Abstract
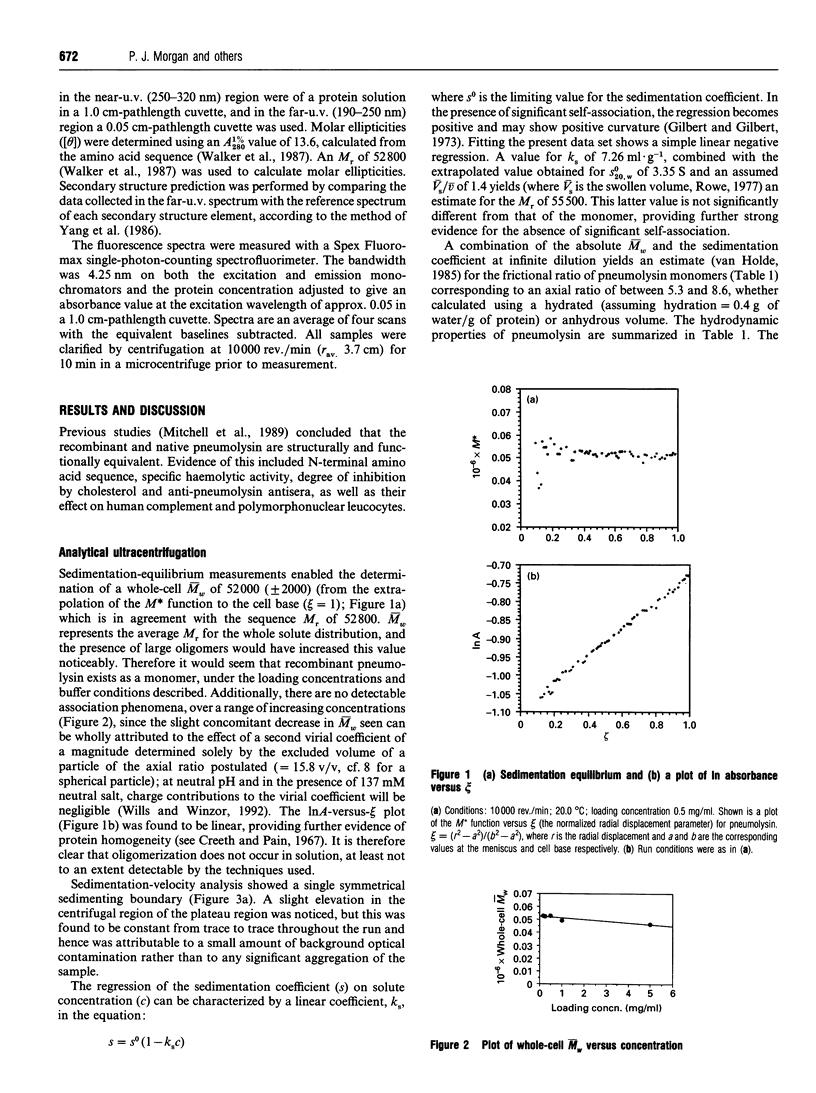
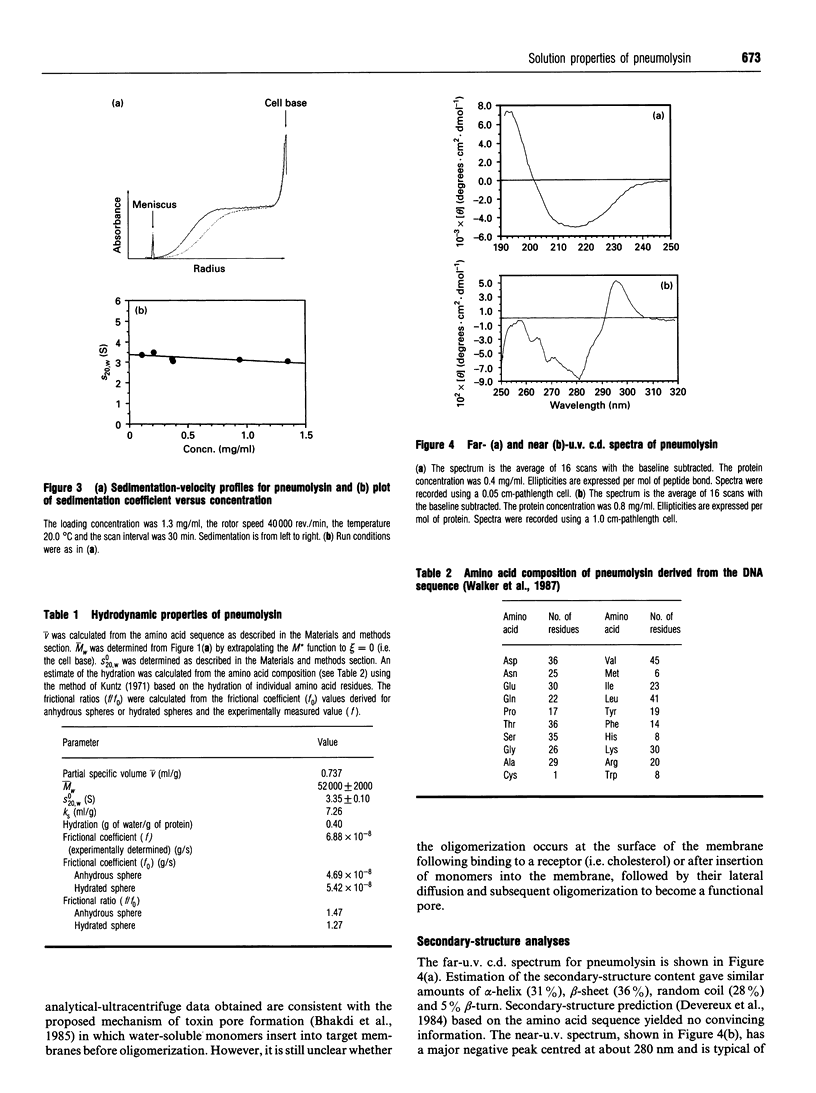
Pneumolysin is a membrane-damaging toxin produced by Streptococcus pneumoniae. In order to understand fully the mode of action of this toxin, it is necessary to have an appreciation of the size, self-association behaviour and solution conformation of pneumolysin. A combination of analytical ultracentrifugation methodologies has shown that pneumolysin lacks self-association behaviour in solution and has provided a weight-average M(r) (M omega) of 52,000 +/- 2000, which was in agreement with that derived from the amino acid sequence. By determining a sedimentation coefficient (S20,w0) of 3.35 +/- 0.10 S, it was possible to suggest a model for the gross solution conformation of pneumolysin monomers. Spectroscopic methods provide additional secondary and tertiary structure information.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry A. M., Yother J., Briles D. E., Hansman D., Paton J. C. Reduced virulence of a defined pneumolysin-negative mutant of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2037–2042. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2037-2042.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J., Sziegoleit A. Mechanism of membrane damage by streptolysin-O. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):52–60. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.52-60.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creeth J. M., Harding S. E. Some observations on a new type of point average molecular weight. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1982 Dec;7(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(82)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creeth J. M., Pain R. H. The determination of molecular weights of biological macromolecules by ultracentrifuge methods. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1967;17:217–287. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(67)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert L. M., Gilbert G. A. Sedimentation velocity measurement of protein association. Methods Enzymol. 1973;27:273–296. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(73)27014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntz I. D. Hydration of macromolecules. IV. Polypeptide conformation in frozen solutions. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jan 27;93(2):516–518. doi: 10.1021/ja00731a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell T. J., Walker J. A., Saunders F. K., Andrew P. W., Boulnois G. J. Expression of the pneumolysin gene in Escherichia coli: rapid purification and biological properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 23;1007(1):67–72. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90131-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins S. J. Protein volumes and hydration effects. The calculations of partial specific volumes, neutron scattering matchpoints and 280-nm absorption coefficients for proteins and glycoproteins from amino acid sequences. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 15;157(1):169–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland E. H. Aromatic contributions to circular dichroism spectra of proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):113–175. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. A., Allen R. L., Falmagne P., Johnson M. K., Boulnois G. J. Molecular cloning, characterization, and complete nucleotide sequence of the gene for pneumolysin, the sulfhydryl-activated toxin of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1184–1189. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1184-1189.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. T., Wu C. S., Martinez H. M. Calculation of protein conformation from circular dichroism. Methods Enzymol. 1986;130:208–269. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)30013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruijff B. Cholesterol as a target for toxins. Biosci Rep. 1990 Apr;10(2):127–130. doi: 10.1007/BF01116571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


