Abstract
Rabbit antisera were raised against synthetic phosphopeptides corresponding to defined or putative sites of insulin receptor serine/threonine phosphorylation (Ser-1305, Ser-1327, Thr-1348). All of these antibodies bound specifically to the immunogenic phosphopeptide but not to the non-phosphorylated form of the peptide or to other phosphopeptides, in a microtitre plate competition enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anti-PS1327 antibody reacted well with native insulin receptor prepared from phorbol ester-treated transfected CHO.T cells, but showed little reaction with receptor from untreated cells. Anti-PT1348 antibody in crude form reacted substantially with receptor from both phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-treated and untreated cells, but displayed specificity for phosphoreceptor after adsorption to remove antibodies reactive with dephosphopeptide. The ability to discriminate between receptor from cells treated with or without phorbol ester was retained when these antibodies were used to probe denatured receptor on Western blots. Thus anti-PS1327 and anti-PT1348 react with insulin receptor in a site-specific and phosphorylation-state-dependent manner. Anti-PT1348, but not anti-PS1327, also showed increased reactivity with receptor prepared from insulin-treated cells. The third antibody, anti-PS1305, did not react with intact insulin receptor under any conditions. It is concluded that serine 1327 is a major, previously unrecognized, site of phorbol ester-induced receptor phosphorylation, and that anti-phosphopeptide antibodies will be valuable reagents with which to examine the serine/threonine phosphorylation state of receptor extracted from tissues.
Full text
PDF

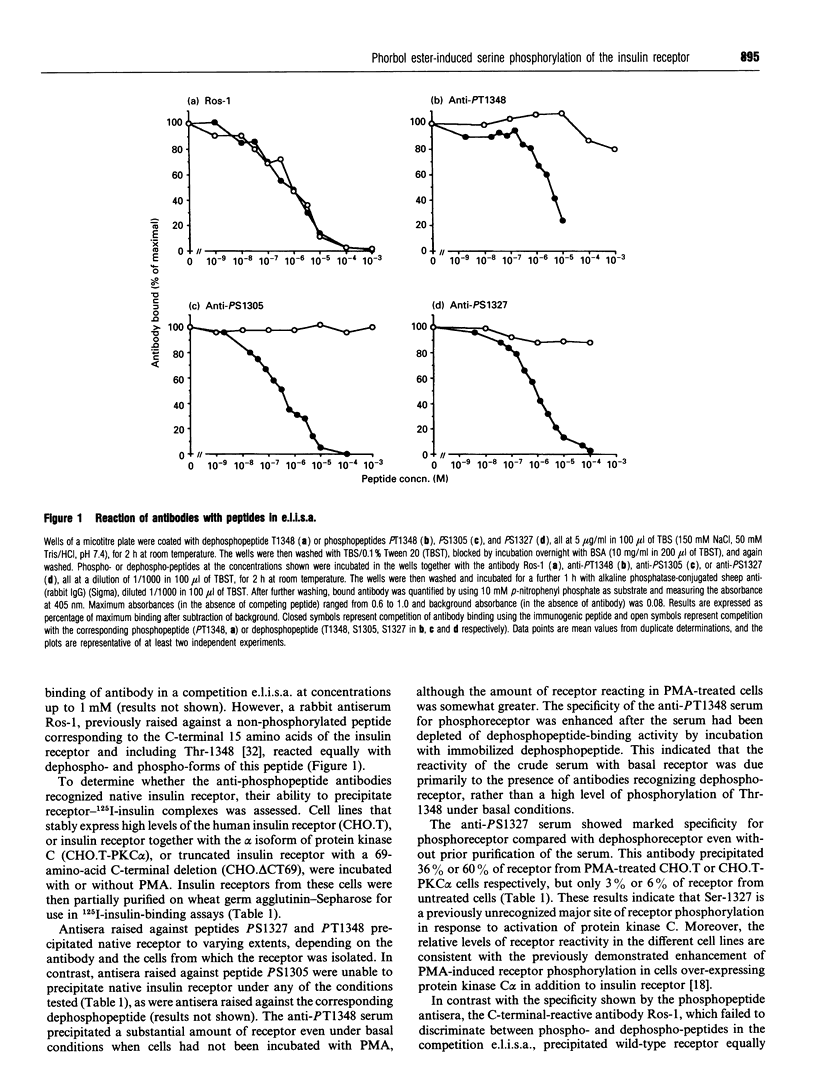


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn J., Rosen O. M., Donner D. B. Human insulin receptor mutated at threonine 1336 functions normally in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16839–16844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. M., Olefsky J. M. Phorbol ester-mediated protein kinase C interaction with wild-type and COOH-terminal truncated insulin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21760–21764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando A., Momomura K., Tobe K., Yamamoto-Honda R., Sakura H., Tamori Y., Kaburagi Y., Koshio O., Akanuma Y., Yazaki Y. Enhanced insulin-induced mitogenesis and mitogen-activated protein kinase activities in mutant insulin receptors with substitution of two COOH-terminal tyrosine autophosphorylation sites by phenylalanine. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12788–12796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews D. M., Kitchin J., Seale P. W. Solid-phase synthesis of a range of O-phosphorylated peptides by post-assembly phosphitylation and oxidation. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1991 Nov;38(5):469–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1991.tb01528.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangalore L., Tanner A. J., Laudano A. P., Stern D. F. Antiserum raised against a synthetic phosphotyrosine-containing peptide selectively recognizes p185neu/erbB-2 and the epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11637–11641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron V., Gautier N., Kaliman P., Dolais-Kitabgi J., Van Obberghen E. The carboxyl-terminal domain of the insulin receptor: its potential role in growth-promoting effects. Biochemistry. 1991 Sep 24;30(38):9365–9370. doi: 10.1021/bi00102a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron V., Gautier N., Komoriya A., Hainaut P., Scimeca J. C., Mervic M., Lavielle S., Dolais-Kitabgi J., Van Obberghen E. Insulin binding to its receptor induces a conformational change in the receptor C-terminus. Biochemistry. 1990 May 15;29(19):4634–4641. doi: 10.1021/bi00471a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron V., Kaliman P., Gautier N., Van Obberghen E. The insulin receptor activation process involves localized conformational changes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23290–23294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag G. E., Roth R. A., Beaudoin J., Mochly-Rosen D., Koshland D. E., Jr Protein kinase C directly phosphorylates the insulin receptor in vitro and reduces its protein-tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5822–5824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. E., Dickens M., Tavare J. M., Roth R. A. Overexpression of protein kinase C isoenzymes alpha, beta I, gamma, and epsilon in cells overexpressing the insulin receptor. Effects on receptor phosphorylation and signaling. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6338–6347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. E., Tavaré J. M., Ellis L., Roth R. A. Evidence for hybrid rodent and human insulin receptors in transfected cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15587–15590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coghlan M. P., Siddle K. Phorbol esters induce insulin receptor phosphorylation in transfected fibroblasts without affecting tyrosine kinase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 May 28;193(1):371–377. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernik A. J., Girault J. A., Nairn A. C., Chen J., Snyder G., Kebabian J., Greengard P. Production of phosphorylation state-specific antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:264–283. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01025-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duronio V., Jacobs S. The effect of protein kinase-C inhibition on insulin receptor phosphorylation. Endocrinology. 1990 Jul;127(1):481–487. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-1-481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frackelton A. R., Jr, Posner M., Kannan B., Mermelstein F. Generation of monoclonal antibodies against phosphotyrosine and their use for affinity purification of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:79–92. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01010-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganderton R. H., Stanley K. K., Field C. E., Coghlan M. P., Soos M. A., Siddle K. A monoclonal anti-peptide antibody reacting with the insulin receptor beta-subunit. Characterization of the antibody and its epitope and use in immunoaffinity purification of intact receptors. Biochem J. 1992 Nov 15;288(Pt 1):195–205. doi: 10.1042/bj2880195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein B. J., Dudley A. L. The rat insulin receptor: primary structure and conservation of tissue-specific alternative messenger RNA splicing. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Feb;4(2):235–244. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-2-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffetz D., Fridkin M., Zick Y. Antibodies directed against phosphothreonine residues as potent tools for studying protein phosphorylation. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jun 15;182(2):343–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14836.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häring H. U., Mehnert H. Pathogenesis of type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: candidates for a signal transmitter defect causing insulin resistance of the skeletal muscle. Diabetologia. 1993 Mar;36(3):176–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00399946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häring H., Kirsch D., Obermaier B., Ermel B., Machicao F. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters increase the Km of the ATP-binding site of the insulin receptor kinase from rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3869–3875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Phosphorylation of receptors for insulin and insulin-like growth factor I. Effects of hormones and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):934–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., White M. F., Shoelson S. E., Backer J. M., Araki E., Cheatham B., Csermely P., Folli F., Goldstein B. J., Huertas P. The insulin receptor and its substrate: molecular determinants of early events in insulin action. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1993;48:291–339. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571148-7.50015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaliman P., Baron V., Alengrin F., Takata Y., Webster N. J., Olefsky J. M., Van Obberghen E. The insulin receptor C-terminus is involved in regulation of the receptor kinase activity. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 21;32(37):9539–9544. doi: 10.1021/bi00088a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono S., Kuzuya H., Yamada K., Yoshimasa Y., Okamoto M., Nishimura H., Kosaki A., Inoue G., Hayashi T., Imura H. Preparation of anti-phosphoserine and anti-phosphothreonine antibodies and their application in the study of insulin- and EGF-induced phosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jan 15;190(1):283–288. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L., Gjika H. B., Van Vunakis H. Antibodies and radioimmunoassays for phosphoserine, phosphothreonine and phosphotyrosine. Serologic specificities and levels of the phosphoamino acids in cytoplasmic fractions of rat tissues. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Nov 30;124(2):239–249. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90360-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. E., Cao L., Perregaux D., Czech M. P. Threonine 1336 of the human insulin receptor is a major target for phosphorylation by protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 20;29(7):1807–1813. doi: 10.1021/bi00459a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. E., Wu G. P., MacDonald R. G., Czech M. P. Insulin-sensitive phosphorylation of serine 1293/1294 on the human insulin receptor by a tightly associated serine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):947–954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F., Roth R. A. Identification of serines-967/968 in the juxtamembrane region of the insulin receptor as insulin-stimulated phosphorylation sites. Biochem J. 1994 Mar 1;298(Pt 2):471–477. doi: 10.1042/bj2980471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. The insulin receptor. A multifunctional protein. Diabetes. 1990 Sep;39(9):1009–1016. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.9.1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang D. T., Sharma B. R., Shafer J. A., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Predominance of tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptors during the initial response of intact cells to insulin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7131–7136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillay T. S., Whittaker J., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Siddle K. Multisite serine phosphorylation of the insulin and IGF-I receptors in transfected cells. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 19;288(1-2):206–211. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quentmeier A., Daneschmand H., Klein H., Unthan-Fechner K., Probst I. Insulin-mimetic actions of phorbol ester in cultured adult rat hepatocytes. Lack of phorbol-ester-elicited inhibition of the insulin signal. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 15;289(Pt 2):549–555. doi: 10.1042/bj2890549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. M., King M. J., Sale G. J. Two systems in vitro that show insulin-stimulated serine kinase activity towards the insulin receptor. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):509–519. doi: 10.1042/bj2500509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soos M. A., Siddle K., Baron M. D., Heward J. M., Luzio J. P., Bellatin J., Lennox E. S. Monoclonal antibodies reacting with multiple epitopes on the human insulin receptor. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 1;235(1):199–208. doi: 10.1042/bj2350199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takata Y., Webster N. J., Olefsky J. M. Intracellular signaling by a mutant human insulin receptor lacking the carboxyl-terminal tyrosine autophosphorylation sites. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9065–9070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama S., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Phorbol ester-induced serine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor decreases its tyrosine kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3440–3447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavaré J. M., Denton R. M. Studies on the autophosphorylation of the insulin receptor from human placenta. Analysis of the sites phosphorylated by two-dimensional peptide mapping. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 1;252(2):607–615. doi: 10.1042/bj2520607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavaré J. M., Dickens M. Changes in insulin-receptor tyrosine, serine and threonine phosphorylation as a result of substitution of tyrosine-1162 with phenylalanine. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 15;274(Pt 1):173–179. doi: 10.1042/bj2740173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavaré J. M., O'Brien R. M., Siddle K., Denton R. M. Analysis of insulin-receptor phosphorylation sites in intact cells by two-dimensional phosphopeptide mapping. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):783–788. doi: 10.1042/bj2530783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thies R. S., Ullrich A., McClain D. A. Augmented mitogenesis and impaired metabolic signaling mediated by a truncated insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12820–12825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornqvist H. E., Pierce M. W., Frackelton A. R., Nemenoff R. A., Avruch J. Identification of insulin receptor tyrosine residues autophosphorylated in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10212–10219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torossian K., Nower P., Schwartz T., Fantus I. G. Phorbol esters inhibit insulin-induced receptor down-regulation in cultured human lymphocytes: association with diminished insulin receptor autophosphorylation. Biochem J. 1993 Feb 15;290(Pt 1):151–158. doi: 10.1042/bj2900151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Horn D. J., Myers M. G., Jr, Backer J. M. Direct activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase by the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):29–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y. Antibodies for phosphotyrosine: analytical and preparative tool for tyrosyl-phosphorylated proteins. Anal Biochem. 1988 Jul;172(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90403-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Backer J. M. Preparation and use of anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies to study structure and function of insulin receptor. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:65–79. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01009-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]