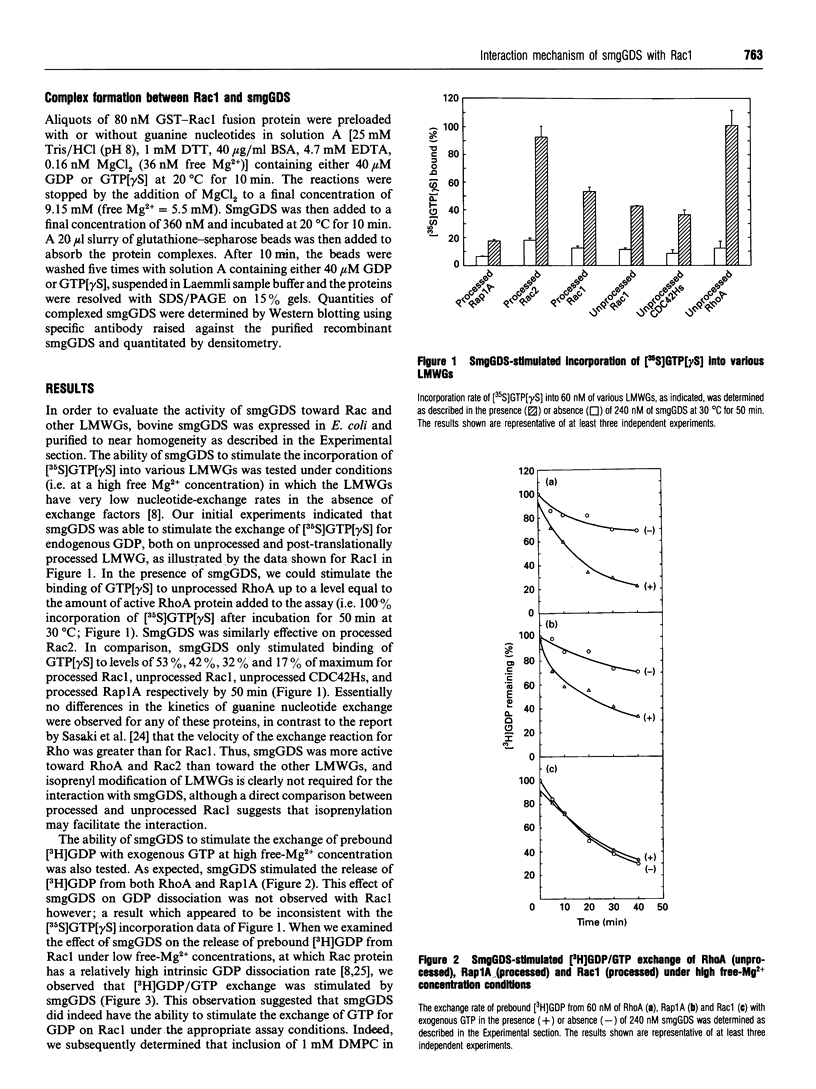
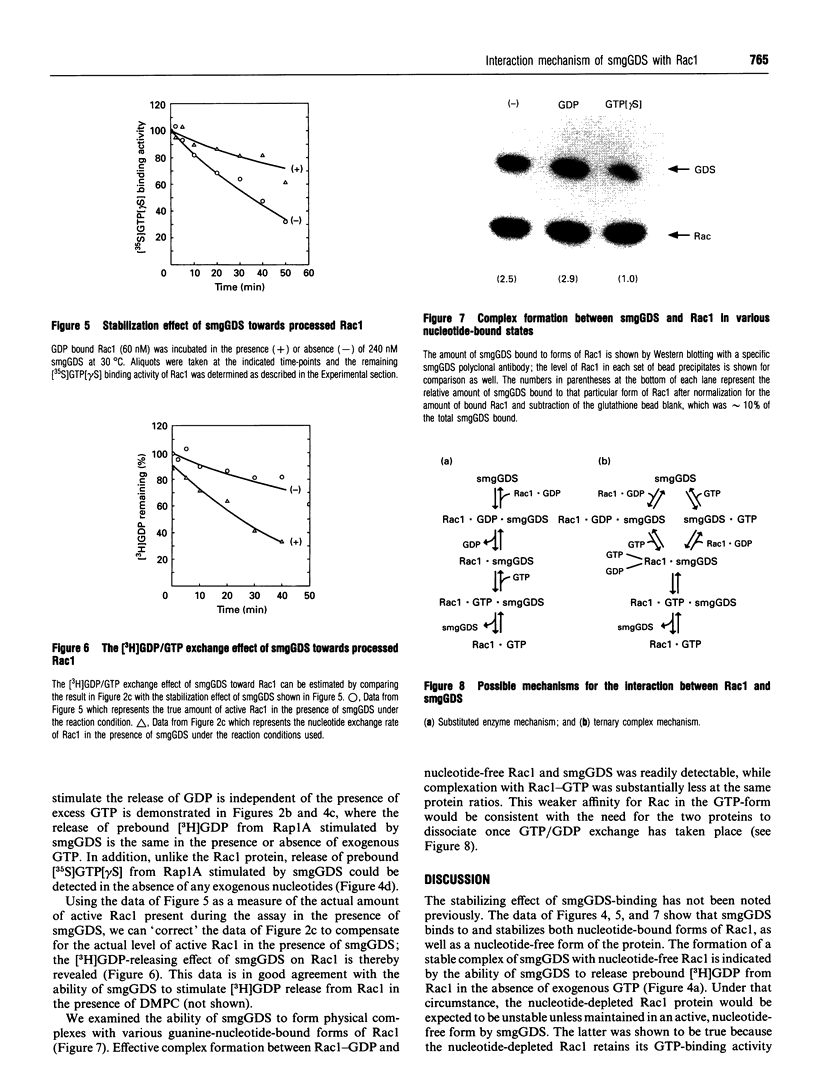
Abstract
The Rac proteins, Rac1 and Rac2, are essential components of the NADPH oxidase system of phagocytes and regulate the actin assembly associated with membrane ruffling. These functions are controlled by the GTP-bound form of Rac. The biochemical interaction between Rac and its only known GDP-dissociation stimulator (termed smgGDS) was characterized. SmgGDS was able to stimulate the incorporation of guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]-triphosphate GTP[gamma S] into the RhoA, Rac2, Rac1, Rap1A and CDC42Hs GTP-binding proteins, but the activity was greatest toward RhoA and Rac2. Isoprenoid modification of these proteins was not absolutely required for the interaction with smgGDS. Interestingly, the activity of smgGDS toward Rac1 could not be observed in a [3H]GDP/GTP exchange assay under conditions where it stimulated incorporation of GTP[gamma S] into Rac1. We determined that smgGDS prevented the loss of Rac1 activity during the [3H]GDP/GTP exchange assay by demonstrating the ability of smgGDS to inhibit the loss of Rac1 GTP[gamma S]-binding during incubations at 30 degrees C. This stabilizing effect was exactly counterbalanced by the ability of smgGDS to stimulate the release of [3H]GDP from Rac1, thereby producing no net observable effect in the exchange assay. SmgGDS was able to effectively stimulate the release of GDP but not GTP[gamma S] from Rac1. SmgGDS maintains Rac1 in a nucleotide-free form after release of GDP, indicating that the reaction between Rac1 and smgGDS involves a substituted enzyme mechanism.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo A., Pick E., Hall A., Totty N., Teahan C. G., Segal A. W. Activation of the NADPH oxidase involves the small GTP-binding protein p21rac1. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):668–670. doi: 10.1038/353668a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Der C. J. Emerging concepts in the Ras superfamily of GTP-binding proteins. FASEB J. 1993 Jun;7(9):750–759. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.9.8330683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang T. H., Bohl B. P., Bokoch G. M. Biologically active lipids are regulators of Rac.GDI complexation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26206–26211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang T. H., Xu X., Knaus U. G., Hart M. J., Bokoch G. M. GDP dissociation inhibitor prevents intrinsic and GTPase activating protein-stimulated GTP hydrolysis by the Rac GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):775–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J. Signal transduction. Exchange rate mechanisms. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):282–283. doi: 10.1038/358282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart M. J., Eva A., Evans T., Aaronson S. A., Cerione R. A. Catalysis of guanine nucleotide exchange on the CDC42Hs protein by the dbl oncogene product. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):311–314. doi: 10.1038/354311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart M. J., Eva A., Zangrilli D., Aaronson S. A., Evans T., Cerione R. A., Zheng Y. Cellular transformation and guanine nucleotide exchange activity are catalyzed by a common domain on the dbl oncogene product. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):62–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyworth P. G., Knaus U. G., Xu X., Uhlinger D. J., Conroy L., Bokoch G. M., Curnutte J. T. Requirement for posttranslational processing of Rac GTP-binding proteins for activation of human neutrophil NADPH oxidase. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Mar;4(3):261–269. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka K., Kaibuchi K., Ando S., Musha T., Takaishi K., Mizuno T., Asada M., Ménard L., Tomhave E., Didsbury J. Both stimulatory and inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange proteins, smg GDS and rho GDI, are active on multiple small GTP-binding proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jan 31;182(2):921–930. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91820-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori Y., Kikuchi A., Isomura M., Katayama M., Miura Y., Fujioka H., Kaibuchi K., Takai Y. Post-translational modifications of the C-terminal region of the rho protein are important for its interaction with membranes and the stimulatory and inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange proteins. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):515–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang Y. W., Miller D. L. A study of the kinetic mechanism of elongation factor Ts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11498–11502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang Y. W., Zhong J. M., Poullet P., Parmeggiani A. Inhibition of SDC25 C-domain-induced guanine-nucleotide exchange by guanine ring binding domain mutants of v-H-ras. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):24692–24698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Mizuno T., Fujioka H., Yamamoto T., Kishi K., Fukumoto Y., Hori Y., Takai Y. Molecular cloning of the cDNA for stimulatory GDP/GTP exchange protein for smg p21s (ras p21-like small GTP-binding proteins) and characterization of stimulatory GDP/GTP exchange protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2873–2880. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura M., Kaibuchi K., Kishi K., Takai Y. Translocation of Ki-ras p21 between membrane and cytoplasm by smg GDS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Feb 15;190(3):832–841. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura S., Kaibuchi K., Hiroyoshi M., Hata Y., Takai Y. Stoichiometric interaction of smg p21 with its GDP/GTP exchange protein and its novel action to regulate the translocation of smg p21 between membrane and cytoplasm. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 14;174(3):1095–1102. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91533-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi A., Kaibuchi K., Hori Y., Nonaka H., Sakoda T., Kawamura M., Mizuno T., Takai Y. Molecular cloning of the human cDNA for a stimulatory GDP/GTP exchange protein for c-Ki-ras p21 and smg p21. Oncogene. 1992 Feb;7(2):289–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus U. G., Heyworth P. G., Evans T., Curnutte J. T., Bokoch G. M. Regulation of phagocyte oxygen radical production by the GTP-binding protein Rac 2. Science. 1991 Dec 6;254(5037):1512–1515. doi: 10.1126/science.1660188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus U. G., Heyworth P. G., Kinsella B. T., Curnutte J. T., Bokoch G. M. Purification and characterization of Rac 2. A cytosolic GTP-binding protein that regulates human neutrophil NADPH oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23575–23582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani K., Kikuchi A., Doi K., Kishida S., Sakoda T., Kishi K., Takai Y. The functional domain of the stimulatory GDP/GTP exchange protein (smg GDS) which interacts with the C-terminal geranylgeranylated region of rap1/Krev-1/smg p21. Oncogene. 1992 Sep;7(9):1699–1704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong C. H., Malech H. L., Rotrosen D., Leto T. L. Regulation of the human neutrophil NADPH oxidase by rho-related G-proteins. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 1;32(21):5711–5717. doi: 10.1021/bi00072a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. C., Boguski M., Broek D., Powers S. Influence of guanine nucleotides on complex formation between Ras and CDC25 proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1345–1352. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Kaibuchi K., Ando S., Musha T., Hiraoka K., Takaishi K., Asada M., Nunoi H., Matsuda I., Takai Y. Regulation of the superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase by a small GTP-binding protein and its stimulatory and inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10215–10218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Kaibuchi K., Yamamoto T., Kawamura M., Sakoda T., Fujioka H., Matsuura Y., Takai Y. A stimulatory GDP/GTP exchange protein for smg p21 is active on the post-translationally processed form of c-Ki-ras p21 and rhoA p21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6442–6446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philips M. R., Pillinger M. H., Staud R., Volker C., Rosenfeld M. G., Weissmann G., Stock J. B. Carboxyl methylation of Ras-related proteins during signal transduction in neutrophils. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.8438158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Gorzalczany Y., Engel S. Role of the rac1 p21-GDP-dissociation inhibitor for rho heterodimer in the activation of the superoxide-forming NADPH oxidase of macrophages. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Oct 1;217(1):441–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quilliam L. A., Der C. J., Clark R., O'Rourke E. C., Zhang K., McCormick F., Bokoch G. M. Biochemical characterization of baculovirus-expressed rap1A/Krev-1 and its regulation by GTPase-activating proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2901–2908. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn M. T., Evans T., Loetterle L. R., Jesaitis A. J., Bokoch G. M. Translocation of Rac correlates with NADPH oxidase activation. Evidence for equimolar translocation of oxidase components. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):20983–20987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Johnston C. L., Diekmann D., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands A. G., Panniers R., Henshaw E. C. The catalytic mechanism of guanine nucleotide exchange factor action and competitive inhibition by phosphorylated eukaryotic initiation factor 2. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5526–5533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Kato M., Nishiyama T., Takai Y. The nucleotide exchange rates of rho and rac small GTP-binding proteins are enhanced to different extents by their regulatory protein Smg GDS. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Aug 16;194(3):1188–1193. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Kikuchi A., Kawata M. Small GTP-binding proteins. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;133:187–230. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61861-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Kaibuchi K., Mizuno T., Hiroyoshi M., Shirataki H., Takai Y. Purification and characterization from bovine brain cytosol of proteins that regulate the GDP/GTP exchange reaction of smg p21s, ras p21-like GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16626–16634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]