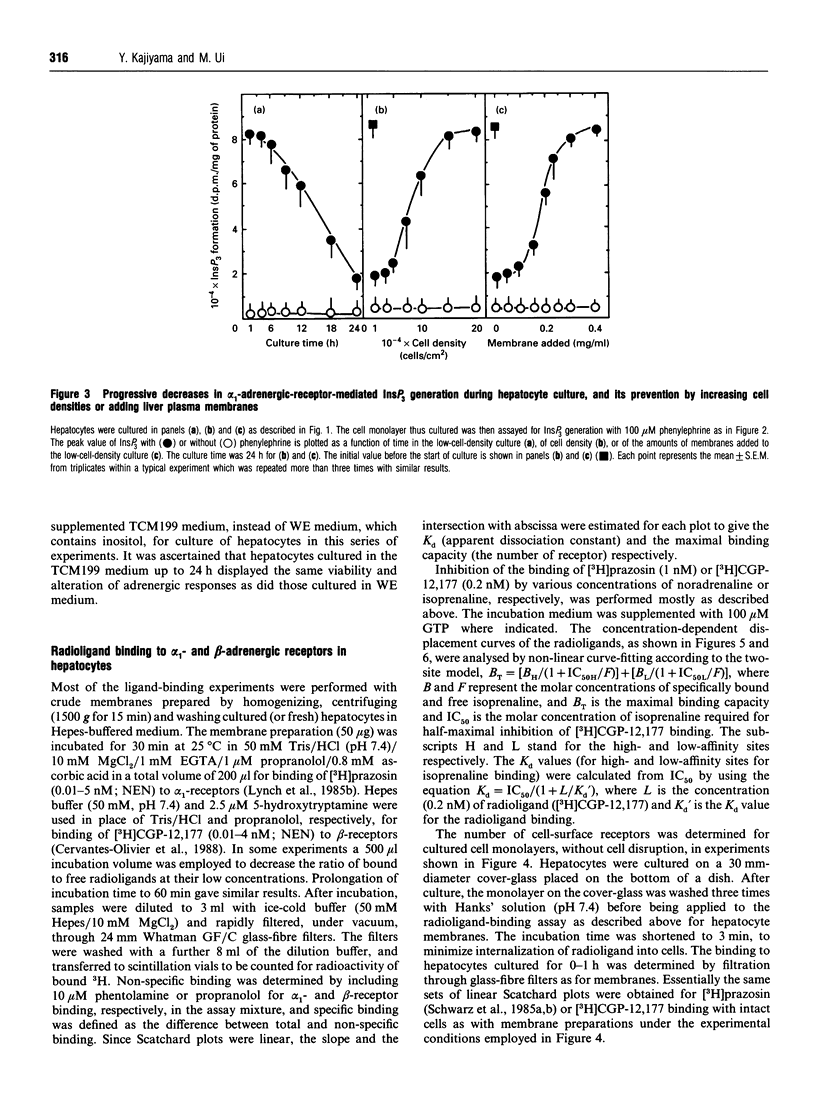
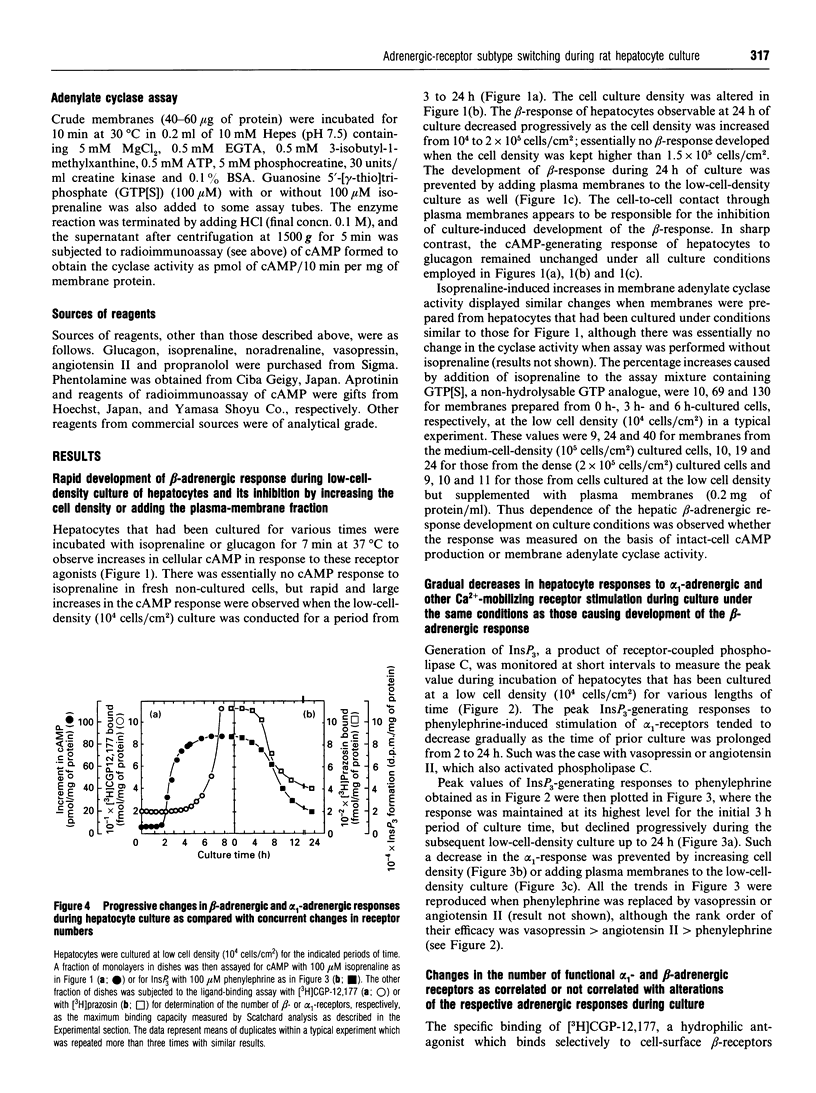
The alpha 1-adrenergic response was predominant over the beta-adrenergic one in adult rat hepatocytes, when the responses were measured as the agonist-induced generations of Ins(1,4,5)P3 and cyclic AMP, respectively. During primary culture of the adult rat hepatocytes, the beta-adrenergic response developed rapidly, whereas the alpha 1-response decreased gradually. Such receptor-subtype switching did not occur unless the cells were cultured under conditions favourable for cell growth, i.e. at low cell density (10(4) cells/cm2). The switching was prevented progressively as the cell culture density was increased up to 20-fold or the low-density culture was achieved by addition of increasing amounts of liver plasma membranes. The gradual decrease in alpha 1-response was accounted for by a concurrent decrease in the receptor site density, whereas rapid development of the beta-response definitely preceded the increase in beta-ligand binding sites during the culture. This rapid development of the beta-response reflected enhanced coupling of the receptor to G-protein during the early stage of culture, as evidenced by the progressively developed ability of GTP to lower the affinity of beta-agonist binding to membranes prepared from these short-time-cultured hepatocytes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggerbeck M., Ferry N., Zafrani E. S., Billon M. C., Barouki R., Hanoune J. Adrenergic regulation of glycogenolysis in rat liver after cholestasis. Modulation of the balance between alpha 1 and beta 2 receptors. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):476–486. doi: 10.1172/JCI110792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. N., Friend D. S. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):506–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair J. B., James M. E., Foster J. L. Adrenergic control of glucose output and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate levels in hepatocytes from juvenile and adult rats. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7579–7584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank J. L., Ross A. H., Exton J. H. Purification and characterization of two G-proteins that activate the beta 1 isozyme of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Identification as members of the Gq class. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18206–18216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocckino S. B., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Stimulation of 1,2-diacylglycerol accumulation in hepatocytes by vasopressin, epinephrine, and angiotensin II. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14201–14207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butlen D., Guillon G., Cantau B., Jard S. Comparison of the developmental patterns of vasopressin, glucagon and alpha-adrenergic receptors from rat-liver membranes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1980 Sep;19(3):275–289. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(80)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervantes-Olivier P., Delavier-Klutchko C., Durieu-Trautmann O., Kaveri S., Desmandril M., Strosberg A. D. The beta 2-adrenergic receptors of human epidermoid carcinoma cells bear two different types of oligosaccharides which influence expression on the cell surface. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):133–143. doi: 10.1042/bj2500133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest R., Prpić V., Exton J. H., Blackmore P. F. Stimulation of inositol trisphosphate formation in hepatocytes by vasopressin, adrenaline and angiotensin II and its relationship to changes in cytosolic free Ca2+. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 1;227(1):79–90. doi: 10.1042/bj2270079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Brewster G., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin and other Ca2+-mobilizing hormones. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):733–747. doi: 10.1042/bj2120733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. C., Yarmush M. L., Koebe H. G., Tompkins R. G. Hepatocyte function and extracellular matrix geometry: long-term culture in a sandwich configuration. FASEB J. 1989 Feb;3(2):174–177. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.2.2914628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemark M., Handwerger S. Glycogenolytic effects of the calcium ionophore A23187, but not of vasopressin or angiotensin, in foetal-rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):441–445. doi: 10.1042/bj2200441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Sáinz J. A., Nájera-Alvarado A. Hormonal responsiveness of liver cells during the liver regeneration process induced by carbon tetrachloride administration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 23;885(1):102–109. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodhardt M., Ferry N., Aggerbeck M., Hanoune J. The hepatic alpha 1-adrenergic receptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Mar 15;33(6):863–868. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90439-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honma M., Satoh T., Takezawa J., Ui M. An ultrasensitive method for the simultaneous determination of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP in small-volume samples from blood and tissue. Biochem Med. 1977 Dec;18(3):257–273. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(77)90060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huerta-Bahena J., García-Saínz J. A. Inositol administration restores the sensitivity of liver cells formed during liver regeneration to alpha 1-adrenergic amines, vasopressin and angiotensin II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 22;763(2):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huerta-Bahena J., Villalobos-Molina R., Corvera S., García-Saínz J. A. Sensitivity of liver cells formed after partial hepatectomy to glucagon, vasopressin and angiotensin II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 22;763(2):120–124. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huerta-Bahena J., Villalobos-Molina R., García-Saínz J. A. Roles of alpha 1- and beta-adrenergic receptors in adrenergic responsiveness of liver cells formed after partial hepatectomy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 22;763(2):112–119. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishac E. J., Kunos G. An arachidonate metabolite is involved in the conversion from alpha 1- to beta-adrenergic glycogenolysis in isolated rat liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):53–57. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Okajima F., Ui M. Conversion of adrenergic mechanism from an alpha- to a beta-type during primary culture of rat hepatocytes. Accompanying decreases in the function of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory component of adenylate cyclase identified as the substrate of islet-activating protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15464–15473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz M. S., Boland S. R., Schmidt S. J. Developmental changes of beta-adrenergic receptor-linked adenylate cyclase of rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jun;248(6 Pt 1):E712–E718. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.6.E712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunos G., Hirata F., Ishac E. J., Tchakarov L. Time-dependent conversion of alpha 1- to beta-adrenoceptor-mediated glycogenolysis in isolated rat liver cells: role of membrane phospholipase A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6178–6182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch C. J., Blackmore P. F., Charest R., Exton J. H. The relationships between receptor binding capacity for norepinephrine, angiotensin II, and vasopressin and release of inositol trisphosphate, Ca2+ mobilization, and phosphorylase activation in rat liver. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Aug;28(2):93–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch C. J., Charest R., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Studies on the hepatic alpha 1-adrenergic receptor. Modulation of guanine nucleotide effects by calcium, temperature, and age. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1593–1600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch C. J., Sobo G. E., Exton J. H. An endogenous Ca2+-sensitive proteinase converts the hepatic alpha 1-adrenergic receptor to guanine nucleotide-insensitive forms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 23;885(1):110–120. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalopoulos G. K. Liver regeneration: molecular mechanisms of growth control. FASEB J. 1990 Feb 1;4(2):176–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan N. G., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Age-related changes in the control of hepatic cyclic AMP levels by alpha 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors in male rats. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5103–5109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Ui M. Phosphatidic acid may stimulate membrane receptors mediating adenylate cyclase inhibition and phospholipid breakdown in 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5522–5529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Nakayama Y., Ichihara A. Reciprocal modulation of growth and liver functions of mature rat hepatocytes in primary culture by an extract of hepatic plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8056–8058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Nakayama Y., Teramoto H., Nawa K., Ichihara A. Loss of reciprocal modulations of growth and liver function of hepatoma cells in culture by contact with cells or cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6398–6402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Tomita Y., Ichihara A. Density-dependent growth control of adult rat hepatocytes in primary culture. J Biochem. 1983 Oct;94(4):1029–1035. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Tomomura A., Kato S., Noda C., Ichihara A. Reciprocal expressions of alpha 1- and beta-adrenergic receptors, but constant expression of glucagon receptor by rat hepatocytes during development and primary culture. J Biochem. 1984 Jul;96(1):127–136. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Tomomura A., Noda C., Shimoji M., Ichihara A. Acquisition of a beta-adrenergic response by adult rat hepatocytes during primary culture. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9283–9289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Yoshimoto K., Nakayama Y., Tomita Y., Ichihara A. Reciprocal modulation of growth and differentiated functions of mature rat hepatocytes in primary culture by cell--cell contact and cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7229–7233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi A., Jett P. A., Gold A. H. cAMP-independent stimulation of glycogen phosphorylase in newborn rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):E560–E566. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.5.E560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Ui M. Conversion of adrenergic regulation of glycogen phosphorylase and synthase from an alpha to a beta type during primary culture of rat hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Feb;213(2):658–668. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90596-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Ui M. Predominance of beta-adrenergic over alpha-adrenergic receptor functions involved in phosphorylase activation in liver cells of cholestatic rats. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 May 1;230(2):640–651. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90445-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer L. S., Black I. B., Reid L. M. Regulation of beta-adrenergic receptor expression in rat liver. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Jul;140(1):52–58. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041400107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz K. R., Lanier S. M., Carter E. A., Graham R. M., Homcy C. J. Transient high-affinity binding of agonists to alpha 1-adrenergic receptors of intact liver cells. FEBS Lett. 1985 Aug 5;187(2):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz K. R., Lanier S. M., Carter E. A., Homcy C. J., Graham R. M. Rapid reciprocal changes in adrenergic receptors in intact isolated hepatocytes during primary cell culture. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;27(2):200–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyfred M. A., Wells W. W. Subcellular incorporation of 32P into phosphoinositides and other phospholipids in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7659–7665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai S., Nakamura T., Komi N., Ichihara A. Mechanism of stimulation of DNA synthesis induced by epinephrine in primary culture of adult rat hepatocytes. J Biochem. 1988 May;103(5):848–852. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Smith J. A., Exton J. H. Purification from bovine liver membranes of a guanine nucleotide-dependent activator of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Immunologic identification as a novel G-protein alpha subunit. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17150–17156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. P., Alexander J., Williamson J. R. Relationship between inositol polyphosphate production and the increase of cytosolic free Ca2+ induced by vasopressin in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5574–5584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto A., Tsujimoto G., Azhar S., Hoffman B. B. Altered responsiveness to alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor stimulation in hepatocytes cultured in defined medium. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Apr 15;35(8):1400–1404. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90290-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wange R. L., Smrcka A. V., Sternweis P. C., Exton J. H. Photoaffinity labeling of two rat liver plasma membrane proteins with [32P]gamma-azidoanilido GTP in response to vasopressin. Immunologic identification as alpha subunits of the Gq class of G proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11409–11412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


