Abstract
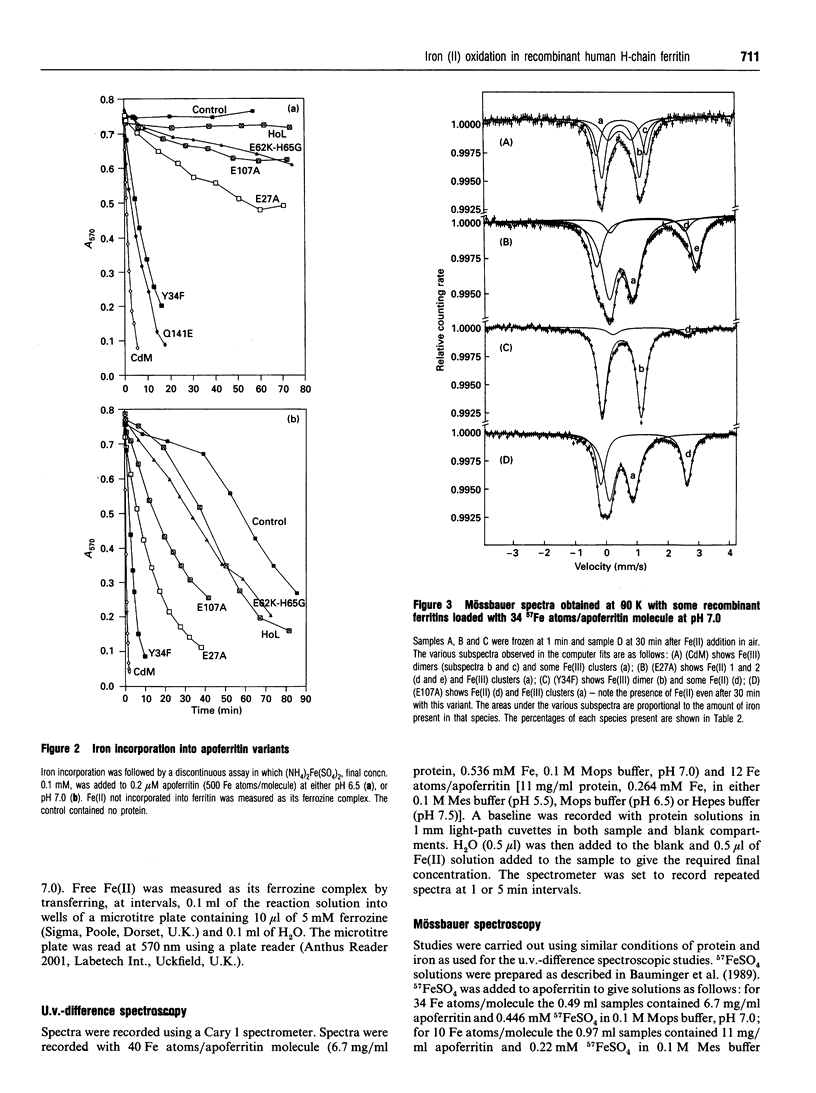
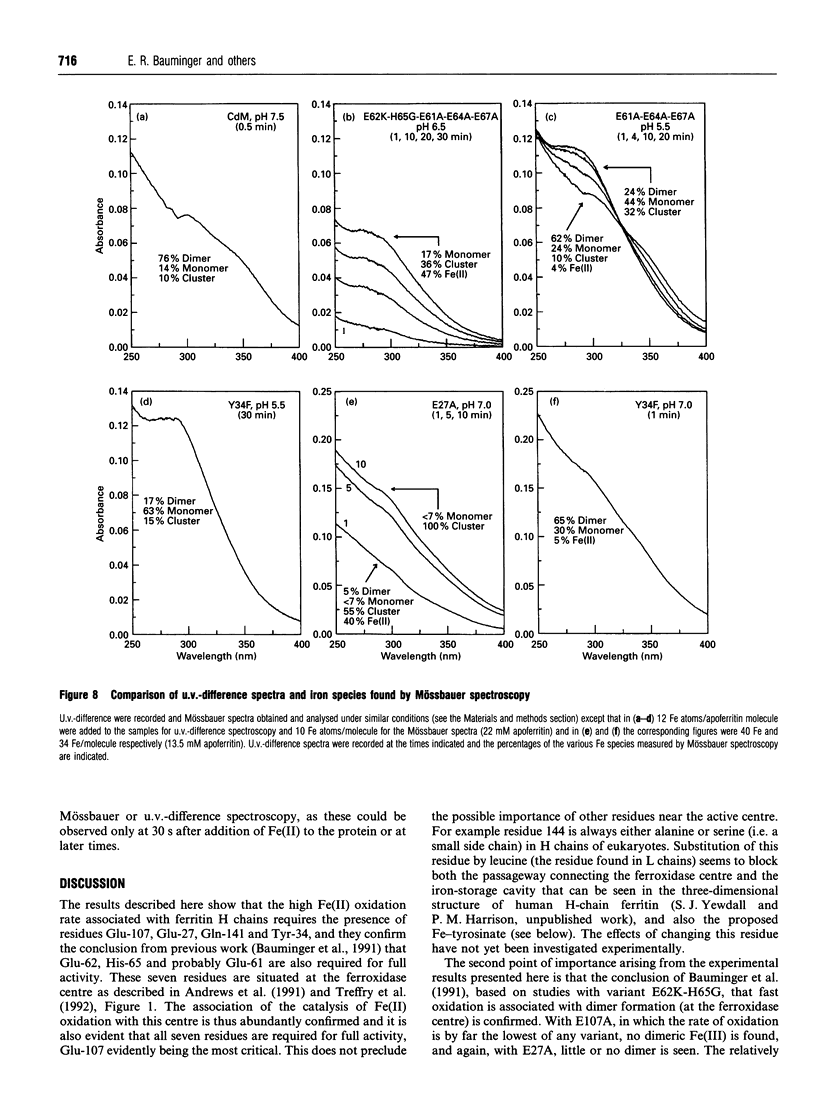
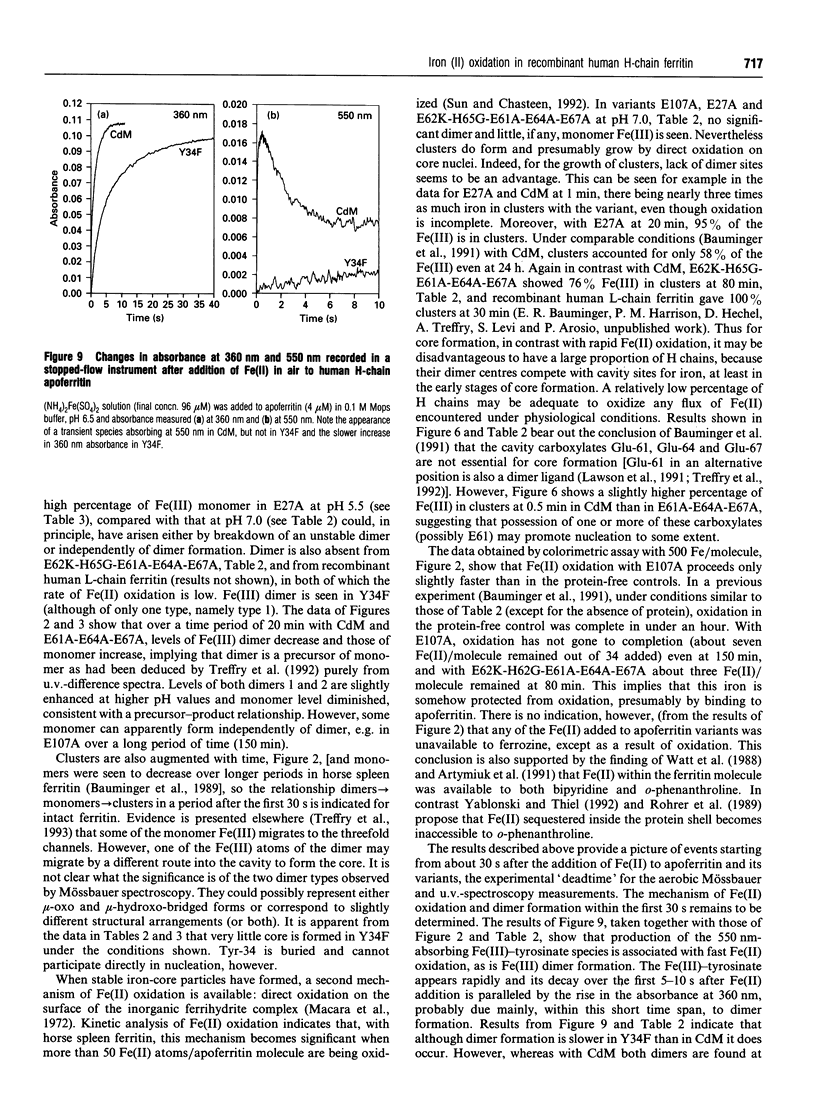
The paper describes a study of Fe(II) oxidation and the formation of Fe(III)-apoferritin complexes in recombinant human H-chain ferritin and its variants. The effects of site-directed changes in the conserved residues associated with a proposed ferroxidase centre have been investigated. A change in any of these residues is shown to reduce the rate of Fe(II) oxidation, confirming the importance of the ferroxidase centre in the catalysis of Fe(II) oxidation. Mössbauer and u.v.-difference spectroscopy show that in the wild-type protein Fe(II) oxidation gives rise to Fe(III) monomers, dimers and larger clusters. The formation of Fe(III) mu-oxo-bridged dimers occurs at the ferroxidase centre and is associated with fast oxidation: in three variants in which Fe(II) oxidation is especially slow, no Fe(III) dimers are seen. Within the time scale 0.5-20 min in wild-type human H-chain ferritin, dimer formation precedes that of the monomer and the progression dimer-->monomer-->cluster is observed, although not to completion. In a preliminary investigation of oxidation intermediates using a stopped-flow instrument, an Fe(III)-tyrosine complex reported by Waldo et al. (1993), is attributed to Tyr-34, a residue at the ferroxidase centre. The Fe(III)-Tyr-34 complex, forms in 0.5 s and then decays, as dimer absorbance increases. The relationship between Fe(III)-tyrosinate and the formation of Fe(III) dimers is uncertain.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews S. C., Arosio P., Bottke W., Briat J. F., von Darl M., Harrison P. M., Laulhère J. P., Levi S., Lobreaux S., Yewdall S. J. Structure, function, and evolution of ferritins. J Inorg Biochem. 1992 Aug 15;47(3-4):161–174. doi: 10.1016/0162-0134(92)84062-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews S. C., Smith J. M., Yewdall S. J., Guest J. R., Harrison P. M. Bacterioferritins and ferritins are distantly related in evolution. Conservation of ferroxidase-centre residues. FEBS Lett. 1991 Nov 18;293(1-2):164–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81177-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arosio P., Adelman T. G., Drysdale J. W. On ferritin heterogeneity. Further evidence for heteropolymers. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4451–4458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauminger E. R., Harrison P. M., Hechel D., Nowik I., Treffry A. Mössbauer spectroscopic investigation of structure-function relations in ferritins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 11;1118(1):48–58. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(91)90440-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauminger E. R., Harrison P. M., Nowik I., Treffry A. Mössbauer spectroscopic study of the initial stages of iron-core formation in horse spleen apoferritin: evidence for both isolated Fe(III) atoms and oxo-bridged Fe(III) dimers as early intermediates. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 27;28(13):5486–5493. doi: 10.1021/bi00439a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzi A., Santambrogio P., Levi S., Arosio P. Iron detoxifying activity of ferritin. Effects of H and L human apoferritins on lipid peroxidation in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 17;277(1-2):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80823-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedman D. J., Treffry A., Candy J. M., Taylor G. A., Morris C. M., Bloxham C. A., Perry R. H., Edwardson J. A., Harrison P. M. Iron and aluminium in relation to brain ferritin in normal individuals and Alzheimer's-disease and chronic renal-dialysis patients. Biochem J. 1992 Oct 15;287(Pt 2):509–514. doi: 10.1042/bj2870509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford G. C., Harrison P. M., Rice D. W., Smith J. M., Treffry A., White J. L., Yariv J. Ferritin: design and formation of an iron-storage molecule. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Feb 13;304(1121):551–565. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson D. M., Artymiuk P. J., Yewdall S. J., Smith J. M., Livingstone J. C., Treffry A., Luzzago A., Levi S., Arosio P., Cesareni G. Solving the structure of human H ferritin by genetically engineering intermolecular crystal contacts. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):541–544. doi: 10.1038/349541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson D. M., Treffry A., Artymiuk P. J., Harrison P. M., Yewdall S. J., Luzzago A., Cesareni G., Levi S., Arosio P. Identification of the ferroxidase centre in ferritin. FEBS Lett. 1989 Aug 28;254(1-2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi S., Luzzago A., Cesareni G., Cozzi A., Franceschinelli F., Albertini A., Arosio P. Mechanism of ferritin iron uptake: activity of the H-chain and deletion mapping of the ferro-oxidase site. A study of iron uptake and ferro-oxidase activity of human liver, recombinant H-chain ferritins, and of two H-chain deletion mutants. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18086–18092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi S., Salfeld J., Franceschinelli F., Cozzi A., Dorner M. H., Arosio P. Expression and structural and functional properties of human ferritin L-chain from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):5179–5184. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi S., Yewdall S. J., Harrison P. M., Santambrogio P., Cozzi A., Rovida E., Albertini A., Arosio P. Evidence of H- and L-chains have co-operative roles in the iron-uptake mechanism of human ferritin. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 1;288(Pt 2):591–596. doi: 10.1042/bj2880591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macara I. G., Hoy T. G., Harrison P. M. The formation of ferritin from apoferritin. Catalytic action of apoferritin. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;135(2):343–348. doi: 10.1042/bj1350343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macara I. G., Hoy T. G., Harrison P. M. The formation of ferritin from apoferritin. Kinetics and mechanism of iron uptake. Biochem J. 1972 Jan;126(1):151–162. doi: 10.1042/bj1260151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederer W. Ferritin: iron incorporation and iron release. Experientia. 1970;26(2):218–220. doi: 10.1007/BF01895596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santambrogio P., Levi S., Arosio P., Palagi L., Vecchio G., Lawson D. M., Yewdall S. J., Artymiuk P. J., Harrison P. M., Jappelli R. Evidence that a salt bridge in the light chain contributes to the physical stability difference between heavy and light human ferritins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14077–14083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S., Chasteen N. D. Ferroxidase kinetics of horse spleen apoferritin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25160–25166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil E. C. The ferritin family of iron storage proteins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1990;63:421–449. doi: 10.1002/9780470123096.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treffry A., Bauminger E. R., Hechel D., Hodson N. W., Nowik I., Yewdall S. J., Harrison P. M. Defining the roles of the threefold channels in iron uptake, iron oxidation and iron-core formation in ferritin: a study aided by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochem J. 1993 Dec 15;296(Pt 3):721–728. doi: 10.1042/bj2960721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treffry A., Harrison P. M., Luzzago A., Cesareni G. Recombinant H-chain ferritins: effects of changes in the 3-fold channels. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):268–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81350-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treffry A., Harrison P. M. Spectroscopic studies on the binding of iron, terbium, and zinc by apoferritin. J Inorg Biochem. 1984 May;21(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0162-0134(84)85035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treffry A., Hirzmann J., Yewdall S. J., Harrison P. M. Mechanism of catalysis of Fe(II) oxidation by ferritin H chains. FEBS Lett. 1992 May 11;302(2):108–112. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80417-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade V. J., Levi S., Arosio P., Treffry A., Harrison P. M., Mann S. Influence of site-directed modifications on the formation of iron cores in ferritin. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1443–1452. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90944-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldo G. S., Ling J., Sanders-Loehr J., Theil E. C. Formation of an Fe(III)-tyrosinate complex during biomineralization of H-subunit ferritin. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):796–798. doi: 10.1126/science.8430332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt G. D., Jacobs D., Frankel R. B. Redox reactivity of bacterial and mammalian ferritin: is reductant entry into the ferritin interior a necessary step for iron release? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7457–7461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yablonski M. J., Theil E. C. A possible role for the conserved trimer interface of ferritin in iron incorporation. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 13;31(40):9680–9684. doi: 10.1021/bi00155a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




