Abstract
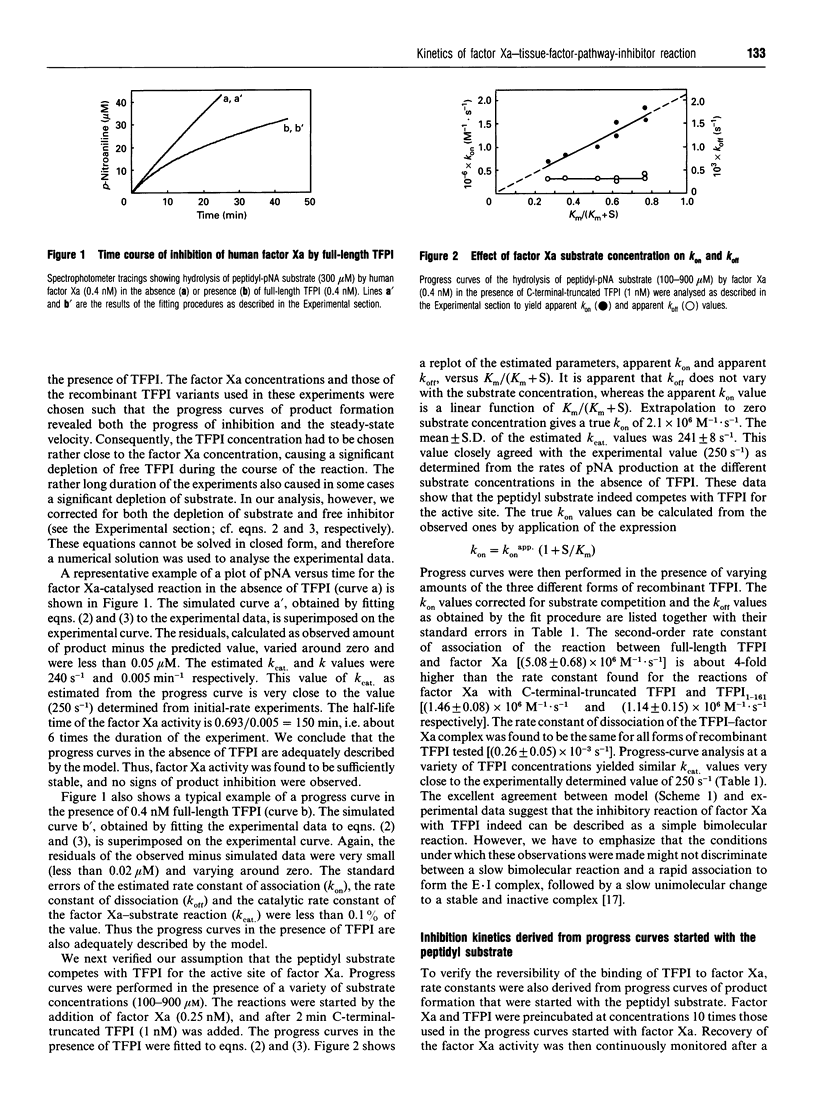
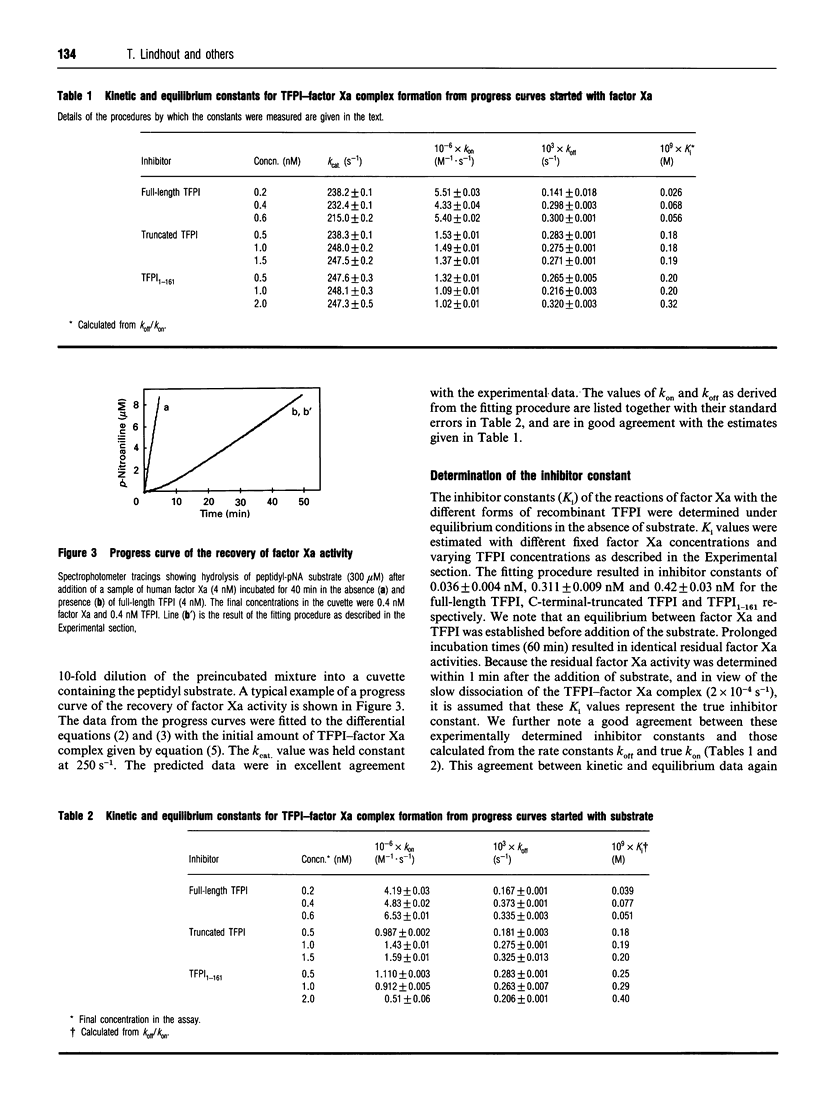
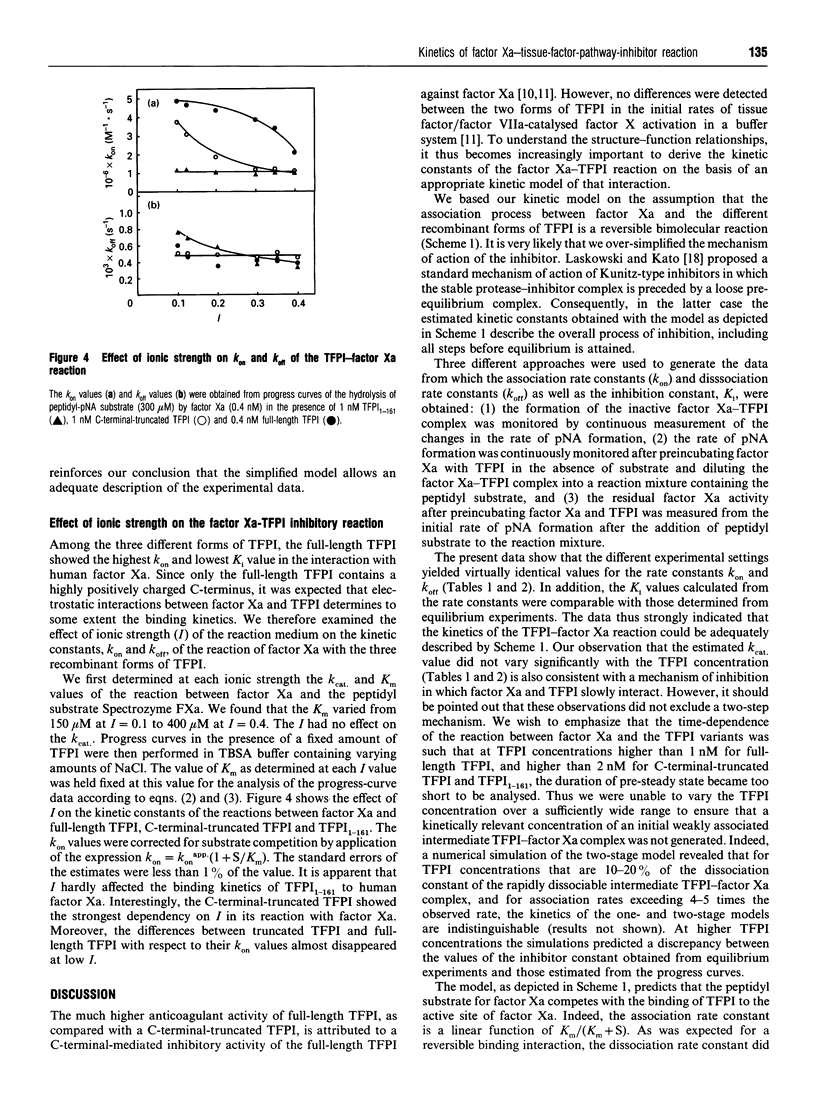
The inhibition equilibrium and kinetics of association and dissociation of the binding of three types of recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), namely full-length TFPI, C-terminal-truncated TFPI, and TFPI without the third Kunitz domain (TFPI1-161), to factor Xa have been measured. Formation and dissociation of the complexes were monitored by continuous measurement of the changes in the rate of hydrolysis of a peptidyl-p-nitroanilide substrate. Progress curves of product formation were fitted to a set of equations describing a one-step bimolecular inhibitory reaction in the presence of a competing substrate. For full-length TFPI the rate constants of association (kon) and dissociation (koff) were (5.1 +/- 0.7) x 10(6) M-1.s-1 and (2.6 +/- 0.9) x 10(-4)s-1 respectively. Thus, although the inhibition constant (50 pM) is far below the plasma concentration (2.5 nM) of TFPI, the half-time for transition to equilibrium in plasma is rather long (66s). The truncated forms of TFPI differ in that they have a 4-fold lower kon value but a similar dissociation rate constant. Therefore the inhibition constant, Ki, is 4-fold higher (0.2 nM) and the half-time to achieve equilibrium is prolonged to 250 s. The kon values of full-length and C-terminal-truncated TFPI, but not that of TFPI1-161, were found to decrease with increasing ionic strength.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broze G. J., Jr, Girard T. J., Novotny W. F. Regulation of coagulation by a multivalent Kunitz-type inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 21;29(33):7539–7546. doi: 10.1021/bi00485a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broze G. J., Jr, Miletich J. P. Characterization of the inhibition of tissue factor in serum. Blood. 1987 Jan;69(1):150–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broze G. J., Jr, Warren L. A., Novotny W. F., Higuchi D. A., Girard J. J., Miletich J. P. The lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor that inhibits the factor VII-tissue factor complex also inhibits factor Xa: insight into its possible mechanism of action. Blood. 1988 Feb;71(2):335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cha S. Tight-binding inhibitors-I. Kinetic behavior. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Dec 1;24(23):2177–2185. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie E. W., Fujikawa K., Kisiel W. The coagulation cascade: initiation, maintenance, and regulation. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 29;30(43):10363–10370. doi: 10.1021/bi00107a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erion M. D., Walsh C. T. 1-Aminocyclopropanephosphonate: time-dependent inactivation of 1-aminocyclopropanecarboxylate deaminase and Bacillus stearothermophilus alanine racemase by slow dissociation behavior. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3417–3425. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski M., Jr, Kato I. Protein inhibitors of proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:593–626. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. F., Walsh C. T. The behavior and significance of slow-binding enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1988;61:201–301. doi: 10.1002/9780470123072.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y. Tissue factor and hemostasis. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordfang O., Bjørn S. E., Valentin S., Nielsen L. S., Wildgoose P., Beck T. C., Hedner U. The C-terminus of tissue factor pathway inhibitor is essential to its anticoagulant activity. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 29;30(43):10371–10376. doi: 10.1021/bi00107a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen A. H., Nordfang O., Norris F., Wiberg F. C., Christensen P. M., Moeller K. B., Meidahl-Pedersen J., Beck T. C., Norris K., Hedner U. Recombinant human extrinsic pathway inhibitor. Production, isolation, and characterization of its inhibitory activity on tissue factor-initiated coagulation reactions. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16786–16793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen J. G., Meyn G., Rasmussen J. S., Petersen J., Bjørn S. E., Jonassen I., Christiansen L., Nordfang O. Characterization of human tissue factor pathway inhibitor variants expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13344–13351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieters J., Lindhout T. The limited importance of factor Xa inhibition to the anticoagulant property of heparin in thromboplastin-activated plasma. Blood. 1988 Dec;72(6):2048–2052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L. V., Rapaport S. I. Studies of a mechanism inhibiting the initiation of the extrinsic pathway of coagulation. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):645–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport S. I. Inhibition of factor VIIa/tissue factor-induced blood coagulation: with particular emphasis upon a factor Xa-dependent inhibitory mechanism. Blood. 1989 Feb;73(2):359–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repke D., Gemmell C. H., Guha A., Turitto V. T., Broze G. J., Jr, Nemerson Y. Hemophilia as a defect of the tissue factor pathway of blood coagulation: effect of factors VIII and IX on factor X activation in a continuous-flow reactor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7623–7627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoen P., Lindhout T., Willems G., Hemker H. C. Continuous flow and the prothrombinase-catalyzed activation of prothrombin. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Dec 28;64(4):542–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore J. D., Olson S. T., Craig P. A., Choay J., Björk I. Kinetics of heparin action. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;556:75–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb22491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesselschmidt R., Likert K., Girard T., Wun T. C., Broze G. J., Jr Tissue factor pathway inhibitor: the carboxy-terminus is required for optimal inhibition of factor Xa. Blood. 1992 Apr 15;79(8):2004–2010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wun T. C., Kretzmer K. K., Girard T. J., Miletich J. P., Broze G. J., Jr Cloning and characterization of a cDNA coding for the lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor shows that it consists of three tandem Kunitz-type inhibitory domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6001–6004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


