Abstract
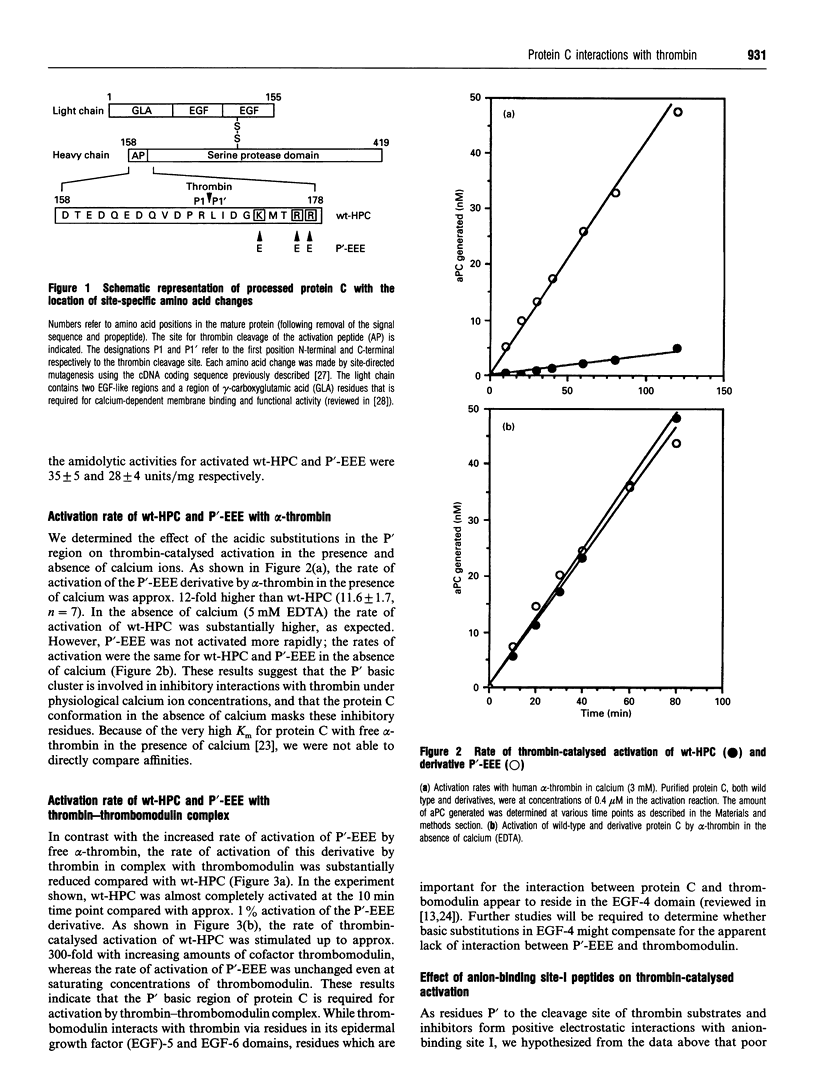
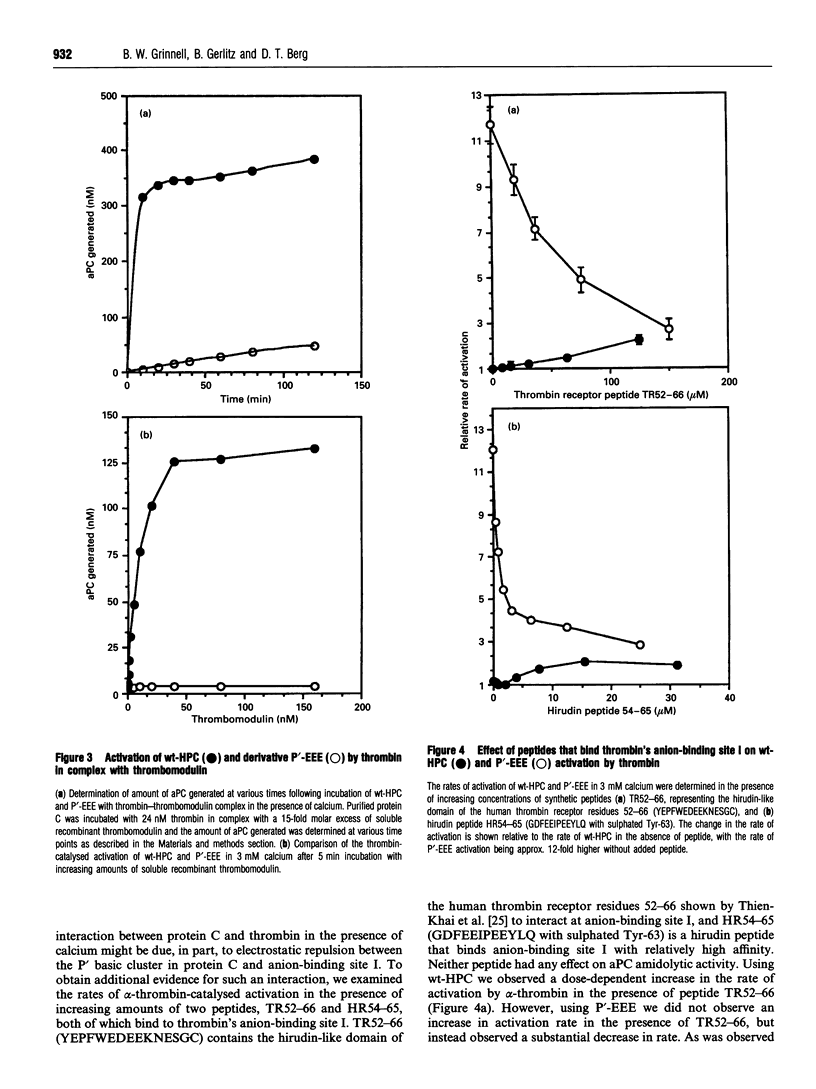
During coagulation human protein C is activated by thrombin; however, this cleavage reaction is slow unless thrombin is complexed with a cofactor, thrombomodulin. Near the thrombin cleavage site in protein C is a cluster of basic residues, at positions P5' (Lys-174), P8' (Arg-177) and P9' (Arg-178). We have explored the role of this basic cluster in the activation of protein C by thrombin, and by thrombin-thrombomodulin complex, by substitution of glutamic acid at each position to generate the acidic protein C derivative P'-EEE. The activation rate of P'-EEE by free alpha-thrombin was approx. 12-fold faster than that observed for wild-type (wt) human protein C zymogen (HPC) in the presence of calcium, but unchanged in the absence of calcium. While the thrombin-catalysed activation of wt-HPC was stimulated approx. 300-fold by thrombomodulin, we observed no effect of thrombomodulin on thrombin-catalysed activation of the P'-EEE derivative. Using synthetic peptides that bind to anion-binding site I of thrombin (thrombin-receptor sequence 52-66 and hirudin sequence 54-65 SO4 Tyr), we found that the rate of thrombin-catalysed activation of wt-HPC in the presence of calcium could be increased severalfold in a dose-dependent manner. However, the enhanced rate of thrombin-catalysed activation of P'-EEE could be progressively reduced to wt-HPC levels with increasing concentrations of both synthetic peptides. Our data suggest that the P' basic cluster in protein C reduces interaction with free alpha-thrombin through electrostatic repulsion with anion-binding site I, a site that is masked when thrombomodulin binds thrombin. Further, the lack of thrombomodulin cofactor activity with thrombin-catalysed activation of P'-EEE suggests that the basic cluster in protein C forms a contact site with thrombomodulin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckmann R. J., Schmidt R. J., Santerre R. F., Plutzky J., Crabtree G. R., Long G. L. The structure and evolution of a 461 amino acid human protein C precursor and its messenger RNA, based upon the DNA sequence of cloned human liver cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5233–5247. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. T., McClure D. B., Grinnell B. W. High-level expression of secreted proteins from cells adapted to serum-free suspension culture. Biotechniques. 1993 Jun;14(6):972–978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich H. J., Grinnell B. W., Jaskunas S. R., Esmon C. T., Yan S. B., Bang N. U. Recombinant human protein C derivatives: altered response to calcium resulting in enhanced activation by thrombin. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2367–2373. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich H. J., Jaskunas S. R., Grinnell B. W., Yan S. B., Bang N. U. Direct expression of recombinant activated human protein C, a serine protease. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14298–14304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. Molecular events that control the protein C anticoagulant pathway. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Jul 1;70(1):29–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The regulation of natural anticoagulant pathways. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1348–1352. doi: 10.1126/science.3029867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The roles of protein C and thrombomodulin in the regulation of blood coagulation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4743–4746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., DeBault L. E., Esmon C. T. Proteolytic formation and properties of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-domainless protein C. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5548–5553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Owen W. G., Esmon C. T. Isolation of a membrane-bound cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):859–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L. Thrombomodulin. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1989;9:29–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell B. W., Walls J. D., Gerlitz B. Glycosylation of human protein C affects its secretion, processing, functional activities, and activation by thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9778–9785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hortin G. L., Trimpe B. L. Allosteric changes in thrombin's activity produced by peptides corresponding to segments of natural inhibitors and substrates. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6866–6871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. E., Esmon N. L., Laue T. M., Esmon C. T. Structural changes required for activation of protein C are induced by Ca2+ binding to a high affinity site that does not contain gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5554–5560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bonniec B. F., Esmon C. T. Glu-192----Gln substitution in thrombin mimics the catalytic switch induced by thrombomodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7371–7375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bonniec B. F., MacGillivray R. T., Esmon C. T. Thrombin Glu-39 restricts the P'3 specificity to nonacidic residues. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13796–13803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. F., Grinnell B. W., Moore R. E., Hoskins J., Vlahos C. J., Bang N. U. Stable expression of a secretable deletion mutant of recombinant human thrombomodulin in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12602–12610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson M. A., Gerlitz B., Grinnell B. W. Enhancing protein C interaction with thrombin results in a clot-activated anticoagulant. Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):261–264. doi: 10.1038/360261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler J. E., Lentz S. R., Sheehan J. P., Tsiang M., Wu Q. Structure-function relationships of the thrombin-thrombomodulin interaction. Haemostasis. 1993 Mar;23 (Suppl 1):183–193. doi: 10.1159/000216927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs M. T., Bode W. A player of many parts: the spotlight falls on thrombin's structure. Thromb Res. 1993 Jan 1;69(1):1–58. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(93)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Wheaton V. I., Hung D. T., Charo I., Coughlin S. R. Domains specifying thrombin-receptor interaction. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):674–677. doi: 10.1038/353674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J., Fay P. J. Regulation of blood coagulation by the protein C system. FASEB J. 1992 May;6(8):2561–2567. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.8.1317308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walls J. D., Berg D. T., Yan S. B., Grinnell B. W. Amplification of multicistronic plasmids in the human 293 cell line and secretion of correctly processed recombinant human protein C. Gene. 1989 Sep 1;81(1):139–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90344-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan S. C., Razzano P., Chao Y. B., Walls J. D., Berg D. T., McClure D. B., Grinnell B. W. Characterization and novel purification of recombinant human protein C from three mammalian cell lines. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Jul;8(7):655–661. doi: 10.1038/nbt0790-655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye J., Esmon N. L., Esmon C. T., Johnson A. E. The active site of thrombin is altered upon binding to thrombomodulin. Two distinct structural changes are detected by fluorescence, but only one correlates with protein C activation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23016–23021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


