Abstract
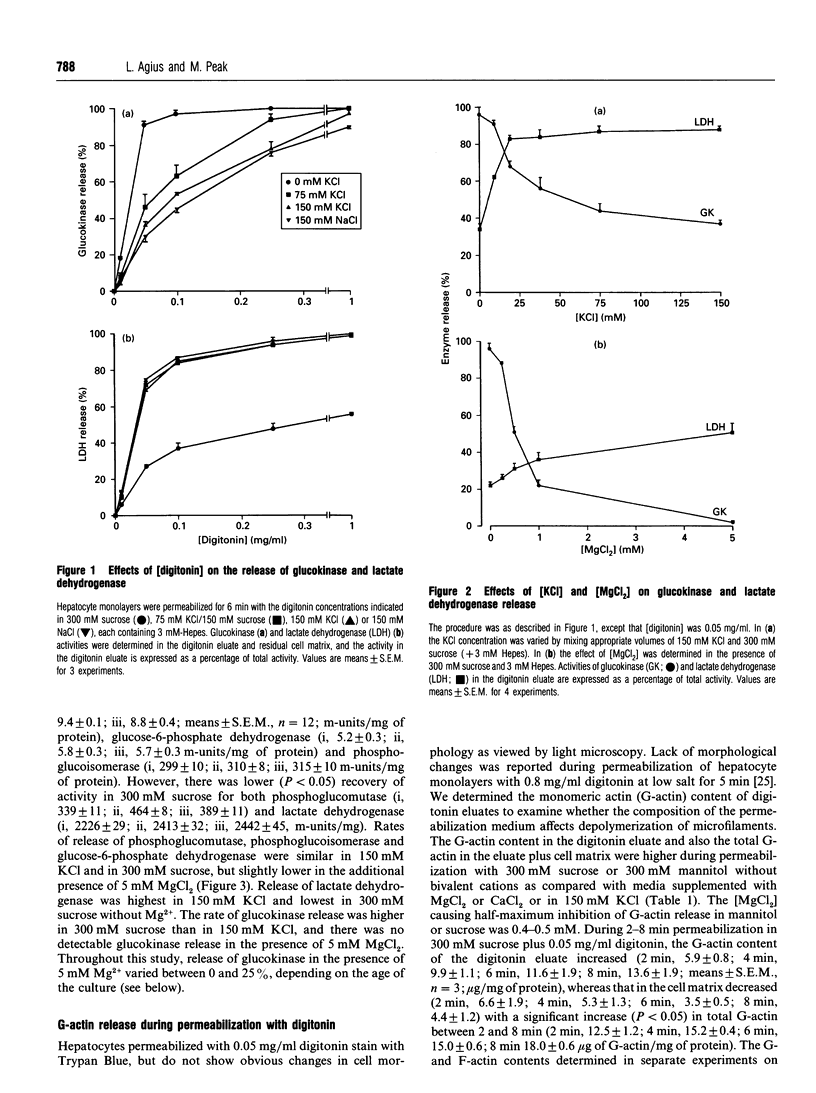
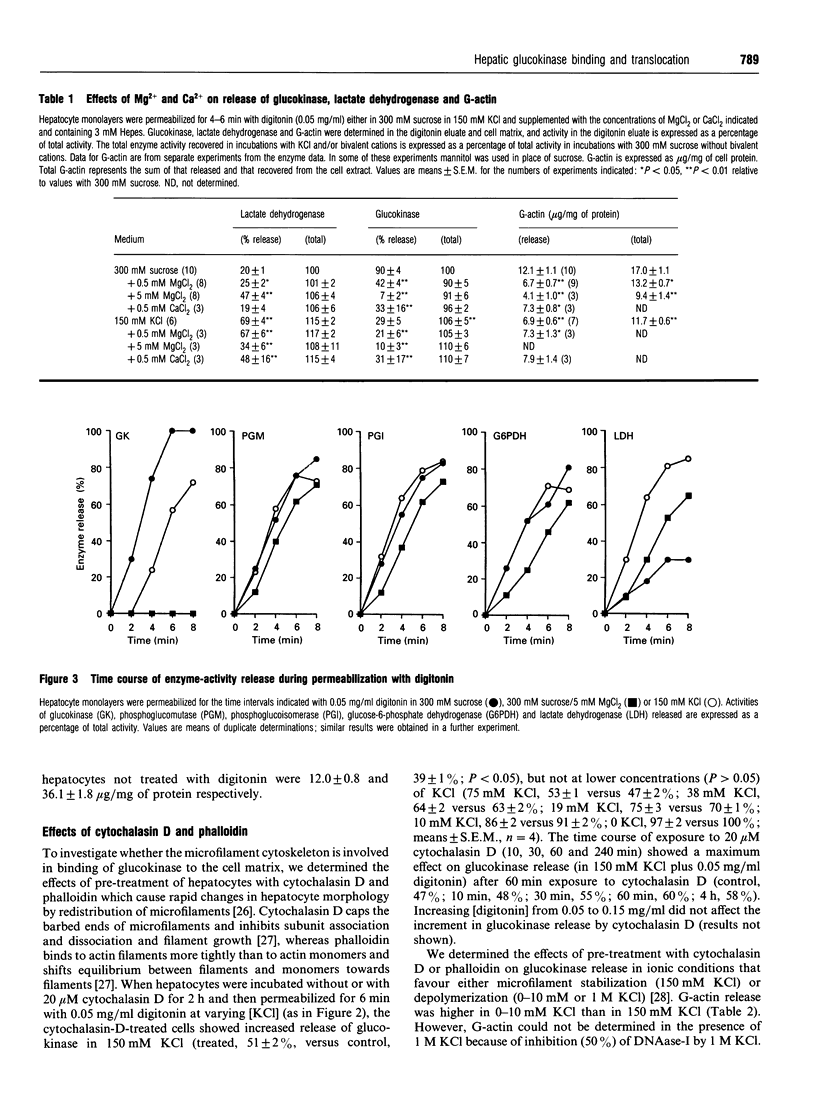
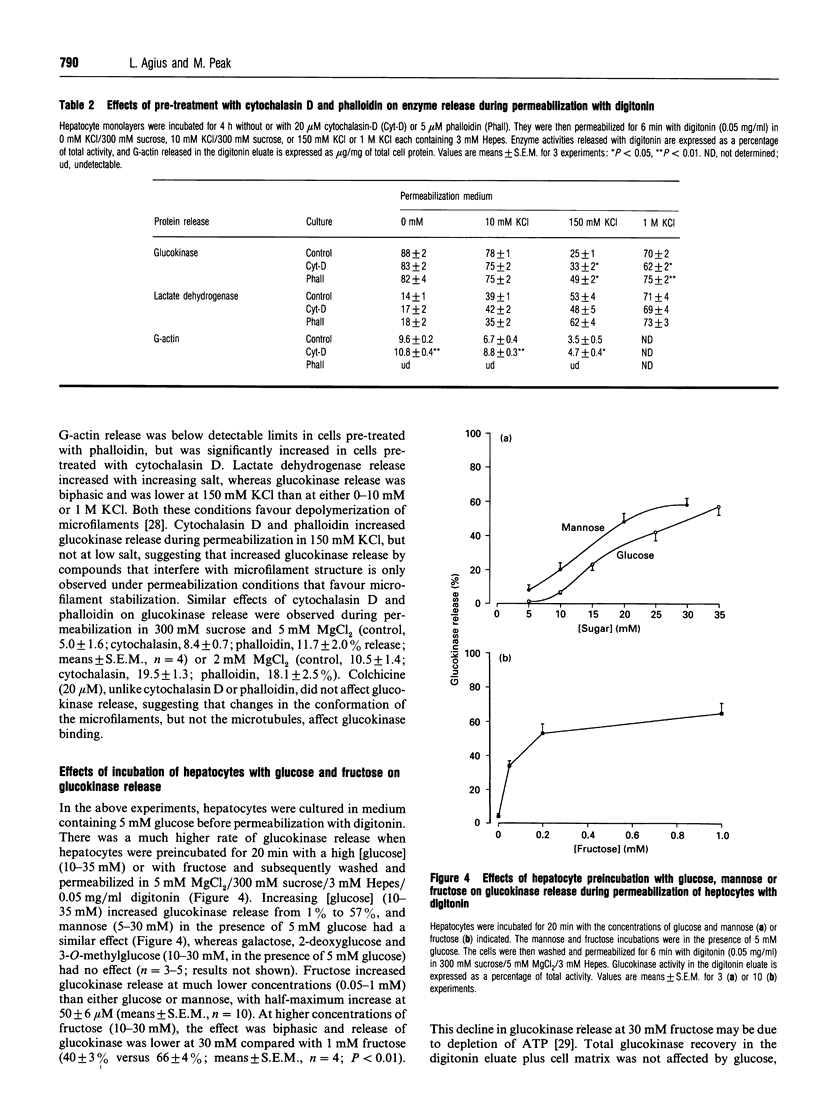
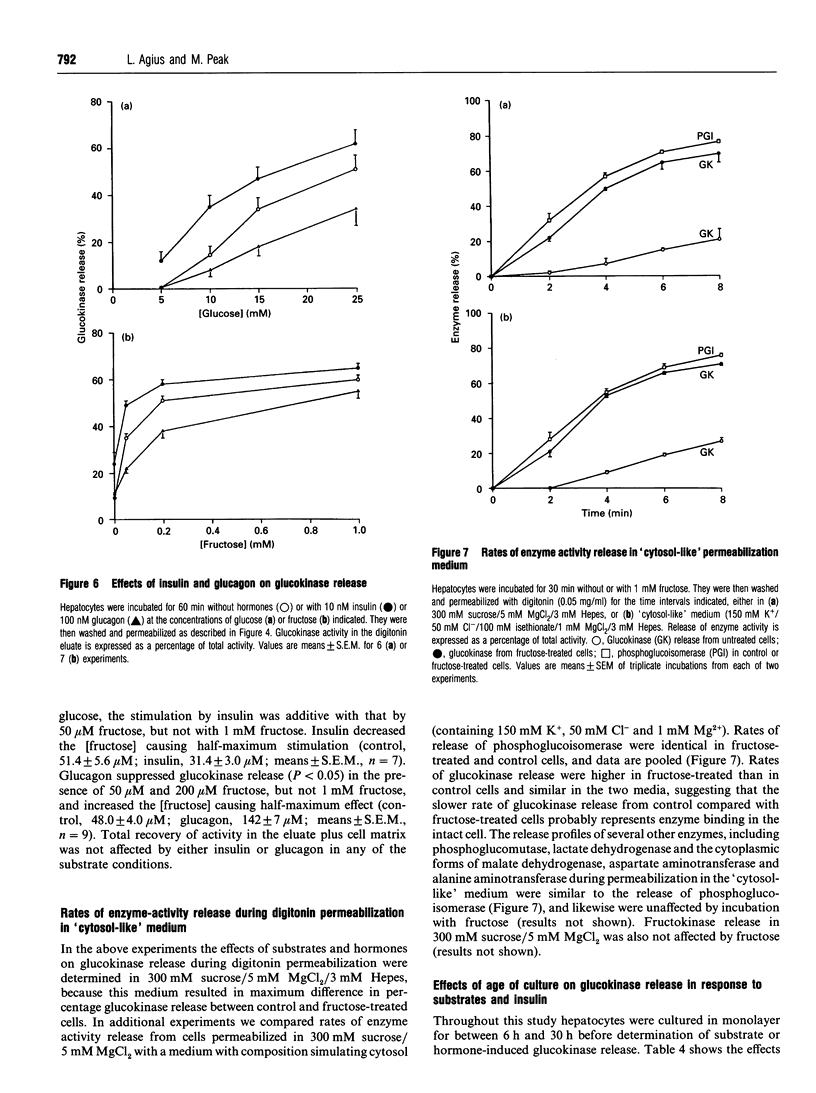
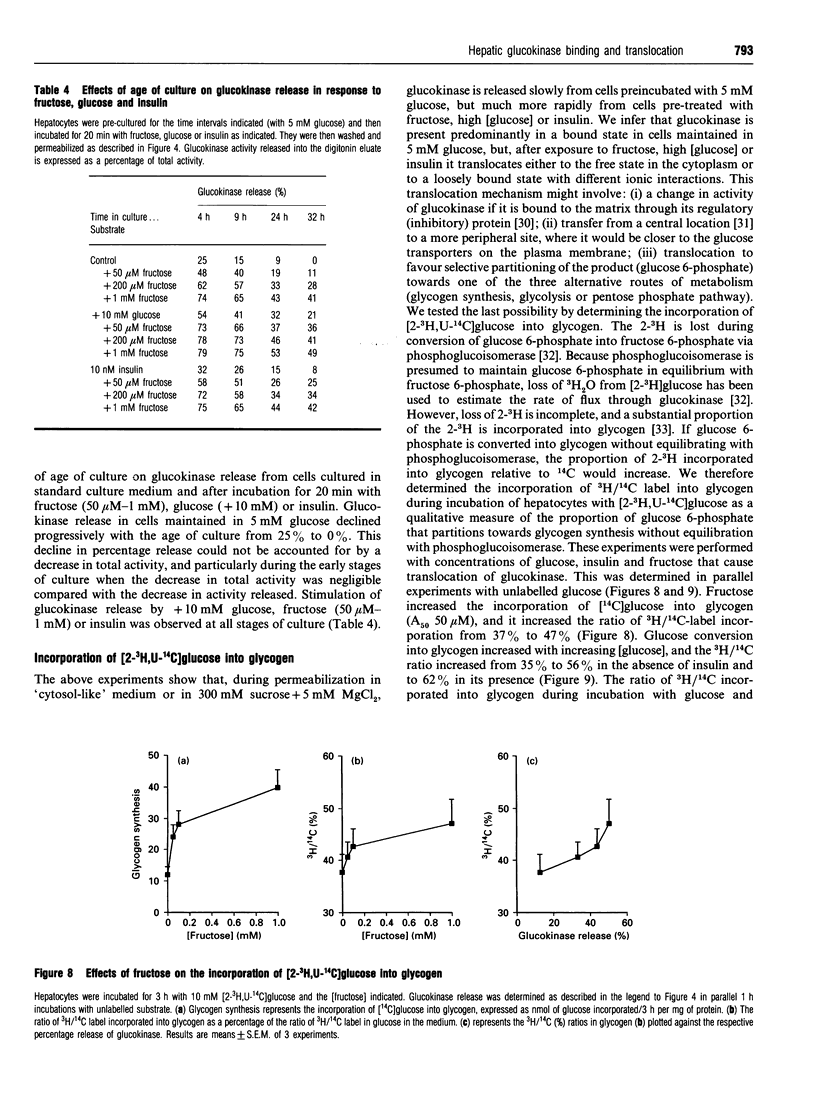
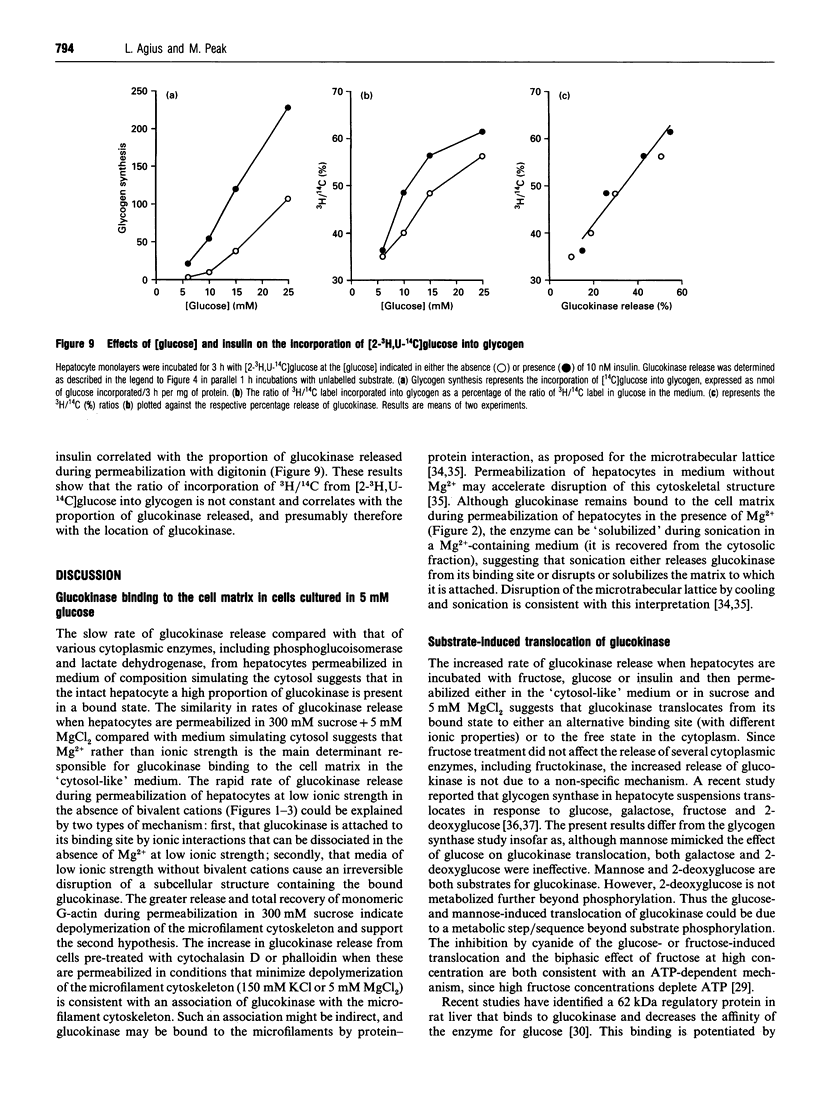
The release of glucokinase from digitonin-permeabilized hepatocytes shows different characteristics with respect to ionic strength and [MgCl2] from the release of other cytoplasmic enzymes. Release of glucokinase is most rapid at low ionic strength (300 mM sucrose, 3 mM Hepes) and is inhibited by increasing concentration of KCl [concn. giving half-maximal inhibition (I50) 25 mM] or Mg2+ (I50 0.5 mM). Release of phosphoglucoisomerase, phosphoglucomutase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase is independent of ionic strength, but shows a small inhibition by MgCl2 (20%, versus > 80% for glucokinase). Lactate dehydrogenase release increases with increasing ionic strength [concn. giving half-maximal activation (A50) 10 mM KCl] or [MgCl2]. The rate and extent of glucokinase release during permeabilization in 300 mM sucrose, 5 mM MgCl2 or in medium with ionic composition resembling cytoplasm (150 mM K+, 50 mM Cl-, 1 mM Mg2+) depends on the substrate concentrations with which the hepatocytes have been preincubated. In hepatocytes pre-cultured with 5 mM glucose the release of glucokinase was much slower than that of other cytoplasmic enzymes measured. However, preincubation with glucose (10-30 mM) or fructose (50 microM-1 mM) markedly increased glucokinase release. This suggests that, in cells maintained in 5 mM glucose, glucokinase is present predominantly in a bound state and this binding is dependent on the presence of Mg2+. The enzyme can be released or translocated from its bound state by an increase in [glucose] (A50 15 mM) or by fructose (A50 50 microM). The effects of glucose and fructose were rapid (t1/2 5 min) and reversible, and were potentiated by insulin and counteracted by glucagon. They were inhibited by cyanide, but not by cytochalasin D, phalloidin or colchicine. Mannose had a glucose-like effect (A50 approximately 15 mM), whereas galactose, 3-O-methyl-D-glucose and 2-deoxyglucose were ineffective. When hepatocytes were incubated with [2-3H, U-14C]glucose, the incorporation of 3H/14C label into glycogen correlated with the extent of glucokinase release. Since 2-3H is lost during conversion of glucose 6-phosphate into fructose 6-phosphate, substrate-induced translocation of glucokinase from a Mg(2+)-dependent binding site to an alternative site might favour the partitioning of glucose 6-phosphate towards glycogen, as opposed to phosphoglucoisomerase.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agius L., Peak M., Alberti K. G. Regulation of glycogen synthesis from glucose and gluconeogenic precursors by insulin in periportal and perivenous rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 15;266(1):91–102. doi: 10.1042/bj2660091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agius L., Tosh D. Acinar zonation of cytosolic but not organelle-bound activities of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and aspartate aminotransferase in guinea-pig liver. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):387–391. doi: 10.1042/bj2710387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agius L., Tosh D., Peak M. The contribution of pyruvate cycling to loss of [6-3H]glucose during conversion of glucose to glycogen in hepatocytes: effects of insulin, glucose and acinar origin of hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 1;289(Pt 1):255–262. doi: 10.1042/bj2890255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreone T. L., Printz R. L., Pilkis S. J., Magnuson M. A., Granner D. K. The amino acid sequence of rat liver glucokinase deduced from cloned cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):363–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arora K. K., Fanciulli M., Pedersen P. L. Glucose phosphorylation in tumor cells. Cloning, sequencing, and overexpression in active form of a full-length cDNA encoding a mitochondrial bindable form of hexokinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6481–6488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessman S. P., Geiger P. J. Compartmentation of hexokinase and creatine phosphokinase, cellular regulation, and insulin action. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1980;16:55–86. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152816-4.50007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blikstad I., Markey F., Carlsson L., Persson T., Lindberg U. Selective assay of monomeric and filamentous actin in cell extracts, using inhibition of deoxyribonuclease I. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):935–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bontemps F., Hue L., Hers H. G. Phosphorylation of glucose in isolated rat hepatocytes. Sigmoidal kinetics explained by the activity of glucokinase alone. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):603–611. doi: 10.1042/bj1740603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway C. A., Carvajal M. E., Li Y., Carraway K. L. Association of p185neu with microfilaments via a large glycoprotein complex in mammary carcinoma microvilli. Evidence for a microfilament-associated signal transduction particle. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5582–5587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. G., Filsell O. H., Topping D. L. Effects of fructose concentration on carbohydrate metabolism, heat production and substrate cycling in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 15;184(3):501–507. doi: 10.1042/bj1840501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. S. Properties and metabolism of the aqueous cytoplasm and its boundaries. Am J Physiol. 1984 Feb;246(2 Pt 2):R133–R151. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.246.2.R133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifton P. M., Chang L., Mackinnon A. M. Development of an automated Lowry protein assay for the Cobas-Bio centrifugal analyzer. Anal Biochem. 1988 Jul;172(1):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90426-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A. Effects of cytochalasin and phalloidin on actin. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1473–1478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das I., Sie H. G., Fishman W. H. Labeling of rat liver glucose-1-phosphate, glucose-6-phosphate, uridine diphosphate glucose, and glycogen during glycogen synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jun;144(2):715–722. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90378-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson A. L., Arion W. J. Factors underlying significant underestimations of glucokinase activity in crude liver extracts: physiological implications of higher cellular activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Feb 15;253(1):156–167. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90648-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. R., Detheux M., Van Schaftingen E. Fructose 1-phosphate and the regulation of glucokinase activity in isolated hepatocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Sep 11;192(2):283–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detheux M., Vandercammen A., Van Schaftingen E. Effectors of the regulatory protein acting on liver glucokinase: a kinetic investigation. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Sep 1;200(2):553–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehmann J. D., Hultin H. O. Substrate inhibition of soluble and bound lactate dehydrogenase (isoenzyme 5). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jan;154(1):471–475. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Novell J. M., Ariño J., Vilaró S., Bellido D., Guinovart J. J. Role of glucose 6-phosphate in the translocation of glycogen synthase in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1992 Dec 1;288(Pt 2):497–501. doi: 10.1042/bj2880497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Novell J. M., Ariño J., Vilaró S., Guinovart J. J. Glucose induces the translocation and the aggregation of glycogen synthase in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 15;281(Pt 2):443–448. doi: 10.1042/bj2810443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelb B. D., Adams V., Jones S. N., Griffin L. D., MacGregor G. R., McCabe E. R. Targeting of hexokinase 1 to liver and hepatoma mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):202–206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iynedjian P. B. Mammalian glucokinase and its gene. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 1;293(Pt 1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2930001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalant N., Parniak M., Lemieux M. Compartmentation of glucose 6-phosphate in hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 15;248(3):927–931. doi: 10.1042/bj2480927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Rognstad R. Futile cycles in the metabolism of glucose. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1976;10:237–289. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152810-2.50013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Wals P. A., Rognstad R. Glucose phosphorylation, glucose-6-phosphatase, and recycling in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4530–4536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz N. R., Nauck M. A., Wilson P. T. Induction of glucokinase by insulin under the permissive action of dexamethasone in primary rat hepatocyte cultures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 14;88(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91691-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackall J., Meredith M., Lane M. D. A mild procedure for the rapid release of cytoplasmic enzymes from cultured animal cells. Anal Biochem. 1979 May;95(1):270–274. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa I., Mitsuyama S., Toyoda Y., Nonogaki T., Aoki S., Okuda J. Evidence for the presence of rat liver glucokinase in the nucleus as well as in the cytoplasm. Biochem Int. 1990 Nov;22(4):759–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. M., Pedersen P. L. Glucose catabolism in brain. Intracellular localization of hexokinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):1059–1066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. M., Pedersen P. L. Intracellular localization of rat kidney hexokinase. Evidence for an association with low density mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8917–8923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley K. C., Jones G. E., Magnani M., Rist R. J., Naftalin R. J. Direct observation of hexokinase translocation in stimulated macrophages. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 15;291(Pt 2):515–522. doi: 10.1042/bj2910515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter K. R., Anderson K. L. The structure of the cytoplasmic matrix preserved by freeze-drying and freeze-substitution. Eur J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;29(1):83–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Chaponnier C., Jeanrenaud B., Gabbiani G. Actin microfilaments, cell shape, and secretory processes in isolated rat hepatocytes. Effect of phalloidin and cytochalasin D. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):592–607. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purich D. L., Fromm H. J., Rudolph F. B. The hexokinases: kinetic, physical, and regulatory properties. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1973;39:249–326. doi: 10.1002/9780470122846.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes A., Cárdenas M. L. All hexokinase isoenzymes coexist in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 15;221(2):303–309. doi: 10.1042/bj2210303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz I. Permeabilizing cells: some methods and applications for the study of intracellular processes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;192:280–300. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)92077-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skilleter D. N., Kun E. The oxidation of L-lactate by liver mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Sep;152(1):92–104. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda K. Interactions of glycolytic enzymes with cellular membranes. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1992;33:31–46. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152833-1.50008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams H. R., Landau B. R. Pathways of fructose conversion to glucose and glycogen in liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jun;150(2):708–713. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Schaftingen E., Vandercammen A., Detheux M., Davies D. R. The regulatory protein of liver glucokinase. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1992;32:133–148. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(92)90013-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


