Abstract
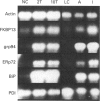
In order to determine whether the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) luminal FK506-binding protein, FKBP13, shares properties of ER molecular chaperones, MDCK cells were treated with either tunicamycin or Ca2+ ionophores. By Northern-blot analysis, tunicamycin resulted in a 2-fold rise in FKBP13 mRNA, whereas ionophores (A23187 and ionomycin) caused a more impressive rise in FKBP13 mRNA (up to 5-fold with ionomycin). Actinomycin D chase experiments in ionomycin-treated cells revealed no change in the half-life of FKBP13 mRNA, indicating that the increase in FKBP13 mRNA observed was not due to greater message stability. Moreover, sequencing of the 5' flanking region of the gene for murine FKBP13 revealed significant similarity to similar regions in human BiP (immunoglobulin-binding protein) and the human glucose-regulated protein grp94, including a 37 bp sequence in FKBP13 with approximately 50% identity with the unfolded protein response element of the BiP gene. Together, these data suggest a role for FKBP13 in ER protein folding.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bierer B. E., Jin Y. J., Fruman D. A., Calvo V., Burakoff S. J. FK 506 and rapamycin: molecular probes of T-lymphocyte activation. Transplant Proc. 1991 Dec;23(6):2850–2855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth C., Koch G. L. Perturbation of cellular calcium induces secretion of luminal ER proteins. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):729–737. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. C., Erwin A. E., Lee A. S. Glucose-regulated protein (GRP94 and GRP78) genes share common regulatory domains and are coordinately regulated by common trans-acting factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2153–2162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. S., Shamu C. E., Walter P. Transcriptional induction of genes encoding endoplasmic reticulum resident proteins requires a transmembrane protein kinase. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1197–1206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90648-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Wasley L. C., Raney P., Haugejorden S., Green M., Kaufman R. J. The stress response in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Regulation of ERp72 and protein disulfide isomerase expression and secretion. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):22029–22034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Lewis C. D., Felsenfeld G. Interaction of specific nuclear factors with the nuclease-hypersensitive region of the chicken adult beta-globin gene: nature of the binding domain. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M. Rapid and quantitative preparation of cytoplasmic RNA from small numbers of cells. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;173(1):93–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson B. A., Zhang W., Craig R. J., Jin Y. J., Bierer B. E., Burakoff S., DiLella A. G. Structural organization of the genes encoding human and murine FK506-binding protein (FKBP) 13 and comparison to FKBP1. Gene. 1993 Dec 8;134(2):271–275. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90106-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin Y. J., Albers M. W., Lane W. S., Bierer B. E., Schreiber S. L., Burakoff S. J. Molecular cloning of a membrane-associated human FK506- and rapamycin-binding protein, FKBP-13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6677–6681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper B., Jackson P. D., Felsenfeld G. Protein-binding sites within the 5' DNase I-hypersensitive region of the chicken alpha D-globin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2059–2069. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. A., Lee A. S. Competitive inhibition of a set of endoplasmic reticulum protein genes (GRP78, GRP94, and ERp72) retards cell growth and lowers viability after ionophore treatment. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3446–3453. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Kong N. Perturbation of cellular calcium blocks exit of secretory proteins from the rough endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10893–10899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCauliffe D. P., Yang Y. S., Wilson J., Sontheimer R. D., Capra J. D. The 5'-flanking region of the human calreticulin gene shares homology with the human GRP78, GRP94, and protein disulfide isomerase promoters. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2557–2562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori K., Sant A., Kohno K., Normington K., Gething M. J., Sambrook J. F. A 22 bp cis-acting element is necessary and sufficient for the induction of the yeast KAR2 (BiP) gene by unfolded proteins. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2583–2593. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05323.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigam S. K., Blobel G. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in canine pancreatic rough endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16927–16932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigam S. K., Denisenko N., Rodriguez-Boulan E., Citi S. The role of phosphorylation in development of tight junctions in cultured renal epithelial (MDCK) cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 16;181(2):548–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91224-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigam S. K., Goldberg A. L., Ho S., Rohde M. F., Bush K. T., Sherman MYu A set of endoplasmic reticulum proteins possessing properties of molecular chaperones includes Ca(2+)-binding proteins and members of the thioredoxin superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1744–1749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigam S. K., Jin Y. J., Jin M. J., Bush K. T., Bierer B. E., Burakoff S. J. Localization of the FK506-binding protein, FKBP 13, to the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 1993 Sep 1;294(Pt 2):511–515. doi: 10.1042/bj2940511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resendez E., Jr, Wooden S. K., Lee A. S. Identification of highly conserved regulatory domains and protein-binding sites in the promoters of the rat and human genes encoding the stress-inducible 78-kilodalton glucose-regulated protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4579–4584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasanen K., Oikarinen J., Kivirikko K. I., Pihlajaniemi T. Promoter of the gene for the multifunctional protein disulfide isomerase polypeptide. Functional significance of the six CCAAT boxes and other promoter elements. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11513–11519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting J., Lee A. S. Human gene encoding the 78,000-dalton glucose-regulated protein and its pseudogene: structure, conservation, and regulation. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):275–286. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]