Abstract
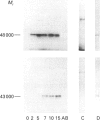
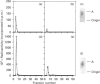
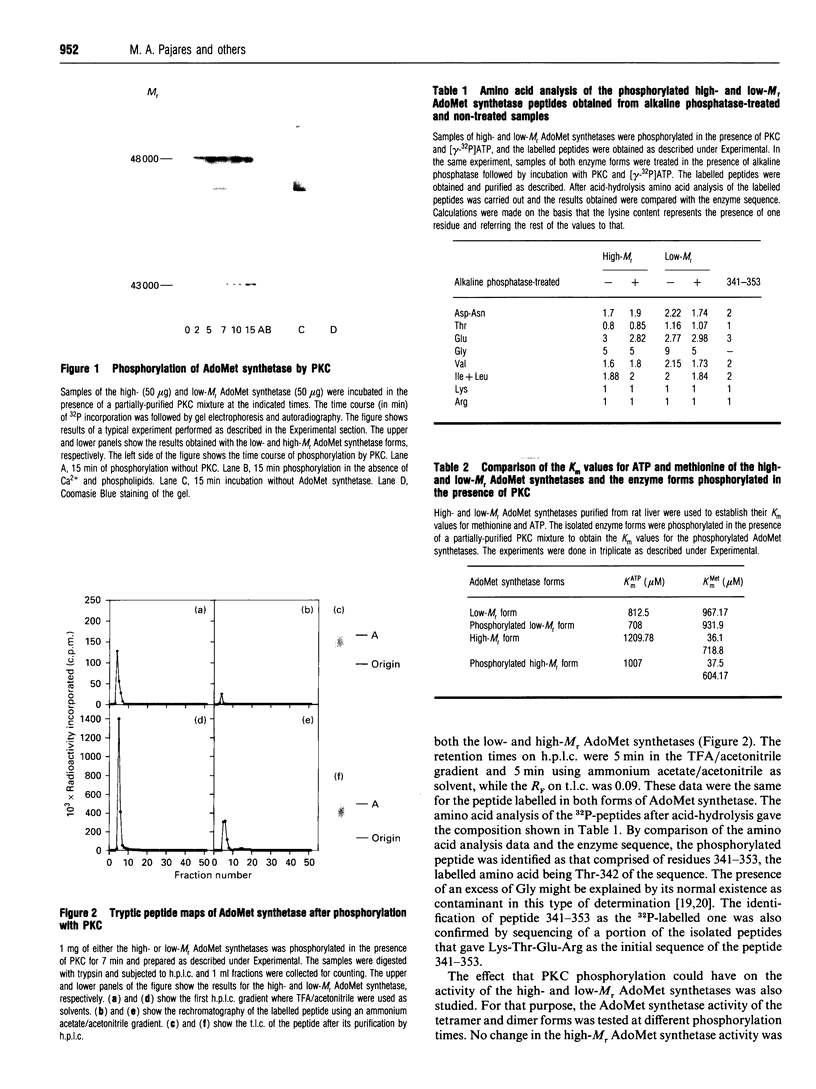
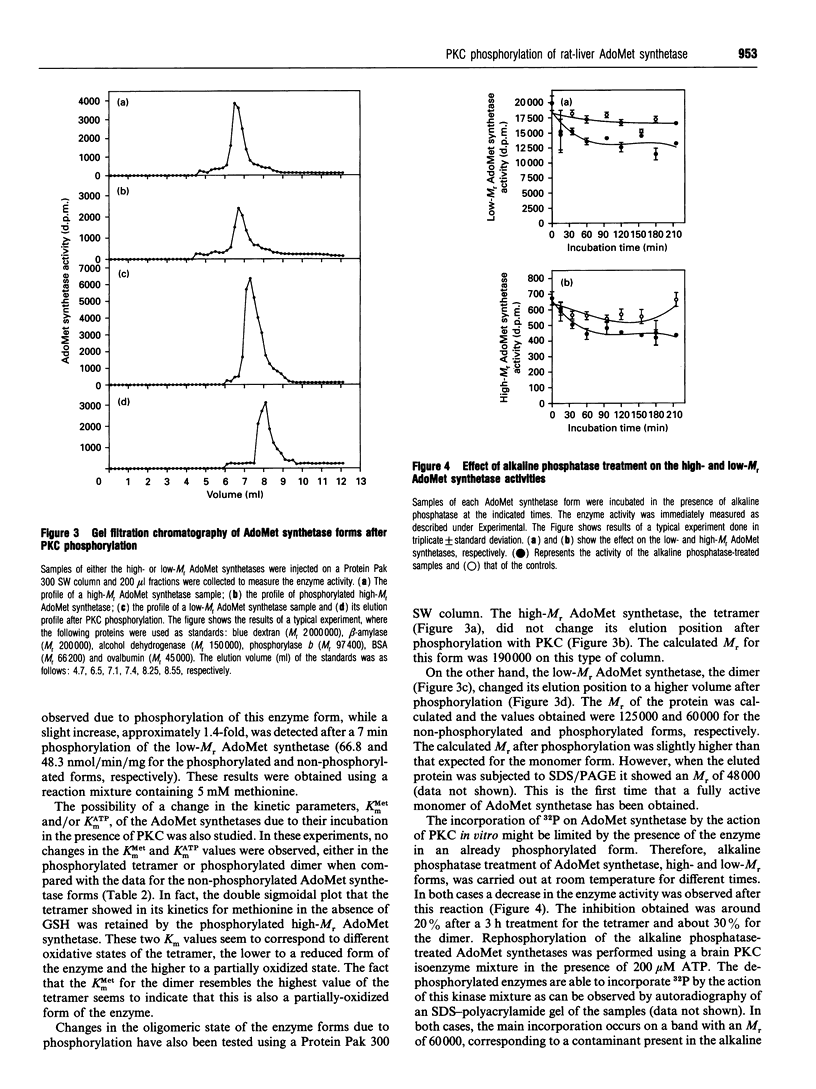
The regulation of rat liver S-adenosylmethionine synthetase (AdoMet synthetase), a key enzyme in methionine metabolism, by protein kinase C (PKC) phosphorylation has been studied. Both enzyme forms, tetramer and dimer, are phosphorylated by this kinase in the same residue, Thr-342, of the sequence. Phosphorylation of the dimer leads to its dissociation, with production of a fully-active monomer. The kinetics of the monomer have been studied, and a KmMet of 931.9 microM, a KmATP of 708 microM and a Vmax of 66.8 nmol/min/mg have been calculated. Alkaline phosphatase treatment of both enzyme forms (tetramer and dimer) produces a reduction in their activity with no change in the oligomeric state. On the other hand, PKC phosphorylation of the alkaline phosphatase-treated AdoMet synthetase forms leads to the dissociation of the dimer to produce a monomer. Rephosphorylation occurs again in the same residue, Thr-342, of the sequence. The significance of AdoMet synthetase regulation by PKC phosphorylation is further discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez L., Asunción M., Corrales F., Pajares M. A., Mato J. M. Analysis of the 5' non-coding region of rat liver S-adenosylmethionine synthetase mRNA and comparison of the Mr deduced from the cDNA sequence and the purified enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 23;290(1-2):142–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81245-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabrero C., Duce A. M., Ortiz P., Alemany S., Mato J. M. Specific loss of the high-molecular-weight form of S-adenosyl-L-methionine synthetase in human liver cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1988 Nov-Dec;8(6):1530–1534. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabrero C., Puerta J., Alemany S. Purification and comparison of two forms of S-adenosyl-L-methionine synthetase from rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):299–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantoni G. L. Biological methylation: selected aspects. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:435–451. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in neural and hormonal control of cellular activity. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):613–620. doi: 10.1038/296613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in neural and hormonal control of cellular activity. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):613–620. doi: 10.1038/296613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrales F., Cabrero C., Pajares M. A., Ortiz P., Martin-Duce A., Mato J. M. Inactivation and dissociation of S-adenosylmethionine synthetase by modification of sulfhydryl groups and its possible occurrence in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1990 Feb;11(2):216–222. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840110210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrales F., Giménez A., Alvarez L., Caballería J., Pajares M. A., Andreu H., Parés A., Mato J. M., Rodés J. S-adenosylmethionine treatment prevents carbon tetrachloride-induced S-adenosylmethionine synthetase inactivation and attenuates liver injury. Hepatology. 1992 Oct;16(4):1022–1027. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrales F., Ochoa P., Rivas C., Martin-Lomas M., Mato J. M., Pajares M. A. Inhibition of glutathione synthesis in the liver leads to S-adenosyl-L-methionine synthetase reduction. Hepatology. 1991 Sep;14(3):528–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duce A. M., Ortíz P., Cabrero C., Mato J. M. S-adenosyl-L-methionine synthetase and phospholipid methyltransferase are inhibited in human cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1988 Jan-Feb;8(1):65–68. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna R., Anderson W. B. Ca2+- and phospholipid-independent activation of protein kinase C by selective oxidative modification of the regulatory domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6758–6762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikawa S., Ishikawa M., Ozasa H., Tsukada K. Isolation of a cDNA encoding the rat liver S-adenosylmethionine synthetase. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Oct 1;184(3):497–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug H., Sarre T. F. Protein kinase C isoenzymes: divergence in signal transduction? Biochem J. 1993 Apr 15;291(Pt 2):329–343. doi: 10.1042/bj2910329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley T. R., Luo K., Sefton B. M. Activators of protein kinase C induce dissociation of CD4, but not CD8, from p56lck. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):407–409. doi: 10.1126/science.2787934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Cohen P. Protein phosphatases: properties and role in cellular regulation. Science. 1983 Jul 22;221(4608):331–338. doi: 10.1126/science.6306765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Peuch C. J., Ballester R., Rosen O. M. Purified rat brain calcium- and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6858–6862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlroy B. K., Walters J. D., Blackshear P. J., Johnson J. D. Phosphorylation-dependent binding of a synthetic MARCKS peptide to calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4959–4964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogita K., Koide H., Kikkawa U., Kishimoto A., Nishizuka Y. The heterogeneity of protein kinase C in signal transduction cascade. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1990;24:218–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pajares M. A., Corrales F. J., Ochoa P., Mato J. M. The role of cysteine-150 in the structure and activity of rat liver S-adenosyl-L-methionine synthetase. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 15;274(Pt 1):225–229. doi: 10.1042/bj2740225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pajares M. A., Corrales F., Durán C., Mato J. M., Alvarez L. How is rat liver S-adenosylmethionine synthetase regulated? FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 31;309(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80726-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pajares M. A., Durán C., Corrales F., Pliego M. M., Mato J. M. Modulation of rat liver S-adenosylmethionine synthetase activity by glutathione. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17598–17605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villalba M., Pajares M. A., Renart M. F., Mato J. M. Protein kinase C catalyses the phosphorylation and activation of rat liver phospholipid methyltransferase. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):911–916. doi: 10.1042/bj2410911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villalba M., Varela I., Mérida I., Pajares M. A., Martínez del Pozo A., Mato J. M. Modulation by the ratio S-adenosylmethionine/S-adenosylhomocysteine of cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of the 50 kDa protein of rat liver phospholipid methyltransferase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 12;847(3):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R., Gould K. L., Hunter T. Substrate specificity of protein kinase C. Use of synthetic peptides corresponding to physiological sites as probes for substrate recognition requirements. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]