Abstract
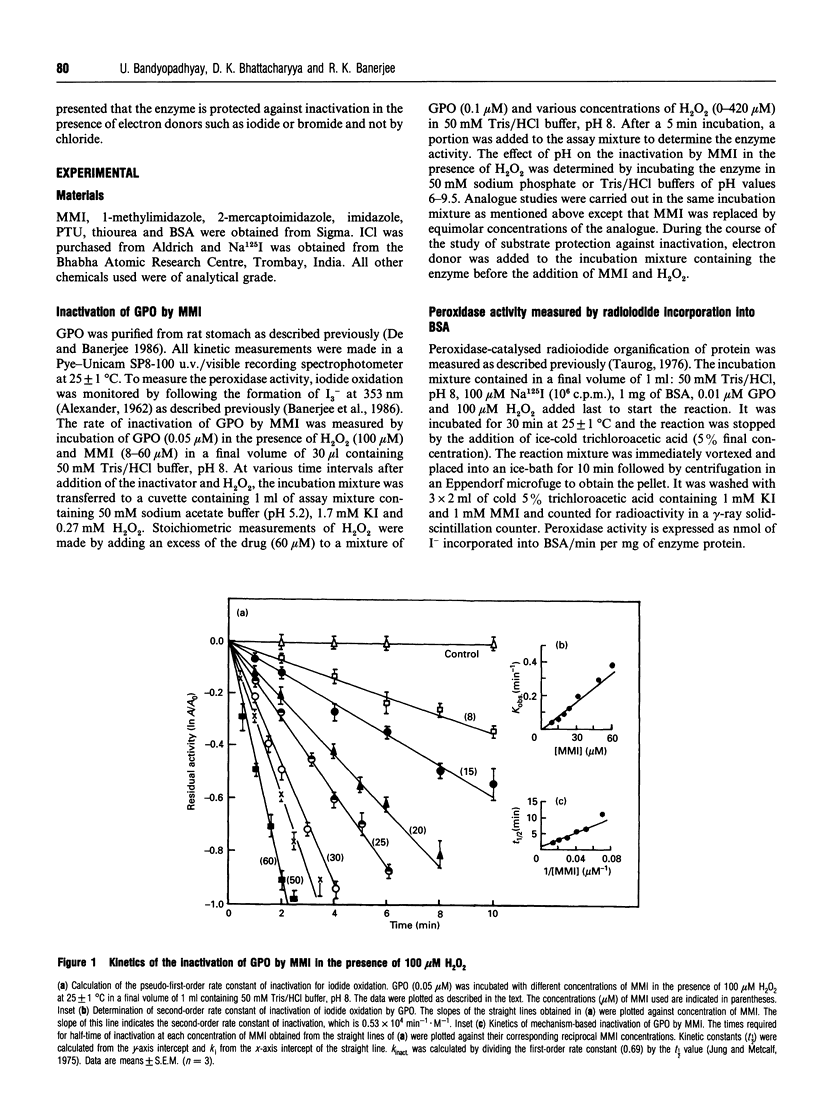
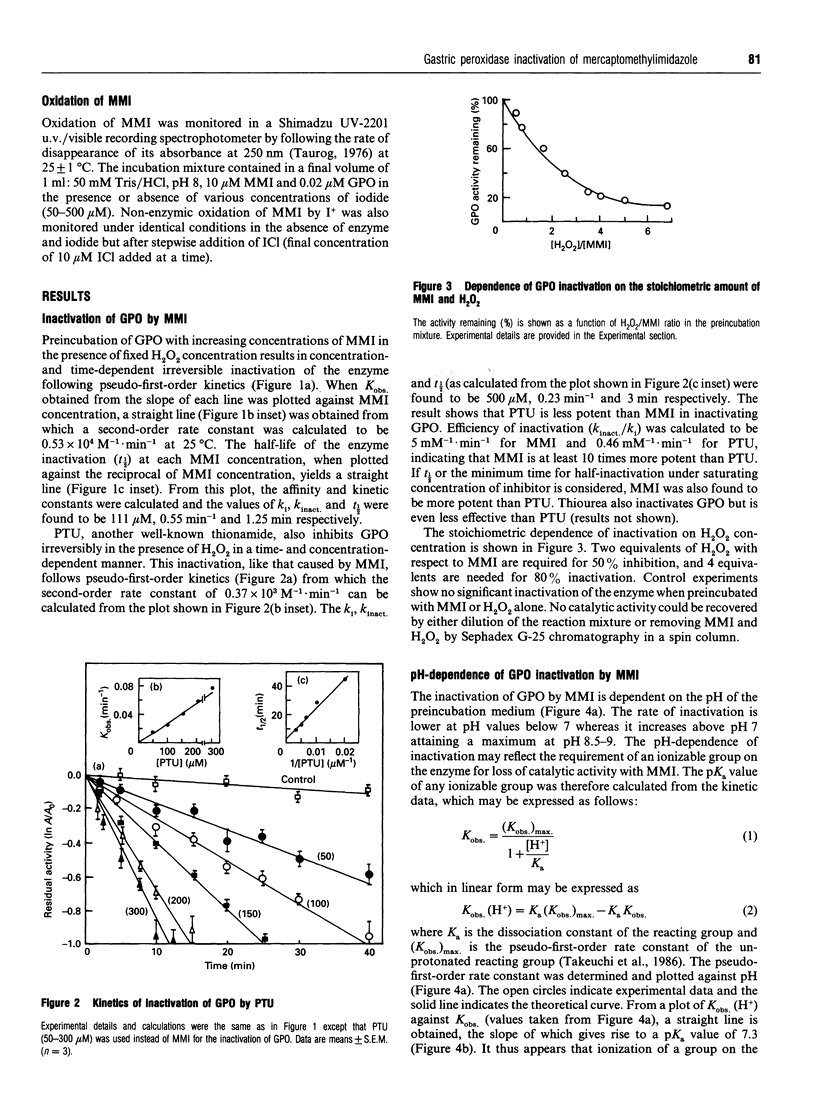
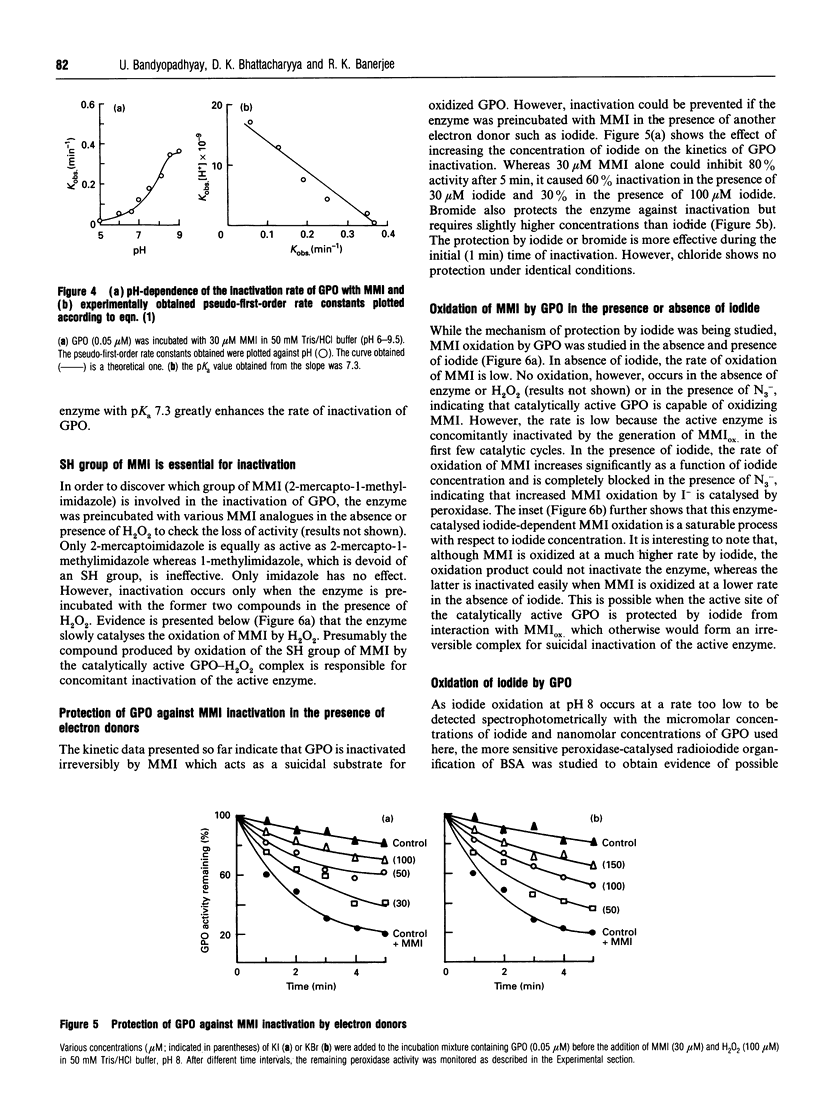
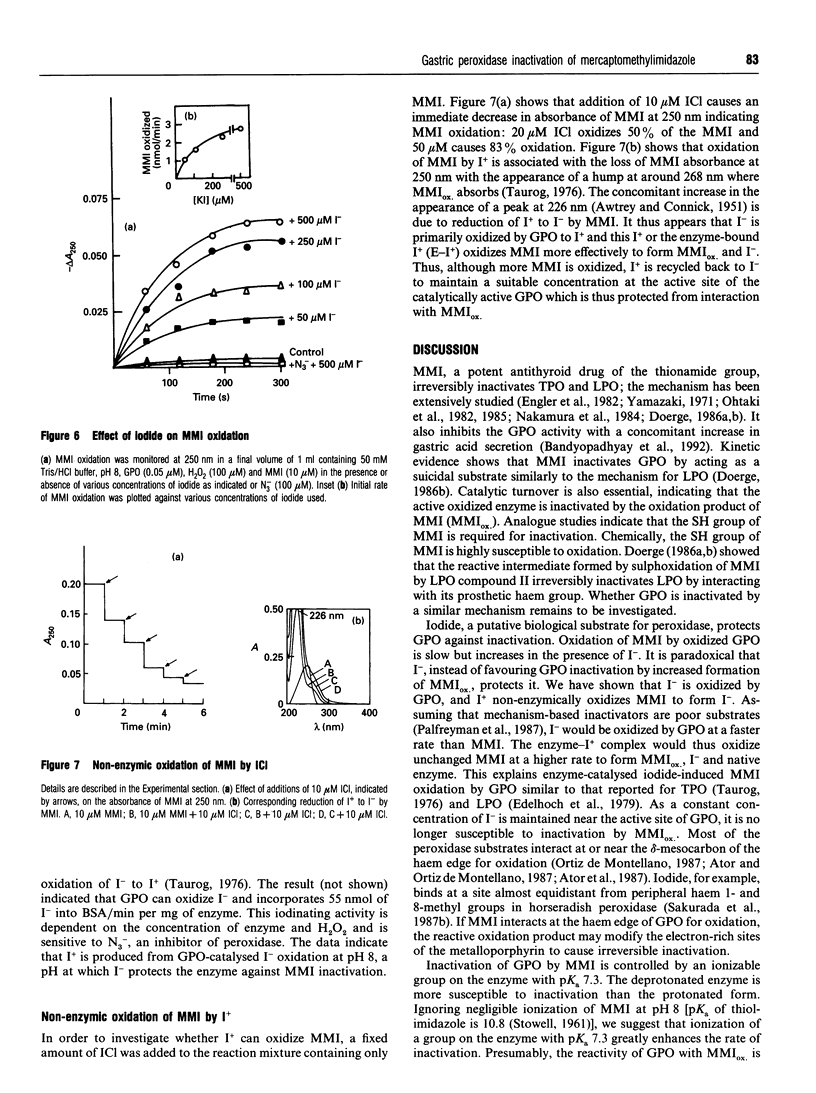
The mechanism of inhibition of gastric peroxidase (GPO) activity by mercaptomethylimidazole (MMI), an inducer of gastric acid secretion, has been investigated. Incubation of purified GPO with MMI in the presence of H2O2 results in irreversible inactivation of the enzyme. No significant inactivation occurs in the absence of H2O2 or MMI, suggesting the involvement of peroxidase-catalysed oxidized MMI (MMIOX.) in the inactivation process. The inactivation follows pseudo-first-order kinetics consistent with a mechanism-based (suicide) mode. The pseudo-first-order kinetic constants at pH 8 are ki = 111 microM, k(inact.) = 0.55 min-1 and t1/2 = 1.25 min, and the second-order rate constant is 0.53 x 10(4) M-1 x min-1. Propylthiouracil also inactivates GPO activity in the same manner but its efficiency (k(inact./ki = 0.46 mM-1 x min-1) is about 10 times lower than that of MMI (k(inact./ki = 5 mM-1 x min-1). The rate of inactivation with MMI shows pH-dependence with an inflection point at 7.3, indicating the involvement in the inactivation process of an ionizable group on the enzyme with a pKa of 7.3. The enzyme is remarkably protected against inactivation by micromolar concentrations of electron donors such as iodide and bromide but not by chloride. Although GPO oxidizes MMI slowly, iodide stimulates it through enzymic generation of I+ which is reduced back to I- by MMI. Although MMIOX. is formed at a much higher rate in the presence of I-, a constant concentration of I- maintained via the reduction of I+ by MMI, protects the active site of the enzyme against inactivation. We suggest that MMI inactivates catalytically active GPO by acting as a suicidal substrate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER N. M. A spectrophotometric assay for iodide oxidation by thyroid peroxidase. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:341–345. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ator M. A., David S. K., Ortiz de Montellano P. R. Structure and catalytic mechanism of horseradish peroxidase. Regiospecific meso alkylation of the prosthetic heme group by alkylhydrazines. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):14954–14960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ator M. A., Ortiz de Montellano P. R. Protein control of prosthetic heme reactivity. Reaction of substrates with the heme edge of horseradish peroxidase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1542–1551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay U., Bhattacharyya D. K., Chatterjee R., Banerjee R. K. Localization of gastric peroxidase and its inhibition by mercaptomethylimidazole, an inducer of gastric acid secretion. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 1;284(Pt 2):305–312. doi: 10.1042/bj2840305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee R. K., Bose A. K., Chakravartty T. K., Datta A. G. Solubilisation & properties of mitochondrial peroxidase from mouse gastric mucosa. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 1982 Oct;19(5):324–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee R. K., Datta A. G. Gastric peroxidase--localization, catalytic properties and possible role in extrathyroidal thyroid hormone formation. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1981 Feb;96(2):208–214. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0960208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee R. K., De S. K., Bose A. K., Datta A. G. Horseradish peroxidase-catalyzed conversion of iodine to iodide in presence of EDTA and H2O2. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10592–10597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee M., Bose A. K., Banerjee R. K. Histamine H2-receptor mediated stimulation of gastric acid secretion by mercaptomethylimidazole. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Mar 15;38(6):907–914. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90279-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya D. K., Bandyopadhyay U., Banerjee R. K. Chemical and kinetic evidence for an essential histidine in horseradish peroxidase for iodide oxidation. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9800–9804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanke S. R., Hager L. P. Chemical modification of chloroperoxidase with diethylpyrocarbonate. Evidence for the presence of an essential histidine residue. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12454–12461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosshard H. R., Bänziger J., Hasler T., Poulos T. L. The cytochrome c peroxidase-cytochrome c electron transfer complex. The role of histidine residues. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5683–5690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson B., Soodak M., Neary J. T., Strout H. V., Kieffer J. D., Mover H., Maloof F. The irreversible inactivation of thyroid peroxidase by methylmercaptoimidazole, thiouracil, and propylthiouracil in vitro and its relationship to in vivo findings. Endocrinology. 1978 Sep;103(3):871–882. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-3-871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De S. K., Banerjee R. K. Glucocorticoid effects on gastric peroxidase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Aug 21;800(3):233–241. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90401-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De S. K., Banerjee R. K. Purification, characterization and origin of rat gastric peroxidase. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):319–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09974.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerge D. R. Mechanism-based inhibition of lactoperoxidase by thiocarbamide goitrogens. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 12;25(16):4724–4728. doi: 10.1021/bi00364a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerge D. R. Oxygenation of organosulfur compounds by peroxidases: evidence of an electron transfer mechanism for lactoperoxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Feb 1;244(2):678–685. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90636-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H., Irace G., Johnson M. L., Michot J. L., Nunez J. The effects of thioureylene compounds (goitrogens) on lactoperoxidase activity. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):11822–11830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler H., Taurog A., Nakashima T. Mechanism of inactivation of thyroid peroxidase by thioureylene drugs. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 1;31(23):3801–3806. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finzel B. C., Poulos T. L., Kraut J. Crystal structure of yeast cytochrome c peroxidase refined at 1.7-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13027–13036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung M. J., Metcalf B. W. Catalytic inhibition of gamma-aminobutyric acid - alpha-ketoglutarate transaminase of bacterial origin by 4-aminohex-5-ynoic acid, a substrate analog. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90316-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michot J. L., Nunez J., Johnson M. L., Irace G., Edelhoch H. Iodide binding and regulation of lactoperoxidase activity toward thyroid goitrogens. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2205–2209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modi S., Behere D. V., Mitra S. Binding of aromatic donor molecules to lactoperoxidase: proton NMR and optical difference spectroscopic studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 6;996(3):214–225. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90250-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modi S., Behere D. V., Mitra S. Binding of thiocyanate to lactoperoxidase: 1H and 15N nuclear magnetic resonance studies. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4689–4694. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. R., Hager L. P. Mechanism of the inhibition of enzymatic halogenation by antithyroid agents. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3582–3589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLLS P. The formation and properties of sulphmyoglobin and sulphcatalase. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:374–383. doi: 10.1042/bj0810374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Nakamura M., Yamazaki I., Morrison M. Reactions of ferryl lactoperoxidase (compound II) with sulfide and sulfhydryl compounds. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7080–7085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtaki S., Nakagawa H., Nakamura M., Yamazaki I. Reactions of purified hog thyroid peroxidase with H2O2, tyrosine, and methylmercaptoimidazole (goitrogen) in comparison with bovine lactoperoxidase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):761–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtaki S., Nakagawa H., Nakamura S., Nakamura M., Yamazaki I. Characterization of hog thyroid peroxidase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):441–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfreyman M. G., Bey P., Sjoerdsma A. Enzyme-activated/mechanism-based inhibitors. Essays Biochem. 1987;23:28–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petry T. W., Eling T. E. The mechanism for the inhibition of prostaglandin H synthase-catalyzed xenobiotic oxidation by methimazole. Reaction with free radical oxidation products. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14112–14118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pommier J., Cahnmann H. J. Interaction of lactoperoxidase with thiols and diiodotyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):3006–3010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos T. L., Kraut J. The stereochemistry of peroxidase catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8199–8205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurada J., Takahashi S., Hosoya T. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance studies on the iodide binding by horseradish peroxidase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4007–4010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurada J., Takahashi S., Shimizu T., Hatano M., Nakamura S., Hosoya T. Proton and iodine-127 nuclear magnetic resonance studies on the binding of iodide by lactoperoxidase. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 6;26(20):6478–6483. doi: 10.1021/bi00394a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi M., Asano N., Kameda Y., Matsui K. Chemical modification by diethylpyrocarbonate of an essential histidine residue in 3-ketovalidoxylamine A C-N lyase. J Biochem. 1986 Jun;99(6):1571–1577. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taurog A. The mechanism of action of the thioureylene antithyroid drugs. Endocrinology. 1976 Apr;98(4):1031–1046. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-4-1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki I. One-electron and two-electron transfer mechanisms in enzymic oxidation-reduction reactions. Adv Biophys. 1971;2:33–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


