Abstract
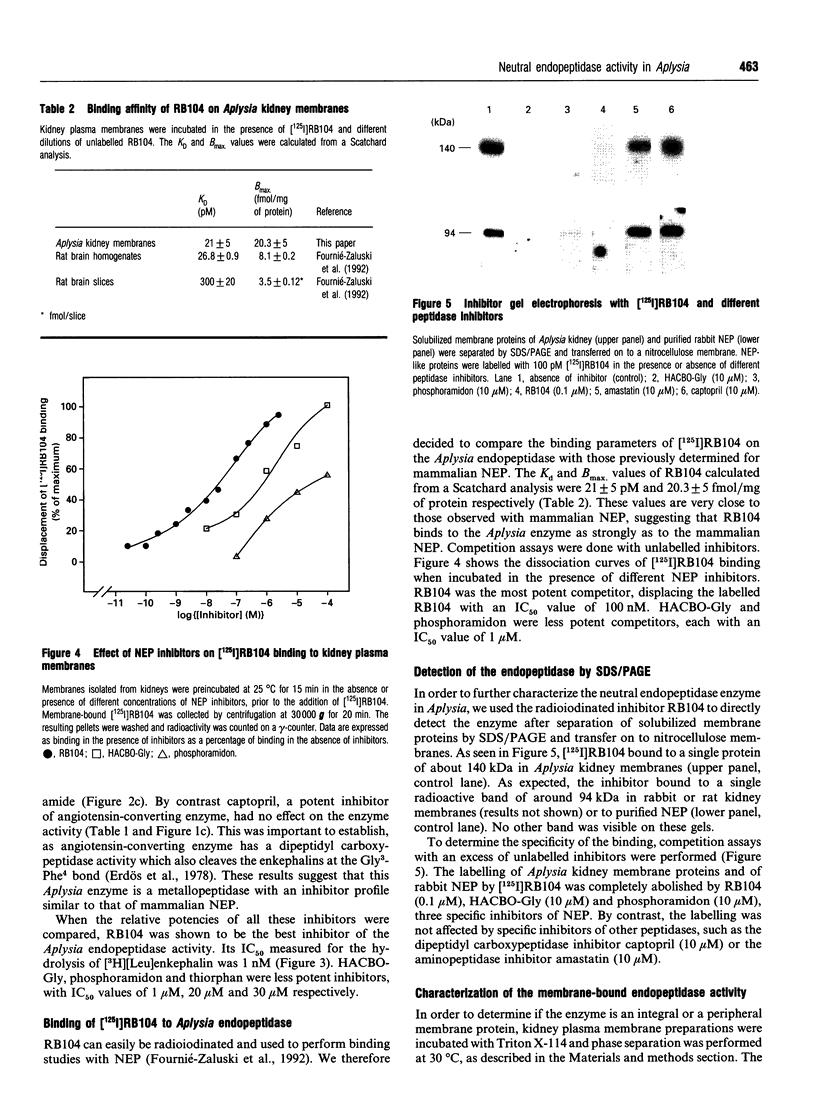
Kidney plasma membranes of Aplysia californica were shown to contain an endopeptidase activity which cleaved [Leu]enkephalin (Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu) and [Leu]enkephalinamide (Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-NH2) at the Gly3-Phe4 bond, as determined by reverse-phase h.p.l.c. analysis of metabolites. The optimal pH was shown to be 6.5. The bivalent cation chelating agent, 1,10-phenanthroline protected [Leu]enkephalin from degradation, suggesting that this enzyme is a metallopeptidase. The degradation of [Leu]enkephalin was also abolished by the neutral endopeptidase-24.11 inhibitors RB104 (2-[(3-iodo-4-hydroxyl)-phenylmethyl]-4-N-[3-(hydroxyamino-3-oxo-1- phenylmethyl)-propyl]amino-4-oxobutanoic acid), HABCO-Gly [(3-hydroxy-aminocarbonyl-2-benzyl-1-oxypropyl)glycine], phosphoramidon and thiorphan, with IC50 values of 1 nM, 1 microM, 20 microM and 30 microM respectively. By contrast, the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor captopril and the serine proteinase inhibitor phenylmethanesulphonyl fluoride were without effect. Phase separation experiments using Triton X-114 showed that about 64% of the neutral endopeptidase activity in the Aplysia kidney membrane corresponds to an integral membrane protein. A specific radioiodinated inhibitor ([125I]RB104) was shown to bind the Aplysia endopeptidase with high affinity; the KD and Bmax. values were 21 +/- 5 pM and 20.3 +/- 5 fmol/mg of proteins respectively. This inhibitor was used to determine the molecular form of the enzyme, after separation of solubilized membrane proteins on SDS/PAGE and transfer on to nitrocellulose membranes. A single protein band with an apparent molecular mass of 140 kDa was observed. The labelling was abolished by specific neutral endopeptidase inhibitors. This study provides the first biochemical characterization of an endopeptidase with catalytic properties similar to those of neutral endopeptidase-24.11 in the mollusc Aplysia californica.
Full text
PDF

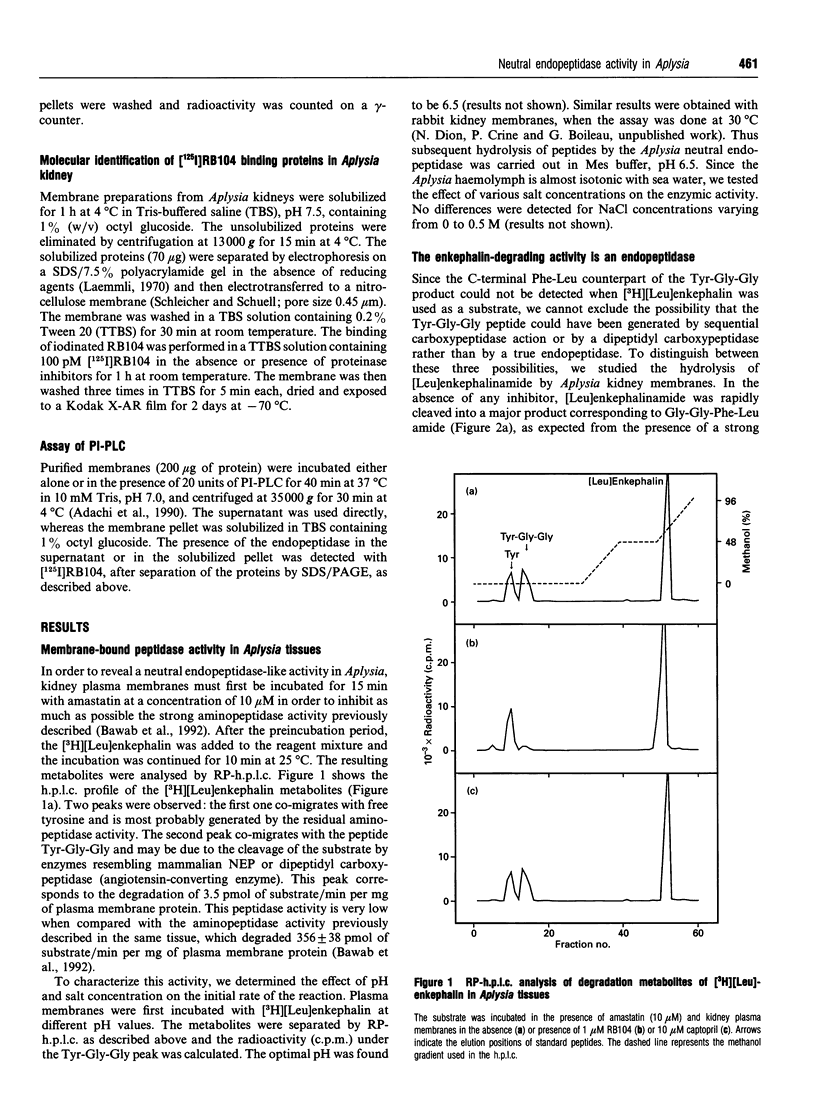
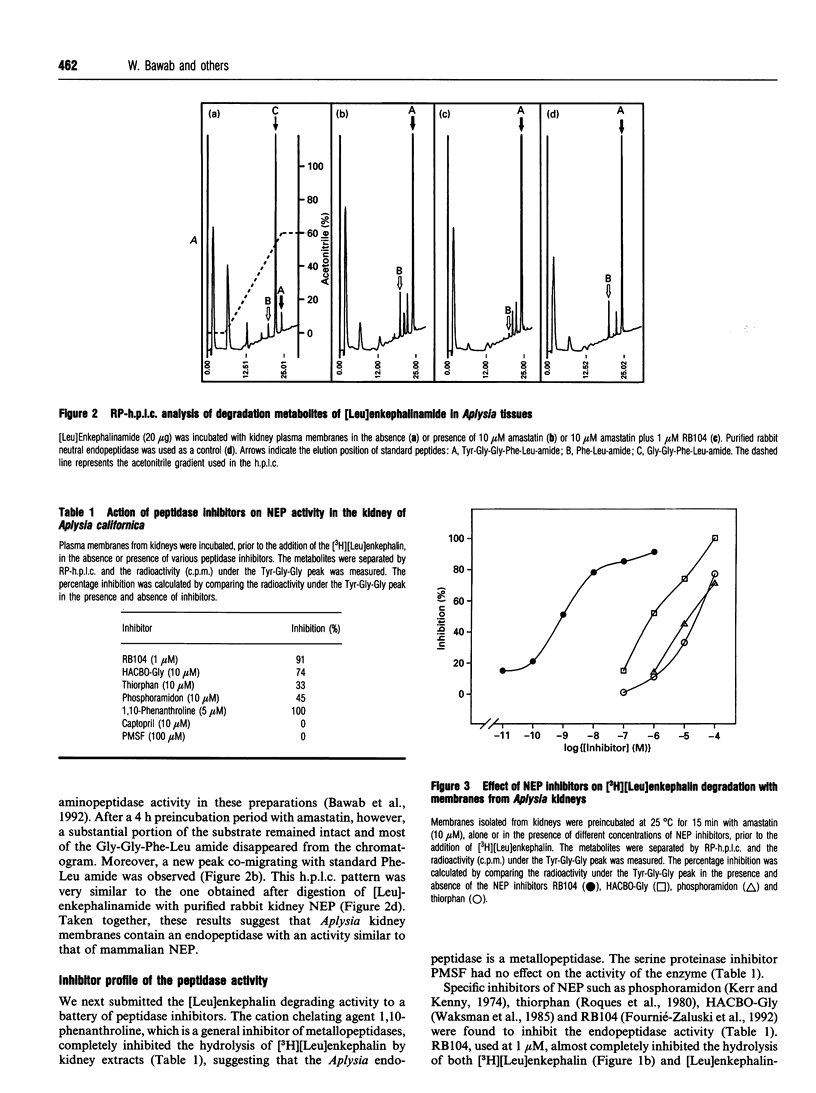


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi H., Katayama T., Inuzuka C., Oikawa S., Tsujimoto M., Nakazato H. Identification of membrane anchoring site of human renal dipeptidase and construction and expression of a cDNA for its secretory form. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15341–15345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bawab W., Querido E., Crine P., DesGroseillers L. Identification and characterization of aminopeptidases from Aplysia californica. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 15;286(Pt 3):967–975. doi: 10.1042/bj2860967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaillet P., Marçais-Collado H., Costentin J., Yi C. C., De La Baume S., Schwartz J. C. Inhibition of enkephalin metabolism by, and antinociceptive activity of, bestatin, an aminopeptidase inhibitor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 21;86(3-4):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crine P., LeGrimellec C., Lemieux E., Labonté L., Fortin S., Blachier A., Aubry M. The production and characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for the 94,000 dalton enkephalin-degrading peptidase from rabbit kidney brush border. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 30;131(1):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91796-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Glycolipid anchoring of plasma membrane proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devault A., Lazure C., Nault C., Le Moual H., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M., Kahn P., Powell J., Mallet J., Beaumont A. Amino acid sequence of rabbit kidney neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (enkephalinase) deduced from a complementary DNA. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1317–1322. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02370.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdös E. G., Johnson A. R., Boyden N. T. Hydrolysis of enkephalin by cultured human endothelial cells and by purified peptidyl dipeptidase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978 Mar 1;27(5):843–848. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90542-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdös E. G., Skidgel R. A. Neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (enkephalinase) and related regulators of peptide hormones. FASEB J. 1989 Feb;3(2):145–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Soleilhac J. M., Turcaud S., Laï-Kuen R., Crine P., Beaumont A., Roques B. P. Development of [125I]RB104, a potent inhibitor of neutral endopeptidase 24.11, and its use in detecting nanogram quantities of the enzyme by "inhibitor gel electrophoresis". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6388–6392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher I. S., Pappin D. J., Kenny A. J. The N-terminal amino acid sequence of pig kidney endopeptidase-24.11 shows homology with pro-sucrase-isomaltase. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):305–308. doi: 10.1042/bj2400305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Low M. G., Turner A. J. Renal dipeptidase is one of the membrane proteins released by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 1;244(2):465–469. doi: 10.1042/bj2440465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaac R. E. Neuropeptide-degrading endopeptidase activity of locust (Schistocerca gregaria) synaptic membranes. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 1;255(3):843–847. doi: 10.1042/bj2550843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaac R. E. Proctolin degradation by membrane peptidases from nervous tissues of the desert locust (Schistocerca gregaria). Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):365–370. doi: 10.1042/bj2450365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Maroux S. Topology of microvillar membrance hydrolases of kidney and intestine. Physiol Rev. 1982 Jan;62(1):91–128. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A., Kenny A. J. The molecular weight and properties of a neutral metallo-endopeptidase from rabbit kidney brush border. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;137(3):489–495. doi: 10.1042/bj1370489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letarte M., Vera S., Tran R., Addis J. B., Onizuka R. J., Quackenbush E. J., Jongeneel C. V., McInnes R. R. Common acute lymphocytic leukemia antigen is identical to neutral endopeptidase. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1247–1253. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Balakrishnan K., Mehdi S. Q. A simple and rapid method for the preparation of plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 26;731(1):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90404-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Kuang W. J., Seeburg P. H., Mason A. J., Schofield P. R. Molecular cloning and amino acid sequence of human enkephalinase (neutral endopeptidase). FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 29;229(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80828-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Swerts J. P., Guyon A., Roques B. P., Schwartz J. C. High-affinity enkephalin-degrading peptidase in brain is increased after morphine. Nature. 1978 Nov 30;276(5687):523–526. doi: 10.1038/276523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies K. B., Cavero P. G., Seymour A. A., Delaney N. G., Burnett J. C., Jr Neutral endopeptidase inhibition potentiates the renal actions of atrial natriuretic factor. Kidney Int. 1990 Jul;38(1):67–72. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Stephenson S. L., Hryszko J., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. The metabolism of neuropeptides. Phase separation of synaptic membrane preparations with Triton X-114 reveals the presence of aminopeptidase N. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 15;231(2):445–449. doi: 10.1042/bj2310445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens D. F., Menon J. G., Rothman B. S. Structure-activity relationship of the neurotransmitter alpha-bag cell peptide on Aplysia LUQ neurons: implications regarding its inactivation in the extracellular space. J Neurobiol. 1992 Aug;23(6):656–670. doi: 10.1002/neu.480230605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patey G., De La Baume S., Schwartz J. C., Gros C., Roques B., Fournie-Zaluski M. C., Soroca-Lucas E. Selective protection of methionine enkephalin released from brain slices by enkephalinase inhibition. Science. 1981 Jun 5;212(4499):1153–1155. doi: 10.1126/science.7015510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H., De la Baume S., Bouthenet M. L., Schwartz J. C., Ronco P., Verroust P. Characterisation of two probes for the localisation of enkephalinase in rat brain: [3H]thiorphan and a 125I-labeled monoclonal antibody. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 13;133(2):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajpara S. M., Garcia P. D., Roberts R., Eliassen J. C., Owens D. F., Maltby D., Myers R. M., Mayeri E. Identification and molecular cloning of a neuropeptide Y homolog that produces prolonged inhibition in Aplysia neurons. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):505–513. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90188-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relton J. M., Gee N. S., Matsas R., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Purification of endopeptidase-24.11 ('enkephalinase') from pig brain by immunoadsorbent chromatography. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 1;215(3):519–523. doi: 10.1042/bj2150519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P., Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Soroca E., Lecomte J. M., Malfroy B., Llorens C., Schwartz J. C. The enkephalinase inhibitor thiorphan shows antinociceptive activity in mice. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):286–288. doi: 10.1038/288286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman B. S., Dekruyff S., Talebian M., Menon J. G., Squire C. R., Yeh C. H., Lee T. D. Aplysia peptide neurotransmitters beta-bag cell peptide, Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-amide, and small cardioexcitatory peptide B are rapidly degraded by a leucine aminopeptidase-like activity in hemolymph. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25135–25140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipp M. A., Stefano G. B., D'Adamio L., Switzer S. N., Howard F. D., Sinisterra J., Scharrer B., Reinherz E. L. Downregulation of enkephalin-mediated inflammatory responses by CD10/neutral endopeptidase 24.11. Nature. 1990 Sep 27;347(6291):394–396. doi: 10.1038/347394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squire C. R., Talebian M., Menon J. G., Dekruyff S., Lee T. D., Shively J. E., Rothman B. S. Leucine aminopeptidase-like activity in Aplysia hemolymph rapidly degrades biologically active alpha-bag cell peptide fragments. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22355–22363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig R., Scheller R. H. The Aplysia FMRFamide gene encodes sequences related to mammalian brain peptides. DNA. 1986 Dec;5(6):453–461. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1986.5.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman G., Bouboutou R., Devin J., Besselievre R., Fournie-Zaluski M. C., Roques B. P. Binding of the bidentate inhibitor [3H]HACBO-Gly to the rat brain neutral endopeptidase "enkephalinase". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 30;131(1):262–268. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91797-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman G., Hamel E., Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Roques B. P. Autoradiographic comparison of the distribution of the neutral endopeptidase "enkephalinase" and of mu and delta opioid receptors in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1523–1527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickham L., Desgroseillers L. A bradykinin-like neuropeptide precursor gene is expressed in neuron L5 of Aplysia californica. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 May;10(4):249–258. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang A. Z., Yang H. Y., Costa E. Nociception, enkephalin content and dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase activity in brain of mice treated with exopeptidase inhibitors. Neuropharmacology. 1982 Jul;21(7):625–630. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(82)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Baume S., Yi C. C., Schwartz J. C., Chaillet P., Marcais-Collado H., Costentin J. Participation of both 'enkephalinase' and aminopeptidase activities in the metabolism of endogenous enkephalins. Neuroscience. 1983 Jan;8(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]